1. Introduction
Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor (DNET) is a benign tumor commonly observed in the supratentorial cerebral cortex, mostly in the temporal lobe. These tumors involve glial and neuronal cells (1). The epileptic seizure is the common presentation that can cause drug-resistant temporal lobe epilepsy and usually affects young adults (2, 3). Since multifocal DNET occurs rare, it is usually reported as a case study (4). The current report presented a case of DNET and discussed radiological findings and common manifestations that should be considered in patients with intractable epilepsy and temporal lesion.
2. Case Presentation
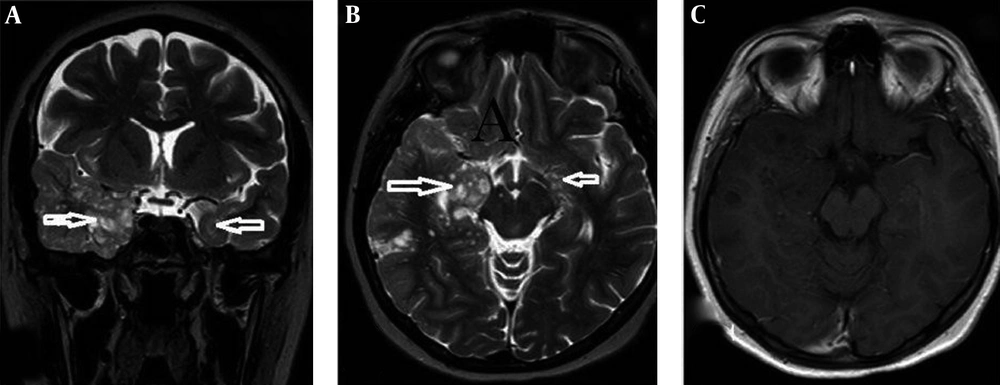
The patient referred to the hospital with four months history of recurrent seizure that did not respond to any treatment. She also had at least four complex partials or secondarily generalized seizure daily that usually lasted for less than five minutes. The family history of seizure was positive in her son without any lesions in brain imaging. In the physical examination, she was conscious, and the neurological examination of the patient was normal. The brain magnetic resonance (MR) showed multiple nonspecific hyperintense lesions in the bilateral temporal lobe, mostly in the right side, in the white and gray matter in association with mesial temporal sclerosis (Figure 1). Moreover, there was no enhancement after gadolinium. She underwent right frontotemporal craniotomy and selective temporal lobectomy was performed, and the tissue sample was sent for histopathological examination. Microscopic examination showed a nodular aggregate of oligodendroglial-like cells bearing some mucin filled cystic space in between that replaced normal cortical neuron. The tumoral cells had round uniform nuclei, some with distinct nucleoli and perinuclear clear zone, which in some foci surrounded neuronal cells (Figure 2). In the follow-up, the patient was seizure-free after surgery.
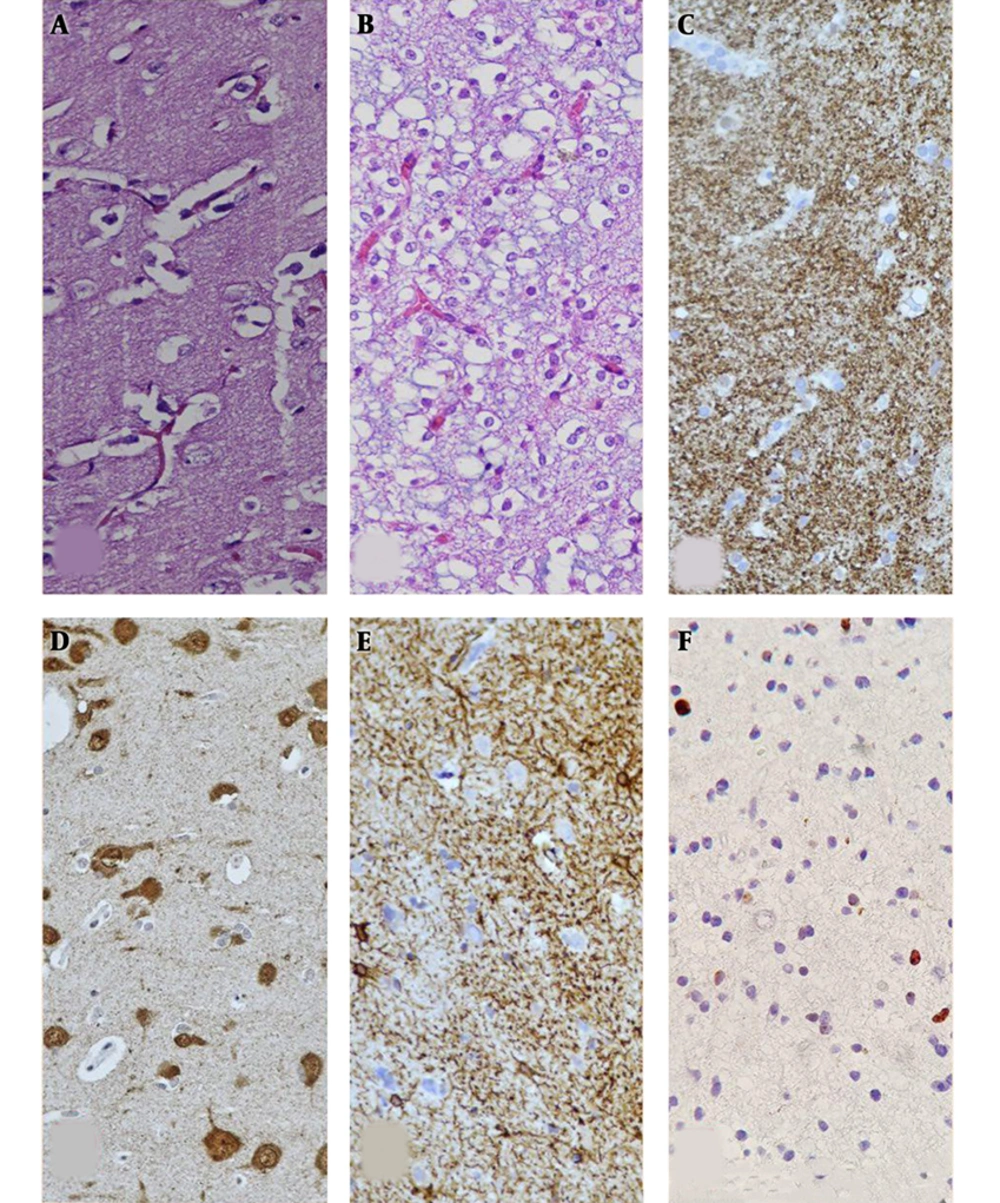
The H&E staining of the left temporal lesion revealed oligodendroglial-like cells, while tumoral cells had round uniform nuclei, which in some foci surrounded neuronal cells (A and B). Additional immunohistochemical findings: synaptophysin immunostain (C), neuronal glial (D), fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) immunostain (E), and Ki-67 immunostain (F).
3. Discussion
The DNET is a benign, mixed neuronal and glial tumor that usually originates in the supratentorial cortex (5). The prognosis of this tumor is good after surgery and many patients become seizure-free. It often presents with complex partial or secondary generalized epilepsy (6, 7). Sirbu presented a case of DNET associated with sudden unexplained death in epilepsy (8). Most of these tumors are located in the temporal lobe that can be associated with mesial temporal sclerosis. The involvement of the cerebellum, thalamus, hypothalamus, pons, and basal ganglia is also reported in this tumor (9-11). Argyroupoulou et al. reported a case of DNET with cerebellar atrophy and involvement of the thalamus and internal capsule (12). In the brain computed tomography (CT), this tumor is usually hypodense and sometimes is associated with calcification and multicystic appearance. This tumor does not usually have edema and mass effect, but Guduru et al. reported a case of DNET presented with seizure and the tumor was located in the temporooccipital with mass effect and edema (13). In the current case there was an atypical presentation in the brain imaging and a multifocal hyper signal lesion in the temporal lobe in association with cortical dysplasia. Multifocal DNET is an extremely rare presentation of this tumor that can be in association with cortical dysplasia. White et al. reported a case of multifocal DNET presented with temporal lobe epilepsy and concomitant intradural spinal cord lipomas (14). In another report, Andrew et al. presented a case of multifocal DNET with seizure and there was a multiple lesion in supra and infratentorial (15). Multifocal DNET is a rare presentation, and since the tumor is multifocal, the main treatment is the medical therapy (15, 16), however, in the current case, since seizures were resistant to treatment, the patient underwent surgery and the patient was seizure-free.