1. Background
Prevention is the most effective way of interfering the medicine and synthesis of vaccines is a reliable approach (1, 2). DNA vaccines induce both humeral and cellular immunity and thus, have a high potential of eradication of pathogens compared to other vaccination routes (3, 4). The recombinant DNA enters the host and is expressed by host machinery in vivo. In addition, it is also presented by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and II (5). In comparison with attenuated and inactivated vaccines, it has been discussed that DNA vaccines as “precious treasures” are appropriate for overcoming the infectious and genetic diseases (6). Several DNA vaccine candidates have been introduced and assessed such as heat shock proteins catalase, heparan sulphate-binding proteins, vacA, and lipoprotein. The hypothetical proteins HP0241 and HP0242 are encoded by an operon with 5 other functionally known proteins including HP0243 (neutrophil activating protein), HP0239 (glutamyl-tRNA reductase), HP0240 (octa prenyl-diphosphate synthase), HP0237 (porphobilinogen deaminase), and HP0238 (prolyl-tRNA synthetase). HP0242 is an acid-adaptive protein and plays an important role in physiology of H. pylori in acidic conditions. The ribbon like structure of HP0242 monomer shows 4 helices including H1, H2, H3, and H4. H2 helix plays an important role in dimer formation and thus, possibly carry out a key role in protein function (7). Therefore, this homodimeric protein attains a unique pseudo-knotted folding topology. It was shown that in the unfolding pathway, the N-terminal region is related to the first transition state, and the C-terminal region is the main sequence for contributing dimerization (8). The protein reportedly fulfills iron uptake and metabolism. There are numerous studies on the association of H. pylori in iron-mediated anemia in children and adults (9, 10).
2. Objectives
In this study, HP0242, as a DNA vaccine candidate, was cloned and the synthesis of the protein in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells was assessed by the SDS-PAGE method.
3. Methods
3.1. Bacterial Strains
The standard strains of H. pylori ATCC 40504 and E. coli TOP10F were prepared from microbiology department of Pasteur institute of Iran and biotechnology research center of Shahrekord Islamic Azad University, respectively. H. pylori isolates were cultured on Brucella agar and LB- broth.
3.2. Antibiotics Preparation
Ampicillin and neomycin were prepared from the Merk company. Ampicillin 100µg/ml was prepared and added to the Luria-Bertani (LB) medium.
3.3. DNA Extraction
For DNA extraction from H. pylori, the DNA isolation kit (Bioneer, Trefflab) was used according to the instructions of manufacturer.
3.4. Cloning of Hypothetical Gene
The PCR was used for hypothetical gene amplification by utilizing specific primers with linkers. The primer sequences including forward: 5'-AAACCGCGGAGAACAATAATGAAAGATTTAC-3' and reverse: 5'-AACCCCGGGAGCCCACCTTTTCACAAACTAC-3' were used to generate a 716 bp fragment. The conditions and amplification thermal profile included initial denaturation at 95°C for 5 minutes and 30 cycles of denaturation at 94°C for 1 minute, annealing at 64°C, 72°C for 1 minute, and final extension for 10 minutes. The sequences “CCGCGG” and “CCCGGG” were designed and added for enzymatic digestion of sacII and smaI (fermentase), respectively. An expression vector (fermentas) PEGFP-C1 was introduced with T4 ligase to construct the recombinant PEGFP-C1 –hypothetical gene using a T/A cloning kit (DNA ligation kit mighty mix, TaKaRa). Escherichia coli TOP10F competent cells (Stratagene) was employed as the host for gene cloning and transformed cells were grown in LB medium with 100 µg/mL ampicillin. The detail protocol of cloning and transformation was followed as described previously (11, 12). All PEGFP-C1-Hypothetical cloned sequences were subsequently confirmed by direct sequencing (Bioneer, Gen Ray Company, South Korea).
3.5. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
The PEGFP-C1-Hypothetical gene vectors were transformed into Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells and HP0242 protein synthesis was investigated with SDS-PAGE (13). HP0242 expression was induced by utilizing 100 mM IPTG.
Detection of the Immunoreactivity of HP0242 expressed by recombinant E. coli HP0242 expressed in recombinant E. coli was electrophoresed on a 15% SDS-PAGE and then transferred to the cellulose nitrate membrane. The membrane was probed with a primary polyclonal mice antiserum (dilution of 1:50) and next, it was incubated at 37° C for 2 hours and washed 3 times with TBS/Tween-20 (TBST) for 15 minutes, and then incubated with the horseradish peroxidase-linked secondary antibody (dilution of 1:1000). Detection of protein was visualized using the DAB western blot detection system.
4. Results
4.1. Hypothetical gene amplification
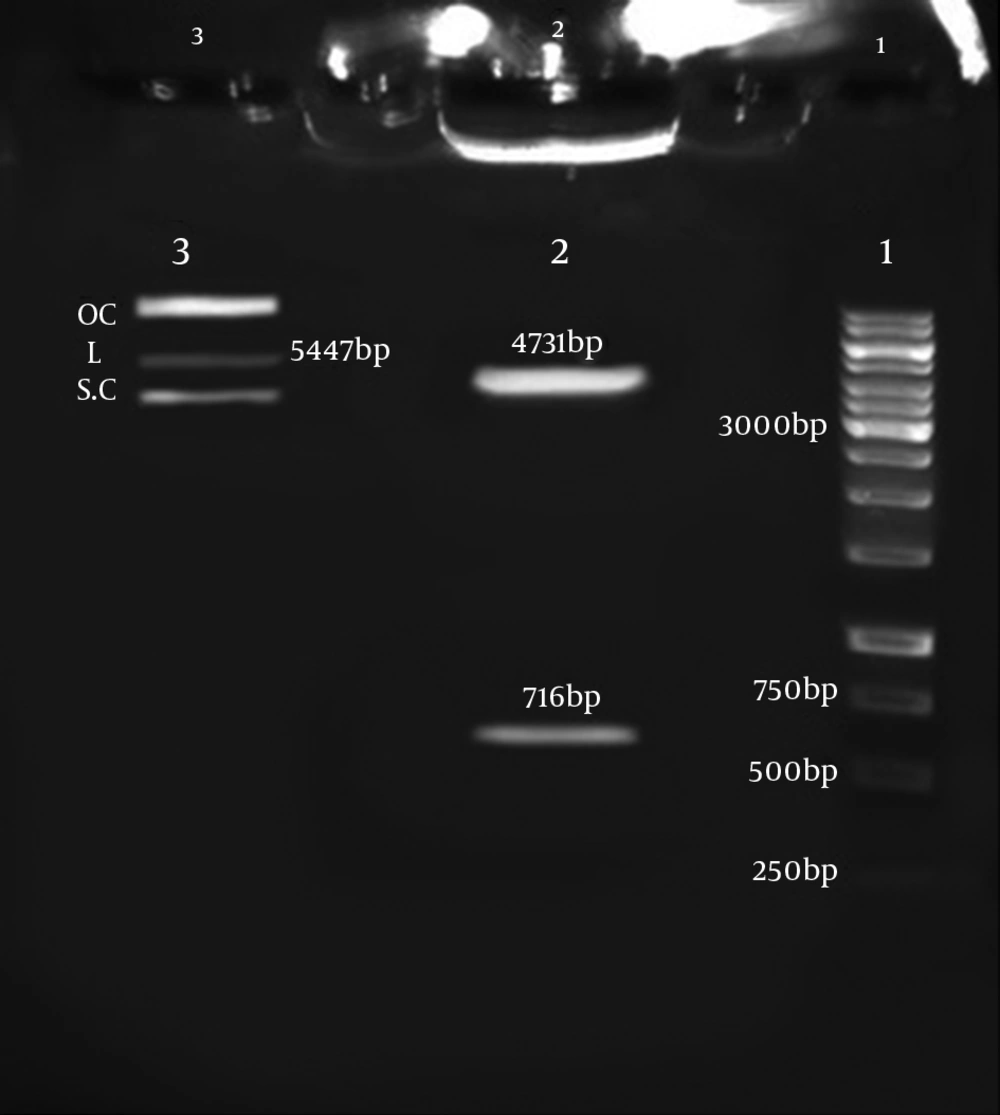
PCR amplification of HP0242 depicted a 716 bp product in 1% Agarose gel. The gene was also amplified after matrix (colonies on culture medium) DNA extraction and enzymatic digestion of PTZ-Hypothetical recombinant plasmids (Figure 1). The PTZ-Hypothetical recombination was confirmed by enzymatic digestion.
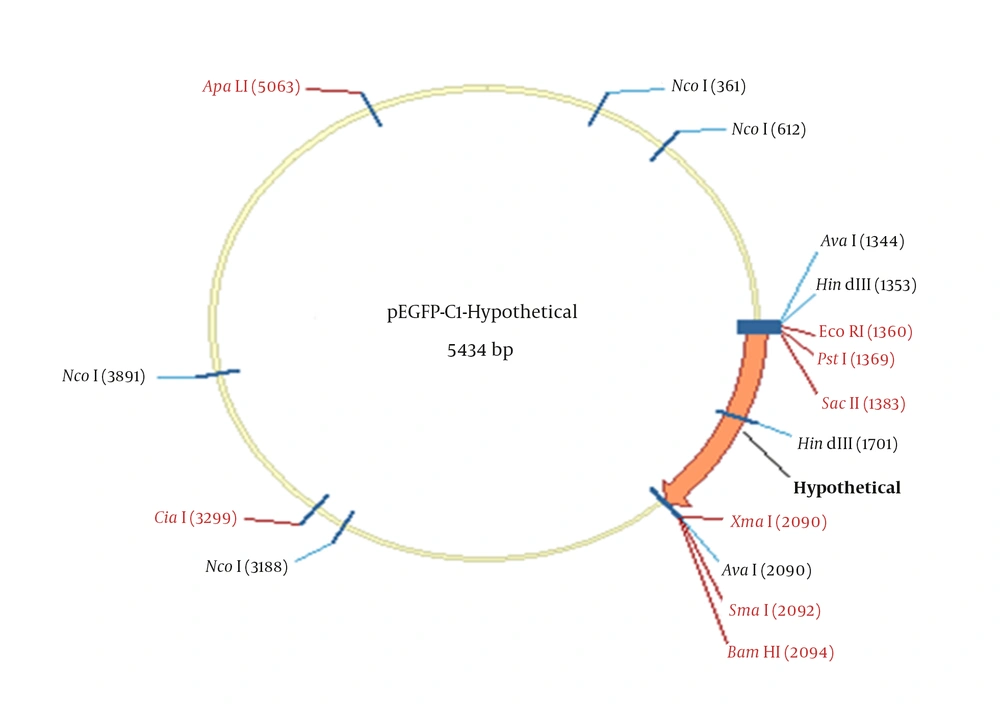
The PEGFP-C1-Hypothetical recombinant expression vector was also confirmed by digestion with smaI and sacII enzymes. As shown in Figure 2, the hypothetical gene and PEGFP-C1-Hypothetical with 716 bp and 4731 bp sizes were obtained. Sequencing the final PEGFP-C1-Hypothetical recombinant and BLAST output in GenBank demonstrated the accuracy of sequences as well. Figure 2 depicts the schematic PEGFP-C1-Hypothetical recombinant plasmid.
4.2. SDS-PAGE
The induced expression of HP0242 by utilizing 100 mM IPTG was depicted in the SDS-PAGE of protein product with a 30.60 kda size in CHO cells.
Identification of the Immunoreactivity of HP0242 was expressed by recombinant E. coli.
The HP0242 expressed by E. coli transformant was recognized by anti-Hp serum. This result indicated that the HP0242 protein expressed by E. coli transformant had favorable immunoreactivity.
5. Discussion
In the current study, the hypothetical gene (HP0242) was cloned in PEGFP-C1 and PTZ vectors and next the protein was translated/ expressed in the CHO cells. Moreover, the immunoreactivity of HP0242 was shown in the western blot analysis. Several other proteins have been introduced as DNA vaccine candidates and induction of immune responses and have been assessed to some extent (14). However, the potential of specific immunogenicity has not been fully examined. In a previous study by Tsai, the HP0242 was cloned into E. coli BL21 (DE3) and digested with BamHI and XhoI (7). This protein is supposedly involved in the persistence of H. pylori in the acidic medium of gut and iron uptake. In a study by Chen, the outer membrane protein A (oipA) was administered intra-dermally (‘gene gun’ immunization) in C57BL/6 mice and promoted a strong Th2 and with adjuvants a Th1immune responses (15). In the present study, the immune responses and adjuvants were not investigated. In another study, Chen et al. showed that oipA DNA vaccine administered orally to C57BL/6 mice could significantly enhance levels of IgG2a/IgG1 antibodies and IFN-γ/IL-4 cytokines (mixed Th1/Th2 immune response) (14). In several other studies, hapA, cagA, and alpA DNA vaccine candidates have been cloned in different vectors and the immune responses have demonstrated to be suitable in case of them, however, hspA results have shown that this protein cannot be considered as an appropriate vaccine candidate (16-19). Study on bacterial vectors such as Lactococcus lactis (L. lactis) carrying UreB subunit of H. pylori fused with human interleukin 2 has also shown effective for oral route of prevention and induction of secretion of antibody and IFN-γ, IL-4, and IL-17 cytokines (20). Moreover, DNA fragments of H. pylori ureI-ureB and Vibrio cholera ctb subunits were fused and injected into the BALB/C mice and led to significant protection against H. pylori via secretion of IgA and a mixed response of Th1/Th2/Th17 cells (21). In this study, the animal model and potential of immunogenicity due to HP0242 was not examined and it is proposed that this experiment be fulfilled in future research. Development of efficient vaccines against H. pylori relies on the exact study over the host-pathogen interactions and also considering molecular structures, epitope mapping, and antigenic regions. In vivo studies and induction of multi-component responses is a more efficient approach (22).
5.1. Conclusions
The PEGFP-C1-Hypothetical recombinant plasmid was expressed and then recognized by serum that contained polyclonal antibodies and therefore, it can be considered as a DNA vaccine candidate in the future for prevention of H. pylori infection. Development of efficient vaccines against H. pylori relies on the exact study over host-pathogen ineractions and also considering molecular structures, epitope mapping, antigenic regions, and work on multi-component vaccine is more efficient way.