1. Background
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are common infectious diseases and public health challenges worldwide. Among the many aspects of epidemiology and controlling STIs, timely diagnosis and treatment are highly important (1). However, in developing countries and populations with limited laboratory services, the diagnosis of STIs is challenging, expensive, and often inaccessible (2).
A widely used alternative to laboratory-based diagnosis is symptom-based diagnosis. The symptom-based diagnosis approach for STIs involves identifying predefined syndromes using a flowchart designed for the diagnosis of these diseases (3). These charts are simple, easy to implement by non-STI specialists, and can be integrated into primary health care settings, allowing for contact tracing, partner management, and counseling (4). Symptom-based treatment and management are also fast and cost-efficient when laboratory tests are not available, allowing for immediate treatment to begin (5). However, the symptom-based approach to STIs surveillance often leads to overdiagnosis and overtreatment (6). There is no consensus on the performance of syndrome-based STI diagnosis, as several studies from different countries have reported conflicting results (2). Symptom management of STIs using algorithms based on self-reported symptoms is sometimes the only available option in many low- and middle-income countries. However, our knowledge about the validity of this approach is severely limited (1, 3).
Considering the advantages of the syndrome-based strategy in diagnosing STIs in developing countries, there is a long-standing need to evaluate the validity of this approach (6, 7).
2. Objectives
The aim of this population-based study (urban, rural) is to determine whether this approach is a suitable tool for screening STIs in the general population of Iran by measuring the clinical and laboratory positive predictive values (PPV) of the symptom-based approach for the diagnosis of STIs in Iran.
3. Methods
3.1. Setting
In 2019, this cross-sectional study was conducted on 3879 individuals (aged 18 - 50 years) who were randomly selected from the general population of Marvdasht county, Iran.
3.2. Data Collection
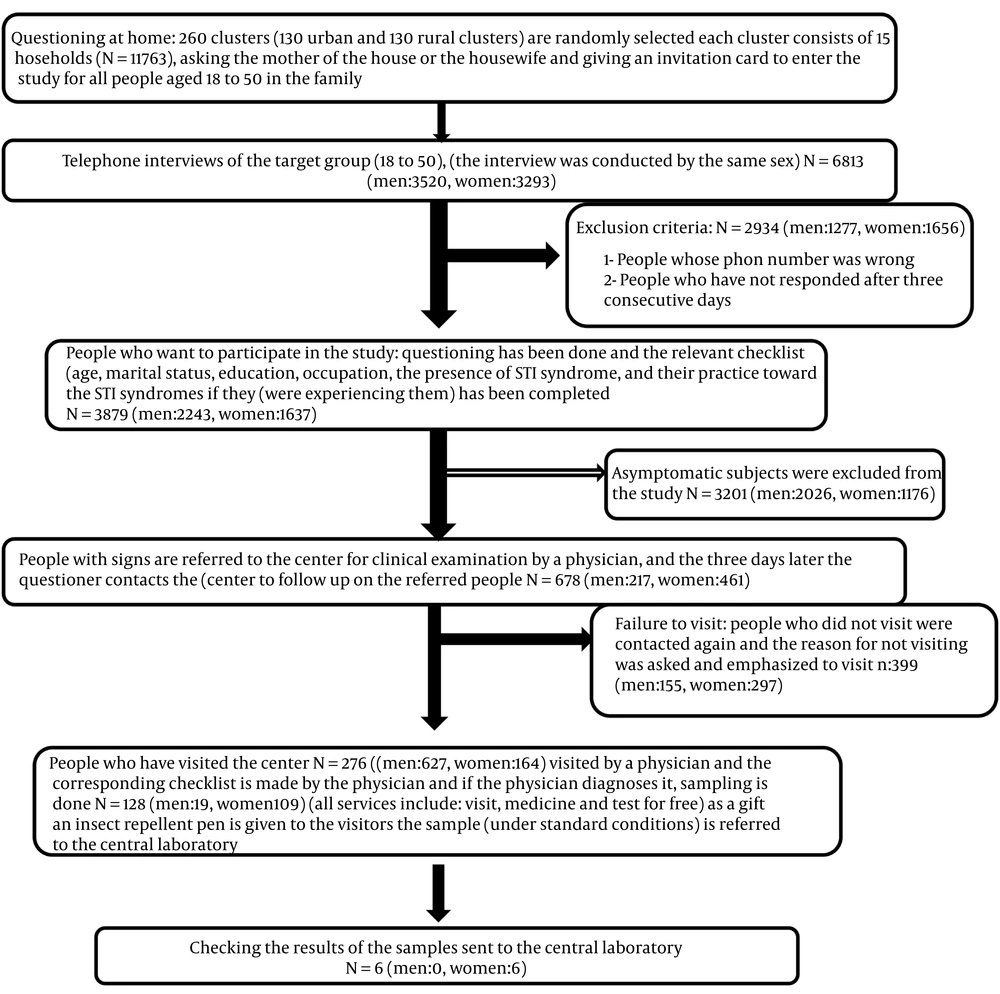
The study was conducted in three steps: (1) self-reporting of STI symptoms, (2) evaluation of the patients by a trained physician, and (3) laboratory confirmation of the clinically diagnosed patients (Figure 1). More details about sampling and methods have been provided in previous studies (8, 9).
3.3. Laboratory Testing Methods
PCR and NAAT (PCR) diagnostic tests were used in this study.
3.4. Data Analysis
Descriptive statistics, including mean, median, and percentage, were used to summarize the data. The positive predictive value of the symptom-based diagnosis strategy was defined. Data analysis was performed using STATA version 13.1.
4. Results
4.1. The Prevalence of Sexually Transmitted Infections-Associated Symptoms, Clinical Exam, and Laboratory Test Results
In total, 3879 individuals with an average age of 34.28 ± 8.74 participated in this study. Among the population sample, 686 (17.68%) individuals reported at least one of the predefined symptoms, of which 217 (9.7%) were male and 469 (28.7%) were female. Among the patients who were referred to the physician, 192 (68.82%) were confirmed by the doctor to have symptoms. The details are presented in Table 1.
| Letter Name | Total People Aged 18 - 50 | Men 18 to 50 Years Old | Women 18 to 50 Years Old |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 6813 (57.92) | 3520 (51.67) | 3293 (48.33) |
| Entered the study | 3879 (56.94) | 2243 (63.86) | 1637 (49.71) |
| Having at least one of the syndromes | 678 (17.48) | 217 (9.67) | 461 (28.16) |
| Referred to the physician | 279 (41.15) | 62 (7.37) | 164 (35.57) |
| Confirmed by a physician | 192 (68.82) | 42 (67.74) | 140 (85.37) |
| Referred to the physician | 128 (66.67) | 19 (45.24) | 109 (77.66) |
| Confirmed by a laboratory | 6 (4.69) | 0 | 6 (5.50) |
a Values are expressed as No. (%).
The results of Table 2 show that most of the participants in the study are married and have a high school education. Additionally, 69.96% of the participants reported being sexually active, and their average age is 34.28 years.
| Variables | Male | Female | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Residency | |||
| Urban | 1119 (49.9) | 961 (58.7) | 2080 (53.62) |
| Rural | 1124 (50.1) | 675 (41.3) | 1799 (46.37) |
| Marital status | |||
| Single | 737 (32.9) | 334 (20.3) | 1071 (27.84) |
| Married | 1493 (66.7) | 1208 (75.2) | 2701 (70.24) |
| Widow/divorced | 9 (0.4) | 64 (4) | 73 (1.89) |
| Education | |||
| Literate | 39 (1.8) | 85 (5.2) | 124 (3.30) |
| Primary | 372 (17.5) | 410 (25.2) | 782 (20.84) |
| Secondary | 555 (26.1) | 290 (17.8) | 845 (22.52) |
| High school | 698 (32.8) | 511 (31.4) | 1209 (32.22) |
| Academic | 461 (21.7) | 331 (20.3) | 792 (21.10) |
| Job | |||
| Worker | 308 (14.8) | - | 308 (8.30) |
| Employee | 170 (8.2) | 81 (5) | 251 (6.76) |
| Farmer | 298 (14.3) | - | 298 (8.03) |
| Housewife/unemployed | 188 (9) | 1390 (85.5) | 1578 (42.53) |
| Free | 926 (44.4) | 74 (4.6) | 1000 (26.95) |
| Soldier/student | 177 (8.5) | 81 (5) | 258 (6.95) |
| Retired | 17 (0.8) | - | 17 (0.45) |
| Having any kind of sexual contact | 1752 (78.1) | 962 (63.5) | 2714 (69.96) |
| Age | 34.75 ± 8.79 | 33.81 ± 8.91 | 34.28 ± 8.85 |
a Values are expressed as No. (%) or mean ± SD.
Of the people who were referred to the physician, 3.52% had a history of premarital sex, and 3.96% had a history of extramarital sex. Additionally, 34.17% of the participants reported using condoms during intercourse. Of the total participants, 13.62% reported a history of anal sex, and 12.90% reported a history of oral sex (Table 3).
| Variables | Population Men | Women | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Job | |||
| Selfe employed | 32 (51.60) | 6 (3.65) | 38 (16.81) |
| Unemployed | 8 (13) | 1 (0.6) | 9 (3.98) |
| Student/soldier | 3 (4.3) | 8 (4.8) | 11 (4.86) |
| Housewife/worker | 13 (30.96) | 149 (90.53) | 162 (71.68) |
| Farmer/rancher | 6 (9.67) | - | 6 (2.65) |
| History of sexually transmitted diseases | |||
| Yes | 4 (6.45) | 8 (5) | 12 (4.30) |
| Age | 31 ± 12.12 | 27.50 ± 13.2 | 29.25 ± 12.66 |
| Received treatment | 3 (75) | 4 (9.8) | 7 (58.33) |
| Sexual status | |||
| With spouse only | 44 (71) | 139 (84.2) | 183 (80.61) |
| Before marriage sex | 6 (9.67) | 2 (1.2) | 8 (3.52) |
| Extramarital affair | 8 (12.9) | 1 (.06) | 9 (3.96) |
| Homosexuality | - | - | - |
| Have no sex | 4 (6.5) | 23 (13.9) | 27 (11.89) |
| Average sex per week | 1.47 ± 0.97 | 1.74 ± 1.03 | 1.60 ± 1.01 |
| Number of sexual partners | 1.58 ± 3 | 1 ± 0.12 | 1.29 ± 1.56 |
| Anal intercourse | |||
| Yes | 9 (15) | 29 (18.6) | 38 (13.62) |
| Oral sex | |||
| Yes | 9 (14.5) | 27 (17.3) | 36 (12.90) |
| Method of prevention | |||
| Condom | 13 (28.88) | 27 (26.2) | 40 (34.18) |
| Tablet | 3 (6.6) | 12 (11.65) | 15 (12.82) |
| IUD | 4 (8.8) | 6 (5.89) | 10 (8.54) |
| Tubectomy and vasectomy | 9 (20) | 13 (12.62) | 22 (18.80) |
| Natural | 16 (35.55) | 27 (26.2) | 30 (25.64) |
| A history of sexually transmitted disease in the sexual partner | |||
| Yes | 11 (20) | 8 (5.8) | 19 (6.81) |
4.2. Positive Predictive Value
The results showed that, in general, the clinical-based PPV for STI syndromes in men and women are 67.74 (62.34 - 73.14) and 85.36 (82.76 - 87.96), respectively. In men, the highest PPV is associated with abnormal discharge from the anus, 32.35 (25.35 - 39.35), and in women, it is related to the presence of abnormal secretions from the cervix, 59.39 (56.39 - 62.39). The laboratory-based PPV of STI syndromes is 0 for men and 5.04 (3.04 - 7.4) for women (Table 4).
| Variables | Self-reporting N (PCI for P) | Doctor's Examination a | Confirmed by a Physician Clinically PPV% | Laboratory Based; PPV% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men | ||||
| Skin rash | 17 (0.76) (0.44 - 1.21) | 3 (4.84) (1.01 - 13.50) | 17.64 (8.6 - 26.4) | - |
| Genital/perineal/perianal warts | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Ulcers in the genital area | 7 (0. 3) (0.13 - 0.64) | 1 (1.61) (0.04 - 8.66) | 14.28 (4.28 - 24.28) | - |
| Enlargement of the lymph nodes in the groin | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Enlargement of lymph nodes in areas other than the groin | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| The presence of abnormal secretions from the genital tract | 107 (4.77) (3.93 - 5.74) | 18 (29.03) (18.20 - 41.95) | 16.82 (13.82 - 19.82) | - |
| Swelling or redness of the scar | 52 (2.32) (1.74 - 3.03) | 9 (14.52) (6.86 - 25.78) | 17.30 (13.3 - 21.03) | - |
| Abnormal discharge from the anus | 34 (1.52) (1.05 - 2.11) | 11 (17.74) (9.20 - 29.53) | 32.35 (25.35 - 39.35) | - |
| Total for all syndromes | 217 (9.67) (8.48 - 10.97) | 42 (67.74) (54.66 - 79.09) | 67.74 (62.34 - 73.14) | 0 |
| Total | 2243 | 62 | 42 | 19 |
| Women | ||||
| Skin rash | 20 (1.22) (0.75 - 1.88) | 5 (3.05) (1 - 6.97) | 25 (6.90 - 34.4) | - |
| Genital/perineal/perianal warts | 5 (0.31) (0.10 - 0.71) | 2 (1.23) (0.15 - 4.39) | 4 (1.30 - 6.7) | - |
| Ulcers in the genital area | 46 (2.81) (2.06 - 3.73) | 19 (11.59) (7.12 - 17.50) | 41.30 (37.9 - 44.7) | - |
| Enlargement of the lymph nodes in the groin | 26 (1.59) (1.04 - 2.32) | 6 (3.66) (0.13 - 7.89) | 23.07 (15.37 - 30.77) | - |
| Enlargement of lymph nodes in areas other than the groin | 17 (1.04) (0.61 - 1.66) | 90 (54.88) (46.93 - 62.65) | 23.52 (13.27 - 33.72) | - |
| Abnormal discharge from the vagina b | 201 (12.28) (10.73 - 13.97) | 79 (48.17) (40.31 - 56.09) | 42.85 (39.85 - 45.85) | - |
| Abnormal secretions from the cervix b | 133 (8.12) (6.85 - 9.55) | 6 (3.66) (1.35 - 7.79) | 59.39 (56.39 - 62.39) | - |
| Abnormal discharge from the anus | 13 (0.79) (0.42 - 1.35) | 31 (19.14) (13.39 - 26.05) | 46.15 (32.45 - 59.85) | - |
| Cervical examination result (abnormal) | - | - | - | - |
| Bimanual examination result (abnormal) | - | - | - | - |
| Total for all syndromes | 461 (28.16) (25.99 - 30.41) | 140 (85.37) (79.01 - 90.39) | 85.36 (82.76 - 87.96) | 5.04 (3.04-7.4) |
| Total | 1637 | 164 | 140 | 109 |
a Only people who went to the doctor were examined.
b Most women had both symptoms of discharge from the cervix and vagina.
5. Discussion
The current study is the first of its kind to assess the accuracy of symptom-based monitoring of STIs in Iran. A significant number of participants in the sample reported experiencing the defined symptoms, with a higher prevalence of symptoms observed among female participants.
The results of our study suggest that the self-reported symptom-based PPV in the population was considerably low, especially in men. This indicates that approximately 32.66% of individuals who reported symptoms did not have the disease based on the physician’s physical examination. Since the PPV of any test is influenced by the prevalence of the disease in a given population, the accuracy of symptom-based diagnosis is heavily dependent on the infection prevalence. Using a syndrome-based diagnosis strategy is more effective when the prevalence of infections is high (3, 8, 10).
The PPV based on laboratory test results in this study was extremely low. In other words, about 95% of individuals diagnosed as positive through symptom-based medical examination were negative in laboratory testing. This low predictive value results in a large number of individuals being falsely diagnosed as positive, leading to inappropriate treatment (11). This, in turn, contributes to increased antibiotic resistance, financial burden (12), and the stigma and social discrimination associated with STIs (12-14).
5.1. Strengths and Limitations
This is a population-based survey with a relatively large sample size. One of the most significant limitations in studying STIs is the high social stigma surrounding these diseases (8), which may reduce participation rates and lead to reporting bias in the study. Additionally, a substantial percentage of STI cases are asymptomatic, and because asymptomatic individuals were not examined in this study, there is a possibility that the findings may underestimate the true prevalence of STIs (14, 15).
5.2. Conclusions
The clinical and laboratory PPV of symptom-based STI management in the study population is alarmingly low. Therefore, the syndrome-based approach is not a suitable method for screening or monitoring STIs in the general population. However, this method may be more appropriate if used in high-risk groups where access to and cooperation with diagnostic facilities is severely limited.