1. Background
Under stress conditions the human body secretes glucocorticoids. In rats, corticosterone is the major glucocorticoid involved in energy regulation, immune responses, and stress reactions. Secretion of this hormone allows a fight-or-flight action by activating the endogenous substrate and motivating a state of insulin resistance in the liver and skeletal muscles.
Chronic stress has damaging effects on the brain and especially affects the hippocampal structure and function leading to cognitive and mood disturbances (1). The hippocampus is an important structure for spatial learning and memory, which is enriched with corticosteroid receptors (2). This means that it is susceptible to stress-induced corticosteroid impairment (3). Stress can induce dendritic retraction in the hippocampal CA3 subregion following prolonged restraint (4-6) or chronic social stress (7). Chronic stress can also increase apoptosis in the hippocampus, thereby causing memory decline (8). Five hours of restraint stress has been shown to produce modest impairment in a novel object recognition task (9). Importantly, these stress-induced cognitive disturbances are likely to be exaggerated in the absence of physical activity (1).
Kim and Seo exposed rats to electric shock stress (seven consecutive days) and treadmill exercise running (30 min/d × 4 d); they showed that exercise increases neurogenesis, inhibits apoptosis, and relieves stress-induced destruction of spatial learning (10). Treadmill running can also alleviate repeated stress-induced spatial memory deterioration by removing reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the hippocampus and activation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) signaling (11). Moreover, physical exercise prevents memory loss and leads to reduced insulin resistance (12). However, little is known about the concurrent effects of exercise and insulin treatments on memory performance.
The high density of insulin/insulin receptors in the brain areas such as the hippocampus and cerebral cortex plays a critical role in higher cognitive function. This indicates that insulin could be involved in the modification of memory (13). Also, it promotes neuroplasticity in the developing and adult brain (14). Accordingly, after water maze training, gene expression of insulin receptors shows up-regulation in the CA1 region (15). Some reports present that insulin prevents memory loss. For example, Moosavi et al. demonstrated that intrahippocampal insulin injection protected against stress-induced memory impairment (3). Similarly, one week of intranasal administration of insulin prevented anesthesia-induced spatial learning and memory deficit (16). On the other hand, other studies report that intraperitoneal (IP) administration of insulin can impair spatial memory in a dose-dependent manner (17, 18).
Moreover, insulin seems to have neuroprotective effects against memory impairment induced by stress, drugs, and diseases (3, 16, 19). The neuroprotective mechanisms of insulin include the regulation of neurotransmitters, promotion of glycogen synthesis, and inhibition of neuronal necrosis and apoptosis (20).
Literature review shows that similar studies have examined the effect of insulin on spatial learning and memory and have produced contradictory results. In addition, there is no evidence as to the effect of systemic insulin administration alone or in combination with exercise on cognitive function in stressed and non-stressed animals. Therefore, this study was designed to examine the effect of i.p. insulin administration and/or exercise on spatial learning and memory under immobilization stress and normal conditions.
2. Methods
2.1. Animals
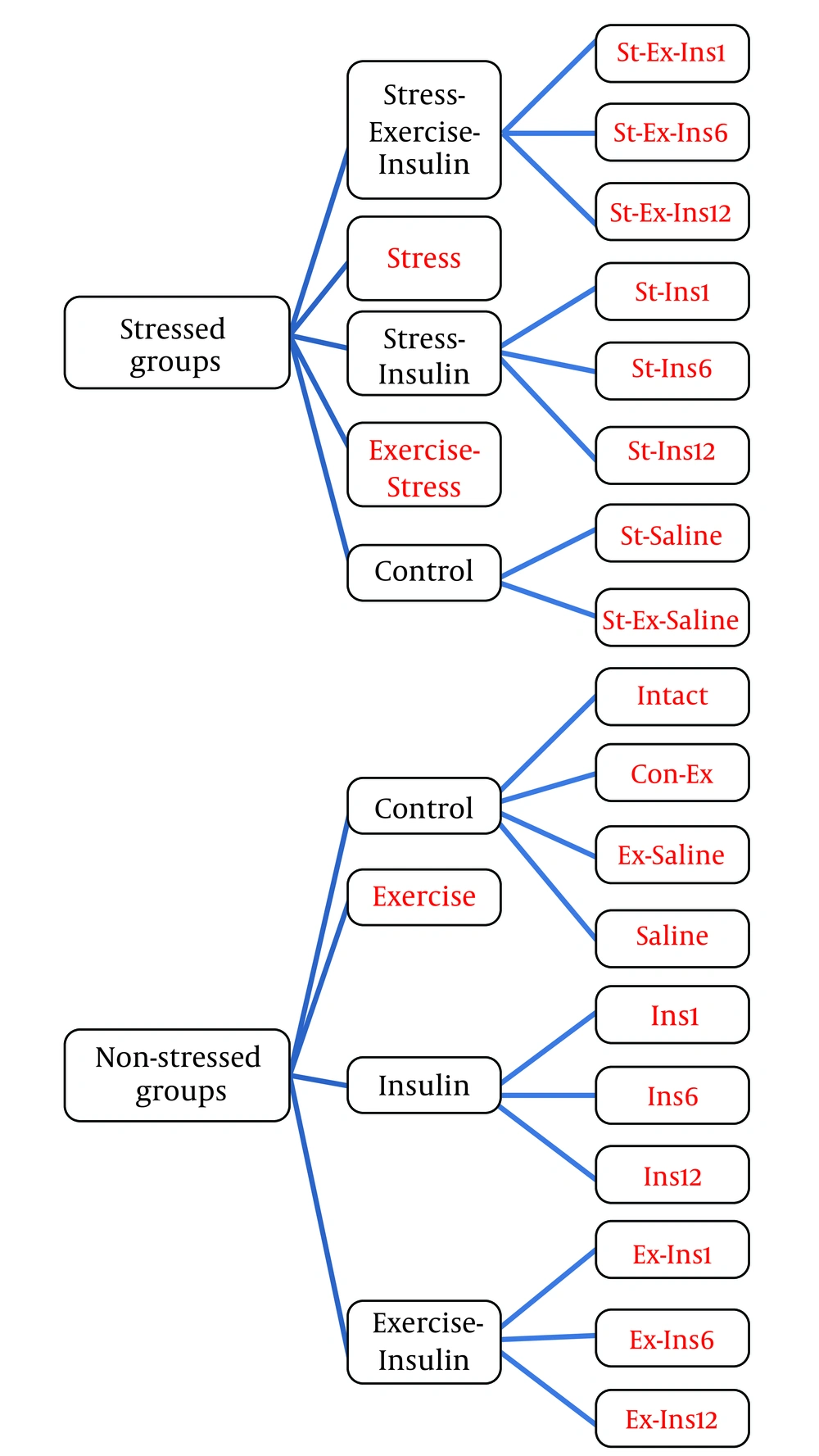
Male Wistar rats (200 - 220 g) were purchased from Pasteur Institute of Iran. They were placed on a 12/12-h light-dark circuit in a temperature (25 ± 2°C) and humidity (%45 ± 5) controlled room. Food and water were provided ad libitum. All experimental procedures were in accordance with the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. After one week of acclimation, the animals were randomly assigned into 21 groups of 10 (Figure 1).
2.2. Drugs
Insulin was provided from Exir Pharmaceutical Company (Borujerd, Iran) and diluted in sterile 0.9% saline. It was administered intraperitoneally at three different doses (1, 6, and 12 IU/kg). Also, normal saline was injected at the same volume as a vehicle to the saline control groups. Drugs were administered once a day for seven sequential days at 10:00 - 10:30 a.m.
2.3. Immobilization Stress, Corticosterone and Glucose Assay
Animals were immobilized in a plexiglass rats restrainer and were placed in the back recumbent position for 2 h/d for 7 days, at 11:00 - 13:00 (3). Evaluation of the effectiveness of immobilization stress was assessed by the physical symptoms of stress, such as body tremors, teeth gnashing, urination, and yawning. At the end of the seventh day of stress induction, after light ether anesthesia, blood samples from all the study groups were taken directly from the heart. Serum corticosterone and glucose levels were assessed using a commercial rat corticosterone ELISA kit (Marburg, Germany) and Glucose Colorimetric Enzymatic kit (Parsazmun, Iran).
2.4. Exercise Protocol
The animals in the exercise group underwent 30-minutes treadmill running. The load for exercise groups included treadmill training at a speed of 4 m/min for 10 minutes. This was followed by running for 10 minutes at a speed of 7 m/min and ended with 10 minutes running at 10 m/min at 0 degrees of inclination. Running was conducted once daily at 7:00 - 8:00 a.m. for seven consecutive days. Low level of exercise intensity was used to eliminate any other stressful conditions that may produce physical and physiological alterations in the laboratory animals (21).
2.5. Behavioral Procedure
Two days after completion of the stress induction, the animals were trained in the Morris water maze. The acquisition phase consisted of one block of four trials per day for four days. Water maze training consisted of placing the rat into the water facing the wall of the tank at each of the four starting points and allowing it to swim and locate the hidden platform. Starting points were different in a quasi-random manner, such that each trial was begun once in each location.
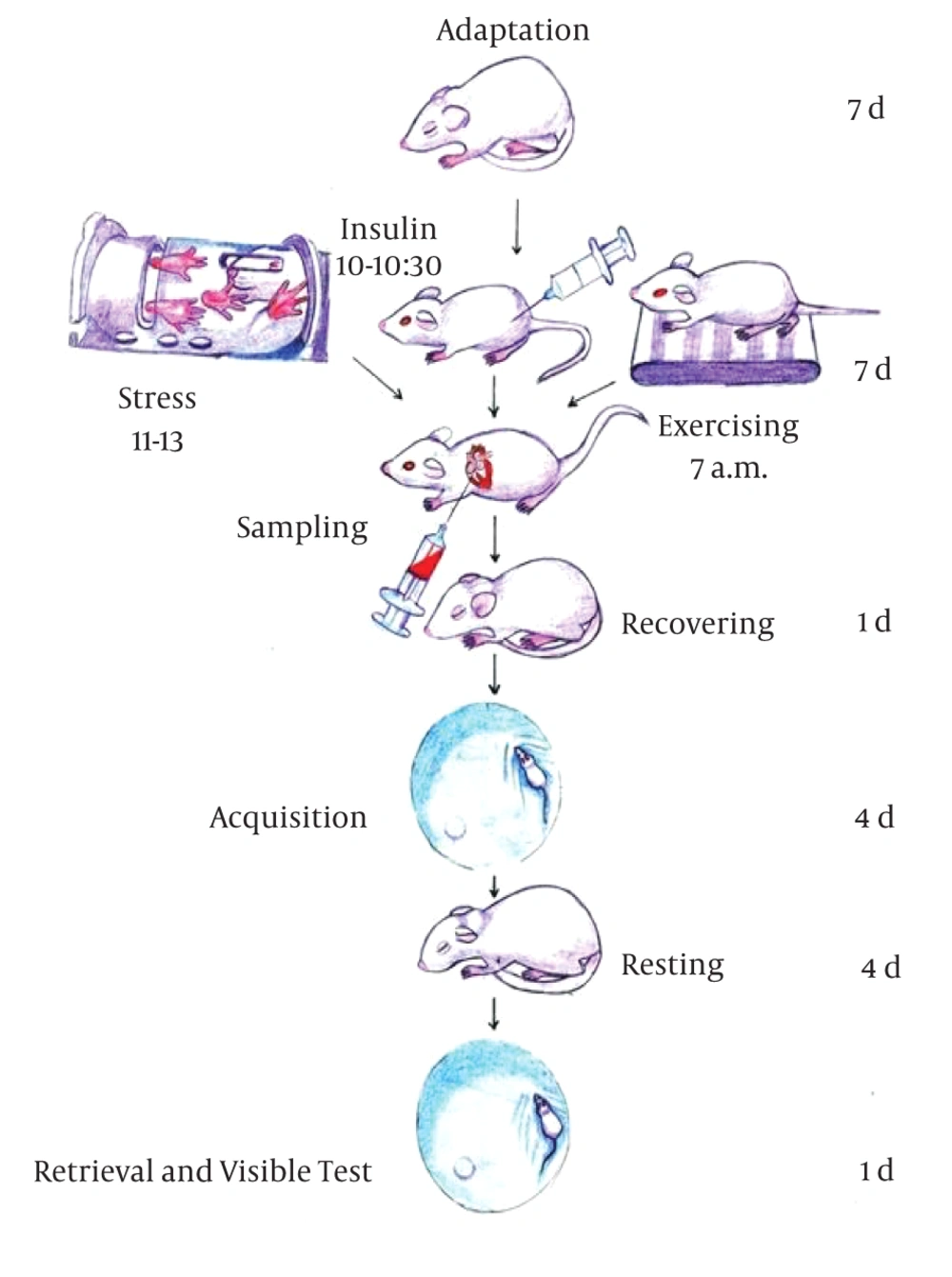
The task needs rats to swim to the hidden platform using periphery spatial cues. After finding the platform, the animals were allowed to stay there for 30 seconds before the start of the next trial. If the rat failed to find the platform during 60 seconds, it was placed on the platform for 30 seconds. Latency to the platform and the swimming distance was recorded. On the 10th day, we repeated the test (recall/retrieval phase); each animal performed one block of four trials as had executed in the first four days. Following 60 minutes, the visible test was conducted. It evaluates animals’ motivation and vision. Performance in the Morris water maze was recorded using EthoVision XT-Noldus video tracking system. Figure 2 illustrates various steps in the study.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
After ensuring about the assumptions of normality (Shapiro-Wilk test) and homogeneity of variance (Levene’s test), data were analyzed using Split-Plot Analysis of Variance (SPANOVA) and LSD post hoc test. The effects of exercise and stress treatments on corticosterone levels were assessed using ANOVA followed by planned comparisons. P value less than 0.05 was considered significant. SPSS version 16.0 was used for statistical analysis. Diagrams were drawn using Microsoft Office Excel 2010.
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Insulin or Exercise Treatment on Corticosterone Levels
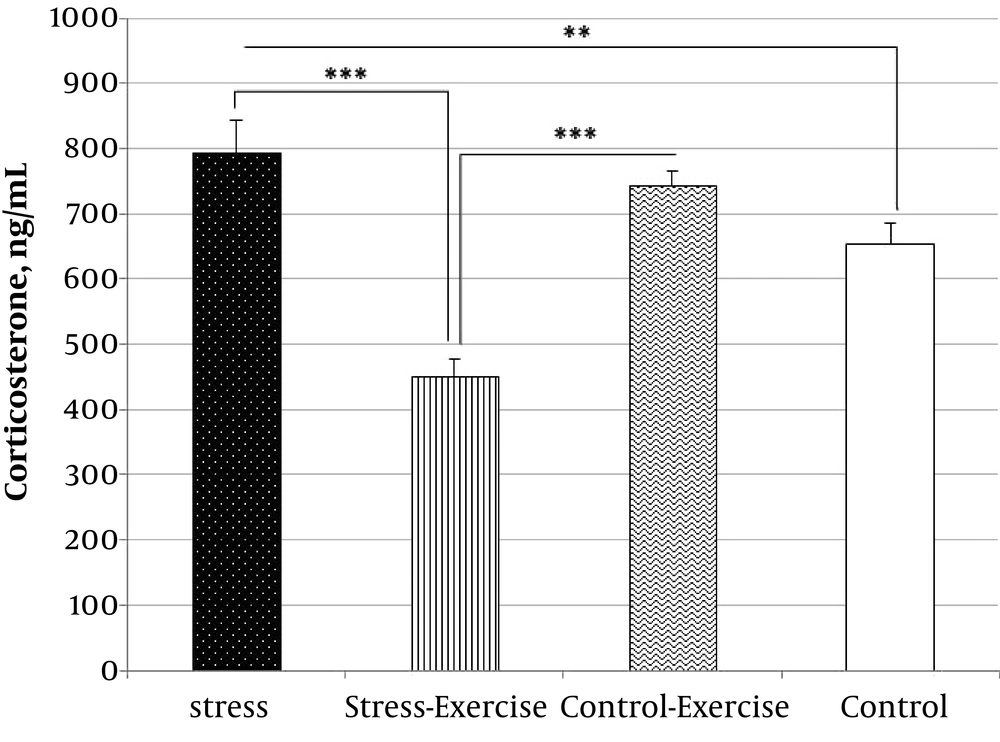
ANOVA showed significant differences in serum corticosterone levels between the groups (F(3,16) = 82.79, P < 0.001, η2 = 0.94; Figure 3). The planned comparison revealed that stressed rats had significantly higher levels of corticosterone than the control group (t(4.26) = -6.65, P = 0.002). On the other hand, exercise ameliorated stress-induced elevation of serum corticosterone (t(8.08) = 70.74, P < 0.001; Figure 3). However, administration of insulin at all the doses (i.e., 1, 6, and 12 IU) did not have any effects on corticosterone level.
3.2. Effect of Immobilization Stress on Learning and Memory
Chronic immobilization stress impaired learning and memory. Stressed animals had a higher escape latency (F(1,18) = 7.45, P = 0.014, η2 = 0.29) and distance traveled (F(1,18) =7.58, P = 0.013, η2 = 0.3) than the control group. Also, there was a significant difference in retrieval phase (F(1,18) =4.86, P = 041, η2 = 0.21) (data not shown).
3.3. Protective Effect of Exercise
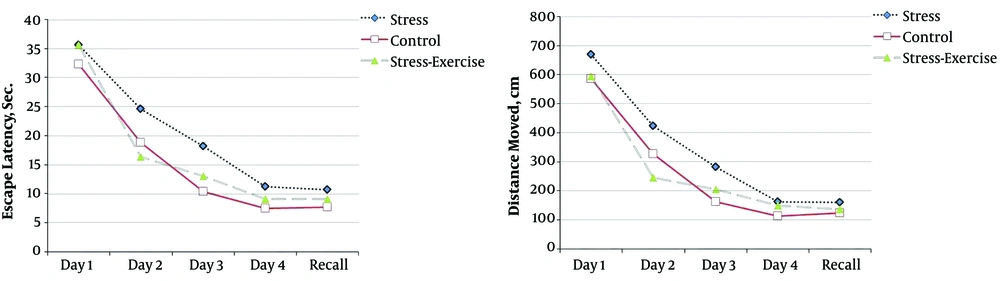
Escape latency (P = 0.023) and distance traveled (P = 0.002) in the animals treated with stress-exercise were better than those in the stress group (Figure 4). There were no significant differences among the groups in recall test (data not shown).
Moreover, exercise in non-stress conditions improved spatial memory retrieval compared to the control group (data not shown).
3.4. Protective Effect of Insulin
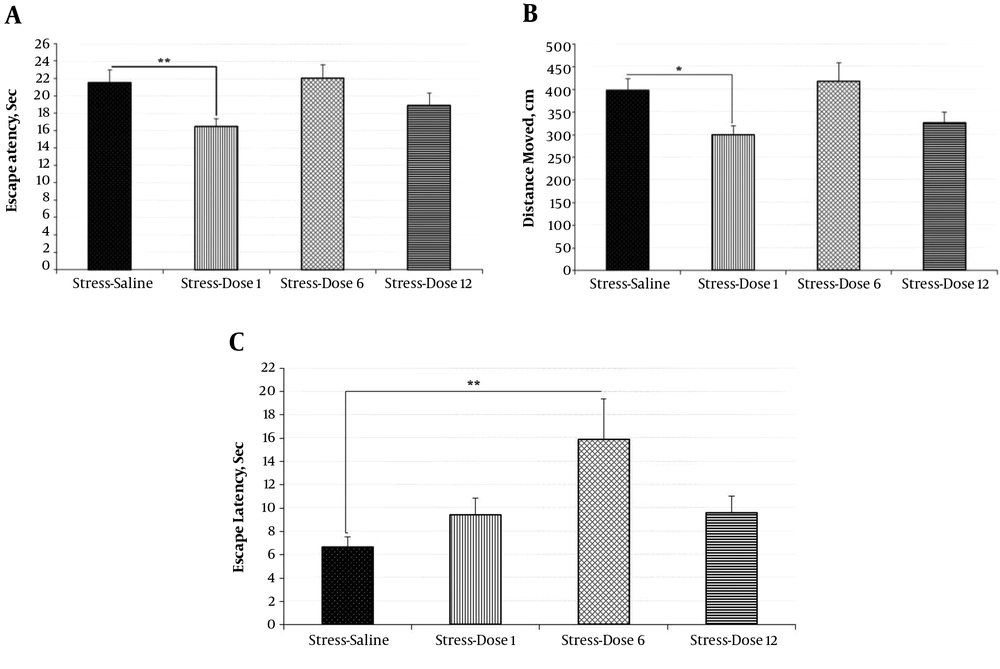
Animals treated with the lower dose of insulin (1 IU insulin-stress) demonstrated better spatial learning than the stress-saline group, as latency to the platform (P = 0.008) and distance traveled (P = 0.014) were significantly better (Figures 5A and 5B). ANOVA revealed significant differences among these groups (F(3,32) =3.95, P = 0.017) in the retrieval phase. The average dose of insulin (6 IU) did not alleviate stress-induced memory impairment (Figure 5C).
Moreover, insulin in non-stress conditions improved learning and memory in a dose dependent manner (data not shown). There were no significant differences in serum glucose levels among the groups; therefore, the water maze performance has not been affected by glucose levels (data not shown).
3.5. Protective Effect of Exercise-Insulin
There were significant differences among interactive groups in escape latency (F(4,44) =3.81, P = 0.01, η2 =0.26) and distance traveled (F(4,44) =4.5, P = 0.004, η2 =0.29). Animals in ex-d0-st (exercise-saline-stress), ex-d1-st (exercise-insulin dose 1- stress), and ex-d6-st (exercise-insulin dose 6-stress) groups demonstrated better spatial learning than stress-saline treated animals. Rats treated with ex-d12-st (exercise-insulin dose12-stress) showed no significant differences compared with the st-d0 (stress-saline) treated group. The results of the recall test revealed no significant differences among the groups (F(4,44) = 1.21, P = 0.32).
In all the study groups, the results of swimming speed and visible test showed no significant differences compared with the control groups.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Stress on Learning and Memory
Immobilization stress significantly impaired performance in both acquisition and retrieval phases. Evidence suggests that chronic stress and exposure to corticosterone can cause dendritic atrophy and nerve damage (22). It also decreases synapse formation in the hippocampus (23). Such changes in the hippocampus have been presented as the underlying mechanisms for stress-induced cognitive impairment, and generally, they are attributed to changes in corticosterone levels.
4.2. Effect of Exercise on Stressed Subjects
Exercise alleviated stress-induced impairment in the acquisition phase. This is consistent with the results of Kim et al. (24). They reported that treadmill running relieved short-term memory loss by increasing cell proliferation and suppression of apoptosis in the hippocampal dentate gyrus (24). Stress increases glutamate and its neurotoxic effects (8), whereas exercise can up-regulate glutamate transporters (EAAC1), which are responsible for the elimination of glutamate within the synaptic gap. Moreover, glutamate receptors that mediate glutamate neurotoxic effects can be down-regulated by exercise (15).
Furthermore, results revealed that exercise significantly decreased corticosterone levels in stressed (stress-exercise) animals. Regular exercise provides opportunities for an organism to react to changes in environmental conditions by means of physiological modifications such as metabolic rate, mitochondrial biogenesis and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) adaptability (15). It seems that normal functioning of spatial learning and memory, which are compromised by immobilization stress, may be affected by physical activity.
In addition, results showed that in non-stress condition exercise has delayed effect. Although exercise had no significant effect in the acquisition phase, it improved memory in the retention stage. This is consistent with the results of Darkhah et al. (25). Plasticity-related responses of genes have different temporal patterns of gene induction in response to exercise (26). Therefore, it seems that the effects of exercise are more long-lasting than previously thought (27).
4.3. Effect of Insulin on Stressed Subjects
Although insulin had no effects on stress-induced corticosterone release, it alleviated the detrimental effects of stress during the acquisition phase at the low dose (1 IU). It seems that low-dose insulin administration has an improving effect on spatial memory. Consistent with this result, Reger et al. showed that following intravenous infusion of insulin, memory improved at only very low doses (28). Dose-dependent responses may be due to the amount of insulin carried to the central nervous system after the systemic administration (28). Future studies should explore these possibilities.
It appears that changes in insulin are independent of changes in serum corticosterone. Likewise, spatial learning, which is compromised by restraint stress, may be dependent on insulin for normal functioning.
Studies have revealed that psychological stress in human and immobilization stress in lab animals increases oxidative stress and apoptosis (29). Oxidative stress decreases the uptake of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glutamate and increases extrasynaptosomal glutamate levels. Insulin treatment reverses the decrease in GABA accumulation. Thus, recovery of neuronal performance is one mechanism whereby insulin can protect neurons against stress (30).
In the present study, despite the protective effect of insulin in the acquisition phase, it had no effects in the retrieval stage. It should be noted that the time interval between the last insulin treatment and retrieval test was nine days. It is postulated that during this period the effect of insulin could have decreased; hence, animals’ performance had returned to levels of the control group.
4.4. Combination Effect of Exercise and Insulin on Stressed Subjects
Our results demonstrated that the interactive effects of exercise and insulin can modulate the degenerative effects of stress. Exercise significantly improves peripheral insulin sensitivity and spatial learning (31). Therefore, insulin intake when its signaling has already increased, for example following exercise, could improve cognitive performance in a dose-dependent manner.
However, the body of research in this area has several limitations. First, the current method to induce stress is not common in real-life situations due to the technical and ethical concerns. Also, in this study, cellular changes such as hippocampal neurogenesis and apoptosis were not assessed; thus, the mechanisms underlying the effects of the treatments remain unclear. Moreover, the length of the exercise regimens may not be long enough to make appropriate changes. Clinical studies have shown that different kinds of exercise, including aerobic, resistance, and dance, can improve cognitive function, even though the appropriate type, quantity, mechanisms, and duration of exercise are unclear (32).
4.5. Conclusion
The present study provides evidence that restraint stress could produce physical, physiological, and cognitive effects. Low-intensity regular exercise and/or peripheral insulin administration counteracts the effects of stress and causes behavioral adaptation in spite of the activation of the HPA axis. In addition, concurrent administration of exercise and insulin can counteract the negative effects of stress on learning in a dose-dependent manner, and exercise alone (exercise-stress) has the same effect. Ultimately, exercise benefits continue even after a delay between exercise and cognitive test.