1. Background
Metastasis to the brain is one of the most common intracranial tumors in adults. An important cause of morbidity and mortality in 10% to 30% of adult cancer patients is brain metastasis (BM) (1). As per the American Cancer Society, in the United States, each year 170000 cancer patients develop brain metastasis, with most of them having two or more metastases (2). Lung cancer is the most common primary cause of brain metastases and is accountable for nearly half of all secondary tumors of the brain. Other major primary tumors comprise of breast cancer, melanoma, and colorectal cancer.
Brain metastasis patients with different signs and symptoms range from an incidental imaging finding to changes in mental status, seizures, headache, dizziness, blurred vision, nausea, weakness or aphasia. Symptoms usually progress over a period of a few weeks. However, with tumors like malignant melanoma, thyroid carcinoma, renal cell carcinoma, and choriocarcinoma, patients may present with hemorrhage into the metastases, which can cause a more dramatic presentation (3). Patients are managed with symptomatic care and definitive treatment. Multiple lesions or widespread metastatic disease is seen in the majority of patients at presentation. Whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT) is the standard treatment (4, 5). SRS have the advantage over resection. With respect to overall survival no statistically significant is noted with different fractionation schedules and doses. With respect to tolerability, short treatment time, cost-effectiveness, and trend for better survival 30 gray/10 fractions have become the standard of care (6). Systemic chemotherapy in brain metastases patients is rapidly growing as a treatment option. Antonadou et al., suggested that concomitant whole brain radiotherapy and temozolomide improves quality of life (7).
The effect of WBRT on neurocognitive dysfunction and dementia is poorly understood. A study conducted at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center demonstrated that patients surviving one year or more after WBRT had an 11% risk of dementia (8).
2. Objectives
However, there is no study clearly showing the decline in memory function in brain metastases patients undergoing WBRT treatment. Hence, in this study we are evaluating memory function outcomes in patients receiving WBRT with two different fractionation schedules with concurrent TMZ.
3. Methods
3.1. Eligibility Criteria
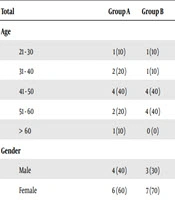
The Medical Ethics Review Board approval was sought for the study protocol and consent procedure. Patients aged 18 - 70 years with Karnofsky performance status (KPS) of more than or equal to 70, with a histologically proven systemic tumor, radiologically diagnosed brain metastases, and without a history of metastatectomy, radio-surgery, or chemotherapy in the previous three weeks and prior radiation to brain were eligible. Patient and tumor characteristics are as shown in Table 1.
| Group A | Group B | P Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 10 (100) | 10 (100) | |
| Age | 0.910 | ||
| 21 - 30 | 1 (10) | 1 (10) | |
| 31 - 40 | 2 (20) | 1 (10) | |
| 41 - 50 | 4 (40) | 4 (40) | |
| 51 - 60 | 2 (20) | 4 (40) | |
| > 60 | 1 (10) | 0 (0) | |
| Gender | 1.000 | ||
| Male | 4 (40) | 3 (30) | |
| Female | 6 (60) | 7 (70) | |
| KPS | 1.000 | ||
| 70 | 2 (20) | 2 (20) | |
| 80 | 5 (50) | 5 (50) | |
| 90 | 3 (30) | 3 (30) | |
| Neurological deficit | 0.160 | ||
| Yes | 2 (20) | 5 (50) | |
| No | 8 (80) | 5 (50) | |
| Site of primary tumor | 1 | ||
| Lung | 8 (80) | 7 (70) | |
| Breast | 1 (10) | 0 (0) | |
| Bronchogenic carcinoma | 1 (10) | 1 (10) | |
| Choriocarcinoma | 0 (0) | 1 (10) | |
| Metastasis of unknown origin | 0 (0) | 1 (10) | |
| BSA | 0.532 | ||
| < 1.3 | 0 (0) | 2 (20) | |
| 1.3 - 1.6 | 10 (100) | 7 (70) | |
| > 1.6 | 0 (0) | 1 (20) | |
| Number of brain metastases | 1.000 | ||
| 1 | 1 (10) | 1 (10) | |
| 2 - 4 | 8 (80) | 8 (80) | |
| > 4 | 1 (10) | 1 (10) |
Patient and Tumor Characteristicsa
Informed consent was taken. Patients were randomly assigned into two groups; whole brain radiation therapy with 40 gray/20 fractions (group A) and 30 gray/10 fractions (group B). Concurrent chemotherapy was given in both groups.
3.2. Radiation Therapy
For WBRT, the entire brain parenchyma and meningeal reflections were treated.
3.3. Chemotherapy
Half an hour before radiation therapy, patients in both arms received capsule temozolomide (TMZ), 75 mg/m2, five days a week, orally, under fasting condition, along with prophylactic oral antiemetic (ondansetron 8 mg OD) before TMZ.
3.4. Memory Function Assessment
Memory function assessment was done using P.G.I. Memory scale before, during, and after the treatment, as well as at three months and 6 months of follow-up (Tables 2-8).
| Remote Memory (Maximum Score 6) | Group A | Group B | P Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before RT | 5.40 ± 0.70 | 5.10 ± 0.32 | 0.232 |
| During RT | 5.70 ± 0.48 | 5.10 ± 0.32 | 0.004** |
| After RT | 5.70 ± 0.48 | 5.00 ± 0.47 | 0.004** |
| 3 months | 5.11 ± 0.93 | 4.43 ± 0.53 | 0.106 |
| 6 months | 5.00 ± 0.00 | 4.50 ± 0.71 | 0.667 |
Remote Memory (Maximum Score 6)
| Recent Memory | Group A (Mean Rank) | Group B (Mean Rank) | P Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before RT | 11.8 | 9.2 | 0.353 |
| During RT | 11.6 | 9.4 | 0.436 |
| After RT | 14.8 | 6.2 | 0.001 |
| 3 months | 9.61 | 10.35 | 0.78 |
| 6 months | 8.56 | 11.3 | 0.315 |
Recent Memory
| Attention and Concentration | Group A (Mean Rank) | Group B (Mean Rank) | P Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before RT | 9.45 | 11.55 | 0.436 |
| During RT | 8 | 13 | 0.063 |
| After RT | 14.05 | 6.95 | 0.005 |
| 3 months | 8.28 | 11.55 | 0.211 |
| 6 months | 9.06 | 10.85 | 0.497 |
Attention and Concentration
| Delayed Recall (Maximum Score 10) | Group A | Group B | P Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before RT | 7.90 ± 0.88 | 7.90 ± 0.88 | 1.000 |
| During RT | 8.20 ± 0.92 | 8.00 ± 0.82 | 0.613 |
| After RT | 8.00 ± 1.05 | 7.90 ± 0.99 | 0.830 |
| 3 months | 7.67 ± 1.22 | 7.86 ± 1.07 | 0.749 |
| 6 months | 7.00 ± 0.00 | 8.00 ± 1.41 | 0.667 |
Delayed Recall (Maximum Score 10)
| Immediate Recall (Maximum Score 12) | Group A | Group B | P Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before RT | 9.10 ± 1.52 | 8.80 ± 1.32 | 0.643 |
| During RT | 9.80 ± 1.69 | 8.90 ± 1.37 | 0.207 |
| After RT | 9.50 ± 1.72 | 8.70 ± 1.64 | 0.300 |
| 3 months | 8.44 ± 1.67 | 8.43 ± 1.62 | 0.985 |
| 6 months | 6.00 ± 0.00 | 9.50 ± 0.71 | 0.154 |
Immediate Recall (Maximum Score 12)
| Verbal Retension For Similar Pair | Group A (Mean Rank) | Group B (Mean Rank) | P Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before RT | 11.45 | 9.55 | 0.481 |
| During RT | 10.25 | 10.75 | 0.853 |
| After RT | 14.45 | 6.55 | 0.002 |
| 3 months | 8.78 | 11.1 | 0.4 |
| 6 months | 9.22 | 10.7 | 0.604 |
Verbal Retention for Similar Pairs
| Verbal Retention for Dissimilar Pairs (Maximum Score 15) | Group A | Group B | P Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before RT | 10.40 ± 0.97 | 10.70 ± 1.06 | 0.517 |
| During RT | 10.70 ± 1.16 | 10.70 ± 1.06 | 1.000 |
| After RT | 10.70 ± 1.06 | 10.10 ± 1.79 | 0.374 |
| 3 months | 8.89 ± 1.83 | 9.43 ± 0.79 | 0.481 |
| 6 months | 8.00 ± 0.00 | 10.00 ± 0.00 | - |
Verbal Retention for Dissimilar Pairs (Maximum Score 15)
3.5. Follow-up
Patients were followed-up for a period of six months’ after chemo radiation therapy.
4. Results
4.1. Statistical Methods
Data analysis was done using the statistical software SAS 9.2, SPSS 15.0, Stata 10.1, MedCalc 9.0.1, Systat 12.0, and R environment Ver.2.11.1. A P value of less than 0.05 is taken as a significant relationship.
5. Discussion
An ability to retain and reproduce intentionally perceived impression is memory (9, 10). This definition includes compartmental views of very short term, short term, and long-term memory. Working memory is often used to denote short term memory. Short-term memory allows a recall for a period of several seconds to a minute without rehearsal. Its capacity is also very much limited. Long-term memory can store much larger quantities of information for potentially unlimited duration (sometimes a whole life span). Its capacity is immeasurable. Information is encoded acoustically in short term memory and semantically in long term memory. Transient patterns of neuronal communication support short-term memory and is dependent on regions of the frontal lobe and the parietal lobe. On the other hand, long-term memory is supported by permanent changes in neural connections. Short term memory is consolidated into long term memory in hippocampus.
Recent research in humans showed that DNA methylation, or prions, are responsible for long-term memory storage (11). In the recognition memory task it is evaluated whether an individual had an encounter with a stimulus like a picture or a word before.
Ecognition memory tasks require individuals to indicate whether they have encountered a stimulus (such as a picture or a word) before. In the recall memory tasks, participants are asked to retrieve previously learned information.
Neuro toxicity is noted in brain metastasis patients who have received WBRT, especially declarative memory. The study of Chang et al., observed a greater decline in memory [as demonstrated by the Hopkins verbal learning test revised (HVLT-R)] at four months, in the SRS plus WBRT group compared to SRS alone (12). This decline in memory has been described as part of a biphasic pattern of cognitive loss. Post WBRT initial deterioration was noted in multiple domains of cognitive function, which peaks around four months post radiation.
They study of DeAngelis et al. (8), on 12 patients treated with WBRT (25 - 39 Gy in three to six Gy per fractions), dementia, ataxia, and incontinence was noted in all the patients at a median of 14 months after WBRT. However, actual incidence of radiation induced dementia is much lower in modern practice as smaller fraction sizes are used.
Studies using these regimens in conjunction with neurocognitive follow-up have suggested general stability in neurocognitive function for most patients in the short to medium term after whole brain radiotherapy in the absence of tumor recurrence. In addition, in our study, we noted the improvement in four domains of memory function in patients treated with two Gy per fraction during radiation therapy.
However, decline in memory function was noted in both groups at three and six months post treatment assessment of memory function. The short-coming of our study is the small population of patients. Hence it needs to be confirmed in a study with a larger population. In addition, an improvement in the memory function might be due to the specific location in the brain, hence it also needs to be analyzed further.
5.1. Conclusions
Therefore, we conclude that 40 Gy in 20 fractions given over four weeks, with concurrent TMZ, is better and a preferable treatment option for patients with brain metastasis with respect to memory function. However, it needs to be confirmed in a study with a larger population.