1. Background
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is an age-related neurodegenerative condition characterized by a gradual decline in cognitive function (1, 2). One of the toxins that lead to AD is trimethyltin chloride (TMT). This nerve poison is often used in industry and agriculture (3). The association of hippocampus injury and TMT-induced cognitive impairment has led to TMT being considered as an effective factor in the studies of AD (3). Neurotrophins in the brain are responsible for axonal targeting, neuronal growth, synaptic maturation, and synaptic flexibility (4). Important neurotrophins in AD include brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF) and nerve growth factor (NGF), which mainly affect the hippocampal neurons. The nerve growth factor is the first discovered member of the neurotrophins family, which is essential for the growth and maintenance of neuronal phenotypes in the peripheral nervous system and functional integration of cholinergic neurons in the central nervous system. However, BDNF has many potential effects on restoring growth and maintaining neuronal populations (5). It plays a regulatory role in neuronal differentiation, synaptic plasticity, and cell death processes, and acts through proteins tyrosine kinase B (TrkB) receptor and low-affinity nerve growth factor receptor (LNGFR) at the cellular level. Researchers have reported that exercises enhance cognitive functions through numerous messaging mechanisms that lead to positive regulation of BDNF, especially in the hippocampal region, which is the central pole of learning and memory organizations.
On the other hand, many studies have shown a relationship between low levels of BDNF and AD and have suggested that exercise can have beneficial effects on BDNF levels (6). Researchers suggest that our behaviors and lifestyles can affect the expression of neurotrophins in the brain, and experiences with emotional well-being such as exercise, happiness environments, and improved nutrition may increase the levels of these important neurotrophins (7). Proper nutrition, in addition to having an impact on physical functioning, has a tremendous effect on mental and brain function so that nutritional deficiencies can cause or aggravate mental and emotional illnesses. It has been reported that the risk of AD may be reduced by the consumption of antioxidants that counteract the adverse effects of oxidative stress (8). Researchers believe that royal jelly (RJ), by enhancing antioxidants without reducing lipid peroxidation, suppressing inflammatory reactions, and inhibiting apoptosis, can offset the effects of oxidative stress and free radicals in various diseases and improve cognitive function and increase neurotrophins in neural cells (9). Research has also shown the essential effects of RJ on the improvement of neurotrophins (8-11). Therefore, it seems that the use of non-synthetic compounds and non-pharmacological methods can help increase neurological growth factors and improve memory.
2. Objectives
Considering the neuroprotective and antioxidant role of RJ ingredients and exercises, and the lack of studies on the interactive effects of training and simultaneous consumption of RJ in patients with AD, this study aimed to examine the neuroprotective effects of swimming training and RJ in hippocampus tissue of rats with AD.
3. Methods
3.1. Animals
In this experimental study, 30 rats were purchased and transferred to the Exercise Physiology Laboratory of Islamic Azad University, Marvdasht Branch, in standard conditions.
3.2. Induction of Alzheimer’s Disease
After seven days of adaptation to the new environment, on day eighth, a single dose (8 mg/kg) of TMT was injected intra-peritoneally to 25 rats to induce AD (12). The AD symptoms were confirmed by several behaviors in rats. These clinical symptoms included (1) muscle tremors, (2) elevated body temperature, (3) nausea, (4) seizures, and (5) tail twists. After 24 hours of ensuring the full effect of TMT on the hippocampus, AD rats were randomly divided into five equal groups including (1) control (C), (2) sham (SH), (3) royal jelly (RJ), (4) training (T), and (5) training with royal jelly (TRJ). Five healthy rats were selected as the healthy control (HC) group to assess the effect of AD induction by TMT on BDNF and NGF. During eight weeks, groups 3 and 5 received 100 mg/kg RJ (13) daily peritoneally, and groups 4 and 5 swam in a rat swimming tank three sessions per week.
3.3. Swimming Training Protocol
For swimming training, rats were trained for five minutes in the first week of swimming training, which reached 60 min at the end of the research period (14).
3.4. Tissue Sampling
Forty-eight hours after the last training session, all rats were anesthetized with ketamine (30 - 50 mg/kg) and xylazine (3 - 5 mg/kg). The hippocampus tissue was extracted by specialists. After setting in a cryotube, it was placed in liquid nitrogen and stored at -70°C for further investigation. The BDNF and NGF levels were measured by the real-time PCR method. The sequence of primers is reported in Table 1.
| Genes | Primer Sequences | Sizes, bp |
|---|---|---|
| B2m | Forward: 5’-CGTGCTTGCCATTCAGAAA-3’ | 244 |
| Reverse: 5’-ATATACATCGGTCTCGGTGG-3’ | ||
| BDNF | Forward: 5’-GAACGGGAGGGGTAGATTTC-3’ | 120 |
| Reverse: 5’-CAACCAGAATGGAGAGTGAAGA-3’ | ||
| NGF | Forward: 5’-CATCGCTCTCCTTCACAGAGTT-3’ | 218 |
| Reverse: 5’-TGTACGGTTCTGCCTGTACG-3’ |
3.5. Statistical Analysis
The Shapiro-Wilk test was used to review the normality of the data and one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc tests for data analysis in SPSS 20 software (P < 0.05).
4. Results
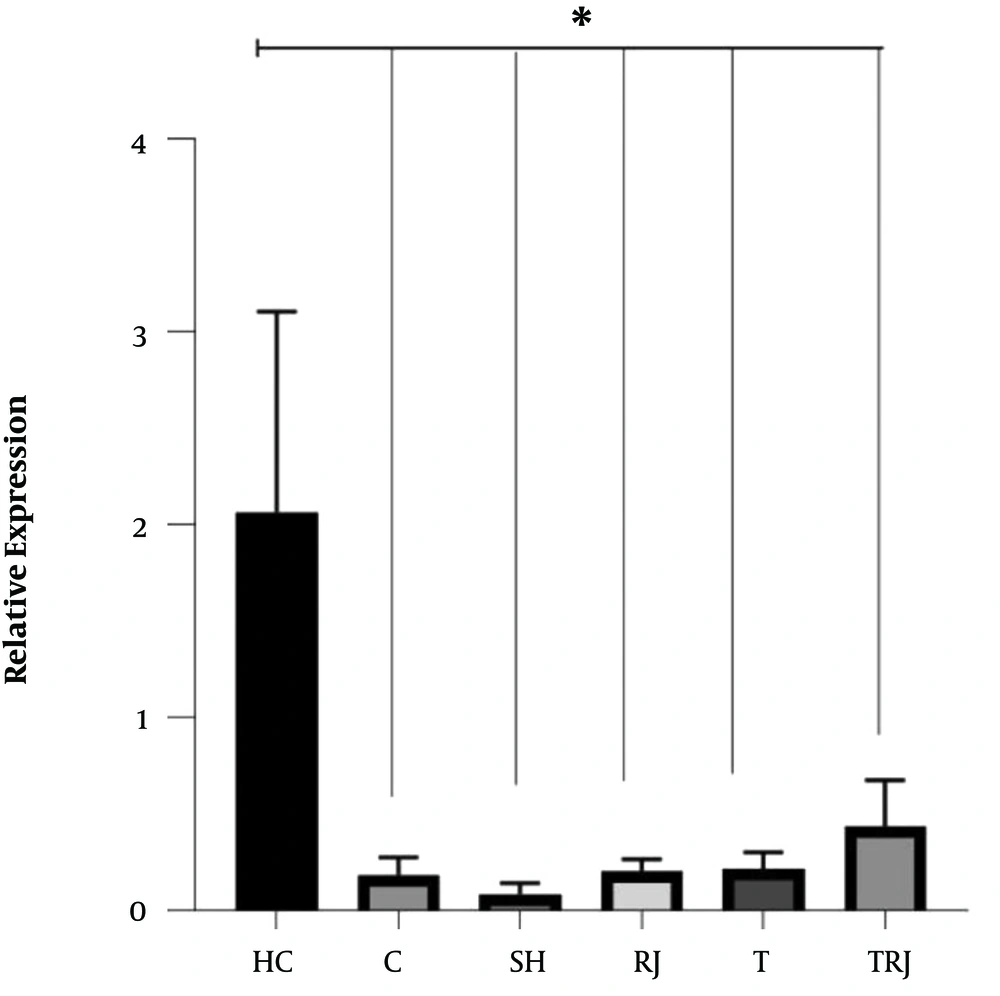
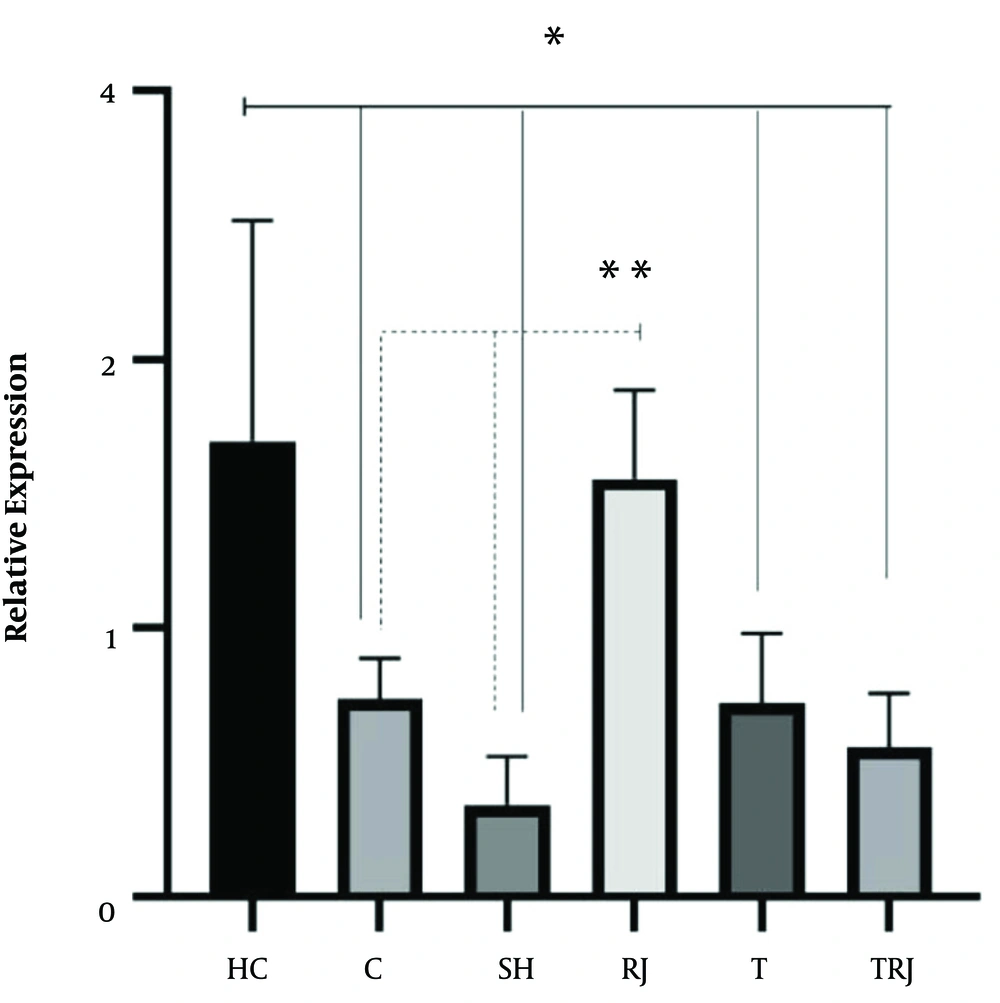
The expression levels of BDNF and NGF are shown in Figures 1 and 2, respectively. One-way ANOVA test results showed significant differences in the BDNF (F = 14.88, P = 0.001) and NGF levels (F = 9.77, P = 0.001) between the six groups. The results of the Tukey’s post hoc test showed that the BDNF levels were significantly higher in the HC group than in the C, SH, RJ, T, and TRJ groups (P = 0.001). Besides, the NGF levels were significantly higher in the HC group than in the C (P = 0.01), SH (P = 0.001), T (P = 0.008), and TRJ (P = 0.002) groups. The NGF levels were significantly higher in the RJ group than in the C (P = 0.03) and SH (P = 0.001) groups. There were no significant differences in the BDNF levels between the C group and the RJ (P = 0.99), T (P = 0.99), and TRJ (P = 0.94) groups. Moreover, there were no significant differences in the NGF levels between the C group and the T (P = 0.99) and TRJ (P = 0.97) groups.
5. Discussion
The results of the present study showed that the induction of AD by TMT significantly reduced BDNF and NGF gene expression in rat hippocampus tissue. Besides, eight weeks of swimming training had no significant effect on BDNF and NGF gene expression in the hippocampus tissue of rats with AD. Studies have shown NGF to promote axonal bud growth and regulate the mechanism of neuron production. Compared to NGF, BDNF protects more sensory neurons. In addition, BDNF plays an important role in the survival and growth of motor-neurons, which points to its broader nutritional role than that of NGF (3). Exercise has been reported to enhance nerve growth and function by increasing cerebral blood flow; these vascular changes, in turn, increase the cortical formation (mostly in the hippocampus) and growth and preserves neural structure (15). In contrast to the present study, 30 days of running wheel significantly increased the BDNF gene expression in mice (16), and moderate treadmill exercise for four weeks significantly increased the hippocampal mRNA and protein levels of BDNF in an animal model of AD (12). Besides, five days per week running on a treadmill for 12 weeks resulted in a significant increase in BDNF gene expression in the cortex tissue of rats with AD (13). Nevertheless, in line with the findings of the present study, Lin et al. (17) reported that 10 weeks of aerobic training at a speed of 12 m/min had no significant effect on the BDNF protein levels in the hippocampus tissue of rats with AD. Although the exact mechanisms underlying the beneficial effects of Exercise on brain function and structure are not yet fully understood, they can be attributed to reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, increasing angiogenesis, secreting neurotrophins, and catecholamines, and neurogenesis, especially in the structure of the hippocampus (3).
Nutritional factors can have a profound effect on brain function through the regulation of neurotransmitters, synaptic transmission, membrane fluidity, and signal transduction pathways. In the present study, eight weeks of RJ consumption significantly increased NGF did not affect BDNF gene expression in the hippocampus tissue of rats with AD. Based on research, RJ can exhibit a variety of pharmacological activities, including anti-inflammatory, vasodilative, antimicrobial, antihypercholesterolemic, and antitumor hypotensive activities, as well as growth-stimulating properties (14). It has been reported that RJ facilitates the differentiation of all types of brain cells, including neurons from cultured neural stem/progenitor cells (NS/NPCs) (8). Besides, RJ or its components would facilitate in vivo neurogenesis in the hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG) (18). In line with the present study, three months of RJ treatment significantly increased the BDNF levels in mice with AD (9) and RJ selectively facilitated the mRNA expression of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), a potent neurotrophic factor acting in the brain in the adult mouse hippocampus (19). Royal jelly contains 10-hydroxy-2-decanoic acid (10-HDA). Because 10-HDA is a small unsaturated fatty acid molecule, it can cross the blood-brain barrier. It has been reported that 10-HDA mimics the effects of BDNF and probably stimulates neurogenesis in the adult brain (20).
Regarding the interactional effects, in the present study, eight weeks of swimming training simultaneously with RJ consumption had no interactive effect on NGF and BDNF gene expression in the hippocampus tissue of rats with AD. Koo et al. (13), reported that exercises could increase BDNF in mice with AD through activating phosphoinositide 3-kinase and protein kinase-B. Therefore, it seems that exercises with mechanisms such as elevated BDNF levels as the mediators of synaptic effects, neuronal connections, and plasticity in the brain can improve AD disorders (3). However, decreased oxidative stress and increased neurotrophins appear to be strongly dependent on intensity, duration, and type of exercise activity. It appears that RJ exerts its neurotrophic effects with a mechanism differently from exercises. The lack of employing various methods of measuring BDNF and NGF such as ELISA and western blot was the limitation of the present study. Therefore, it is recommended that future studies measure the BDNF and NGF by ELISA and western blot methods and examine the effect of swimming training on BDNF and NGF levels at different times of a day in the hippocampus tissue of rats with AD.
5.1. Conclusions
According to the results of the present study, it appears that RJ has a significant effect on the increase of NGF gene expression in the hippocampus tissue of rats with AD. Nevertheless, RJ consumption simultaneously with swimming training had no significant effect on BDNF and NGF.