1. Context
Breast cancer (BC) treatment exposes patients and their caregivers to a series of challenges that make coping with the situation a struggle. At the same time, the burden of the disease impacts society at large (1). Younger women with BC are more likely to experience psychosocial and menopause-related concerns, weight gain, and physical inactivity (2). The broad spectrum of psychosocial issues experienced by women with BC can be categorized into 4 groups, including (1) dealing with cancer, (2) the importance of caring, (3) the aftermath of cancer, and (4) fertility and infertility (3).
Owing to improvements in cancer detection and treatment, BC is increasingly becoming a chronic illness with longer survival years. Therefore, for BC rehabilitation to be comprehensive and effective, patients and their caregivers should be taught how to incorporate health-promoting habits in their lives by redesigning their lifestyles (4). There is strong evidence that BC patients and survivors can benefit enormously from exercise interventions in terms of quality of life (QoL), cardiorespiratory fitness, physical functioning, and fatigue (5, 6). For instance, yoga practice has been shown to enhance health and alleviates some treatment-related side effects for patients recovering from BC (7). In total, acknowledging practitioners and clinicians may help to improve a BC prognosis through recommending exercise, anticipating the physiological effects on cancer (8).
2. Objectives
According to the published research, BC patients need various services during and after treatment in order to maintain a better QoL. It seems that most of these aspects are unclear in Iranian women. In this study, we systematically reviewed articles that begin with rehabilitation in BC patients in Iran. Presenting the research map of rehabilitation activity in the past 10 years in Iran may provide a useful perspective for future research to establish the efficient and beneficial services for developing the QoL of these patients.
3. Methods
This study is part of a big project to study the different aspects of BC in Iran. All of the published articles about BC in Iran, within a defined time, were included in the study. Then they were divided into 5 subgroups, and a specific process of systematic review was followed in each subgroup. Details of the methodology are as follow:
4. Data Sources
All articles published from January 2006 to October 2015 were included. To achieve the most comprehensive medical electronic databases, keywords were extracted from the medical subject headings (MeSH) of PubMed. Studies were searched in English and Persian databases. English online international electronic databases consisted of Web of Science, PubMed, and Scopus. The English search formula was “breast cancer” OR “breast carcinoma” OR “breast tumor” OR “breast neoplasm” AND “Iran”. In total, 1 986 English abstracts were included.
Persian databases consisted of SID and IranMedex, the most comprehensive national electronic databases, with the most coverage of Iranian public health and medical journals. It was not possible using a combined formula in a Persian search; so, keywords were searched separately (Saratan-e-Sineh, Saratan-e-Pestan, breast tumor, breast cancer, breast carcinoma, breast neoplasm and Iran). Then, they were combined with each other. In total, 1 345 Persian abstracts were retrieved.
5. Study Selection
Three reviewers (two surgeons and one epidemiologist) screened the primary search and divided it into subgroups; 50 articles were randomly selected for validation of the reviewers’ agreement assessment. They were instructed to decrease their disagreements in article classification. The trained experts divided the articles into 5 subgroups (epidemiology and risk factors, genetic, prevention, diagnosis and treatment, and rehabilitation), although some of them were allocated to more than one group. Being classified according to titles and abstracts, the duplicated and unrelated articles were excluded. Totally, 763 English and 572 Persian abstracts were divided into 5 subgroups to find and assess the full-texts. Irrelevant studies were evaluated again by the team supervisor. So, the final number of eligible articles for systematic review in 5 subgroups was 1 646 abstracts. The full text of abstracts was found, and in some occasions, a letter was sent to the author to get the necessary information. Two reviewers used a checklist to critically appraise the full text of the selected articles. If there was any disagreement, the reviewers would discuss the eligibility of the articles and make a decision about it.
6. Data Extraction
The necessary information of retrieved articles was extracted and recorded in the designed data extraction spreadsheet in Excel software. Datasheet consisted of general information (title, the place of study, study year, journal name, and publication year), methodological information (study design, sample size, data source, studied population, measurement tools, sampling method), and results of the study (main outcome, effect size, and measurement tools). All of the articles were extracted by two people. A representative of each subgroup organized the two extracted forms into one sheet.
In the third step, the extracted data should be analyzed. Because of the variety in the field of studies, the results were categorized according to their study design, except for specific fields such as lymphedema and validation of instruments. Thus, the rehabilitation subgroup reviewed articles were categorized into 5 groups, including qualitative, instrument, lymphedema, interventional, and observational studies. Interventional studies were divided into educational, social, psychological, exercise, and other interventions. Observational studies consisted of anxiety and depression, QoL, sexual status, emotional distress, complementary medicine, and social studies.
7. Results
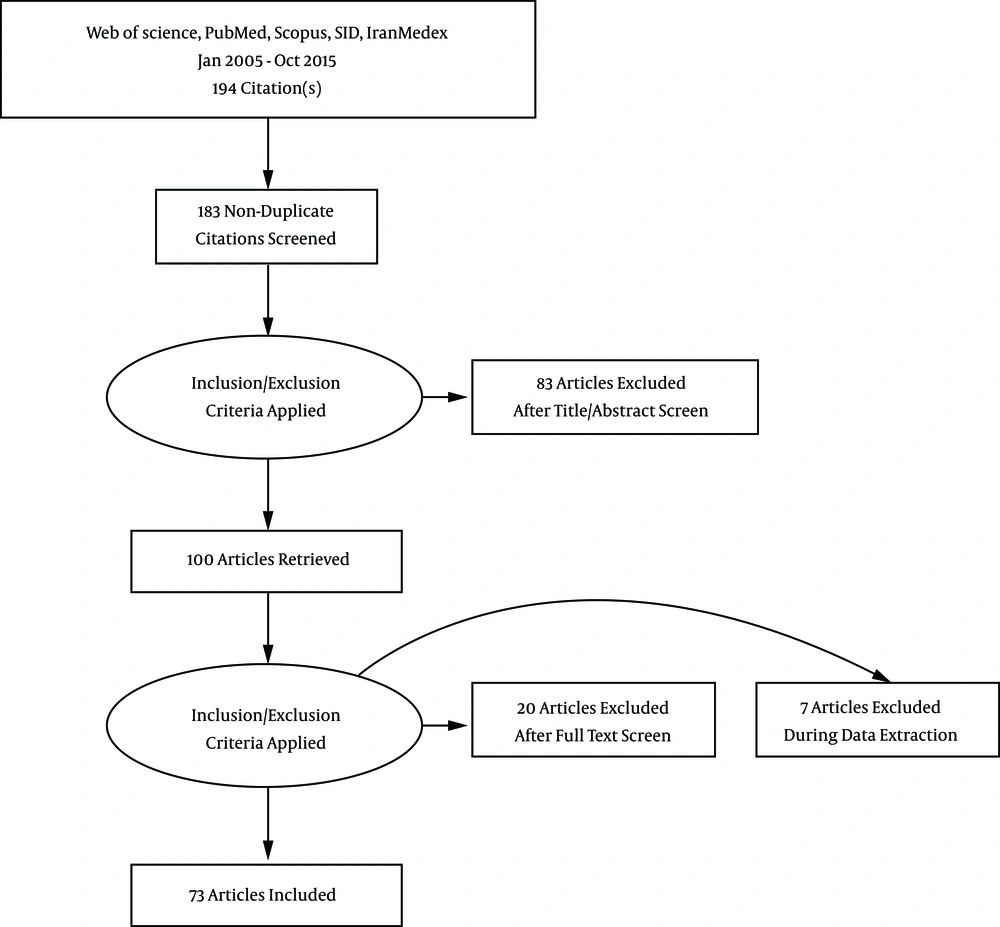
In total, 194 articles, consisting of 102 English and 92 Persian, were considered eligible for study in this group, of which 11 studies were duplicated and removed. From 183 studies, 83 studies were irrelevant and excluded. In the next step, more than 27 studies were excluded based on full text. The reasons for exclusion were as follows:
Nine articles were just abstracts, 7 were not specifically related to BC, 7 were review studies, 2 articles were not related to the Iranian population, and 2 studies were on animals (Figure 1). The reviewed articles were categorized into 5 groups according to their main themes. The results of the papers in each group were as follow:
7.1. Qualitative
As qualitative studies must be analyzed differently in the systematic review, we are just reporting an overview of them. In total, 14 studies were conducted by qualitative design. All of these studies (9-20), except two (21, 22), were done on BC patients. A study was on BC caregivers. Different purposes were assumed for these studies. The assumed purposes were patients’ needs (14, 18), caregivers experiences (22), their religious experience (10, 16), their experience with BC and symptoms (12, 13, 17), coping with BC and treatment side effects (9, 19, 20), their perceptions of life (15) and role of social and cultural factors in a patient’s life (11), and the patient’s husband’s perception toward their sexual life (21). Different extracted articles in this theme have been presented in Table 1.
| Study | Sample Size | Age, Mean ± SD | Age Range | Outcome of Interest | Main Extracted Themes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taleghani et al. (19) | 19 | N/A | 31 - 25 | Coping with BC | Religious approach, thinking about the disease, accepting the disease, social and cultural factors, support sources |
| Taleghani (20) | 45 | N/A | 31 - 56 | Patient’s experiences in adjusting to the disease | Perceived threat to life, living with the disease with tolerance, religious aspects, and barriers to efforts leading to health, will to recover, supportive dimensions, increase in endurance, and inhibitors and facilitators of tolerance |
| Harandy et al. (10) | 39 | N/A | 30 - 87 | Patient’s experience with religious context | Religiosity does not prevent Iranian women from seeking medical care |
| Harandy et al. (11) | 39 | N/A | 30 - 87 | Correlated factors of health-related quality of life | Fatigue, pain, and lymphedema are the most common complaints |
| Sajadian et al. (17) | 51 | 48.4 ± 10.5 | 25 - 72 | Patient’s experience with BC | Importance of spirituality and family support, especially husband and children, during the diagnosis and treatment; chemotherapy as the worst experience |
| Nasrabadi et al. (15) | 23 | N/A | N/A | Patient’s perception of life | Cancer as a kind of divine test, a very bitter and debilitating experience, chemotherapy as the most difficult experience of cancer, a continuous struggle |
| Joulaee et al. (12) | 13 | N/A | 34 - 67 | Patient’s experience with BC | Negative aspects: losing something important, uncertainty, living with fear, emotional confusion, needing support, positive aspects: new aspects of life |
| Moradian et al. (14) | 30 | 42 ± N/A | 19 - 59 | Patients’ needs | Treatment costs, psychological distress |
| Nasiri et al. (21) | 18 | 51.5 ± 10.47 | 33 - 70 | Patient’s husband perceptions | Altered sexual relations; sexual abstinence, avoidance, or restraint; attempt to normalize relationship |
| Fouladi et al. (9) | 20 | N/A | 33 - 71 | Coping with mastectomy | Loss and death contest, reconstruction of evaluation system, reactions and troubles after a loss, health, reorganization and compatibility with changes |
| Khakbazan et al. (13) | 27 | 42.8 ± N/A | 26 - 71 | Patient’s experience with symptoms | Symptom recognition, confronting the fear of cancer, labeling symptoms, interactive understanding |
| Sadati et al. (16) | 8 | N/A | N/A | Patient’s experience with religious context | Fatalism, hope, and empowerment |
| Taleghani et al. (18) | 19 | N/A | 34 - 60 | needs of patients | Information, beliefs, and skills |
| Hashemi-Ghasemabadi et al. (22) | 23 | 37.5 ± N/A | 20 - 69 | Caregivers | Being involved in a new situation, abandoned in the role, infinite absence, perceived inefficiency |
7.2. Instrument
Articles in which different instruments had been translated and validated were categorized in another theme. In sum, we found 5 studies. All of them except one had studied BC patients (23-26). The other one had been conducted on the BC patient’s caregivers (27). Most of the studies had validated an instrument in the field of QoL. FACT-B, mini MAC scale, need questionnaire, QoL index-cancer scales, and QLQ-C30 had been validated in these studies (Table 2).
| Study | Sample Size | Age, Mean ± SD | Age Range | Validated Instrument | Main Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Safaee et al. (25) | 132 | 48.61 ± 11.22 | NA | QLQ-C30 | Cronbach’s alpha: fitted in all subscales except fatigue (0.65), pain (0.69) and nausea and vomiting (0.66). Convergent validity correlation: > 0.40 for all subscales. Item discriminant validity: significant difference in all subscales except for item 4 of the physical functioning |
| Khanjari et al. (26) | 166 | 40.7 ± 13.1 | 18 - 75 | Caregiver quality of life index-cancer scale | Cronbach’s alpha: 0.72 - 0.90 |
| Ghaffari et al. (24) | 160 | 44.6 ± 12.63 | NA | Self-assessed support needs questionnaire for BC cases | Cronbach’s alpha for all items: 0.83, stability of test: 0.78, Cronbach’s alpha of the first factor: 0.90 |
| Patoo et al. (23) | 300 | 43.34 ± NA | 23 - 72 | Functional assessment of cancer therapy-breast (FACT-B) | Cronbach’s alpha (total): 0.92, Cronbach’s alpha (subscales): 0.63 to 0.93, significant concurrent and discriminant validity was fitted. |
| Patoo et al. (27) | 320 | NA | NA | Mini-mental adjustment to cancer scale (mini-MAC scale) | Cronbach’s alpha: 0.84 |
7.3. Lymphedema
Seven studies (28-34) were conducted on BC patients, who suffered from lymphedema (Table 3). Although some of these studies were looking at lymphedema treatment methods, we tried to discuss the rehabilitation aspects because of their importance in BC QoL and rehabilitation of which 3 were interventional (29-31), and the remaining 4 were observational (28, 32, 33). Two kinds of intervention were used in this field; 2 of them were a combination of complex decongestive therapy (CDT) vs. CDT + intermittent pneumatic compression (29, 31), and they both reported the significant effects of this method on BC-related lymphedema. The third interventional study evaluated the effect of a home-based rehabilitation education on edema reduction (30). It also had a significant effect on lymphedema reduction.
| Study | Study Design | Sample Size | Age, Mean ± SD | Intervention | Outcome | Main Extracted Themes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haddad et al. (28) | Cross sectional | 355 | NA | - | Lymphedema | Mean prevalence of lymphedema: 17% |
| Haghighat et al. (29) | Trial | 112, INT: 56, CON: 56 | INT: 53.4 ± 11.4, CON: 52.7 ± 10.8 | CDT vs. CDT + IPC | Edema volume | CDT was more effective than CDT + IPC, acute phase: P = 0.036, maintenance phase: P = 0.167 |
| Khosh-Nazar (30) | Trial (before-after) | 16 | 53 ± 9.5 | Education (SLD + self-care + exercise) | Edema volume | Decrease of lymphedema P < 0.001 |
| Moattari et al. (31) | Trial (before-after) | 21 | 50.38 ± 9.92 | CDT + IPC | Edema volume | Decrease in lymphedema, P < 0.001 |
| Haghighat et al. (32) | Cross sectional | 137 | 53.5 ± 10 | - | Edema volume in CDT and predictive factors | Initial lymphedema volume and the duration of lymphedema are predictors of outcome (P = 0.003 and 0.002, respectively) |
| Hemmati et al. (33) | Cross sectional | 170 | NA | - | Lymphedema and related factors | Correlation of lymphedema and BMI (P = 0.02) and involved lymph nodes (P = 0.0001) |
| Haghighat et al. (34) | Case-control | 410, case: 123, CON: 287 | Total: 49 ± 10.9, case: 50.6 ± 11.4, CON: 48.4 ± 10.6 | - | Lymphedema and correlated risk factors | High BMI (OR: 1.09; 95% CI, 1.05 - 1.15), No. of involved lymph nodes (OR: 1.15; 95% CI, 1.08 - 1.21), and a longer period after surgery (OR: 1.01; 95% CI, 1.01 - 1.02) are associated with an increased risk of lymphedema |
Abbreviations: CDT, complex decongestive therapy; IPC, intermittent pneumatic compression; SLD, self lymphatic drainage.
7.4. Interventional Studies
In total, we found 20 articles, which looked at different intervention modalities on BC patients. These studies were conducted on distinct fields including education, social status, psychological, exercise, and other aspects. Those fields have been reported in Table 4.
| Study | Field | Design | Population | Sample Size | Age, Mean ± SD | Intervention | Purpose/Area | Main Extracted Themes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poorkiani et al. (35) | Rehabilitation | RCT | BC survivors | 66, EG: 28, CG: 30 | 40.7 9 ± NA/ 36.7 ± N/A | physiotherapy, education, and counseling (2-months) | QoL/QLQ-C30 and BR23 | Improvement in all the scales of QoL. Potential benefit for physical, psychological and overall QoL |
| Rahnama et al. (36) | Exercise | Clinical trial | Post-menopausal women with BC | 342 | NA | 60 minute resistance training twice weekly (15 weeks) | VO2 max/resting heart rate/heart rate monitor belt/blood pressure/anthropometric variables | Positive effects on VO2 max, RHR, body weight, BMI, and WHR (P < 0.05) especially in postmenopausal patients. No significant effect on blood pressure |
| Bakhtiary et al. (37) | Education | Trial without control | BC patients | 60 | NA | education on self-care against chemotherapy side effects (3 weeks) | Mental health/GHQ-28 | self-care significantly improved mental health (P < 0.001), except for 61 - 70 y age group (P = 0.147) |
| Fadaei et al. (38) | Psychological | Quasi-experimental | 2 - 6 months after mastectomy | 72 | 43.46 ± 7.6 | Consultation based on REBT method for 6 sessions (3 weeks) | Body image/Ellis rational emotive behavior therapy (REBT) | The body image score decreased in the intervention compared to control group (P < 0.001). |
| Malekpour Tehrani et al. (39) | Social | Trial | BC patients | 68 | 44.6 ± 7.5 | participate in peer groups (12 weeks) | Quality of life/SF36 questionnaire | Increase in vitality score (P < 0.001) and mental health score (P < 0.001) in experimental group |
| Ghavam-Nasiri et al. (40) | Education | Trial | BC patients | 102 | 46.6 ± 3.9/48.7 ± 1.23 | 3 sessions of self-care education | QoL/QLQ-C30 | Group teaching could maintain better quality of life than individual teaching over time (P > 0.05) |
| Sharif et al. (41) | Social | Trial without control | BC patients | 99 | NA | weekly peer-lead educational programs | QoL/EORTC QLQ-30 and QLQ-BR23 | significant improvements in all aspects of QoL in the intervention group (P < 0.001) |
| Taleghani et al. (42) | Social | Clinical trial | BC surgery for the first time, Isfahand | 150 | NA | Peer support group | QoL/standard instruments of National Medical Center and Beckman Research Institute questionnaire | The mean score of QoL were different during the second stage (P = 0.003) and 2 stages in Tehran. significant difference between 2 groups in social aspect during both stages in Tehran, spiritual aspect in Isfahan and first stage in Tehran |
| Salehi et al. (43) | Pscychological | Trial | Non-metastatic BC patients | 25 | NA | Benson relaxation technique: daily, 15 - 20 min/d at home (3 weeks) | QoL/QLQ-C-30 and QLQ-BR23 | Significant improvement in QoL (P value not available) |
| Jafari et al. (44) | Psychological | Trial | BC patients undergoing radiation therapy | 65 | 47.9 ± 10.6 /48.1 ± 10.2 | Spiritual therapy sessions (6 weeks) | QoL/QLQ-C30 BR-23 | Increased QoL (P < 0.001) and all functional scales of QLQ-C30 after intervention (P < 0.05) |
| Parizadeh et al. (45) | Psychological | Semi-experimental trial | Undergone mastectomy | 24 | 47.38 ± 6.3 | (1) existential group therapy, (2) reality group therapy, (3) no intervention | Body-image/multidimensional body-self relation questionnaire (MBSRQ) | Significant effects were observed for appearance orientation in both intervention groups (P = 0.039). Mean score for the existential group therapy was greater than that for the reality group therapy (P = 0.004) |
| Taleghani et al. (46) | Exercise | Trial | BC patient who had completed the treatment | 80 | NA | Exercise training/3 sessions a week, 60 minutes (8 weeks) | Quality of life/the National Medical Center and Beckman Research Institute instrument | Total mean score of the quality of life showed no significant difference before and after intervention (P = 0.29) |
| Fathi et al. (47) | Exercise + supplement | Before after | Obese BC patients | 40 | 46.4 ± 5.5 | (1) 750 mg ginger capsules four times a day, (2) water exercises, (3) both of them, (4) none | Cardio-pulmonary indexes and IL-10 | Exercise training plus ginger supplement were associated with a decrease in IL-10, BMI, body fat percentage and increase in cardiopulmonary indexes |
| Bosak et al. (48) | Massage therapy | RCT | BC patients under chemo | 34 | NA | Massage therapy (3 sessions on consecutive days, 30 min before chemotherapy) | Nausea/visual analogue scale | Nonsignificant (P = 0.51) decrease in the severity of nausea |
| Ebrahimi et al. (49) | Supplement | Trial | BC patients under chemo | 80 | 41.8 ± 8.4 | 250 mg ginger capsules four times a day | Nausea/visual analogue scale and some questions about severity and frequency | The severity and frequency of delayed nausea were lower in patients receiving ginger (P < 0.01). No complication in taking ginger capsules compared to placebo (P = 0.50) |
| Haghighi et al. (50) | Psychological | Non-randomized trial | BC patients | 22 | 45.5 ± 9/46.3 ± 6.5 | Logotherapy: 10 2-h sessions, a session per week. | Depression/Beck’s depression inventory | Improvement in depression, P < 0.001 |
| Izadi-Ajirlo et al. (51) | Psychological | RCT | Mastectomized BC patients | 23 | NA | Cognitive behavioral intervention, 12 × 90-min sessions, 2 sessions per week | Body image and self-esteem/“body image and relationships self- esteem questionnaire” | Improvements in body image and self-esteem due to cognitive behavioral group intervention (P < 0.01). |
| Rahmani et al. (52) | Psychological | RCT | BC patients | 36 | 44.08 ± 3.3/43.25 ± 3.1/44.92 ± 1.8 | Mindfulness-based stress reduction program (8 weekly sessions) vs. metacognition treatment (8 sessions) | Global and specific QoL/QLQ-C30 and QLQ-BR23 | Mindfulness-based stress reduction treatment causes effective in QoL improvement |
| Shabani et al. (53) | Education | Trial | BC patients | 50 | 46.7 ± 9.3 | Life skills training classes | GHQ-28 scores | Intervention significantly reduced somatization disorders, sleep disorders, disorders of social functioning, and depressive and anxiety symptoms (P < 0.0001) |
| Rahmani et al. (54) | Psychological | RCT | BC patients | 24 | NA | Group mindfulness-based stress reduction program + conscious yoga (8 weekly group sessions) | QoL/fatigue severity scale, QLQ-C30, QLQ-BR23 | Mindfulness-based stress reduction treatment is effective in improving global and specific QoL and fatigue in women with BC |
Abbreviations: BC, breast cancer; CG, control group; EG, experimental group; RCT, randomized clinical trials.
There were 3 papers in the education field (37, 40, 53). Two, out of the 3 studies, were controlled trials (40, 53), and the 1 remaining was a trial without a control group (37). All 3 studies had a sample size of more than 50. One study found that a life skill educational program was associated with improvements in somatization disorders, depressive and anxiety symptoms, disorders of social functioning, and sleep disorders (53). Two other studies had looked at the effects of self-care education on QoL and mental health (37, 40). The results showed that self-care educational intervention was associated with the significant improvement of mental health (37); however, the other study reported non-significant changes in QoL (40).
Three studies looked at the effects of social intervention on the QoL of BC patients (39, 41, 42). In all 3 studies, the intervention was participation in a peer support group. They studied the intervention effect on QoL. In total, social intervention had a significant effect on vitality, mental health, and the total score of QoL.
We found 8 studies that had investigated the effects of psychological interventions on BC patients. All 8 studies were done on BC patients. Five out of 8 studies had a sample size between 20 and 30 (43, 45, 50, 51, 54). Two studies had sample sizes of more than 50 (38, 44). A variety of psychological interventions were used; a complete list of interventions is presented in Table 4. Three different kinds of outcomes were assessed including QoL (43, 44, 52, 54), body image (38, 45, 51), and depression (50). Interestingly, all psychological interventions led to improvement in the selected outcomes.
Two papers had used exercise as an intervention (36, 46). One of them had measured physiological indices (36) and the other one measured QoL (46). Exercise had a significant effect on physiological outcomes (36) related to cardiopulmonary fitness. The other study reported no significant effect on QoL (46).
One study looked at exercise plus ginger supplementation on cardiopulmonary and IL-10. Results of the study showed that this intervention had a significant effect on the selected outcomes (47). One study looked at the effect of ginger supplement on nausea and the result showed a significant effect of ginger on nausea (49). Also, there was a study about the effect of massage therapy on nausea and its result showed no significant effect (48). Finally, one study had looked at the effect of a rehabilitation intervention on QoL and result showed significant improvement in all subscales of QoL (35).
7.5. Observational Studies
In total, 27 studies had been conducted by observational design. All of these studies except 4 were performed on BC patients. Three of the mentioned studies were on BC caregivers and the 4th was on cancer patients. Different purposes were assumed for these studies. The main purposes of these studies were anxiety (55, 56), depression (55-57), QoL (58-64), sexual status (65-67), emotional distress (68), caregiver’s QoL (69-71), complementary use status (72, 73), QoL status relationship with lifestyle (74), QoL relationship with nutritional status (75), QoL status along with sense of coherence (76), the relationship between quality of sleep and with spiritual well-being (77), the relationship between hope, body esteem, and mental health (78), QoL status relationship with spiritual well-being (79), and social (80, 81). Also, different themes were extracted that are presented in Table 5. In all of these groups of articles, the frequency of outcome, its range of variation during a time interval, and some of their correlated factors in a specified sample size had been reported.
| Study | Field | Study Design | Population | Total Sample Size | Age, Mean ± SD | Outcome/Instrument | Main Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Montazeri et al. (72) | Complementary use status | Cross sectional descriptive | BC | 177 | 49.5 ± 15.1/46.9 ± 14.7 | Association between QoL and the use of complementary medicine /HADS and QLQ-C30 | Significant association between depression and the use of comp. med. (logistic reg.) P = 0.04 |
| Montazeri et al. (73) | Complementary use status | Cross sectional | BC | 625 | 49.5 ± 15.2/46.6 ± 15.1 | Factors associated with the use of complementary or alternative medicine | The use of comp./alt. medicine among Iranian patients is not common; however, it is correlated with fear, anxiety and mental distress (P < 0.001 for all) |
| Garrusi and Faezee (65) | Sexual status | Descriptive | BC | 82 | 49.9 ± 11.8 | Conceptualize sex and body image/research made questionnaire | Desire was diminished in 70.6%. No. of coitus was decreased in 15% of participants. Excitement and orgasm were decreased in 72% of women |
| Safaee et al. (59) | QoL | Cross sectional | BC | 119 | 48.27 ± 11.42 | QoL/QLQ-C30 | QoL total score 64.92 ± 24.28. The grade of tumor (P < 0.0001), occupational status (P = 0.01), menopausal status (P = 0.01), financial difficulties (P = 0.03), and dyspnea (P = 0.01) were correlated with QoL |
| Pourhoseingholi et al. (64) | QoL | Cross sectional | BC | 119 | 48.3 ± 11.4 | QoL/QLQ-C30 | Tumor grade (P < 0.001), occupational status (P = 0.01), menopausal status (P = 0.01), financial difficulties (P = 0.03), and dyspnea (P = 0.01) were correlated with QoL |
| Hadi et al. (56) | Anger | Case-control | BC | 578 | Case: 48.6 ± 9.16, control: 45.4 ± 7.12 | Anger and depression /symptom checklist- 90 revised (SCL-90R) | The mean anger score in BC cases was significantly lower than the control group (0.57 vs. 0.42, P = 0.002). In cases, higher mean depression and anger scores were correlated with age (P = 0.008 and P = 0.020). Patients with college degrees tnded to have higher anxiety scores compared with those with degrees below high school level (1.36 vs. 0.70; P = 0.030). Tumor size of > 2 cm was associated with higher anxiety scores |
| Vahdaninia et al. (55) | Anxiety and depression | Prospective | BC | 167 | 47.2 ± 13.5 | Depression and anxiety through 18 months follow-up/HADs | Anxiety and depression improved over the time (P < 0.001) |
| Kiadaliri and Bastani (63) | QoL | Cohort | BC | 100 | 48.49 ± 10.63 | QoL/QLQ-C-30 | Adverse effects of chemo regimens after chemo: TAC (64) > FAC (68) (P < 0.005); improvement after 4 months: TAC (11.45 pts) > FAC (7.14 pts) P = 0.02 |
| Didehdar Ardebil et al. (60) | QoL | Cross sectional descriptive | BC | 60 | 43.81 ± 47.12 | Health-related QoL/FACT-B Persian Version | Depression symptoms found in 50% of subjects; significant correlation between depression and overall HRQoL (β = -17.77, P < 0.001); significant dif. Observed between different modalities of treatments: chemotherapy > radiotherapy, P = 0.006 |
| Hatam et al. (61) | QoL | Prospective cohort | BC | 100 | 48.49 ± 10.63 | Health-related QoL/QLQ-C30 | Decrease in HRQoL due to chemo with TAC > FAC, P < 0.001 |
| Musarezaie et al. (62) | QoL | Cross sectional | BC | 330 | 43.2 ± 5.8 | QoL/SF-36 version 2 | QoL is inversely correlated with the No. of chemo sessions, P < 0.05 and education level (P = 0.002) |
| Tirgari et al. (58) | QoL | Descriptive | Mastectomised BC | 50 | 47.3 ± 8.62 | 1-mood states/ the profile of mood states 2-quality of life/ FPQLI | Participants had low mood state and QoL. The mood state was a predictor of participants’QoL (R2 = 0.67; P = 0.007 |
| Heidari Gorji et al. (69) | Caregiver QoL | Cross sectional, descriptive | BC caregivers | 63 | 52.48 ± 14.04 | QoL and depression/caregiver quality of life index-cancer, Beck depression inventory | Negative correlation between depression and QoL in caregivers (r = -0.67, P = 0.01) |
| Khanjari et al. (71) | Caregiver QoL | Prospective, descriptive, correlational | BC family caregivers | 115 | N/A ± N/A | QoL, sense of coherence, well-being/ the caregiver QoL INDEX-CANCER; the brief religious coping scale; the spirituality perspective scale; the sense of coherence scale | QoL improves over time (adjustment). However, ratings of sense of coherence, spirituality, and negative religious coping |
| Harirchi et al. (66) | Sexual status | Prospective | BC | 216 | 44.3 ± 8.6 | Sexual function/female sexual function index (FSFI) | Sexual dysfunction was 52% before treatment and 84% after treatment; diminished sexual functioning in BC patients; post-treatment sexual disorders were associated with younger age (OR: 0.95; 95% CI, 0.93 - 0.98; P = 0.04), receiving endocrine therapy (OR: 3.34; 95% CI, 1.37 - 7.91; P = 0.007), and poor pretreatmment sexual functioning (OR: 12.3, 95% CI, 3.93 - 39.0; P < 0.0001). |
| Safarinejad et al. (67) | Sexual status | Cross sectional | BC | 390 | 37.7 ± 6.4 | Physical function (PF)/SF36 | 57% experienced lubrication problems, 53.8% satisfaction disorders, 42.5% desire disorders, and 37% arousal disorders (all patients vs. healthy controls < 0.01). Patients receiving hormone therapy had more sexual dysfunctions (P = 0.006). RT+CT+HT was associated with a 6-fold increase in the risk of lubrication and satisfaction problems (adjusted OR: 6.4; 95% CI, 4.6 - 12.6, and adjusted OR: 5.7; 95% CI, 3.4 - 11.4) |
| Mohammadi et al. (74) | QoL-relation with lifestyle | Cross sectional | BC | 100 | 47.9 ± 6.7 | (1) QoL/QLQ-C30 BR-23, (2) eating practices/women’s healthy eating and living (WHEL), (3) physical activity/international physical activity questionnaire(IPAQ) | Healthy eating practices were significantly correlated with social (r = 0.2, P = 0.05), role (r = 0.2, P = 0.022), cognitive (r = 0.2, P < 0.01) and emotional (r = 0.2, P = 0.010) scales, global QoL (r = 0.3, P < 0.01), and reduced symptoms of financial difficulties (r = -0.2, P = 0.026). Physical activity was significantly correlated with emotional (r = 0.2, P = 0.004) and cognitive (r = 0.2, P = 0.03) scales |
| Mohammadi et al. (75) | QoL-relation with nutritional status | Cross sectional | BC | 100 | 47.8 ± 6.7 | (1) nutritional status/patient-generated subjective global assessment(PG-SGA), (2) QoL/QLQ-C30 | Significant correlations between nutritional status and QoL scales (physical: P < 0.001; emotional: P = 0.026; cognitive: P = 0.020; global QoL: P = 0.026; fatigue: P < 0.001; nausea/vomiting: p < 0.001; pain: P < 0.001; dyspnea: P < 0.001; insomnia: P < 0.001; appetite loss: P < 0.001; constipation: P < 0.001; diarrhea: P = 0.003 |
| Jafari et al. (79) | QoL-spiritual | Cross sectional | BC patientses under radiotherapy | 68 | 48 ± 10.3 | spiritual well-being/FACIT-Sp12, (2) QoL/QLQ-C30 amd QLQ-BR23 | QoL was positively correlated with spiritual well-being (P < 0.001). Spiritual well-being, pain (P < 0.001), social functioning (P < 0.001), and arm symptoms (P < 0.001) were significant predictors of QoL |
| Mashhadi et al. (57) | Depression | Prospective | Patients with cancer | 400 | 45 ± 8.5 | Depression/Beck depression inventory (BDI) | Patients with BC had a significantly higher prevalence of depression. |
| Khanjari et al. (70) | Caregiver QoL | Descriptive and prospective | BC caregivers | 88 | 41.1 ± 13.9 | QoL/the schedule for the evaluation of individual quality of life (SEIQoL-DW)- by interview ( at two times: T1: a time close to diagnosis and T2: after 6 months | Psychological impacts affect family caregivers of women with BC 6 months after the diagnosis as well as directly after the diagnosis |
| Moghaddam Tabrizi et al. (81) | Social | Predictive design | BC | 262 | 47.9 ± 11.4 | General health/health-promoting lifestyle profile II developed by Walker et al | Significant correlation between GH and health-promoting lifestyle (P < 0.05) |
| Rohani et al. (76) | QoL along with sense of coherence | Longitudinal | BC | 372 | Case: 46.1 ± 9.8, control: 46.6 ± 8.4 | (1) QoL/QLQ-C30, (2) sense of coherence (SOC), (3) spiritual perspective scale, (4) religious coping +/-/brief religious coping (brief RCOPE) | Significantly lower scores on physical and role scales, along with fatigue and financial difficulties, during the first 6 months compared with the controls. Women had better scores on QoL (P < 0.001), and emotional scale (P < 0.01) during the same period of time. SOC (P < 0.01) and baseline ratings of several dimensions of HRQoL (P < 0.05) were the most important predictors of HRQoL changes |
| Khoramirad et al. (77) | QoL-quality of sleep | Cross sectional | BC | 80 | 48 ± 6.9 | Relationship between quality of sleep and spiritual well-being, religious activities/pittsburgh sleep quality index (PSQI), spiritual well-being scale (SWBS), and religious activities (RA) questionnaire | (1) No significant correlation between global PSQI and total score on SWBS or its two subscales, (2) global PSQI score was not significantly correlated with total score of RA questionnaire (P = 0.278) |
| Heidari et al. (78) | QoL-hope | Descriptive | Mastectomised BC | 100 | N/A ± N/A | Hope/herth hope index; body esteem/body esteem scale, mental health/symptom checklist 25 (SCL 25) mental health questionnaire | Significant relationship between body esteem and hope (P < 0.001, r = 0.583) , between body esteem and mental health (P = 0.001, r = 0.472), between hope and mental health (P < 0.001, r = 0.565) |
| Saeedi-Saedi et al. (68) | Emotional distress | Cross sectional | BC | 82 | N/A ± 10.96 | Emotional distress/a standard worldwide questionnaire (NCCN) | 39% of patients had severe emotional distress, which was related to their physical functioning (P < 0.009). Taking care of children, anxiety, fear, difficulty taking bath and wearing clothes, family issues, fever, and nasal dryness were the most common issues related to emotional distress (P < 0.001) |
| Azarkish et al. (80) | Social | Cross sectional | BC | 175 | 44.3 ± 6.7 | Return to work/interview | Older patients and those with longer work experience were less likely to return to work, while patients with no pain, surgery scar, or lymphedema after the treatment were more likely to return to work |
8. Discussion
The aim of this study was presenting all of the articles that had studied Iranian BC patients and looked at outcomes related to HRQoL. In total, we found 73 studies. As studies were so varied, we divided them to 5 parts, including qualitative, instrument, lymphedema, interventional, and observational studies. Interventional and observational studies contained different structures.
8.1. Qualitative Studies
Though we present the results of the qualitative studies, the conclusions of these studies were not presented because the method for reviewing these kinds of studies is different than in quantitative studies (72). Thus, there is just a report of them. Qualitative studies were conducted on BC patients and also on their caregivers. Such different themes were extracted that a discussion on these themes is beyond the scope of this article. In these studies, different goals were followed, including general experience and perspective, religious experience, ways of coping, their needs, and the role of other factors in that experience (9-22). Only two of 14 articles were about husbands (21) and caregivers (22). Unfortunately, none of the qualitative studies have led to a quantitative guideline for future studies. Developing some native quantitative instruments for the evaluation of patients’ needs or experiences is suggested to provide applicable guidelines for the promotion of rehabilitation services.
8.2. Instruments Validation
This review introduced 5 Iranian validated questionnaires for evaluating QoL (QLQ-C30), the caregiver QoL index-cancer scale, self-assessed support needs questionnaire for breast cancer cases, mini-mental adjustment to cancer scale (Mini-MAC scale), and functional assessment of cancer therapy-breast (FACT-B) (23-27). It is possible that some instruments have been validated before this time interval or might have been published in some references that have not been included in this study. The development of more valid and reliable instruments in different aspects of cancer rehabilitation can present a more accurate measurement of problems and provide more effective interventions for solving them. Thus, it seems that introducing native and national valid instruments should be considered in future researches.
8.3. Lymphedema
Breast cancer patients often experience lymphedema, which could compromise their QoL and interfere with their daily activities (65, 73). A mean prevalence of 17.5% was reported for Iranian BC patients according to one study (28). The prevalence of BC-related lymphedema had been reported at 6% to 70%, depending on the kind of surgery (64). Despite a lot of studies about lymphedema in the world, it still has many unknown aspects (82). In Iran, lymphedema treatment started 13 years ago. During this time, only a few clinics have been involved in treatment. So, very limited research is accessible. Among 7 studies presented in this systematic review, 3 clinical trials and 4 observational studies have been published. Risk factors of lymphedema have been studied in 2013. It showed that body mass index (BMI) and the numeration of involved lymph nodes were significantly related to BC-related lymphedema incidence (33). The standard method for controlling lymphedema is CDT or complete decongestive therapy (82). CDT results have been evaluated in limited studies. Though outcomes and methods of studies reviewed were completely different, 2 studies indicated that a combined decongestive therapy and pneumatic compression pump reduce the BC-related lymphedema (29, 31). In a study, it was shown that initial lymphedema volume and duration of lymphedema were important predictive factors for edema volume reduction following decongestive therapy (32). Also, a home-based rehabilitation that contains drainage, exercise, and behavioral practice education was reported significantly effective in reducing BC-related mild lymphedema (30). Presented articles insisted on the valuable effects of CDT in controlling lymphedema. Definitely, more studies are warranted to study the epidemiology, risk factors, prognostic factors, and effective modalities for diagnosis and treatment of lymphedema in the Iranian population.
8.4. Interventional Studies
Reviewed studies revealed that educational programs could increase patients’ QoL and mental health (37, 40, 53). The results of reviewed studies were similar to other studies, which indicated self-care educational programs have an important role in promoting QoL and decreasing mental distress after a BC diagnosis (56). A self-care concept or life skill education consisted of different parts. In the reviewed studies, the details of interventions were somehow less than expected (63), so more studies with exact definitions of interventions are warranted. Finally, all 3 studies used traditional educational programs. As technology is integrating into our lives very quickly, it is suggested to conduct a technology-based educational program for BC patients, who often have difficulty to attend in individual classes. We found 3 studies in social part. In the reviewed article, all social interventions were about the effects of participation in a peer support group (39, 41, 42). One study indicated that this kind of intervention has a significant effect on all aspects of QoL (41); however, other studies reported its significant effect on vitality and mental health (39). Regarding the positive effect of this kind of interventions in improving QoL, designed clinical trials with various social interventions and distinct outcomes are necessary to give better insight into the effects of that on BC.
Studies categorized in psychological groups had used different interventions. Two studies conducted mindfulness-based interventions, and the results showed that these kinds of psychological modalities promote QoL and decrease fatigue (52, 54). Also, innovative relaxation therapies, like the Benson relaxation method, were used and claimed that these methods improved the QoL, although their effect size had not been reported clearly (43). Spiritual therapy was among the other psychological interventions for improving the QoL (45). In addition, one researcher studied the effect of Ellis’s rational emotive behavior therapy (REBT) intervention on body image outcomes. The results showed that the intervention changed body image favorably (38). Also, in another study, existential group therapy was compared with a reality group therapy, and the results revealed that existential therapy was more effective than other group therapy methods in improving body image (45). Generally, as there were huge differences in intervention types, we could not have a consensus; however, studies show that psychological interventions have an important role in enhancing QoL and body image after a BC diagnosis. Comparing their effects in controlled clinical trials can individualize the treatments and present the most effective methods in each patient.
Two studies looked at the effect of exercise intervention on BC outcomes. In one study, it was revealed that exercise could improve cardiopulmonary measures (36). Another study assessed the effect of exercise on QoL (46). The results of this study reported no significant effect of exercise on QoL. In another study, the effect of a combined exercise and ginger supplement on IL-10 and cardiopulmonary indices was compared (47). The results of the current study reveal that this combined exercise was associated with improvement in cardiopulmonary and immunity indices. According to McNeely, larger trials with a greater focus on study quality, adverse effects, and long-term benefits of exercise are needed to introduce more beneficial rehabilitation methods in BC patients (5). Some of conflicting results show that we need more studies to define proper exercise programs for BC patients and survivors in different steps of treatment.
Decreasing chemotherapy inducing nausea has been evaluated in different researches. Ginger supplements (49) and massage therapy (48) have been introduced as effective interventions for decreasing nausea in 2 studies. Only one article had studied the application of a rehabilitation program on QoL and it had resulted in a significant effect on outcome of interest (35).
8.5. Observational Studies
8.5.1. Anxiety and Depression
According to our results, 3 studies were focused on anxiety and depression as main outcomes. Vahdaninia et al. (55) evaluated anxiety and depression, using the hospital anxiety and depression scale before treatment, 3 months after initial treatment, and 1 year after the completion of treatment. According to the findings, anxiety improved over time. Hadi et al. (56) evaluated anxiety and depression, using the symptom checklist-90 revised (SCL-90R) in BC cases and control (healthy) groups. The mean score of anger subscales was significantly higher in the control group compared to cases. Younger patients had higher anger mean scores. Education and tumor size correlated significantly with anxiety. Mashhadi et al. (57) evaluated depression, using the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) in cancer patients. Findings showed a significantly higher prevalence of depression in patients with BC. According to Vahdaninia et al. (55), depression improved over time. In Hadi et al.’s study (56), depression was not significantly different between the 2 age groups, and higher depression mean scores were found among younger patients. These 3 studies used different instruments with different methods, but the common limitation was a disability to differentiate the anxiety and depression caused by cancer or other factors. We need more ecological studies to determine the anxiety and depression status in cancer patients and general population.
8.5.2. Quality of Life
The largest group of studies evaluated QoL. QLQ-C30 is the most current questionnaire to measure QoL in Iranian studies. These studies focused on patients and their caregiver’s QoL and it is relationship with various variables. Tirgari et al. (58) pointed out that a mastectomy in BC participants induced a low mood state and QoL. Safaee et al. (59) mentioned that all symptoms’ scores had a reverse association with QoL except loss of appetite and diarrhea. Pourhoseingholi et al. (64) introduced tumor grade, employment, financial status, menopausal status, and dyspnea as the major predictors of patients’ QoL. Didehdar Ardebil et al. (60) studied HRQoL, using the Persian version of FACT-B. Frequency of depression symptoms was reported in 50% of the subjects. Significant correlation was observed between depression and overall HRQoL and between different modalities of treatments. Qol of patients treated by chemotherapy was significantly better than radiotherapy. Also, Hatam et al. (61) and Kiadaliri and Bastani (63) both reported a decrease in HRQoL due to chemotherapy with TAC more than a FAC regime. Musarezaie et al. (62) mentioned that QoL is inversely correlated with the no. of chemo sessions and educational status. Mohammadi et al. (74) reported that healthy eating practices were associated with higher scores on social, role, cognitive, and emotional scales, global QoL, and reduced symptoms of financial difficulties. Also, physical activity was significantly correlated with emotional and cognitive scales. These researchers in their other papers (75) reported significant correlations between nutritional status parameters and quality of life subscales: physical, emotional, cognitive, global QoL, symptoms scales fatigue, nausea/vomiting, pain, dyspnea, insomnia, appetite loss, constipation and diarrhea. Rohani et al. (76) reported that women with BC tended to score worse on physical and role scales, along with fatigue and financial difficulties, during the first 6 months when compared with healthy women. The sense of coherence (SOC) and baseline scores on several dimensions of HRQoL were the most important predictors of HRQoL changes. Jafari et al. (79) reported a significant, positive correlation between global QoL and spiritual well-being. Exercise can be an effective strategy to improve QoL in women with BC. It seems that most of the studies observe the effect of BC and its treatment modalities on QoL fluctuations. None of them have suggested a protocol for improving the QoL during the diagnosis and treatment processes. It is not clear if measuring the QoL index is the main problem or not? Is the measurement instrument appropriate in our population? It seems that special demographic characteristics, beliefs, and behaviors of our patients should be considered in new research instruments in order to suggest more applicable and useful interventions.
According to previous studies, exercise reduces fasting insulin levels in BC survivors. This may be due to exercise-induced reductions in body weight. Practitioners and clinicians may better help BC prognosis be improved through exercise, anticipating physiological effects on cancer (8). Future research is necessary to determine optimal exercise modes and parameters (6). According to the mentioned articles’ results, patient’s QoL are affected by several factors. Therefore, we need more proportional attention to patients according their chemotherapy plan. Psychological consultation, exercise programs, nutritional advice, and educational programs may be helpful to improve patients’ QoL.
Caregivers’ QoL showed a negative correlation with depression (69). Family caregivers of BC patients are reported to be affected by psychological impacts for up to 6 months after the diagnosis (70). Caregiver’s QoL improves over time (71). Family members as main caregivers should be empowered in order to prepare strong support for cancer patients in all steps. It seems that more studies and educational programs should be designed in future research.
Khoramirad et al. (77) showed the relationship between quality of sleep with spiritual well-being and religious activities; even though it was not significant. Heidari et al. (78) reported a significant relationship between body esteem with hope and mental health. There was a positive correlation between hope and mental health too.
8.5.3. Sexual Status
Garrusi and Faezee (65) studied BC patients’ sexual status in 2008. She showed that desire was diminished in 70.6% of the women. The number of instances of coitus decreased in approximately 15% of the participants. About 30% of women reported lubrication and arousal problems, and 72% reported decreased orgasms. Sexual satisfaction did not have a significant correlation with orgasm. Harirchi et al. (66) reported pre-treatment and post-treatment sexual dysfunction rates to be 52% and 84%, respectively, indicating a significant deterioration in sexual function among BC patients. A younger age, reception of endocrine therapy, and poor sexual function at pre-treatment were the most significant contributing factors to post-treatment sexual disorders. Safarinejad et al. (67) mentioned the significant prevalence of lubrication problems, satisfaction disorder, desire disorder, and arousal disorder in BC patients compared with healthy controls. Patients receiving hormone therapy were more likely to experience sexual dysfunctions; therefore, this group of patients needed more attention and sexual therapy during and after treatment. It seems that there has been limited research in the study of frequent sexual dysfunctions in BC patients, but no intervention has been tried or suggested to solve this common problem.
8.5.4. Emotional Distress
Saeedi-Saedi et al. (68) reported that 39% of the BC patients had severe emotional distress, which was significantly associated with lower functional status. Taking care of children, anxiety, fear, difficulty taking bath and wearing clothes, family issues, fever, and nasal dryness were the most common contributors to emotional distress. Designing some longitudinal research or clinical trials to evaluate important interventions to manage these unpleasant symptoms is necessary. Yoga practice has been shown to improve health and helps alleviate some treatment-related side effects in BC survivors (7).
8.5.5. Complementary Medicine
Montazeri et al. reported a significant association between depression and the use of complementary medicine (72). The use of complementary medicine among Iranian patients is not common; however, it is correlated with fear, anxiety, and mental distress (73). Leggett et al. reported evidence of different qualities to support that Guarana and Ganoderma lucidum may improve fatigue, while glutamine may be effective in improving oral mucositis symptoms. Overall, current evidence does not provide definitive recommendations regarding the effectiveness of complementary or alternative medicine in women with BC (83). Considering that there is a lack of effective chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy interventions, natural products and complementary therapies merit further investigation (84). We need more trials to approve the effectiveness of complementary medicine in the Iranian population.
8.5.6. Social
Azarkish et al. (80) mentioned that older patients and those with longer work experience were less likely to return to work, while women with no pain, surgery scar, or lymphedema after the BC treatment were more likely to return to work. Moghaddam Tabrizi et al. reported a significant relationship between general health and a health-promoting lifestyle (81). “Return to life” is an important goal in BC patients, which has not been studied in Iranian research. Fortunately, at present in Iran, most of the diagnosis and treatment modalities are accessible. It can lead to early diagnosis and higher survival in these patients; so, the frequency of survivors is increasing. Designing some projects to define a useful protocol to provide a high QoL for these survivors and a return to familial and social roles may be an important health priority.
To our knowledge, it is the first study that attempted to look at all of the different aspects of BC in Iran. The result of that study could help to draw a better framework to promote QoL of BC patients. Also, this study has some limitations. As our goal was gathering all of the studies done in Iran, some Iranian databases were searched. Despite their great contents, their search engines were somehow weak. Finally, numerous studies were selected and, then, divided into 4 parts. So, we have to discuss all QoL and rehabilitation-related studies in one article, although distinct designs were used by the included studies.
9. Conclusions
Several main problems have been demonstrated in Iranian studies about BC patients’ rehabilitation. Most of them consist of the prevalence of physical, psychological, functional, and spiritual problems of BC survivors and their caregivers. More interventional trials in the fields of social aspects, emotional distress, complementary medicine, psychological and family consultations, exercise programs, nutritional plans and educational programs are necessary. Designing a mega project to offer a palliative rehabilitation service package according to the need of Iranian patients may be a priority in their health care system.