1. Context
Spinal cord and brain diseases are among the sensitive and important diseases related to the central and peripheral nervous system (1-3). These diseases can have destructive health-related effects, including the patient's quality of life (4-6). Primary brain tumor (PBT) includes benign and malignant tumors, whose origin is related to the brain parenchyma and its surrounding structures, which occur at all ages, but its prevalence is higher in adults (7, 8). Like other types of tumors, the PBT etiologies are also unknown, but factors such as environment, genetics, ionizing radiation, and some hereditary disorders have been effective in causing it (7, 9).
Due to its different prevalence, nature of the treatment, and survival rates, PBT is of special importance and, thus, special prevention and treatment measures should be taken. PBT causes poor prognosis and significant complications, which include movement problems such as balance disorders, failed return to work, and daily life activities (10-12). Primary brain tumor can be primary or metastatic and appear in different parts of the brain. According to the anatomical location of involvement in BT, the clinical symptoms of these types of tumors are different from other types of cancer, but complications such as pain, vision impairment, weight loss, dry mouth, dysphagia, fatigue, and sleep disorders may occur in all these patients (13, 14).
The most common types of PBT in adults include glioblastoma (GBM), ependymoma, miscellaneous, astrocytoma, and medulloblastoma/PNET. Glioblastoma is one of the most aggressive and common PBTs, which proliferates widely in the healthy brain and poses a challenge to the patient's survival due to subsequent chemical changes in the brain; that is, the survival rate may survive 3 and 12 months (15-17). Brain metastases (BMs) are one of the most common intracerebral malignancies in adults, and surgery or radiation therapy are chosen as the main treatment for these patients. Brain metastas symptoms are caused by edema, and this type of edema can expand several times more than the volume of tumors and interfere with the patient's treatment due to neurological dysfunction (18-20).
Cancer prevention is very important and epidemiological studies and meta-analyses can provide accurate information to researchers so that they know the disease severity (21-24).
2. Objectives
Estimating the disease prevalence can be regarded as an important step in the planning of preventive and therapeutic measures for a disease; for this reason, the aim of this study is to estimate the prevalence of PBT in Iran, using a meta-analysis method.
3. Methods
This meta-analysis study was conducted in Iran and articles published until the beginning of 2023 (January) were included in the study, using the English keywords of brain cancer, brain tumor, tumor prevalence, prevalence, PBT, cancer, nervous system cancer, and their Persian equivalents. Articles that investigated the age-standardized incidence rates (ASRs) of cancer in adults were included in the study.
The search was carried out in the domestic databases of Iran such as the international databases of Cochrane, Embase, ScienceDirect, Scopus, PubMed, and Web of Science.
If the information requested in the articles is complete (Table 1) and inclusion criteria are met, including the incidence rate report ASRs of BT in each of the cities of Iran, and the complete information are available, the eligible article entered the meta-analysis phase. Data analysis was carried out, using CMA 3 software.
| Authors | City | Years | Sample Size | ASRs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Male | Female | ||||
| 1 | Araghi et al. (25) | Goleston | 2004 - 2013 | 480 | 370 | 6.9 | 5.3 |
| 2 | Roshandel et al. (26) | Registry | 2014 | 60469 | 51628 | 6.66 | 4.88 |
| 3 | Asgarian et al. (27) | Kashan | 2004 | 738 | 476 | 2.37 | 1.64 |
| 2005 | 761 | 496 | 2.46 | 1.67 | |||
| 2006 | 863 | 602 | 2.77 | 2.04 | |||
| 2007 | 895 | 629 | 2.84 | 2.17 | |||
| 2008 | 1300 | 894 | 4.16 | 3.09 | |||
| 4 | Salimi et al. (28) | Cancer registry | 2020 | 9695 | 6852 | 5.56 | 3.93 |
| 5 | Sadjadi et al. (29) | Ardabil | 2003 | 2072 | 1309 | 4.4 | 3.1 |
| 6 | Fateh and Emamian (30) | Cancer registry | 2013 | 1234 | 1006 | 3.65 | 2.79 |
| 7 | Babaei et al. (31) | Semnan | 2005 | 936 | 796 | 7 | 6.26 |
| 8 | Mohagheghi et al. (32) | Cancer registry | 2009 | 17407 | 15154 | 6 | 4.5 |
| 9 | Somi et al. (33) | East Azerbaijan | 2009 | 2546 | 1175 | 9.39 | 8.06 |
| 10 | Somi et al. (34) | East Azerbaijan | 2008 | 2798 | 2085 | 4.98 | 5.48 |
| 11 | Vafajo Diantai et al. (35) | Ghom | 2014 | 1961 | 1438 | 1.88 | 1.5 |
| 12 | Mousavi et al. (36) | - | 2003 - 2004 | 21620 | 16849 | 1.88 | 1.26 |
| 2004 - 2005 | 26743 | 20473 | 2.37 | 1.64 | |||
| 2005 - 2006 | 31360 | 24495 | 2.51 | 1.71 | |||
| 13 | Mehrabani et al. (37) | Fars | 2008 | 1495 | 1620 | 2.08 | 1.46 |
| 14 | Amori et al. (38) | Iran | 2016 | 168 783 | 132 272 | 2.71 | 1.64 |
| 15 | Tolou-Ghamari (39) | Isfahan | 2020 | 620 | 423 | 8.2 | 3.8 |
| 620 | 423 | 6.3 | 3.8 | ||||
| 620 | 423 | 7.3 | 4.6 | ||||
| 620 | 423 | 6.4 | 5 | ||||
| 16 | Almasi et al. (40) | Cancer registry | 2016 | 44,838 | 39991 | 4.6 | 3.8 |
| 17 | Tolou-Ghamari (41) | Isfahan | 2020 | 15,827 | 14638 | - | - |
| 18 | Norouzirad et al. (42) | Dezful | 2017 | 1270 | 932 | 3.09 | 1.10 |
| 19 | Sadjadi et al. (43) | Kerman | 2007 | 3264 | 2620 | 2.9 | 2.3 |
| 20 | Masoompour et al. (44) | Registry | 2011 | 4549 | 3810 | 3 | 2.2 |
Abbreviation: ASRs, age-standardized incidence rates.
4. Results and Discussion
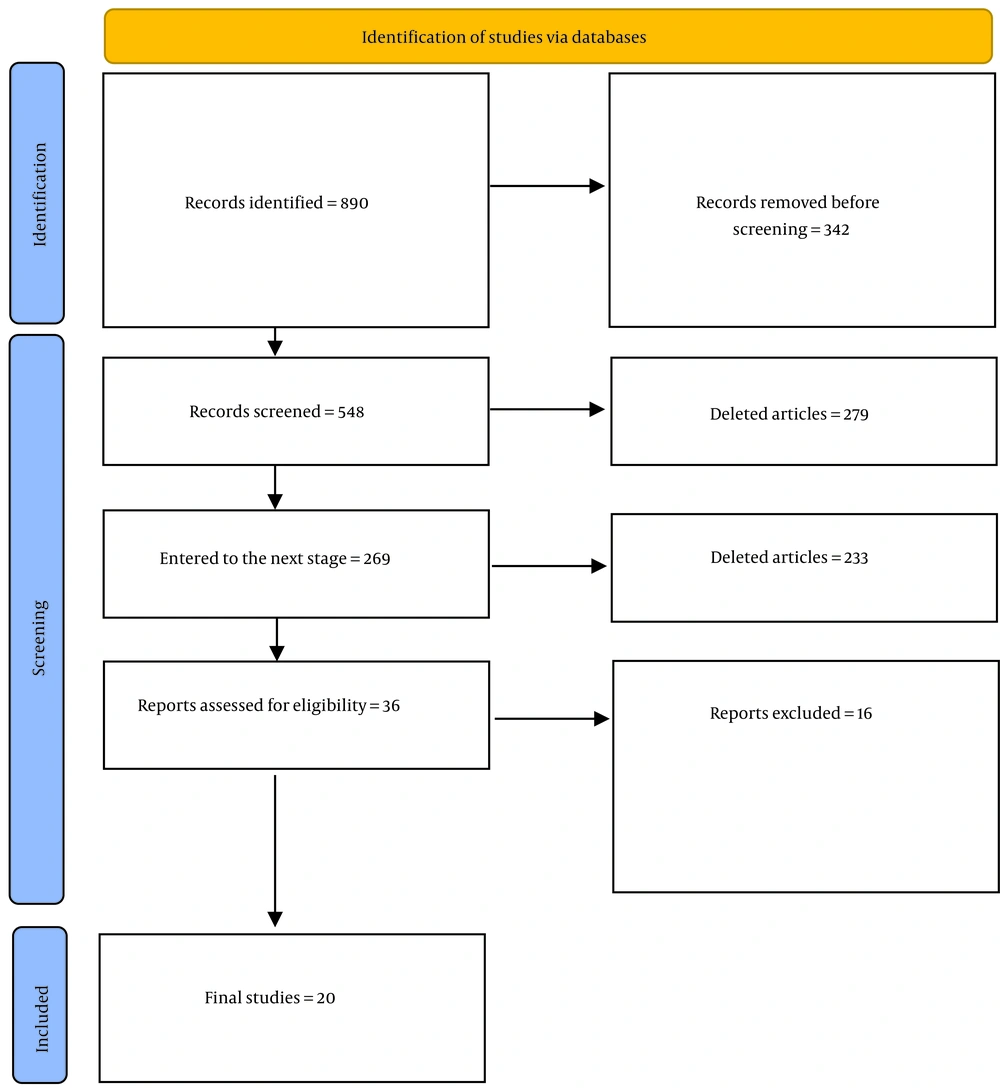
After the initial search, 890 articles on BT were found and 21 eligible articles were included in the study (Figure 1).
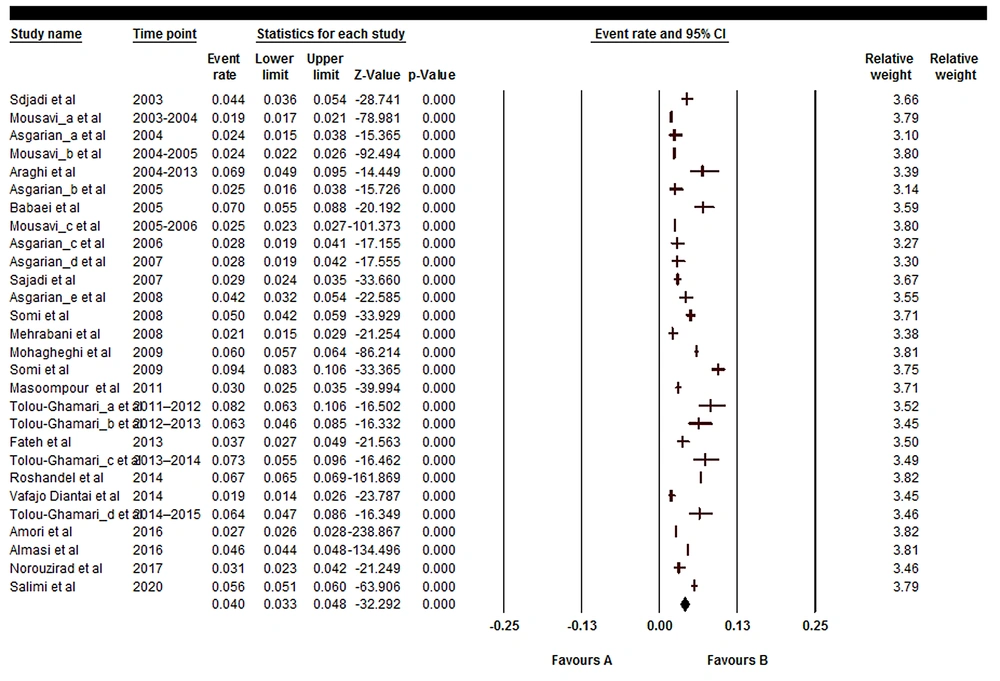
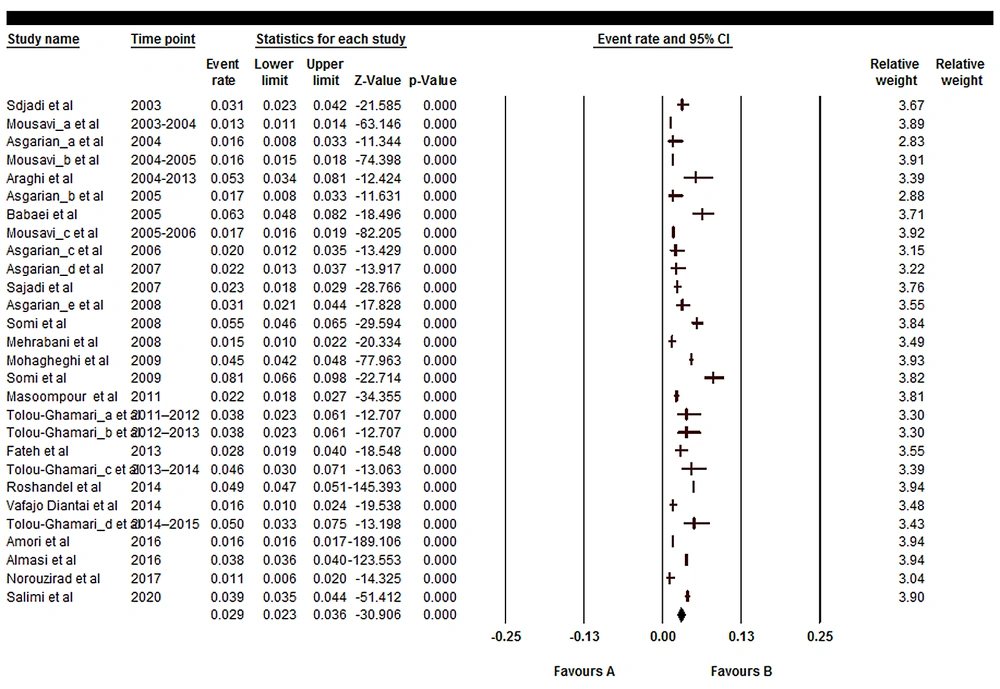
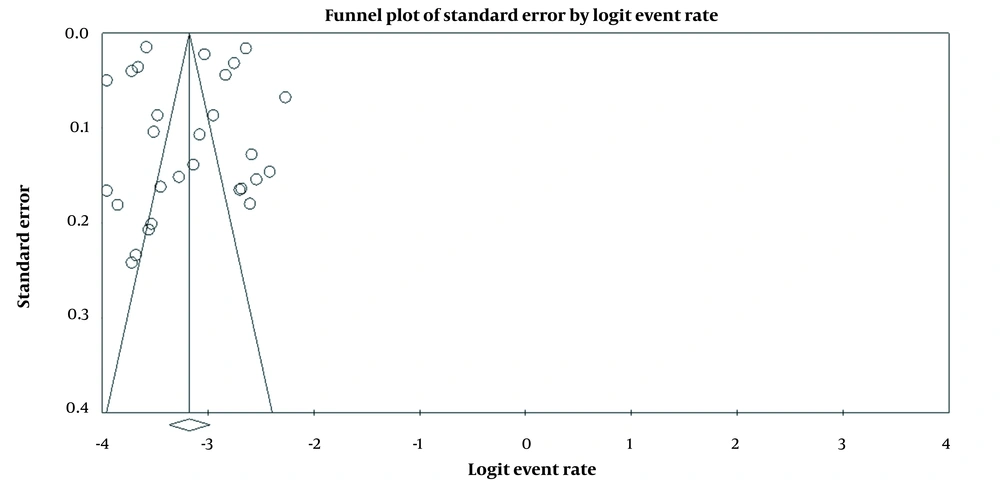
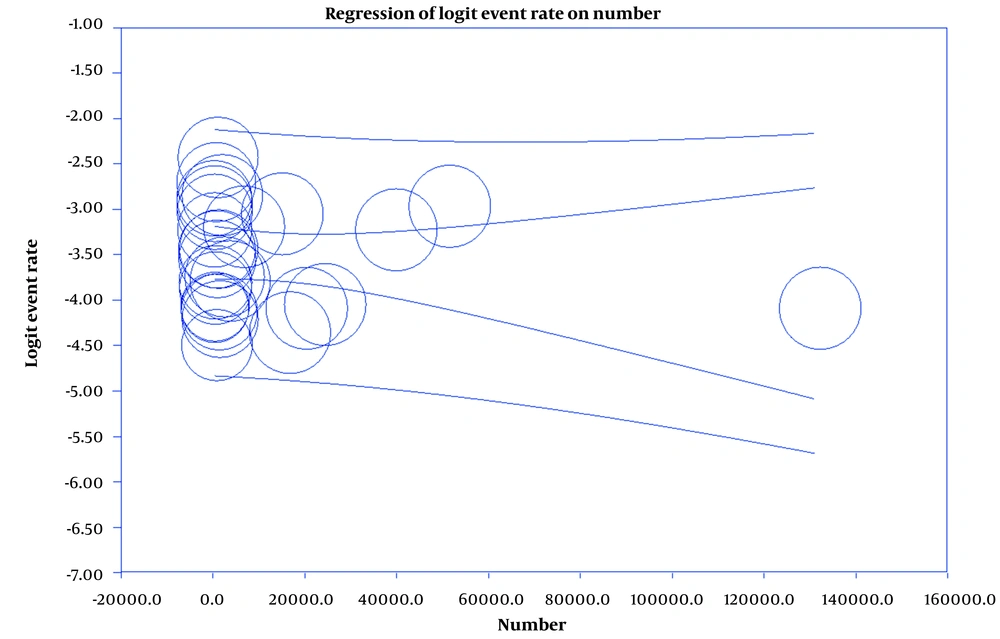
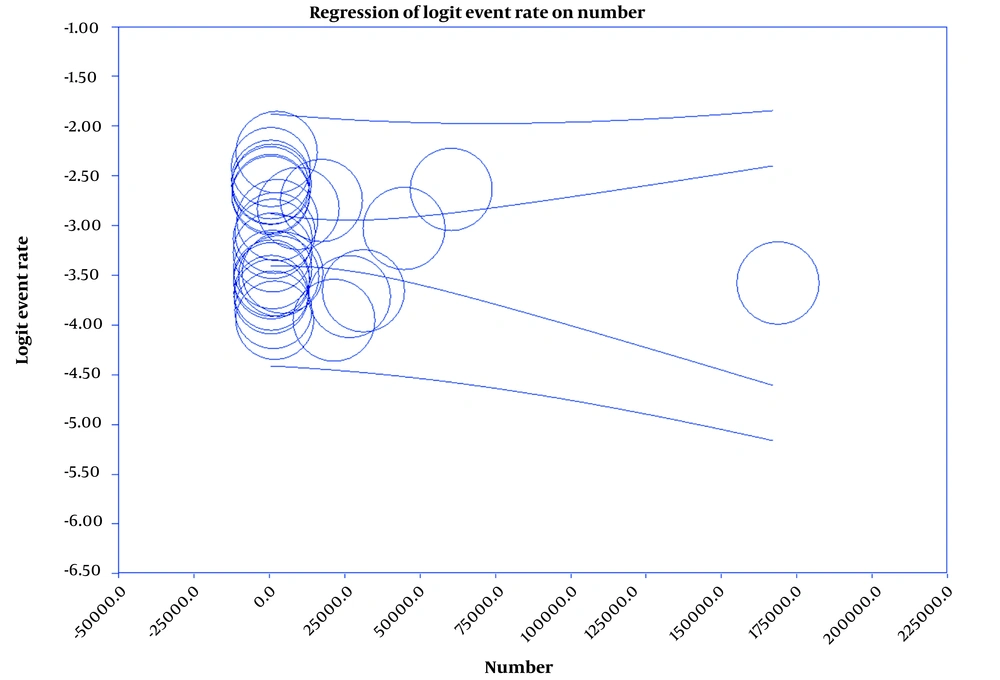
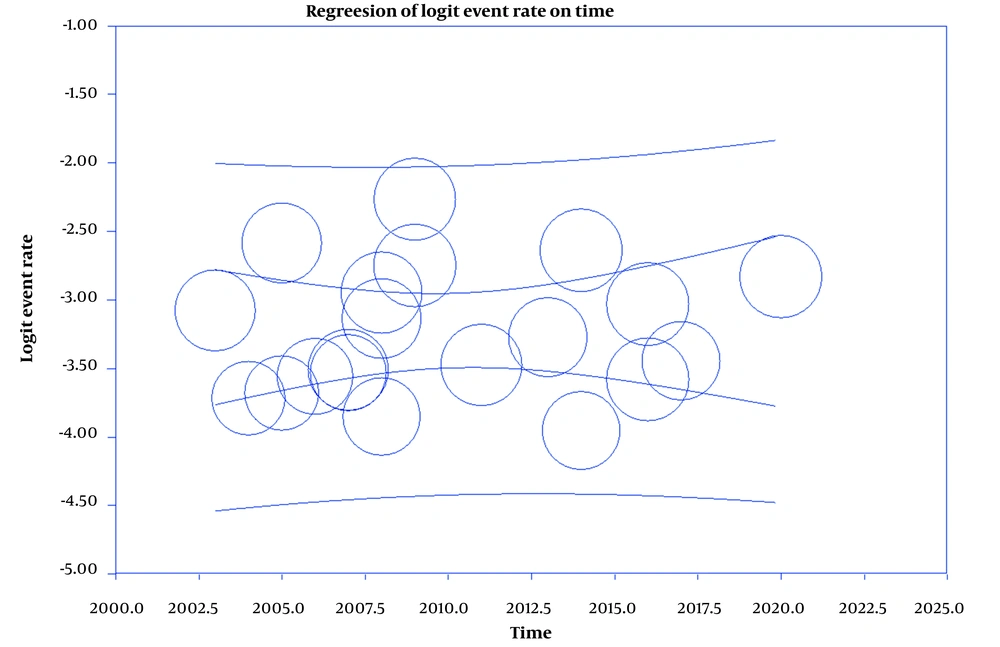
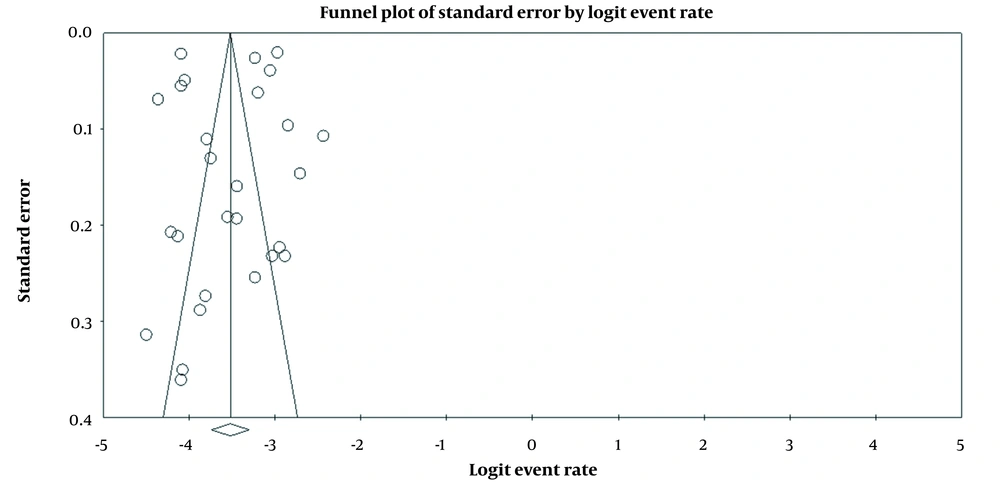
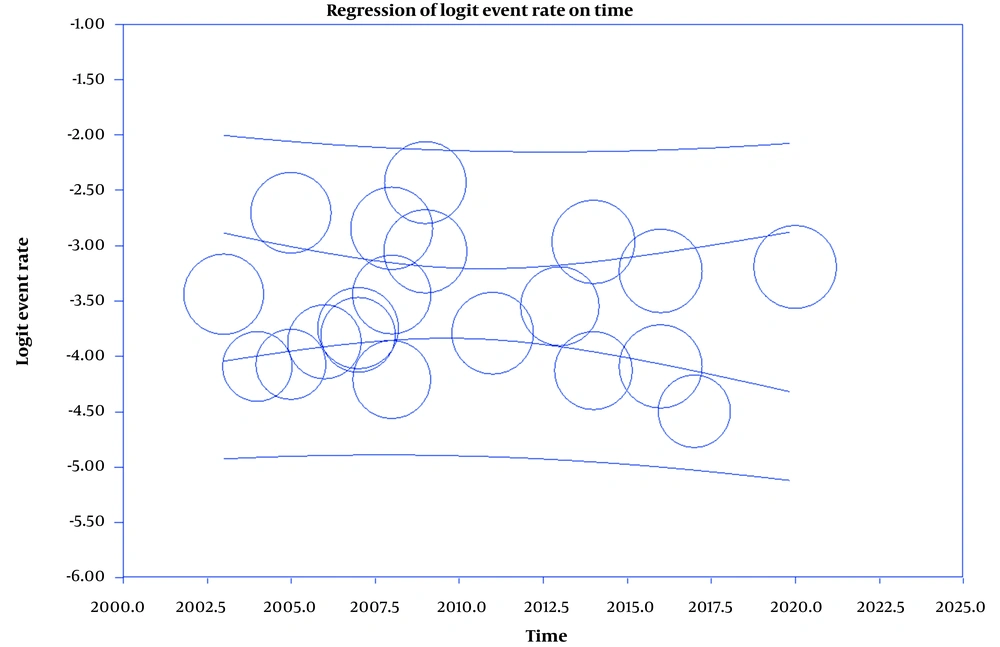
Results showed that the prevalence of BT is 4% (95%CI: 3.3 - 4.8) in men and 2.9% (95%CI: 2.3 - 3.6) in women (Figures 2 and 3). Also, in Figures 4 and 5, the state of bias publication is shown. On the other hand, according to Figures 5, 6, 7, 8 and 9, there was no relationship between the year of conducting the studies and the sample size with the status of ASRs.
The results also showed that the prevalence of brain cancer is 4% (95%CI: 3.3 - 4.8) in men and 2.9% (95%CI: 2.3 - 3.6) in women. The cancer prevalence was analyzed in meta-analyses in Iran and other studies. In this regard, in a review of 24 articles, Kazeminia et al. investigated the prevalence of breast cancer in 39 596 patients from 1965 to 2019 and it was observed that the overall ASR of breast cancer was 23.6% (45). In a meta-analysis of 17 articles published until 2017, Hassanipour et al. reported that the ASR rate for kidney cancer in men and women was 1.94 and 1.36, respectively (46). In another meta-analysis of 21 articles, Hassanipour et al. found that the ASR rate for prostate cancer was 9.11% (47). In another meta-analysis of 28 articles with a sample size of 100 869, Salari et al. reported that the ASR for thyroid cancer was 3.5% (48). According to the results of the aforementioned studies, in Iran, the cancer incidence in each organ of the human body has been variable. Such differences can be attributed to the role of background factors such as age, gender, environment, and pathogenic risk factors that may have influenced the prevalence of different types of cancer (49-51).
Sadeghi et al. found that the BT prevalence in Iranian people under 18 years of age was 2%, which is lower than the results of the present study (52). This discrepancy may be due to the difference in the number of reviewed articles (21 articles in the present study and 8 articles in Sadeghi et al.'s study), diversity in the sample size, and the difference in the age group under study (all age groups in the current study, but only people under 18 years of age in Sadeghi et al.'s study), each of which affects the BT incidence. On the other hand, the BT incidence was investigated between 2000 and 2009 in Iran; in a study by Jazayeri et al., it was observed that the incidence of malignant PBTs was 3.3% of all tumors (per 100 000) compared to other tumors, which was 3.9 in men and 2.8 in women (53). All the data reviewed in Jazayeri et al.'s study were related to the annual national reports of cancer registration (n = 11 cases), while only the data available in the published articles (original or national reports of cancer registration in the form of registry) were included in the present study.
In a meta-analysis of 36 articles with a sample size of 37 697, Nakasu et al. reported that the incidence of meningiomas and gliomas was 0.52% (54). Also, BT was reported in 4 400 cancer patients out of 267 450 patients (incidence rate = 2%) in a study by McKinney (55), which is consistent with the results of the present study that suggest the significant incidence of BT in cancer patients. In the context of high prevalence in men compared to women, in the study of Jiang et al., the prevalence in men and women is equal (56), Also, in Porter's study, the prevalence in women was higher than in men, which is not consistent with this study (57).
5. Conclusions
According to the result, the BT incidence rate is 4% for males and 2.9% for females. Therefore, it is necessary to take necessary preventive measures in this regard.