1. Background
Contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN) is one of the most important possible complications after angiography, with a prevalence rate of 15% in patients with chronic renal failure (1, 2). This complication can lead to longer hospital stays, renal dysfunction (1, 3), poor long-term clinical outcomes (4), and increased morbidity and mortality (5). Diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolemia, and underlying chronic kidney disease (CKD) are the major risk factors for CIN (6). CIN can be caused by inflammatory mechanisms, endothelial dysfunction, and oxidative stress (7, 8). Short-term treatment with hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme-A inhibitor (statins) before some medical procedures leads to better clinical outcomes (independent of lipid reduction) in various clinical conditions-for instance, by preventing myocardial injury during percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) (9-12) or reducing ventricular fibrillation after heart surgery (11, 13). Statins have anti-inflammatory effects and can reduce oxidative stress and increase nitric oxide, conferring a beneficial effect on renal function (14). Different studies have reported the positive effect of atorvastatin on the incidence of CIN (15-19), while some studies have rejected this positive effect (20, 21).
2. Objectives
Given that CIN after angiography in diabetes and CKD is relatively prevalent and can increase the hospitalization period and mortality (22, 23), decreasing the incidence of CIN after angiography can help reduce the cost of treatment, days of hospitalization, and hospital-bed occupancy rates. Therefore, the present study was designed to investigate the effect of atorvastatin at a dose of 80 mg on reducing the rate of CIN following angiography in CKD and diabetic patients.
3. Patients and Methods
In this single-center, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial, patients aged between 55 and 75 who were candidates for elective angiography or patients who were hospitalized in the cardiac care unit for angiography were selected via the accessible sampling method (Figure 1).
The study protocol was approved by the ethics committee of Baqiyatallah university of medical sciences. Informed consent was obtained from each patient included in the study, and the study protocol conforms to the ethical guidelines of the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki. The confounding factor of age was eliminated by assessing the patients ranging in age from 55 to 75 years. Patients were included who had at least 1 of the following criteria: 1) diabetes (fasting blood sugar > 126 mg/dL, random blood sugar > 200 mg/dL, and glucose tolerance test > 200 mg/dL) and 2) chronic renal failure (creatinine > 1.5 mg/dL or 15 < glomerular filtration rate [GFR] < 60 mls/min/1.73m2). The exclusion criteria comprised recent treatment with 80 mg of statin (not low-dose atorvastatin), need for emergency angiography, contraindications to statin prescription, previous contrast-media administration during the preceding 10 days, chronic dialysis treatment, and informed refusal of consent. All the patients in both groups had a drug history of low-dose atorvastatin before our study. The patients were divided into 2 groups with a computerized randomization list and with blocks of 6 pieces. Details of the treatment process were explained to all the patients, and their informed consent for participation in the study was obtained. Atorvastatin (80 mg/d) and a placebo were prescribed from 48 hours before angiography in the case and control groups, respectively. The placebo was similar to atorvastatin in shape. Subsequently in both the case and control groups, isotonic saline (0.9% sodium chloride or half saline, 1 - 3 mL/kg/h), intravenously, and N-acetylcysteine (NAC) 1200 mg, orally, twice a day, 1 day before to 2 days after intervention were prescribed from 1 hour before angiography until 4 hours thereafter. In the patients with congestive heart failure or those with an ejection fraction less than 40%, hydration at a dose of 0.5 mL/kg/h was prescribed. For all the patients, nonionic iso-osmolar was used as the contrast medium. All the angiographic procedures were performed by a cardiovascular specialist in the Angiography Center in Baqiyatallah hospital, and the results were recorded. Before performing angiography and 24 and 48 hours afterward, blood samples were taken. All the experiments were conducted in the Laboratory of Baqiyatallah Hospital. CIN was defined as an increase in serum creatinine more than 0.5 mg/dL or more than 25% from the baseline. The GFR of the patients was calculated with the modification of diet in renal disease (MDRD) formula using the information at www.mdrd.com.
3.1. Statistical Analysis
The data were entered into statistical package for the social sciences (SPSS), version 21. The quantitative variables were compared between the 2 groups and also between the patients with positive CIN and those with negative CIN using the independent t-test and its non-parametric equivalent (Mann-Whitney). Creatinine levels before and 24 and 48 hours after angiography were compared in the patients in each group using repeated-measures analysis of variance and its non-parametric equivalent (Friedman). The parametric and non-parametric variables were determined using the one-sample Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. CIN was considered positive if a comparison of the serum creatinine baseline levels with those 24 and 48 hours after angiography showed an increase of 0.5 mg/dL or 25%. The quantitative variables were compared between the 2 groups and between the CIN-positive and CIN-negative cases using the χ2 test and the Fisher exact test. The continuous variables were summarized as median and interquartile range, and the categorical data were summarized as numbers and proportions.
4. Results
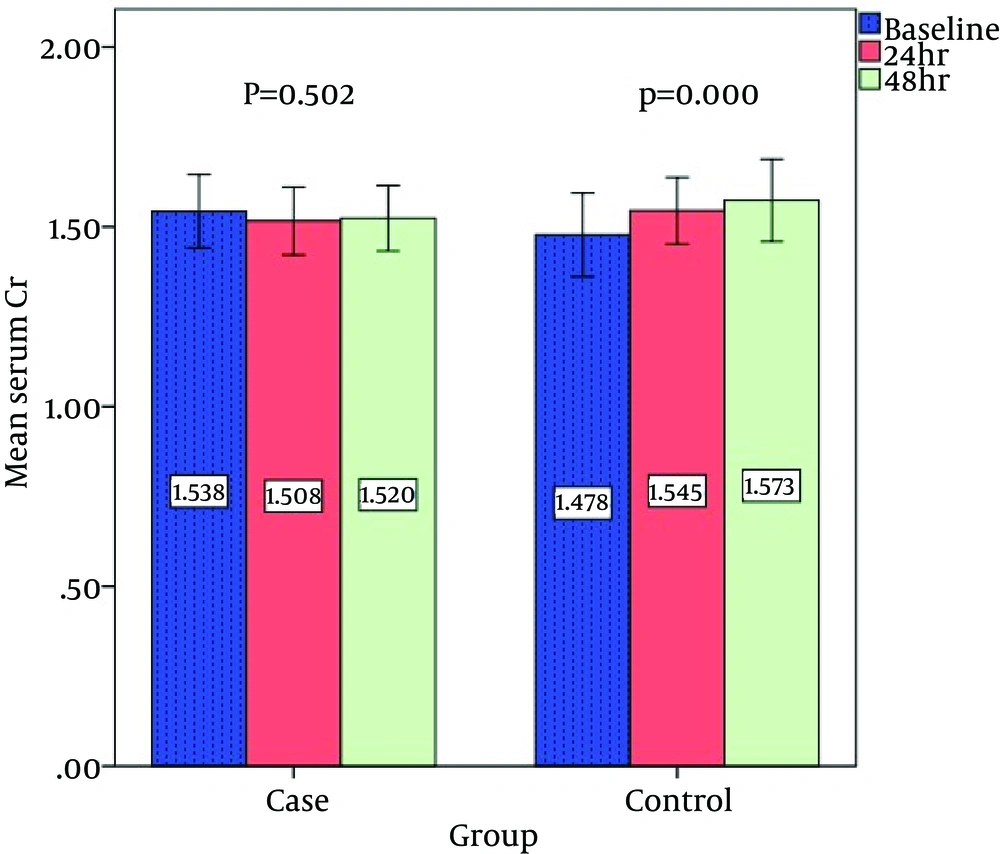
The study population was comprised of 220 patients at a mean age of 63.85 ± 8.89 years and a mean body mass index (BMI) of 31.41 ± 5.99 kg/m2. There were no significant differences between the 2 groups in sex, age, and average BMI (Table 1). The comorbidities (i.e., hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, myocardial infarction, coronary artery bypass grafting, and previous PCI) exhibited no significant differences between the 2 groups (Table 1). The angiographic results were not significantly different between the 2 groups (Table 2). The laboratory data of the patients exhibited no significant differences between the groups in terms of hemoglobin, hematocrit, and triglyceride levels (Table 2). The mean cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein levels in the patients in the case group were significantly higher than those in the patients in the control group, and the mean high-density lipoprotein level exhibited no significant differences between the 2 groups (Table 2). The mean GFR was not significantly different between the patients of the 2 groups (Table 2). The mean serum creatinine level before angiography exhibited no significant difference between the 2 groups, nor did it indicate any significant differences 24 and 48 hours after angiography between the 2 groups (Table 3 and Figure 2).
| Case | Control | P Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Angiography result, % | 0.088 | ||
| Normal | 5 (3.6) | 8 (7.3) | |
| LM | 3 (2.1) | 5 (4.5) | |
| SVD | 30 (27.2) | 40 (36.4) | |
| 2VD | 53 (48.1) | 34 (30.9) | |
| 3VD | 19 (17.2) | 23 (20.9) | |
| Hb, mg/dL | 12.87 ± 1.90 | 13.03 ± 1.63 | 0.801 |
| Hct, % | 39.01 ± 5.33 | 39.06 ± 3.79 | 0.878 |
| TG, mg/dL | 173.41 ± 100.21 | 185.71 ± 130.25 | 0.521 |
| Cholesterol, mg/dL | 172.06 ± 46.72 | 137.35 ± 51.11 | 0.008 |
| HDL, mg/dL | 39.66 ± 14.75 | 37.46 ± 6.21 | 0.141 |
| LDL, mg/dL | 93.22 ± 36.02 | 75.91 ± 22.18 | 0.016 |
| GFR, mL/min/1.73m2 | 43.89 ± 18.01 | 46.78 ± 16.98 | 0.871 |
| < 30 | 16 (14.5) | 24 (21.8) | 0.166 |
| 30 - 60 | 70 (58.3) | 66 (60) | |
| 60 - 90 | 21 (19) | 20 (18.2) | |
| > 90 | 3 (2.7) | 0 (0) | |
| LVEF, % | 0.212 | ||
| < 40 | 28 (25.4) | 22 (20) | |
| > 40 | 82(74.5) | 88 (80) | |
| Contrast volume, mL | 0.472 | ||
| < 200 | 106 (96.3) | 108 (98.2) | |
| > 200 | 4 (3.6) | 2 (1.8) |
| Case | Control | Intragroup P Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Creatinine | |||
| Before | 1.53 ± 0.44 | 1.47 ± 0.42 | 0.103 |
| 24, h | 1.50 ± 0.23 | 1.54 ± 0.45 | 0.504 |
| 48, h | 1.52 ± 0.52 | 1.57 ±0.39 | 0.589 |
| IntergroupP Value | 0.502 | 0 | - |
| CIN | |||
| 24, h | 3 (2.7) | 11 (10) | 0.01 |
| 48, h | 3 (2.7) | 6 (5.5) | 0.102 |
| CIN + (N = 14) | CIN - (N = 206) | P Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DM | 9 (64.2) | 142 (68.9) | 0.313 |
| HTN | 14 (100) | 145 (70.3) | 0.011 |
| HLP | 8 (57.1) | 62 (30) | 0.042 |
| GFR, mL/min/1.73m2 | 45.3 ± 16.43 | 58.09 ± 18.43 | 0.039 |
| < 30 | 7 (50) | 37(17.9) | 0.027 |
| 30 - 60 | 4 (28.5) | 131 (63.5) | |
| 60 - 90 | 3 (21.4) | 34 (16.5) | |
| > 90 | 0 (0) | 4 (1.9) | |
| Ejection fraction | 0.008 | ||
| < 40% | 14 (100) | 36 (17.4) | |
| > 40% | 0 (0) | 170 (87.3) | |
| TG, mg/dL | 143.3 ± 44.09 | 178.05 ± 112.41 | 0.647 |
| Chol, mg/dL | 157.35 ± 35.44 | 156.2 ± 49.31 | 0.986 |
| HDL, mg/dL | 38.98 ± 10.45 | 39.87 ± 12.62 | 0.922 |
| LDL, mg/dL | 86.77 ± 10.12 | 86.87 ± 30.16 | 0.91 |
A comparison of the creatinine values before and after angiography demonstrated a significant rise in the serum creatinine level in the control group, with no significant changes in the serum creatinine level in the patients in the case group (Table 3 and Figure 2). CIN was seen in 3 (2.7%) patients 24 hours after angiography in the case group and in 11 (10%) patients in the control group, with 3 (2.7%) patients in the case group and 6 (5.5%) patients in the control group 48 hours after angiography exhibiting CIN (Table 4). There were no significant differences in contrast medium volumes between the 2 study groups (Table 2). There were no significant differences between the 2 groups in the ejection fraction (Table 2). Compared to the positive and negative CIN cases, the frequencies of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and ejection fraction less than 40% were higher in the patients with CIN, and the mean GFR in the patients with CIN was significantly lower than that in the other cases. In addition, the incidence of CIN in the patients with a low GFR was higher than that in the patients with a high GFR (Table 4).
| Study | Result (Positive Effect of Statins on Contrast-Induced Nephropathy Reduction) | Target Population (High-Risk Patients) | Comparison With Our Study |
|---|---|---|---|
| Khanal et al (16) | Yes | No | Consistent |
| Leoncini et al (17) | Yes | No | Consistent |
| Ozhan et al (18) | Yes | No | Consistent |
| Patti et al (19) | Yes | No | Consistent |
| Barbier et al (24) | Yes | No | Consistent |
| Hoshi et al (15) | Yes | No | Consistent at 24 hours but not Consistent after 24 hours |
| Alpert’s editorial Article (25) | Yes | Yes | Consistent |
| Li Y et al systematic review (26) | Yes | No | Consistent |
| Toso et al (20) | No | No | Not Consistent |
| Kandula et al (21) | No | No | Not Consistent |
Comparison of Previous Studies With Our Study
5. Discussion
According to our results, prescription of 80 mg of atorvastatin before angiography reduced the incidence of CIN 24 hours after angiography; nevertheless, 48 hours after angiography, there were no significant differences between the 2 groups in the incidence rates of CIN. The results of the present study were different from those of many previous studies examining high-risk patients. The patients in the present study had a higher risk of CIN than did those recruited in some other studies (Table 4).
The present study had some limitations. First, we did not investigate the effect of atorvastatin without NAC. Atorvastatin and NAC may work through similar mechanisms to prevent CIN. Second, there was a lack of longer periods of access to patients for follow-ups so as to determine the long-term effects of atorvastatin. Third, a limited number of CIN cases resulted in the inability of the present study to analyze subgroups.
In light of our results, CIN can be significantly decreased in high-risk patients with high-dose NAC and atorvastatin, under proper hydration. Additionally, this medication regimen is more effective than is the medication regimen of hydration and NAC (without atorvastatin). Therefore, logically and ethically, atorvastatin should be prescribed at a dose of 80 mg in high-risk patients before angiography and even before PCI. However, further interventions and reviews with a greater number of patients with CIN are necessary for more accurate decisions on this subject.
We recommend that more studies be carried out with larger sample sizes and more cases of CIN along with subgroup analysis among CIN patients to further assess the effect of atorvastatin on the prevention of CIN. Future studies might be retrospective cohort studies with an appropriate number of patients with CIN.