1. Introduction
Pleomorphic Xanthoastrocytoma (PXA) is a rare WHO grade II neoplasm which accounts for less than 1% of astrocytic tumors. More than 98% of these tumors are located in supratentorial area of the brain. Also it mostly affects young individuals between their first 3 decades with no gender difference (1). Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), also known as von Recklinghausen’s disease, is an autosomal dominant genetic neurocutaneous disorder which was first described in 1882. It is the most common phakomatosis with a prevalence of one in 3,500 births, which equally affects males and females (2). Cafe au lait spots and axillary freckles along with neurofibromas are possible findings in these patients. Although not uncommon, optic nerve glioma which is the most serious ophtalmologic manifestation is found in 20% of NF1 patients (3). Less than 10 cases of NF1 with PXA have been reported in the literature (4). On the other hand, once a rare cancer, the incidence of cutaneous malignant melanoma (CMM) which is the neoplasm of pigment-producing melanocytes in the basal layer of the epidermis is rapidly growing. In contrast to NF1 and PXA which affect children and young patients, CMM attacks individuals in their 5th decade (5). Furthermore, more than 30 mutations of the B-Raf proto-oncogene (BRAF) have been recently identified in the pathophysiology of human cancers (6). Although strong association between BRAF gene mutations and melanoma, and PXA have been found (7), some authors report positive BRAF gene mutations in malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors associated with NF1 patients (8).
We report the first case of a female patient with NF1 and PXA in cerebellopontine angle with simultaneous CMM and possible role of BRAF gene mutation for all mentioned manifestation.
2. Case Presentation
2.1. History
The patient was a 34-year-old female presenting with visual impairment, drop attacks and decreased level of consciousness, with established diagnosis of NF1 and left optic nerve glioma from 28 years before. The patient underwent surgery and radiotherapy for her glioma which resulted in slight visual field improvement. Also, our case had been suffering from viral encephalitis in childhood.
2.2. Examination
Physical examination revealed right VI and VII cranial nerve paresis. In addition to multiple café au lait spots, an irregular elevated firm hyperpigmented skin lesion in thoracic area was identified during physical examination. Excisional biopsy was performed and sent for histopathological study.
2.3. Imaging Findings
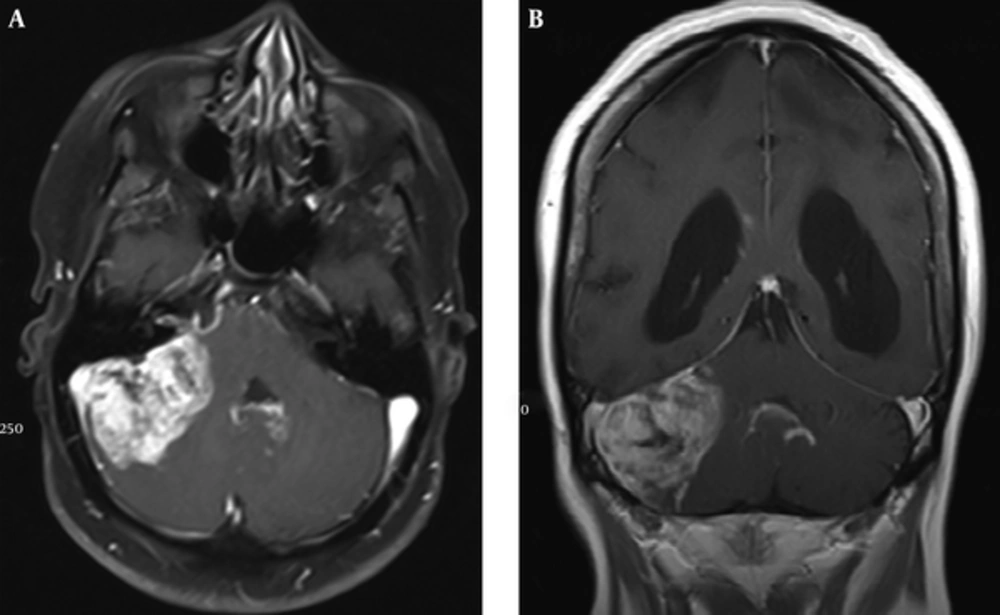
In addition, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of brain showed a hyper intense lesion on T2-weighted image in right cerebellar lobe with mass effect on vermis and fourth ventricle. Porencephaly was also noted in left frontal, parietal and temporal lobes (Figure 1).
2.4. Operation
Based on the clinical scenario and imaging findings, right retro-mastoid craniectomy and total resection of tumor was performed.
2.5. Histopathological Findings
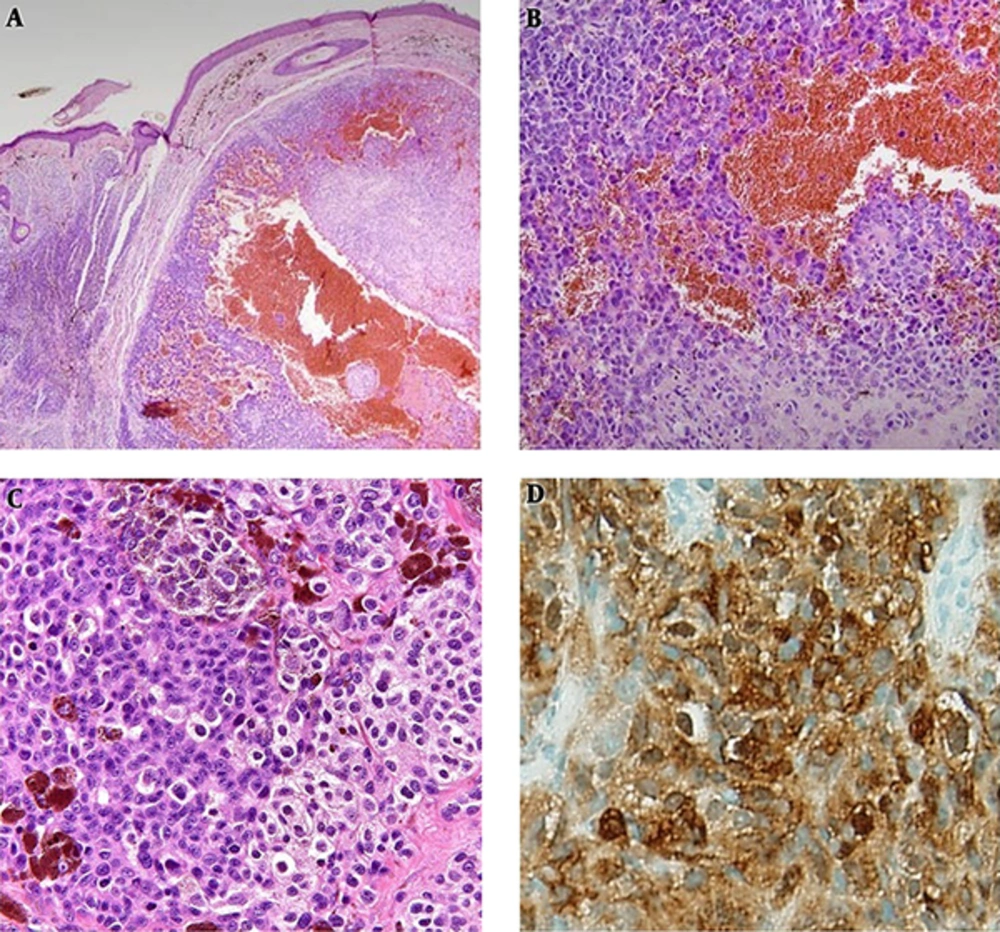
Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) stained sections of the skin lesion showed atypical melanocyte proliferation which has epitheloid cytologic feature, abundant cytoplasm, vesicular nuclei and eosinophilic macro nucleoli, predominant in nests and sheets associated with foci of melanin pigment deposition (Figure 2A - 2C). These features along with positive immunohistochemistry (IHC) with S100 stain confirmed the diagnosis of nodular type CMM (Figure 2D).
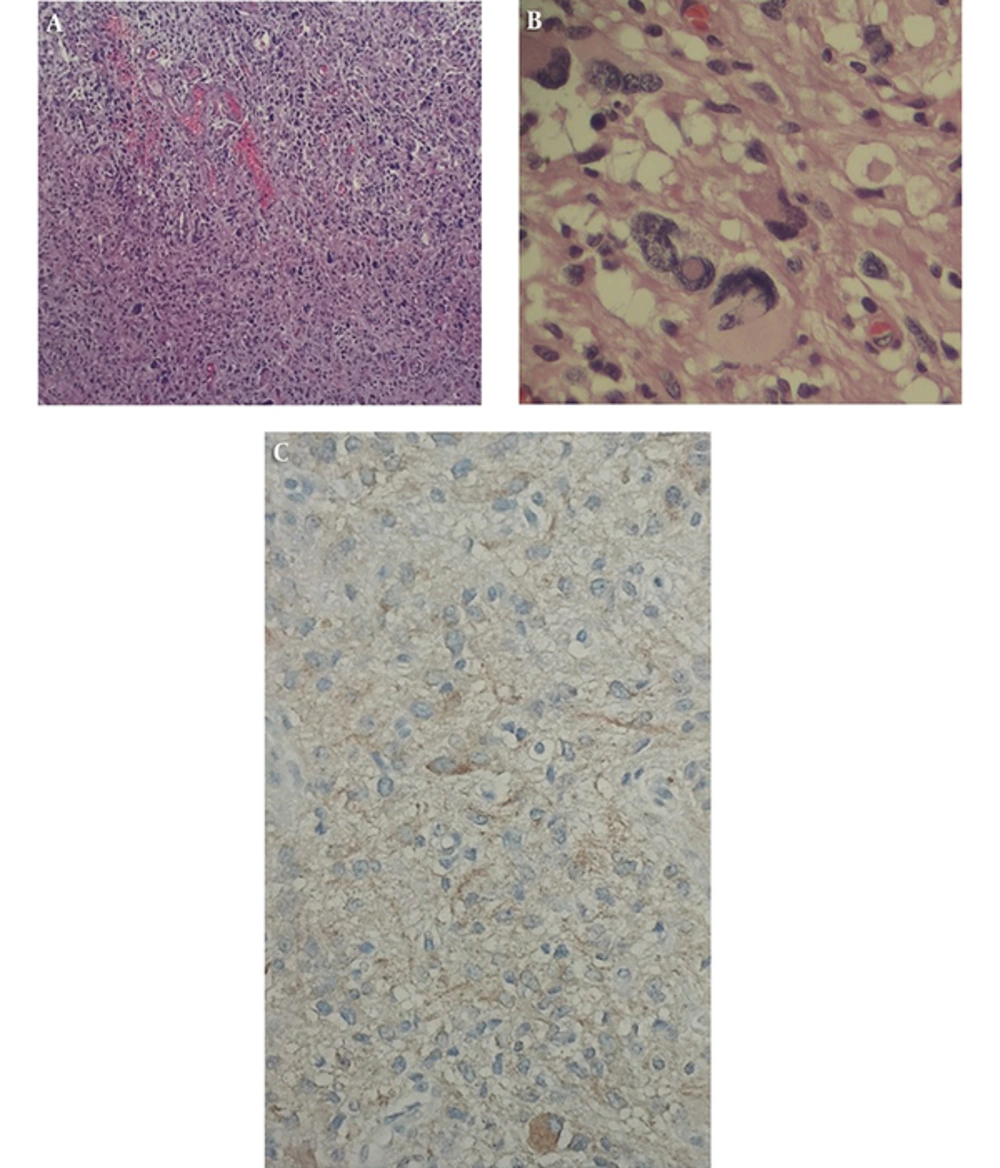
Excised lesion from brain which had yellowish color at sight by the surgeon was immediately sent for histopathological examination. Histopathology of the lesion revealed multiple irregular pieces of tan yellow to brown, soft to elastic tissue in macroscopic view. H&E and Reticulin stained sections show cerebellum tissue with a hypercellular neoplasm composed of atypical pleomorphic tumor cells with abundant pink cytoplasm arranged in fascicles. Many large bizarre nuclei, multi-nucleation foamy cells and markedly hyalinized vessels were noted as microscopic features (Figure 3A and 3B). Also, tumor cells showed positive immunoreactivity for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in IHC study (Figure 3C). Based on imaging and histopathological examination, the diagnosis of PXA was established.
2.6. Genetic Study
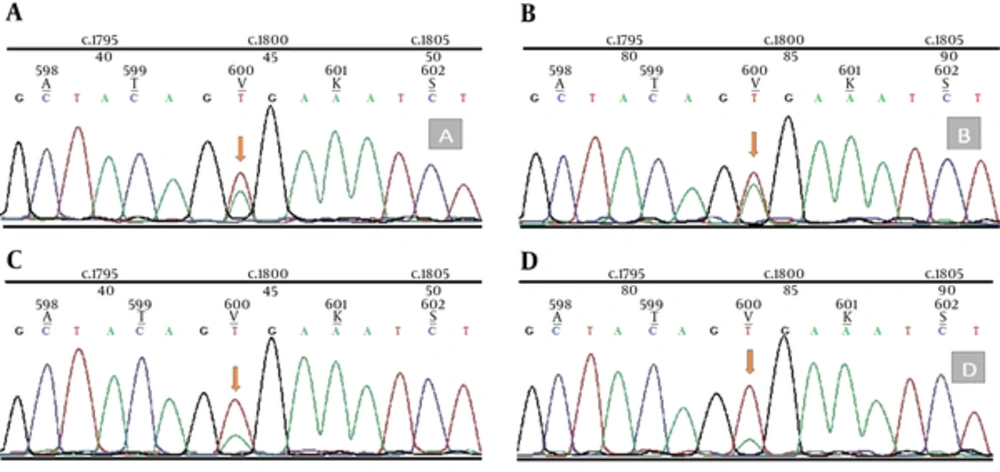
In addition, genomic DNA was extracted from 20 μm thick whole tissue sections from formalin fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) samples of PXA and melanoma’s tissue using the QIAamp FFPE Tissue Kit (Qiagen, USA). Mutation analysis was performed by dideoxy (Sanger) sequencing for PXA and melanoma’s tissue. Amplification of the region of exon 15 containing V600 nucleotide is performed by Sanger sequencing primers. Forward and reverse strands were sequenced on an Applied Biosystems 3730xl DNA Analyzer. Sequence Scanner v1.0 software (Applied Biosystems, USA) analysis revealed positive BRAF T1799A mutation in both PXA and melanoma’s tissue (Figure 4).
2.7. Postoperative Course
In postoperative course, despite accurate follow up imaging plans, the patient died 6 months later due to brain tumor recurrence and respiratory arrest. Written informed consent was obtained from the patient’s parents with ethical approval of ethics committee of Shohada Tajrish hospital. Under the principles of the Helsinki Declaration.
3. Discussion
Diagnosis of NF1 is based on clinical criteria initially established by national institute of health (NIH) in 1987 (3). Our patient had multiple café au lait spots and left optic nerve glioma. Co-occurrence of NF1 with PXA is very rare, with only less than ten cases reported in literature (9). Due to superficial leptomeningeal involvement, PXA is seen as a solid firm tumor usually with cystic component. Microscopically, PXAs are composed of spindle cells which usually are arranged in fascicles with an admixture of pleomorphic giant cells. Eosinophilic granular bodies, rich reticulin network which surrounds individual cells and small cell nests and also large xanthomatous cells with intracellular lipid droplets are mostly seen (10). Following supratentorial regions, uncommon sites for PXA are cerebellum and spinal cord. Cerebellar PXA has been reported for 3 patients with NF1 (11). However, Kurschel et al. reported the first cerebellopontine PXA in a child (12). Our patient is the second reported case with mentioned lesion in the cerebellopontine area. Solid portions of PXA often shows isointense signal on T1-weighted images; however, cystic component which is present in half of the cases, is predominantly seen as a hypointense lesion on T1-weighted image. PXAs tend to have higher signal intensity on T2-weighted images both before and after contrast administration (13). Similarly, high signal intensity mass on T2-weighted image was noted for our presented case. There are multiple studies regarding the pathogenesis and genetic base of NF1, PXA and also CMM, which our presented case showed the combination of the mentioned disorders for the first time. Since Davies et al. showed the role of BRAF gene mutations in pathogenesis of human cancers in 2002 (6), authors have reported multiple associations between BRAF gene and different disorders. The association between BRAF V600E mutation and PXA has been identified in individual cases (14), until Dias-Santagaba et al. (7) and Schindler et al. (15) reported positive BRAF V600E mutations in about 60% of cases with PXA. The mentioned mutation was mostly detected in temporal lobe PXAs (7). Notably, similar mutations have been reported in up to 60% of patients with CMM (6, 16). However, based on our review of literature, there is no study addressing the co-occurrence of PXA and CMM. On the other hand, although no study has shown a direct correlation between BRAF mutations and pathogenesis of NF1, two separate studies have found positive BRAF V600E mutation in patients with NF1-related malignant peripheral nerve sheet tumors (MPNST) compared with isolated MPNSTs (8, 17). In addition, an individual case with positive BRAF V600E mutation has been reported for his pilocytic astrocytoma (18), which is the histopathological form of optic nerve glioma in NF1 patients (3). Besides, BRAF kinase inhibitors such as PLX-4032 and HSP90 inhibitors, which can destabilize mutated BRAF, showed clinical responses in BRAF V600E positive PXAs as well as CMMs in previous trials (19). We presented the first combination of cerebellopontine PXA in a 34-year-old female patient with established diagnosis of NF1 and CMM. Based on the review of literature, this case raises the question that whether BRAF gene is responsible for this very rare co-occurrence. Also, the significance of this case is that whether mentioned agents could serve as an adjuvant treatment to facilitate resection of complex lesions in such co- incidences.