1. Background
Escherichia coli is a commensal bacterium living in the intestinal tract of animals and humans (1). In particular, adherent-invasive E. coli (AIEC) pathotype was one of the key bacterial triggers of IBD (2). Certain strains are the member of the extraintestinal pathogenic E. coli (ExPEC). Besides, it is possible to classify E. coli strains into the phylogenetic groups, such as B1, A, C, B2, E, D, F, as well as clade I/II (3). Moreover, the ExPEC strains, in which diverse virulence factor genes are used to characterize, are the members of D and B2 phylogenetic groups fundamentally. Most E. coli types, including EPEC (carrying bfp and eae genes), may be commonly assigned to 1 of the 4 clusters of B1, A, D, as well as B2 (4). Among E. coli phylogenetic groups, B2 phylogroup is believed to be more important than others. These strains indicate more ability to persist in the gut microbiota compared to the ones in other E. coli phylogenetic groups, which may be caused by accumulating pathogenicity islands (PAIs) as well as ExPEC virulence genes (5). Furthermore, B2 strains have at least 10 phylogenetic sub-groups (I–X) or lineages, including I (STc131), II (STc73), III (STc127), IV (STc141), V (STc144), VI (STc12), VII (STc14), VIII (STc452), IX (STc95), and X (STc372) (6). Studies indicated the predominance of subgroups I (STc131), II (STc73), as well as IX (STc95) in a majority of ExPEC strains (7). The present study subtyped the phylogenetic group B2 strains previously isolated from the commensal feces of healthy children. Their serogroups, virulence markers, as well as abilities to persist in the microbiota are associated with certain B2 groups.
Antimicrobial resistance such as third-generation cephalosporin-resistant (3GCR) in the commensal bacteria and acquiring virulence factors by these strains is worrisome in terms of its ability to spread to pathogens. These challenges result in increased healthcare costs and mortality. However, there is no sufficient data on the antimicrobial resistance profile, the virulence traits of these commensal strains, especially in a developing country like Iran. Therefore, the present study involves the identification profiles of these isolates from the stool of healthy children under 10 years old (8, 9).
2. Objectives
This study aimed to identify B2 phylogenetic groups in the extended-spectrum Cephalosporins resistant E. coli isolated from the stool of healthy children under 10 years old.
3. Methods
3.1. Ethical Statements and Bacterial Isolate
We performed this cross-sectional study in Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran, from January 2020 - February 2021. According to the research design, we examined 100 strains of E. coli resistant to broad-spectrum Cephalosporins (CTX, CAZ = 100% and ESBL genes (TEM = 26%, CTX-M1 = 98%, SHV = 51%) isolated from the feces of healthy children under 10 years (57 males and 43 females). Subsequently, all the strains were transferred in Tryptic Soy Broth and incubated at 37°C overnight. In the next step, we streaked these strains on the MacConkey agar and performed incubation at a temperature of 37°C for 24 hours, and finally, pink colonies were subcultured on EMB (Eosin Methylene Blue), so that the colonies over them exhibited a green-metallic sheen color. Ultimately, we used a set of biochemical experiments for further confirmation. Then, in order to store them for a longer period, we used a tryptic soy broth consisting of 20% glycerol (provided by Merck Company: Germany) for storing the treated isolates at a temperature of -20°C.
3.2. Virulence Typing
Through the use of primers and PCR, particular genes were specified: cytolethal distending toxin (cdt), cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 (cnf1), invasion of brain endothelium (ibeA), secretion autoinducer toxin (sat), uropathogenic-specific protein (usp), pathogenicity island marker (malX), Dr-antigen binding adhesins (afa/Dr), bundle-forming pili (bfp), shiga-like toxins (stx) intimin (eae), and transcriptional activator aggR. Table 1 presents the primers and temperature conditions.
| Target Gene | Primers, Genes, and Sequence (5’- 3’) | Amplicon Size (bp) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| eae | F: GTAAGTCTCAAACGCAAGCAACCAC | 229 | (10) |
| R: AACCTTGTTGTCAATTTTCAGTTCATCA | |||
| bfp | F: AATGGTGCTTGCGCTTGCTGC | 268 | (10) |
| R: GCCGCTTTATCCAACCTGGTA | |||
| papGI | F: TCGTGCTCAGGTCCGGAATTT | 461 | (11) |
| R: TGGCATCCCCCAACATTATCG | |||
| papGII | F: GGGATGAGCGGGCCTTTGAT | 190 | |
| R: CGGGCCCCCAAGTAACTCG | |||
| papGIII | F: GGCCTGCAATGGATTTACCTGG | 258 | |
| R: CCACCAAATGACCATGCCAGAC | |||
| Stx1 | F: TAAATCGCCATTCGTTGACTAC | 180 | (12) |
| R: AGAACGCCCACTGAGATCATC | |||
| Stx2 | F: GGCACTGTCTGAAACTGCTCC | 255 | |
| R: TCGCCAGTTATCTGACATTCTG | |||
| cdt | F: TAAATGGAATATACATGTCCG | 588 | (13) |
| R: TTTCCAGCTACTGCATAATC | |||
| Cnf-1 | F: GAACTTATTAAGGATAGT | 543 | (13) |
| R: CATTATTTATAACGCTG | |||
| ibeA | F; AGGCAGGTGTGCGCCGCGTAC | 170 | (14) |
| R: TGGTGCTCCGGCAAACCATGC | |||
| usp | F: CGGCTCTTACATCGGTGCGTTG | 615 | (15) |
| R: GACATATCCAGCCAGCGAGTTC | |||
| malX | F: GGACATCCTGTTACAGCGCGCA | 930 | (15) |
| R: TCGCCACCAATCACAGCCGAAC | |||
| aggR | F: GTATACACAAAAGAAGGAAGC | 194 | (16) |
| R: ACAGAATCGTCAGCATCAGC | |||
| afa-Dr | F: CGAAAACGGCACTGACAAG | 230 | (17) |
| R: AGGCTTTCCGTGAATACAACC |
Primers and Amplicon Size (bp) for Detection of Virulence Genes
3.3. Phylotyping Method and Detection of Phylogroups in Isolates
In this step, we applied PCR based method as described by Clermont et al. for determining nine phylogroups, e.g., B1, A, C, B2, E, D, F as well as clade I/II. Moreover, PCR was employed to amplify the key targeted genes such as yjaA, chuA, arpA, and TspE4.C2. To characterize the phylogroups E and C, we utilized the allele-specific PCR primers (3). Table 2 depicts the primers and temperature conditions.
| Target Gene | Primers, Genes, and Sequence (5’- 3’) | Amplicon Size (bp) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| chuA | F: GAC GAA CCA ACG GTC AGG AT | 279 | (3) |
| R: TGC CGC CAG TAC CAA AGA CA | |||
| yjaA | F: TGA AGT GTC AGG AGA CGC TG | 211 | |
| R: ATG GAG AAT GCG TTC CTC AAC | |||
| TspE4.C2 | F: GAG TAA TGT CGG GGC ATT CA | 152 | |
| R: CGC GCC AAC AAA GTA TTA CG | |||
| arpA | F: AACGCTATTCGCCAGCTTGC | 400 | |
| R: TCTCCCCATACCGTACGCTA |
Primers and Amplicon Size (bp) for Detection of Phylogroups
3.4. Subtyping of B2 Subgroups
Utilizing PCR method, B2 subgroups, including I (STc131), II (STc73), III (STc127), IV (STc141), V (STc144), VI (STc12), VII (STc14), IX (STc95), and X (STc372)) were performed for 27 strains that were determined in Phylogrouping stage. Table 3 represents the primers and the product size.
| Primer Designation | Primer Sequences | Target | Sub-group | Product Size | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pabBgpII.F | 5 ′-GAGTCACTGCCAGAAATTGCA-3′ | pabB | II | 415 | (6) |
| pabBgpII.R | 5 ′-GGCGAAAGGCTTAAAATTGCACT-3′ | ||||
| trpAgpIII.F | 5 ′-GACGCGCTGGAATTAGGCTC-3′ | trpA | III | 255 | |
| trpAgpIII.R | 5 ′-ATCGGCAACCAGCACCGAAT-3′ | ||||
| dinBgpVI.F | 5 ′-CAGCGGTGGAGATGCGCGAT-3′ | dinB | VI | 652 | |
| dinBgpVI.R | 5 ′-CAGCGGTGGAGATGCGCGAT-3′ | ||||
| icdgpVII.f | 5 ′-GCGGTATTCGCTCTCTGAAT-3′ | icd | VII | 810 | |
| icdgpVII.r | 5 ′-CAATTAAATCAGCCGCTTCG-3′ | ||||
| aesgpIX.f | 5 ′-CCTGGCCTGCAACGGGAG-3′ | aes | IX | 160 | |
| aesgpIX.r | 5 ′-TCTGGCTGCGGATAAAAGAG-3′ | ||||
| putPgpI.f | 5 ′-GGTATCGCTTACTTTAACGG-3′ | putP | I | 373 | |
| putPgpI.r | 5 ′-ACCACCGGACCAAACGCC-3′ | ||||
| trpAgpIV.f | 5 ′-TGCCAGTGGAAGAGTCCGCT-3′ | trpA | IV | 261 | |
| trpAgpIV.r | 5 ′-CCGGGGCGGAAATACCAAAG-3′ | ||||
| polBgpV.f | 5 ′-GCCGTTTCGCCGAAGATAAA-3′ | polB | V | 530 | |
| polBgpV.r | 5 ′-TAATGATCTTCAGCGCCTGT-3′ | ||||
| aesgpX.f | 5 ′-GACCGTTGTGAATACTCTTCA-3′ | aes | X | 713 | |
| aesgpX.r | 5 ′-TATAACAGGGCGGCACATTT-3′ | ||||
| chuAgene.1 | 5 ′-CGATACGGTCGATGCAAAAG-3′ | chuA | Internal control | 1013 | |
| chuAgene.2 | 5 ′-TTGGACAACATCAGGTCATC-3′ |
Primers and Amplicon Size (bp) for Detection of B2 Subgroups
3.5. Amplification of O-Serogroup
According to the analysis, the commonest serogroups of the extraintestinal E. coli entail O2, O1, O6, O4, O12, O7, O16, O15, O25, O18, O157, as well as O75 antigens that were examined with PCR. Table 4 reports the primers and the product size.
| Target Gene | Primers, Genes, and Sequence (5’- 3’) | Ampliconsize (bp) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| gndbis.f | 5-ATACCGACGACGCCGATCTG-3 | - | (18) |
| rfbO1.r | 5-CCAGAAATACACTTGGAGAC-3 | 189 | |
| rfbO2a.r | 5-GTGACTATTTCGTTACAAGC-3 | 274 | |
| rfbO18.r | 5-GAAGATGGCTATAATGGTTG-3 | 360 | |
| rfbO16.r | 5-GGATCATTTATGCTGGTACG-3 | 450 | |
| rfbO6a.r | 5-AAATGAGCGCCCACCATTAC-3 | 584 | |
| rfbO7.r | 5-CGAAGATCATCCACGATCCG-3 | 722 | |
| rfbO4.r | 5-AGGGGCCATTTGACCCACTC-3 | 193 | |
| rfbO12.r | 5-GTGTCAAATGCCTGTCACCG-3 | 239 | |
| rfbO25a.r | 5-GAGATCCAAAAACAGTTTGTG-3 | 313 | |
| rfbO75.r | 5-GTAATAATGCTTGCGAAACC-3 | 419 | |
| rfbO15.r | 5-TGATAATGACCAACTCGACG-3 | 536 | |
| rfbO157.r | 5-TACGACAGAGAGTGTCTGAG-3 | 672 |
Primers and Amplicon Size (bp) for Detection of O-Serogroup Amplification (O1, O2, O4, O6, O7, O12, O15, O16, O18, O25, O75, and O157)
3.6. Statistical Analyses
SPSS21 and t-test were employed for analyzing the obtained data. Moreover, the confidence interval was considered to be 95% (CI = 95%), and P-value < 0.05 was considered to be significant.
3.7. Ethical Statement
As mentioned earlier, the present research was verified by the Ethical Committee of the Faculty of Medical Sciences, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran (IR.MODARES.REC.1399.085).
4. Results
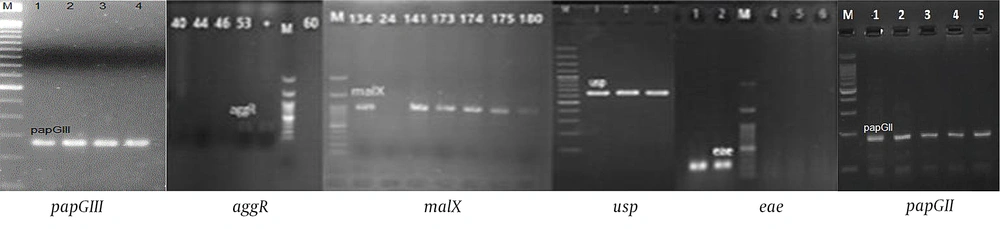
Of 100 isolates tested for virulence encoding genes, papGII 23% (n = 23), papGIII 8% (n = 8), usp 14% (n = 14), aggR, eae 1% (n = 1), malX 29% (n = 29), bfp, stx1, stx2, cnf, afa-Dr, cdt, ibeA, and papGI = 0 were recognized (Figure 1).
PCR reactions for virulence encoding genes of Escherichia coli in all strains (papGII, papGIII, usp, aggR, eae, malX were positive), (bfp, stx1, stx2, cnf, afa-Dr, cdt, ibeA, papGII were negative); M: Ladder 1000 bp; papGIII, 258 bp; aggR, 254 bp; malX, 930 bp; usp, 615 bp; eae, 167 bp; papGII, 190 bp.
4.1. Detection of Phylogroups
As reported in Clermont et al.’s study, the researchers showed the generation of a specific profile by one of the quadruplex genotypes relative to the absence or presence of the 4 genes; for example, (+, −, +, −) demonstrates arpA (+), chuA (−), yjaA (+), and TspE4.C2 (−). Considering this method, the percentage of phylogroup B1 was 6% (6/100), B2 was 27% (27/100), clade I/II was 1% (1/100), D/E was 16% (16/100), and E/clade I was 1% (1/100); also, 49% (49/100) of the strains were unknown. None of the isolates were recognized as phylogroups A, C, D, E, and F.
4.2. Analysis of B2 Subgroups
According to the analysis, the commonest B2 sub-groups were determined among the E. coli strains in the healthy infants: I (2%), IX (1%), V (8%), IV, V, VII (1%), IX, V (3%), IX, V, III, I (1%), IX, V, III, VII, I (%1), V, I (6%), V, III, I (3%), and V, III, VII (1%).
4.3. Serogroup Typing in Escherichia coli Isolates
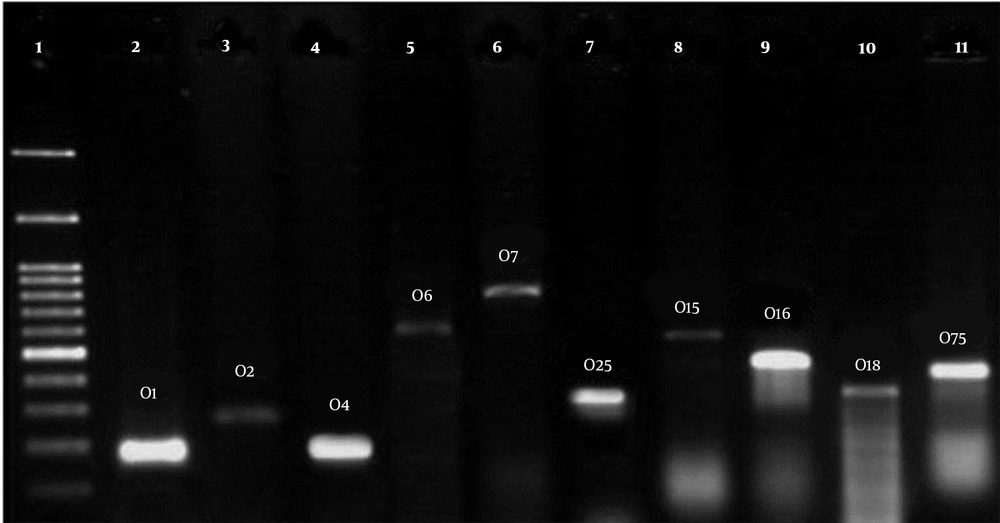
Table 5 presents the serogroup distribution in phylogroups of the E. coli strains isolated from the stool of healthy children below the age of 10. O2, O1, and O4 serogroups were the most abundant known serogroups among all the phylogroups, respectively. However, O157 was not in either of the strains (Figure 2).
| Phylogroups | Serogroups | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1 | O2 | O4 | O6 | O7 | O12 | O15 | O16 | O18 | O25 | O75 | O157 | Unknown | |
| A | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| B1 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| B2 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 11 |
| C | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| D | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| E | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| F | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| D/E | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| Clade I/II | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| E/clade I | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Unknown | 6 | 19 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 14 |
Serogroup Distribution in Phylogroups of Escherichia coli Strains; B2 Phylogroups Had the Highest Serogroup and in Clade I/II, E/Clade I Phylogroups Had the Lowest Serogroups.
4.4. Phylogenetic Groups and Pathogenicity Genes
Analysis of the relationship between virulence genes with the phylogenetic groups showed that the spread of each virulence gene enhanced largely in the phylogenetic group B2 than that in the remaining phylogenetic groups.
Table 6 demonstrates the relationship between phylogenetic groups and pathogenicity genes.
| Phylogenetic Group | Virulence Gene Pattern (No. Isolate) |
|---|---|
| B1 | papGII (3), aggR (1) |
| B2 | malX (17), usp (10), papGIII (4), papGII (9) |
| Clade I/II | - |
| D/E | malX (2), papGII (2) |
| E/clade I | papGII (1) |
| Unknown | malX (10), usp (4), papGII (1), eae (1) |
The Relationship of Phylogenetic Groups and Pathogenicity Genes
5. Discussion
The emergence and spread of third-generation cephalosporin-resistant E. coli in developing countries are a great concern. Healthy children colonized with ESBL-producing strains may transmit the resistant strains to other individuals, including the hospitalized patients (19). Based on four genes, namely arpA, chuA, yjaA, and TspE4.C2, E. coli strains could be categorized into the phylogenetic groups presented as follows: A, B1, B2, C, D, E, F, and clade I/II (3). Among these phylogroups, the phylogroup B2 mainly includes the strains which cause extraintestinal infections in humans as opportunistic pathogens (18). The present study was conducted to investigate the virulence factors, determine phylogroups, B2 subgroups, and serogroups of E. coli strains resistant to the broad-spectrum Cephalosporins isolated from the fecal samples of healthy children below 10 years of age. The study showed that 27% of the strains belonged to B2 phylogroup and 6% to B1 phylogroup. Among B2 phylogroup strains, the highest frequency belonged to subgroup V (polB genes). The malX, papGII, usp, papGIII, aggR, and eae virulence genes, respectively, had the highest to lowest supply among the tested strains. However, among B2 phylogroup strains, only malX, papGII, usp, and papGIII virulence genes were reported. We observed that 14 strains were positive for usp genes (is prevalent among strains causing urinary tract infections), one strain was positive for eae gene (a marker for EPEC pathovar), one strain was positive for aggR gene (a marker for EAEC pathovar), 29 strains were positive for malX gene (it is enriched in the strains causing extraintestinal infections). The results of serogroup determination based on O antigen indicated that the highest frequency was observed in the serogroups O1, O2, and O4 among all phylogroups, yet serogroups O2, O16, and O25 were predominant among phylogroup B2 strains. Nowrouzian et al. reported that among 140 commensal E. coli B2 strains, 47% of the Pakistani strains and 84% of the Swedish strains belonged to a major B2 subgroup (subgroups I-X) (7). Alizade et al. conducted a study on 216 strains of E. coli isolated from fecal samples of the patients with watery diarrhea. Although most strains belonged to B1 phylogroup, most strains contained the broad-spectrum beta-lactamase gene (CTX-M1) (20). Nojoomi and Ghasemian addressed E. coli strains isolated from the feces of the healthy children, about 98% of E. coli strains had CTX-M1 gene, which indicates the difference between serogroup and antigenic profile of the strains and the virulence genes (21). Our results indicate the diversity of phylogroups among E. coli strains with the predominance of B2 group, and none of the isolates were recognized as phylogroup A, C, D, E, and F. This is, while in another similar study in Tunisia on community fecal carriage of broad-spectrum cephalosporin-resistant was B1, D, B2, and A phylogroups, respectively (22). It is the first study in Iran that showed a higher frequency of B2 phylogroup than other phylogroups among the E. coli isolates from fecal samples of the healthy children, while most similar studies were performed on urine, feces, and or blood samples of children or adults with urinary tract infection, diarrhea, and or sepsis. According to the obtained findings herein and similar articles, it seems that phylogroup B2 strains play a major role in the extraintestinal infections and carrying resistance genes that can result in the dissemination in hospital settings, and increase frequency in nosocomial infections with human health impact. Meanwhile, their frequency in healthy individuals is a function of lifestyle, customs, geographical area, nutritional status, and level of public health. The frequency of virulence genes in these bacteria varies depending on their invasive conditions or coexistence with the host, how they interact with the host immune system, and the infection site. The obtained findings suggested the evolution of features in the group B2 E. coli strains, which enable them to survive in the complicated context of the humans’ intestines.
5.1. Conclusions
As shown in this research, we addressed the typing of the phylogenetic group B2 strains isolated from the commensal gut microbiota of healthy children under 10 years old. Virulence genes were more prevalent in group B2, carrying resistance genes, and the virulence factors like usp and papG by these strains can result in extraintestinal infections and increased frequency in nosocomial infections with the human health impact and leave few treatment options for the infections when caused by these strains in these children.