1. Introduction
RMS, a mesenchymal tumor of skeletal muscle, is exceedingly uncommon in adults accounting for less than 4% of all soft tissue sarcomas specifically and 1% of all malignancies generally (1). Because of the extreme rarity of cervical RMS, there is a paucity of literature on the subject, mainly of case reports in which the treatment is not standardized (2).
2. Case Presentation
It is the case of a 30-year-old woman with no pathological history. The patient, hailing from North Africa, has a non-Caucasian ethnicity. She is unmarried, nulliparous, and denies any prior sexual activity. Menarche occurred at thirteen, and she has had regular and non-spotting menstrual cycles.
The disease history began a year before diagnosis, marked by the progressive onset of a vaginal lump sensation exacerbated during coughing or defecation, with no other concomitant symptoms. On gynecological examination, a polypoid mass measuring 3 cm developed in the lower lip of the cervix with an extension to the vulva.
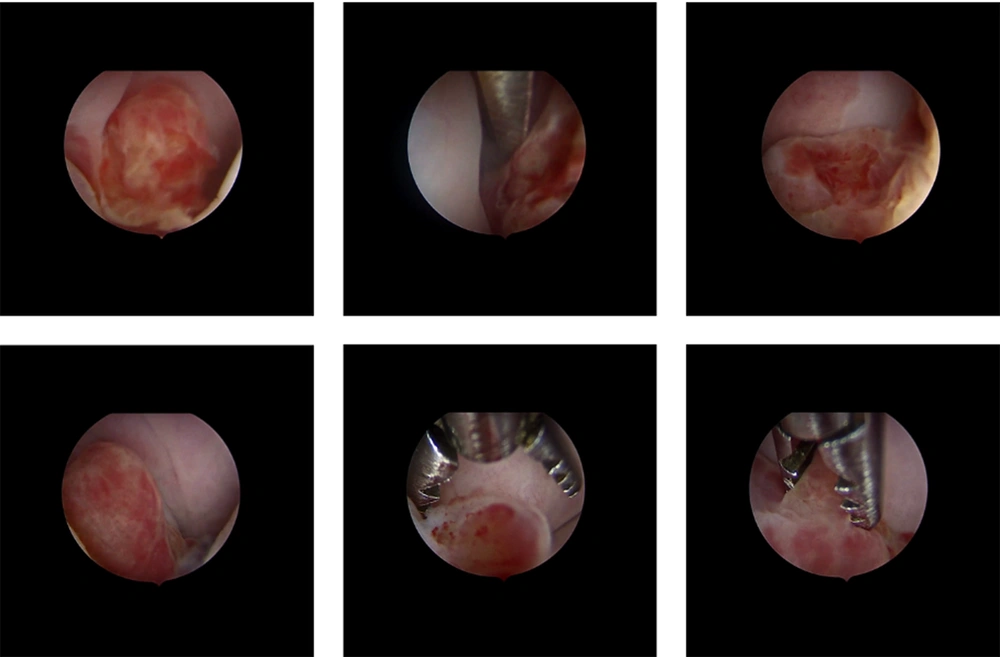
At first, cervical polyp removal was performed, showing at macroscopy several microscopically non-characterizable polypoid fragments measuring up to 1.5 cm. Hysteroscopy showed a budding cervical mass originating at the endocervix, with a regular endometrium (Figure 1), leading gynecologists to opt for conization. Definitive histology concluded an embryonic RMS with spindle cells (desmin+, myogenin+) of the uterine cervix with microscopically involved margins (margin to vaginal slice = 3mm, and margin to isthmic border = 11mm). As a result, it was decided to perform complementary surgery to achieve carcinological clearance by removing the whole cervix and ovarian transposition. The postoperative course was uneventful, with no complications. The pelvic MRI showed no residual mass. The PET-CT didn’t find any hypermetabolic site.
Classifying the patient into the IA IRSG favorable group (T1a according to the TNM classification) corresponds to the low risk of recurrence subgroup. Multidisciplinary reunion decided to treat with adjuvant chemotherapy and did not retain the indication of postoperative radiation therapy. The patient received adjuvant chemotherapy with good tolerance based on 4 cycles of doxorubicin at 60/m2 (day 1) and ifosfamide at 3000 mg/m2 (days 1 and 2). Six months after the surgical procedure and one month after chemotherapy treatment, the patient remains in good general condition with no gynecological or other symptoms. A pelvic MRI is planned.
3. Discussion
RMS, a mesodermal tumor, is developed from immature mesenchymal cells committed to skeletal muscle differentiation (1-3). The cervix is a particularly rare site, representing less than 1% of cervical cancers (4). Vaginal localization is five times more frequent than cervical localization and is generally seen in sexually active women or young girls with an average age between 10 and 20 years (4, 5).
Clinically, a polypoid mass can reveal cervical RMS or, more commonly, a grape-like appearance, but most of the time, there is a paucity of symptoms that delay the diagnosis. Less often, it manifests itself as iterative bleeding, leukorrhea, or malodorous discharge. MRI is currently the gold standard imaging modality used to determine local invasion, distant metastases, and surgical intervention plans and helps delineate disease extent (6).
This diagnosis was made more easily in the later era due to improvements in immunohistochemistry (IHC) and molecular pathology, leading to better RMS characterization.
RMS was classified by the World Health Organization in 2013 into embryonal (including botryoid and anaplastic), alveolar (including solid and anaplastic), pleomorphic, and spindle cell (or sclerosing). All these RMS histotypes are associated with different features, with a predilection for certain primary sites and age groups. Moreover, the alveolar histological subtype is known to have a poor prognosis (7). IHC staining (vimentin, desmin, or actin) is highly recommended to ensure the correct diagnosis is reached (8).
Through the years, major clinical trials on RMS have been conducted by international cooperative groups, for the IRSG, now the Soft Tissue Sarcoma Committee of the Children’s Oncology Group (COG) and in Europe 3 groups; the International Society of Pediatric Oncology – Malignant Mesenchymal Tumor Committee (SIOP-MMT), the German Soft Tissue Sarcoma Cooperative Group (CWS) and the Italian Cooperative Group (ICG). SIOP-MMT and ICG have lately formed the European Pediatric Soft Tissue Sarcoma Study Group (7).
IRSG, created in 1972 by the National Cancer Institute, studied patients under 21 years old in large, multi-institutional trials designed over a 25-year period to answer successively critical questions in a total of 5 clinical procedures (IRS I-V) in which 4292 patients were included. It is important to mention that many of these trials were randomized. The goal is stabilizing and establishing therapeutic approaches according to disease staging (9).
Patients were allocated into three different categories predicting recurrence risk (low, intermediate, and high risk), depending on the amount of residual disease after initial surgery, metastases, histologic subtype, tumor size, and anatomic size. A treatment protocol was established for each subgroup (7, 9). IRSG findings and protocols have shown its benefice. Indeed, around 70% of children suffering from RMS disease have been cured, according to the multimodal approach proposed by the IRSG. Nevertheless, all existing studies report a poorer outcome for adults than children, despite the extrapolation of multimodal treatment from pediatric experience.
A retrospective study published in the American Cancer Society in April 2003 was conducted in Italy, enrolling 171 patients aged between 19 and 83 years old. All were treated according to the same protocols proposed for children (by the IRSG and ICG) with a follow-up varying from 8 to 260 months, aiming to compare results between children and adults on both overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS). For that, three scores were assigned to each patient: one for the adequacy of local treatment (surgery, radiotherapy), one for the adequacy of chemotherapy, and one for the adequacy of the overall treatment strategy. The three scores were correlated to give a single number, 0 or 1. An overall score of 1 corresponds to a treatment regimen that is in total conformity with current recommendations for treating pediatric RMS. In the embryonal and alveolar RMS group, scores of 1 were associated with greater overall survival, in terms of local treatment or chemotherapy, with a combined score of 1 corresponding to the overall survival of up to 61.5%. Results in adults were similar to those in children. Concluding that adults and children should receive the same treatment (10).
This treatment is based on three therapeutic modalities (chemotherapy, surgery, and radiotherapy), given the aggressiveness of the disease. Chemotherapy is a mainstay in RMS treatment, as every RMS patient is assumed to have micrometastatic disease at diagnosis.
Four ISRG studies have shown that in pediatric patients, surgeries such as local resection and polypectomy followed by VAC type chemotherapy, including vincristine, actinomycin D, and cyclophosphamide, could replace radical surgery and radiotherapy, without significant change in survival, thus allowing patients to preserve their fertility (11). However, the optimal chemotherapeutic schedule for adjuvant treatment in adults remains debated.
The use of chemotherapy in treating embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (ERMS) in adults is also not well-documented, and pediatric protocols have not shown to be as effective as for adults. Several drug combinations, including vincristine, dactinomycin, cyclophosphamide, dacarbazine, doxorubicin, ifosfamide, and etoposide, have yielded promising results. Thus, further research is required to identify the best chemotherapeutic regimen for managing RMS in adult patients (12). In addition, given the RMS chemo-sensitivity, it has led to an evolution in the role of local therapies (12).
Surgery has moved from an aggressive approach to a more conservative one, with organ and fertility-sparing. RMS of the female genital tract has evolved toward conserving the genitourinary organs, polypectomy, and simple or radical trachelectomy improved prognosis and decreased morbidity (13).
Radiation therapy is indicated for local control of tumors in patients with microscopic or gross residual disease following initial surgical resection or chemotherapy. Patients with completely resected tumors (Group I) of embryonal histology, like the case of our patient, do well without radiation therapy, but those with worse histology may benefit from radiation (13).
Radiations are delivered using megavoltage equipment with doses generally ranging between 40 and 55 Gy (depending on the patient’s age, tumor size, site, response to primary chemotherapy, histological features, and extent of residual tumor after surgery) (7). But still, radiotherapy indications are extremely variable, ranging from no radiotherapy to external radiotherapy or brachytherapy. Due to the rarity of this tumor, no clear data are present in the literature on its role in adults (13).
A good response to multimodal therapy generally characterizes RMS. Several factors predict a poor response to treatment, such as residual disease after surgery, which appears to be the most important factor, histological type, and anatomic site (14).
According to the IRSG classification, our patient has a 3-year recurrence-free survival rate of around 88%.
3.1. Conclusions
Given the rarity of RMS in adults and the absence of standardized protocols for managing these tumors, a multidisciplinary decision is essential, and case reports remain highly relevant.