1. Background
Different theories about learning are associated with different knowledge views. Experiential theories discuss about how each person learn things in different ways as they react to personal perceptions of experiences during their lives (1). One of the important factors that affect learning among students is their learning styles. To achieve the desired level of learning, differences among students and their learning style must be identified (2). There has been interest about different learning styles because of individual learners characteristics (1, 3). There is a prediction about matching learning preference with learning style could develop learning and there has been a huge effort to identify personal learning preference (1, 4) There are several learning style modes which among them, The Kolb method was mostly used (5, 6) and the latest version of the Kolb Learning Style Inventory instrument is version 3 (LSI 3) (7). Researchers found that Kolb’s learning theory is useful for explaining Substructure which is related to learning process in medical education (1, 8, 9) According to the Kolb theory, learning styles consist of four stage cycle (Figure 1) (10).
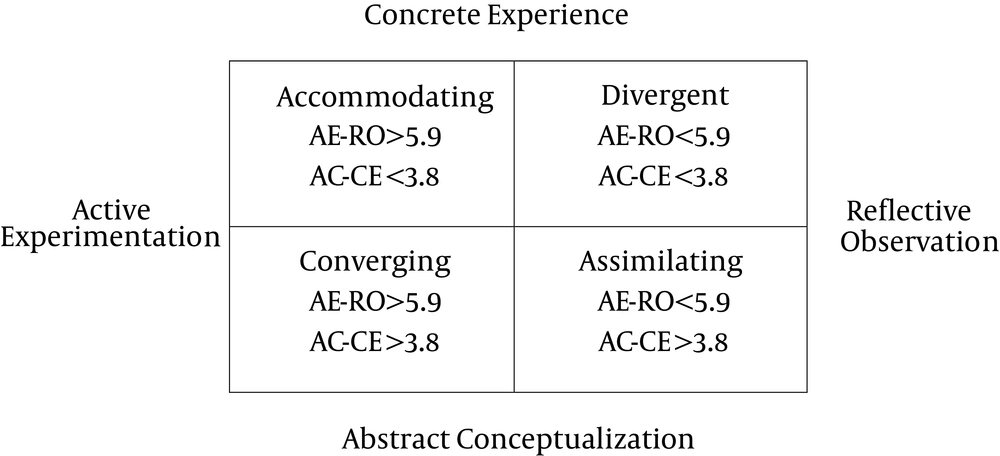
The four modes of adaptive learning that constituted his cycle were ‘concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization and active experimentation’ (11). In this model, there are two processes for perceiving information: concrete experience mode and abstract conceptualization mode and two processes for processing experience into learning: active experimentation mode and reflective observation mode. These four processes are combined into four learning styles as follows:
1) Converging (abstract conceptualization mode and active experimentation mode)
2) Accommodating (concrete experience mode and active experimentation mode)
3) Diverging (concrete experience mode and reflective observation mode) and
4) Assimilating (abstract conceptualization mode and reflective observation mode).
Diverging style these individuals value generating skills including building relationships with others, preferring to help others and they have sense making (reasoning). Assimilating learning style is related to thinking abilities including collecting information, analyzing data and they like to build theory. Converging learning style is related to decision skills including ability of quantitative analysis, technical device use and formulation of goals. Accommodating learning style is related to acting skills including leadership, initiative and action (6, 11-13). Learning styles of the Kolb model are not only associated with skill, but also with adaptively and flexibility concerning management of different situations. Curry (12) mentioned that learning styles are different from capability and strategy. Styles might be monitored along content domains, personalities and interpersonal treats and they are assessed in terms of ordinary performance. According to Curry, learning style is spontaneously demonstrated without conscious awareness or choice from different situations. Strategies are results of conscious awareness for making decisions and methods might be monitored in specific performing situations (6, 12).
Searching among different articles support that the learning styles of medical students in different countries which have different culture are diverse (14-19). There was a research has conducted in Germany which showed that the preferred learning style among medical students was assimilator and has relationship with psychological ailments (20). Moreover, a research on nursing students in USA showed that the preferred learning style was assimilating (21).
In Iran, various studies declared, students’ preferred learning styles: medical students’ preferred learning style in Alborz University of Tehran was convergent and had relationship with their gender, field, semester, and job (14); the preferred learning style in Tehran University was divergent but master students more preferred convergent style and has no relationship with their gender, (22) and the preferred learning style in Isfahan University was divergent (23). The preferred learning style in Brijand on medical students was convergent and has no relationship with their age, sex and their score in university (24) and in a study that was conducted in Qazvin University on nursing students, it was more assimilating and had no relationship with their demographic features (25). Since university educational managers and teachers have the responsibility of teaching and learning activities; the positive role of learning styles assessment has been proven in development of students’ academic achievement, motivation, and professors teaching methods, so, it is essential to take these assessing learning styles into consideration (2, 4, 14, 15, 17, 20). There is a criticism of investigating about individual learning style in learning system; this could lead to the individual training which would put a burden on educational systems (26). Despite such criticism, the majority of studies about searching the preferred learning style were declared the positive role of learning styles on students’ success and improve their motivation (20, 27). Determining individuals’ learning styles, based on their differences has been found to be effective for programming (17, 18, 20). So, determining effective kind of learning based on people’s characteristics is so important (28). Studies performed to determine learning styles and baseline characteristics to meet the learning needs also can provide valuable information about the relationship between learning styles and these characteristics. The results gained from the current study for training programs can be configured to meet the needs of staffs and students, and thus progress can be made for students and university.
2. Objectives
As long as learning styles have an important impact on student learning, and different cultures of students affects that, and also for preparing the best learning curriculum for students, it is necessary to know what is their learning styles. Therefore, this study aimed to assess learning styles of individuals and examine the relationship between learning styles and baseline characteristics of students at Kerman University of Medical Sciences.
3. Patients and Methods
In this cross-sectional single stage study, the study population consisted of 400 masters’ and doctoral postgraduate students in Kerman University of Medical Sciences in the second semester of the academic year 2013-14. . The sample size was determined by using the formula of limited population (29-31). In this regard, 365 cases were identified but in order to increase the reliability of data 400 cases were included. To collect data, the students were randomly selected and were given a questionnaire.
3.1. Tool
We used a questionnaire to gather data. This questionnaire consisted of 2 parts. The first part contained baseline characteristics or demographic features such as sex, age, place of living, marital status, and job. The second part was Kolb learning style inventory (7), which is widely used and accepted as a measuring tool to determine the learning styles of the learners (32). The questionnaire has 12 questions and each question has 4 multiple choice answers as Concrete Experience (CE), Reflective Observation (RO), Abstract Conceptualization (AC), and Active Experimentation (AE). Students were asked to give numbers 1 to 4 to each question (number 4 completely agreeable and number 1 not agreeable). By summing the scores for each of the 4 options, we can determine the learning style of each individual. By subtracting the AC score from CE score (AC - CE) and RO from AE (AE - RO), two scores can be obtained. These two scores are then placed on the x and y axes. At one end of the vertical axis and on the other end AC and CE are placed, respectively. This is true for AE and RO on horizontal axis as well. These can form 4 quadrants in which each square represents one quarter of the learning styles (Figure 1). The quarter of CE and RO represents a divergent learning style and the quarter of CE and AE represents an accommodating learning style. In a similar vein, the quarter of AC and AE represents a convergent learning style and the quarter of AC and RO represents an assimilating learning style.
3.2. Reliability and Validity
The content validity of this questionnaire that was approved in a study by Brower Cronbach was 0.73 to 0.88 (33). Ibrahimoglu et al. Cronbach’s alpha was 0.64 to 0.77 (34) and in Romanelli study was 0.69 (17). In the study by Darvishzadeh and Sabzevari (28) in Iran the correlation coefficient (to determine learning styles) was 50%. In addition, to determine the internal consistency, Cronbach’s alpha coefficient was calculated to be 0.7 (28). In this study, the validity of the tool was assessed andthe scale factors were determined to be 0.75 for the Cronbach’s alpha reliability value, which meant that the scale was reliable. To analyze data, SPSS version 22 software was used. We applied descriptive statistics (frequency distribution, mean, and standard deviation) as well as analytical tests (ANOVA).
4. Results
In our study, 246 women (61.5%) and 154 men (38.5%) were participated. Among the participants, 376 cases (94%) lived in town and only 24 (6%) lived in a village. Moreover, 334 cases (83.5%) used the dormitory and the rest (n = 66, 16.5%) did not use dormitory. In terms of marital status, 297 cases (74.3%) were single and 103 (25.7%) were married. In addition, 108 cases (27%) had a job and 292 (73%) did not have a job. In the initial research process, the learning styles of the participants were determined. The distribution frequency and percentages are shown in Table 1. Findings indicate that the highest frequency of learning style is 204 out of 400 cases (51%) for learners with convergent learning style. No correlation was found between the baseline features and the learning styles. Moreover, the results showed that learners living in town had convergent style more than other learning styles, while learners living in village had assimilating style more than other learning styles. Additionally, both genders had more convergent learning style.
| Learning Styles | No. (%) |
|---|---|
| Divergent | 32 (8) |
| Assimilating | 124 (31) |
| Converging | 204 (51) |
| Accommodating | 40 (10) |
| Total | 400 (100) |
5. Discussion
In this paper, we assessed the relationship between the learning styles and baseline characteristics. The results of various studies demonstrate that learners have different learning styles and this diverse is due to dissimilar places and variant personality (14-19, 28, 34). The results also showed that the learning styles of women and men are different (14, 35).
In this study, most participants had convergent learning style and the learning style had no correlation with baseline characteristics. However, it had a relationship with the place of living in which those participants who lived in town had more convergent learning style compared to other learning styles. In comparison, those participants who lived in village had more assimilation learning style. Both men and women had the same preferred learning style. But the percentage among women was 3% higher than that in men. In preferred learning those people who stay in dormitory had the same results in comparison with others. Regarding marital status both single and married participants had a convergent learning style more than other learning styles. According to Table 2 both single and married learners had convergent learning styles which in single learners convergent style percentage was almost 10% higher than married learners (53.5 > 43.7%). In terms of occupation, both single and married learners had a higher convergent style. Employed participants had 6% more convergent learning style. Various study showed preference of convergent style: study of Alborz university more convergent style and had relationship with gender, and job (14).
| Baseline Characteristics | Learning Style | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assimilating | Convergent | Divergent | Accommodating | Total | P Value | |
| Gender | 0.309 | |||||
| Female | 69 (28) | 128 (52) | 23 (9.3) | 26 (10.6) | 246 | |
| Male | 55 (35.7) | 76 (49.4) | 9 (5.8) | 14 (9.3) | 154 | |
| Place of live | 0.191 | |||||
| Town | 112 (29.8) | 194 (51.6) | 31 (8.2) | 39 (10.4) | 376 | |
| Village | 12 (50) | 10 (41.7) | 1 (4.2) | 1 (4.2) | 24 | |
| Stay in dorm | 0.261 | |||||
| Yes | 110 (32.9) | 167 (50) | 26 (7.8) | 31 (9.3) | 334 | |
| No | 14 (21.2) | 37 (56.1) | 6 (9.1) | 9 (13.6) | 66 | |
| Marital status | 0.232 | |||||
| Single | 85 (28.6) | 159 (53.5) | 22 (7.4) | 31 (10.4) | 297 | |
| Married | 39 (37.9) | 45 (43.7) | 10 (9.7) | 9 (8.7) | 103 | |
| Employment status | 0.496 | |||||
| Employed | 30 (27.8) | 60 (55.6) | 10 (9.3) | 8 (7.4) | 108 | |
| Unemployed | 94 (32.2) | 144 (49.3) | 22 (7.5) | 32 (11) | 292 | |
a Data are presented as No. (%).
In a study which was conducted in Birjand, showed that medical students had more convergent learning style and their styles had no relationship with their age, sex and score of university (24) besides in Richard et al. study, which was conducted in Pennsylvania on postgraduate medical students demonstrated preferring converging learning style and had correlation with their individual features (36) which their findings almost followed our results. However, the study of Hosseini and Seif in Tehran indicated that learners had more assimilating learning style (30%) and then convergent learning style was prominent with 1% difference (29%) (22). In the study conducted by Burger and Scholz in Germany, the preferred learning style was assimilator and has relationship with psychological ailments (20). Furthermore, in a research of Shinnick and Woo in California the preferred learning style was assimilating (21). In the study of Darvishzadeh and Sabzevari (28), medical students preferred the assimilating learning style and no correlation was found between learning styles and variables such as age, sex, and marital status. However, a significant correlation was found between student’s living place and learning styles. Furthermore, findings highlighted that learners who lived in town used assimilating learning style more than other learning styles and learners in villages used divergent learning style more than other styles (32). In Ibrahimoglu et al. research, which was performed on 421 students in Gaziantep University of turkey using the Kolb questionnaire, it was shown that most students used assimilating learning style and their learning styles had a correlation with their personal characteristics (34). The result of this study is not consistent with our findings. This can be concluded that the learning style of students differs in various cultures. For example, those learners who lived in different places had different learning styles. In the studies of Darvishzadeh et al. (28) and Ibrahimoglu et al. (34) due to the differences we have various styles. Furthermore, we should consider that these styles can have different results in individuals. For example, in this study the participants were postgraduate students but in the study of Darvishzadeh (28) they were medical students and in Ibrahimoglu et al. (34) they were undergraduate students. The convergent learning style is suitable for those students who are more logical. Our research is suitable for teachers and the educational system. we hope the findings of our research be used in planning the curriculum and we also suggest more research in other disciplines of Kerman Medical University for instance, among undergraduate and dental students to find their preferred learning style in order to plan teaching and learning methods.