1. Background
Hypertension (HTN) continues to be a significant global health crisis. In developed nations such as Canada, South Korea, and Germany, the prevalence of HTN has declined due to effective treatment strategies aligned with clinical guidelines. Conversely, developing countries are witnessing an upward trend in HTN prevalence (1). According to a meta-analysis covering studies conducted from 1990 to 2020 across Asia and Africa—primarily involving participants from China and India—the prevalence of HTN was observed to be 27.7% in rural areas and 30.5% in urban centers (2). A review by Oori et al. estimated that the prevalence of HTN among Iranian adults is approximately 25%, with rates rising to 42% among the elderly population (3).
Hypertension is a leading risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD), strokes, and chronic kidney disease (4). Research demonstrates that a 10 mmHg reduction in systolic blood pressure (SBP) or a 5 mmHg reduction in diastolic blood pressure (DBP) is associated with significantly lower rates of major cardiovascular events (5). Effective management of HTN is achievable with timely and appropriate treatment (6).
Various classes of medications are available for HTN management. Many patients require multiple drugs to achieve adequate blood pressure control. Recently, single-pill combinations (SPCs) that integrate two or three antihypertensive agents into a single tablet have emerged as a practical approach (7). Research indicates that using combination therapies at intermediate doses achieves better blood pressure control compared to monotherapy at higher doses. Additionally, SPCs are associated with improved medication adherence, fewer side effects, and reduced organ damage (8). A variety of SPCs combining different antihypertensive categories—such as ACE inhibitors (ACEi), angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), calcium channel blockers (CCBs), beta-blockers (BBs), and diuretics—are available in different doses. Studies suggest that patients generally prefer SPCs due to enhanced adherence and reduced adverse effects (9, 10).
Despite the potential benefits of SPCs, their adoption in clinical practice faces several challenges. Factors affecting the prevalence and effectiveness of SPC treatments in Iranian populations include limited availability and variety of SPCs, high costs and lack of accessibility, insufficient familiarity among healthcare providers, and low awareness of their benefits among patients.
2. Objectives
The objective of this study is to analyze the types of antihypertensive treatments used and to assess the prevalence of SPCs within an Iranian population, focusing on variations and patterns in treatment strategies.
3. Patients and Methods
3.1. Setting
The statistical population of this research included all eligible hypertensive patients who visited the research clinics during the study period in Birjand (Sought Khorasan-Iran). The study adhered to ethical principles, with approval granted by the Ethics Committee of Birjand University of Medical Sciences. The approval code is IR.BUMS.REC.1401.330.
3.2. Study Design
This cross-sectional and prospective study was conducted on patients diagnosed with HTN for at least six months and undergoing treatment in Birjand, located in the east of Iran. The study took place between December 2022 and September 2023. Participants were recruited from health centers supervised by general practitioners (GPs) as well as cardiology and internal medicine clinics in university hospitals.
Eligible patients provided informed consent before participating in the study.
3.2.1. Inclusion Criteria
Adults aged 18 years or older diagnosed with HTN and currently receiving antihypertensive treatment (monotherapy or combination therapy).
3.2.2. Exclusion Criteria
Patients with HTN caused by secondary factors, individuals with significant comorbid conditions (e.g., severe heart failure or terminal illness) that could interfere with treatment adherence or confound the results, and patients with cognitive impairments.
3.3. Data Collection
A structured checklist was used to collect comprehensive data, including demographic information (age, gender, educational background, and urban/rural residence), comorbidities (presence of other chronic conditions such as diabetes mellitus, CVDs, and obesity), and details of antihypertensive medications (type and dosage). Physical measurements, such as blood pressure, height, and weight, were taken according to standard protocols. The antihypertensive medications were categorized into the following groups: Monotherapy (use of a single antihypertensive drug), combination therapy (administration of at least two antihypertensive medications from different drug classes separately), SPC therapy (use of a single-pill combination containing at least two antihypertensive agents), and SPC with other drugs (combination of single-pill therapy with at least one additional antihypertensive medication provided separately).
3.4. Statistical Analysis
Data analysis was performed using SPSS software version 22.0. Chi-square tests and Fisher's exact tests were utilized to identify significant associations between categorical variables. A P-value of ≤ 0.05 was considered statistically significant, ensuring the robustness of the findings.
4. Results
Between November 2022 and September 2023, a total of 1,208 patients with known HTN were assessed in this study. The patients were categorized into four medical therapy groups: Monotherapy, combination therapy, SPC therapy, and a combination of single-pill and other drugs.
The majority of the patients (89%) were on monotherapy, while only 11% utilized SPC therapy. The mean age of the patients was 62.69 ± 10.38 years; 66% were women, and 80% resided in urban areas.
Table 1 summarizes the comparison of demographic information, comorbidities, and prescribing physician characteristics across different HTN treatment groups. The use of SPC therapy was significantly associated with certain demographics, including urban residency, higher education levels, and obesity. The most prevalent comorbidities among the patients were diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia. Patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) and heart failure (HF) were more likely to be prescribed combination therapies rather than monotherapy. General practitioners prescribed monotherapy more frequently, whereas cardiologists and internists were more involved in prescribing combination therapies.
| Variables | Monotherapy (N = 669) | Combination Therapy (N = 325) | SPC Therapy (N = 133) | Other Drug +SPC (N = 81) | Total (N = 1208) | P-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y) | 62.10 ± 9.90 | 64.70 ± 11.32 | 60.94 ± 10.26 | 62.10 ± 9.43 | 62.69 ± 10.38 | 0.01 a |
| Gender | 0.50 | |||||
| Male | 264 (39.5) | 111 (34.0) | 53 (39.8) | 30 (37.0) | 462 (37.9) | |
| Female | 404 (60.5) | 215 (66.0) | 80 (60.2) | 51 (63.0) | 758 (62.1) | |
| Place of residence | < 0.001 a | |||||
| Urban | 583 (87.7) | 261 (80.6) | 126 (94.7) | 74 (94.9) | 1054 (86.6) | |
| Rural | 82 (12.3) | 63 (19.4) | 7 (5.3) | 4 (5.1) | 158 (13.4) | |
| Education | < 0.001 a | |||||
| Illiterate | 54 (40.6) | 262 (39.4) | 128 (39.5) | 36 (45.0) | 228 (18.7) | |
| Elementary | 71 (53.4) | 284 (42.7) | 105 (32.4) | 38 (47.5) | 486 (40.0) | |
| College | 8 (0.7) | 119 (17.9) | 91 (28.1) | 6 (7.5) | 500 (41.3) | |
| Occupation | < 0.001 a | |||||
| Unemployed | 6 (0.9) | 11 (3.4) | 3 (2.3) | 1 (1.2) | 21 (1.7) | |
| Clerk | 49 (7.4) | 27 (8.3) | 10 (7.5) | 7 (8.6) | 93 (7.7) | |
| Housekeeper | 308 (46.5) | 174 (53.7) | 52 (39.1) | 33 (40.7) | 575 (47.4) | |
| Retired | 227 (34.7) | 90 (27.8) | 58 (43.6) | 33 (40.7) | 411 (33.9) | |
| Self-employment | 73 (11.0) | 11 (3.4) | 10 (7.5) | 7 (8.6) | 113 (9.3) | |
| BMI | 27.19 ± 4.52 | 27.27 ± 4.41 | 27.92 ± 4.39 | 29.30 ± 5.70 | 27.46 ± 4.61 | 0.008 a |
| Comorbidities | ||||||
| DM | 224 (52.7) | 124 (29.2) | 45 (10.6) | 31 (7.3) | 425 (34.8) | 0.11 |
| DLP | 146 (53.9) | 77 (28.4) | 29 (21.8) | 14 (17.3) | 271 (22.2) | 0.38 |
| CAD | 59 (39.1) | 66 (43.7) | 10 (6.6) | 15 (9.9) | 151 (12.4) | < 0.001 a |
| CHF | 7 (17.5) | 31 (77.5) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (5.0) | 40 (3.3) | 0.05 a |
| CVA | 8 (36.4) | 11 (50.0) | 1 (4.5) | 2 (9.1) | 2 (1.8) | 0.12 |
| CKD | 9 (39.1) | 11 (47.8) | 1 (4.3) | 2 (8.7) | 28 (2.3) | 0.17 |
| BPH | 8 (72.7) | 2 (18.2) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (9.1) | 11 (0.9) | 0.57 |
| Prescribing physician | < 0.001 a | |||||
| General practitioner | 284 (66.3) | 93 (21.7) | 37 (8.6) | 14 (3.2) | 428 (35.4) | |
| Cardiologist | 179 (44.1) | 130 (32.1) | 54 (13.3) | 42 (10.3) | 405 (33.5) | |
| Internist | 205 (54.7) | 103 (27.4) | 42 (11.2) | 25 (6.6) | 375 (31.1) |
Abbreviations: BMI, Body Mass Index; DM, diabetes mellitus; DLP, dyslipidemia; CAD, coronary artery disease; CHF, congestive heart failure; CVA, cerebrovascular accident; CKD, chronic kidney disease; BPH, benign prostatic hyperplasia.
a Statistically significant (P ≤ 0.05).
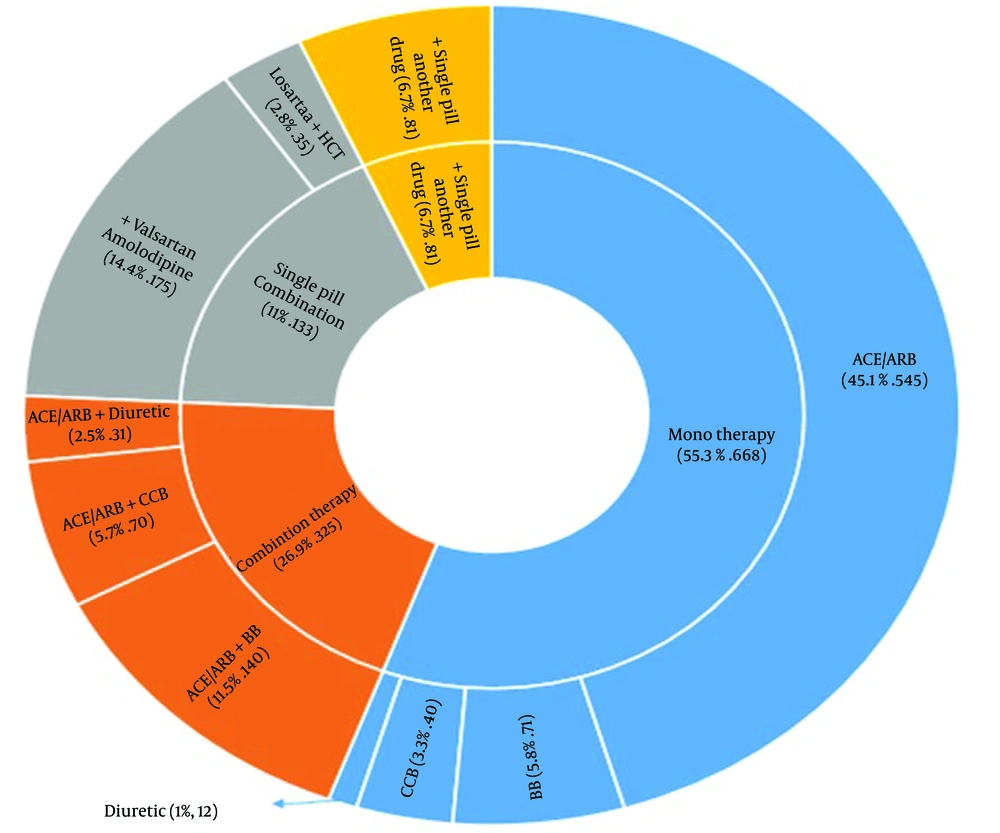
In Figure 1, the commonly used drugs among our patients are displayed. As shown, 55.3% of the patients used monotherapy for HTN treatment, with the most common drug class being ACEi or ARBs. Additionally, 26.9% of patients were on two or more drugs separately, with the most frequent combination being ACEi/ARB + BB. Only 11% of patients were on SPC therapy, with the most common SPC observed being Valsartan/Amlodipine (ARB + CCB). Furthermore, 6.70% of patients were taking an SPC alongside another antihypertensive drug.
Table 2 presents antihypertensive drug prescriptions by physician type. General practitioners prescribed significantly more monotherapy compared to internists and cardiologists (P < 0.001). There was a notable variation in prescribing patterns, with combination therapy being favored by specialists, particularly cardiologists (P < 0.001). General practitioners prescribed the fewest SPCs, whereas cardiologists were the most frequent prescribers (P < 0.001). The most commonly prescribed SPC across all physician types was ARB + CCB. Another notable SPC was the combination of ARB + diuretic, specifically losartan + thiazide.
| Drug Type | Cardiologists | Internist | General Practitioner | P-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monotherapy | 179 | 205 | 284 | < 0.001 a |
| ACE/ARB only (n = 545) | 132 | 171 | 242 | < 0.001 a |
| BB only (n = 71) | 32 | 15 | 24 | 0.007 a |
| CCB only (n = 40) | 12 | 12 | 16 | 0.81 |
| Diuretic only (n = 12) | 3 | 7 | 2 | 0.10 |
| Combination therapy | 130 | 103 | 93 | < 0.001 a |
| ACE/ARB + CCB (n = 7O) | 13 | 26 | 31 | 0.02 a |
| ACE/ARB + BB (n = 140) | 63 | 41 | 36 | 0.005 a |
| ACE/ARB + diuretic (n = 31) | 16 | 7 | 9 | 0.09 |
| ACE/ARB + CCB + BB + diuretic (n = 12) | 3 | 6 | 2 | 0.10 |
| SPC | 54 | 42 | 37 | < 0.001 a |
| SPC (ARB/CCB) (n = 178) | 83 | 60 | 35 | < 0.001 a |
| SPC (ARB/ diuretic) (n = 36) | 13 | 7 | 16 | 0.51 |
| Other drug + single pill (n = 81) | 42 | 25 | 14 | < 0.001 a |
Abbreviations: ACEi, ACE inhibitors; ARB, angiotensin receptor blockers; BB, beta-blocker; CCB, calcium channel blocker.
a Statistically significant.
5. Discussion
The findings of our study align closely with previous research on antihypertensive treatment patterns among patients. Specifically, we found that the majority of the 1,208 hypertensive patients utilized monotherapy, while only 11% were prescribed SPC therapy. This low utilization of SPC is consistent with findings from various studies conducted in other regions (11-13). For example, in a study by Czech et al. in Poland, 87.2% of hypertensive patients were on monotherapy or combination therapy, while only 12.8% used SPC for blood pressure management (11). Similarly, a study in the United States reported that 74.2% of hypertensive individuals were prescribed monotherapy, with just 8.6% utilizing SPC therapy (12). Additionally, research by Rea et al. in Italy found that 85% of patients were treated with monotherapy, while 15% were on SPC (13). These findings reflect a broader trend in HTN management, where reliance on monotherapy remains predominant and SPC usage is relatively low across diverse populations.
In our study, we observed that the utilization of SPC therapy was notably higher among urban residents and individuals with higher education levels. This finding aligns with existing literature highlighting disparities in medication adherence and treatment access between urban and rural populations (14, 15). For instance, a study conducted in Myanmar involving 1,200 hypertensive patients aged over 60 found that regular medication consumption was significantly lower in rural areas compared to urban counterparts (14). Similarly, research in a Chinese cohort of 2,115 hypertensive patients indicated that urban residents exhibited higher rates of regular medication use. This trend suggests that urban populations may have better access to healthcare services and medications, leading to improved adherence to prescribed treatments (15).
To address inequalities in treatment access for rural populations, it has been suggested that enhancing the availability of medications through innovative approaches, such as electronic and online consultations, could be beneficial (15). Rural patients often face barriers such as limited access to healthcare providers and specialized medical visits. As a result, they are anticipated to have lower usage rates of newer therapies, particularly SPCs, which may require greater health system infrastructure to support their implementation.
Moreover, the link between health literacy and medication adherence is well-established, demonstrating that individuals with higher levels of education are more likely to understand the importance of effectively managing their condition. Educated hypertensive patients may have a greater awareness of the significance of proper blood pressure control and the efficacy of their medications, which can lead to higher rates of SPC usage and overall adherence (16).
In our study, we observed that the utilization of SPC therapy was particularly prevalent among patients with obesity, CAD, and congestive heart failure (CHF). This finding is consistent with the observations of Lauder et al., who recently discussed the complexities of managing HTN in patients with CVDs (17). The treatment of HTN in these conditions often requires tailored pharmacotherapy due to the distinct pathophysiological mechanisms involved. For instance, patients with CAD may benefit from a combination of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or ARBs alongside BBs or CCB to manage both blood pressure and the associated cardiovascular risks effectively.
In the case of patients with CHF, the pharmacological regimen is even more complex, typically involving angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitors (ARNi), ACEi or ARBs, BB, diuretics, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRA), and, increasingly, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i). Lauder et al. emphasize the importance of using single-pill formulations in such instances, as they can simplify adherence to complex medication regimens and improve overall management outcomes (17).
Obesity is a key component of metabolic syndrome, profoundly influencing HTN. In a review article by Stanciu et al., treatment strategies for HTN in the context of metabolic syndrome are thoroughly examined. The authors identify various factors contributing to HTN within this syndrome, including insulin resistance, inflammatory processes, and alterations in sympathetic nervous system activity. Given this multifactorial pathogenesis, effective pharmacological approaches are critical for obese hypertensive patients (18). Stanciu et al. emphasize that managing HTN in obese individuals often requires combination therapy, particularly at low doses, to achieve optimal blood pressure control. Single-pill combinations are strongly preferred, as they not only enhance adherence but also simplify medication regimens that might otherwise be complex and burdensome for patients (18).
The collective evidence from the literature (17, 18) and our findings underscores the critical role of combination therapies, particularly SPCs, in managing HTN among patients with complex health profiles, such as those with metabolic syndrome, CAD, and CHF. This highlights the importance of implementing these treatment strategies to improve adherence and achieve better clinical outcomes in these populations.
In our study, GPs predominantly prescribed monotherapy, particularly ARBs such as losartan. In contrast, cardiologists and internists were more likely to prescribe combination therapies, with a notable preference for SPCs. These observations align with the findings of Mills et al., who reviewed the impact of various healthcare providers on blood pressure management. Their work suggests that pharmacists and community health workers often achieve better blood pressure control than general doctors and nurses (19), highlighting the varying expertise and approaches that different practitioners bring to HTN management.
Further context is provided by a study by Luo et al. on treatment outcomes among 305,624 hypertensive patients across different hospitals in China from 2019 to 2021 (20). The study found a predominant use of monotherapy in general hospitals, with CCBs being the most commonly prescribed (50%), followed by ARBs (20%). Notably, an increasing trend in combination therapy was observed, rising from 58.8% in 2019 to 64.1% in 2021. Higher rates of combined drug prescriptions were associated with patients who had greater educational attainment and multiple comorbidities (20). These findings are consistent with our results, which indicate a preference for monotherapy among GPs and a shift towards more comprehensive management strategies, including SPCs, by specialists such as cardiologists and internists.
In our study, SPCs were limited to two-drug formulations, specifically ARB + CCB or ARB + diuretic. This contrasts with trends observed in other countries, where SPCs often include more diverse combinations of two, three, or even four different antihypertensive agents. For example, research conducted in Poland highlighted a wide range of SPC options, including ARB/ACE + CCB, ARB/ACE + BB, and ARB/ACE + BB + CCB (7, 21). The variability in SPC combinations is likely due to differences in medication accessibility and formulations tailored to local healthcare needs.
Regarding specific medications, while potent ARBs such as azilsartan, telmisartan, and irbesartan are widely used internationally, the most common ARBs prescribed in Iran include valsartan, losartan, and, more recently, telmisartan for SPC formulations. Similarly, within the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACE-I) class, lisinopril and ramipril are preferred globally, whereas captopril and enalapril are more frequently prescribed in Iran.
Among CCBs, amlodipine remains the drug of choice in Iran, consistent with global practices. For diuretics, hydrochlorothiazide is commonly used both in Iran and internationally. A study conducted in Germany compared SPCs with multiple combination therapies at equivalent dosages and found that popular SPCs included valsartan/amlodipine/HCTZ and ramipril/amlodipine, formulations that are not commonly available in Iran (22).
Several barriers may contribute to the low usage of SPCs among hypertensive patients in Iran. Cultural barriers include a lack of awareness or misunderstanding about HTN, fear of long-term dependence on medications or potential side effects, and a preference for traditional remedies over modern drugs, which can lead to non-adherence to prescribed SPCs. Economic barriers involve the high cost of SPCs compared to generic monotherapy options and inadequate insurance coverage, making SPCs less accessible to patients with limited financial resources. Systemic barriers include the limited availability of SPCs, insufficient familiarity or training among healthcare providers—particularly GPs—and the absence of clear clinical guidelines promoting SPC use for HTN management.
Addressing these multifaceted barriers can enable stakeholders to develop effective strategies to increase awareness and utilization of SPCs among hypertensive patients in Iran. Ultimately, this would improve treatment adherence and health outcomes (23-25).
5.1. Limitations
This study has several potential limitations. The cross-sectional design restricts the ability to establish causal relationships between the use of SPCs and patient outcomes. Consequently, changes in medication adherence and health status over time could not be assessed. Additionally, the study was conducted in a specific region (Birjand, the east of Iran), which may not be representative of the entire Iranian population. This geographical limitation could impact the generalizability of the findings to other regions with different demographics or healthcare practices. Furthermore, the study focuses exclusively on prescribing patterns and does not evaluate clinical outcomes or the effectiveness of the treatments prescribed, potentially overlooking the broader impact of medication choices on patient health.
5.2. Conclusions
In our study, the usage of SPCs among hypertensive patients was notably low. The findings indicate that SPC therapy was more common among hypertensive individuals with higher educational attainment, obesity, and multiple comorbidities. Conversely, GPs predominantly prescribed monotherapy, reflecting a preference for simpler treatment regimens. Additionally, the available SPC formulations were limited to combinations of ARB + CCB and ARB + diuretic.
To address these gaps and enhance HTN management, several recommendations can be proposed. First, implementing community-based training programs to increase health literacy is crucial. By improving public understanding of HTN and the importance of effective control measures, patients will be more empowered to manage their condition and adhere to prescribed treatments. Second, healthcare providers, particularly GPs, should engage in regular and continuous training programs to stay informed about the latest clinical guidelines and treatment innovations. Such initiatives can help address therapeutic inertia and encourage the adoption of evidence-based interventions, including SPCs.
Finally, there is an urgent need for pharmaceutical manufacturers to develop a wider range of SPC drugs with diverse dosages. Expanding the available options would allow healthcare providers to better tailor treatments to individual patient needs, ultimately improving the efficacy of HTN management strategies.