1. Context
Despite advancements in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular disease, it remains the leading cause of death worldwide (1, 2). Prosthetic valve endocarditis (PVE) accounts for 20% of infective endocarditis cases. It is the most severe form of infective endocarditis, associated with high morbidity and mortality.
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines herbal medicine as encompassing plants, herbal materials, herbal products, and their effective ingredients, including parts of herbal materials (3). Currently, hundreds of herbal medicines are available, and their use has steadily increased in Western countries over the past 20 years (4-7). However, despite the rise in herbal medicine use, there remains significant uncertainty regarding the identification of active compounds, their mechanisms of action, effectiveness, as well as potential adverse effects (AEs) and drug interactions (8, 9).
Recent studies have demonstrated that natural compounds can control or inhibit factors such as oxidative stress and inflammatory mediators, both of which play a role in cardiovascular diseases (10). The therapeutic properties of medicinal plants are attributed to their bioactive compounds (11-14). Moreover, reducing the consumption of certain foods or replacing them with legumes, vegetables, seeds, nuts, and fruits contributes to better overall health (15).
2. Materials
In this review, studies were identified through online searches without any restrictions. Articles published in both Farsi and English were reviewed by searching the Iran Medex, SID, Google Scholar, Scopus, Web of Science, and PubMed databases.
3. Results
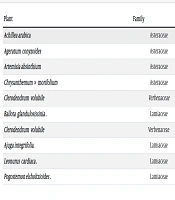
The results of the study indicated that various parts of medicinal plants have demonstrated effectiveness in treating heart disease (see Table 1).
| Plant | Family | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Achillea arabica | Asteraceae | (16) |
| Ageratum conyzoides | Asteraceae | (17) |
| Artemisia absinthium | Asteraceae | (18) |
| Chrysanthemum × morifolium | Asteraceae | (19) |
| Clerodendrum volubile | Verbenaceae | (20) |
| Ballota glandulosissinia. | Lamiaceae | (21) |
| Clerodendrum volubile | Verbenaceae | (22) |
| Ajuga integrifolia. | Lamiaceae | (23) |
| Leonurus cardiaca. | Lamiaceae | (24) |
| Pogostemonelsholtzioides. | Lamiaceae | (25) |
Plant Is Effective in Heart
In experimental, epidemiological, and clinical research, drinking green tea has been associated with a reduction in cardiovascular disease (15, 26, 27). One study demonstrated that administering green tea at a concentration of 300 mg per kilogram of body weight for four weeks reduced lipid levels in diabetic rats with heart disease (28).
Garlic (Allium sativum L.), an edible and medicinal plant from the Liliaceae family, has been traditionally used in Iran for treating various diseases (29). One of its primary uses is to reduce cardiovascular risk factors (30). Freeze-dried garlic contains at least 0.45% allicin. Since 2015, numerous studies have investigated the effect of garlic consumption on blood pressure, showing that it can lead to a reduction in blood pressure in patients (31) and has long-term effects on cardiovascular mortality (32). Ancient civilizations, including those in Thebes, Greece, and Ayurvedic medicine, recognized garlic for its rejuvenating properties (33).
Flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum) from the Linaceae family contains alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), lignans, and fiber as its main components (34, 35). Diets rich in fiber have been shown to reduce the risk of heart disease, diabetes, colon cancer, constipation, and inflammation (36). Grape seeds (Vitis viniferae), one of the most abundant fruit crops globally, are rich in phenolic compounds (37-40). Some uncommon side effects associated with grape seed extract include itching, dizziness, nausea, diarrhea, headache, sore throat, and cough (41).
The medicinal plant Silybum marianum, a member of the Asteraceae or Compositae family, contains thorns and pearls (42). Silibinin, a bioactive component of this plant, exhibits cardioprotective properties, particularly after cardiac myocyte damage caused by isoproterenol (43-45).
Tea (Camellia sinensis L.) is rich in phenolic substances (46). Moreover, coffee consumption has been shown to significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, neurological disorders, and even suicide (47, 48).
In a study by Soroushzadeh, the borage plant (Borago officinalis), a medicinal plant rich in gamma-linolenic acid, was highlighted for its medicinal properties. Borage seed oil is the richest plant source of gamma-linolenic acid, which is commonly used in food supplements and prescription medications for the treatment of heart disease, eczema, cyclical mastalgia, diabetes, arthritis, and multiple sclerosis. Due to its therapeutic benefits, the cultivation of this valuable medicinal plant has garnered increased attention (49).
4. Conclusions
There is substantial evidence indicating that eating habits play a significant role in the development of cardiovascular and metabolic disorders (14). The consumption of legumes, vegetables, seeds, nuts, and fruits is associated with improved health outcomes (15, 22, 50).
Despite advances in the treatment of heart disease with synthetic drugs, the reduction in mortality remains below 30%, and cardiovascular risks continue to require attention.
The results of this study demonstrate that medicinal plants have beneficial effects in the treatment of cardiovascular and infectious diseases.