1. Background
Linum usitatissimum (flax), an annual herb from the genus Linum of family Linaceae, grows in Mediterranean and temperate belts. The flax seed essential oil is known as the primordial oil applied in varnishes, bio-insecticides, paints, and herbicides. It contains flavonoids, phenols, and lignins, which can influence cell growth and survival (1, 2). Linum usitatissimum Seed Essential Oil (LSEO) has individual phytochemical components containing lignans, flavonoids, and phenolic acids, which have been approved as strong radical scavenging and antibacterial agents (3).
The medicinal application of essential oils is limited due to their low bio-accessibility and water-solubility. In this regard, various types of influencer tools called drug delivery systems have been utilized to optimize therapeutic efficiency, such as nanoemulsions of nonpolar compounds like herbal essential oils (4). The 20 to 200 nm hydrophobic or hydrophilic droplets in opposite solutions encapsulating either polar or non-polar compounds are called nanoemulsions (5).
Several types of emulsification processes are available based on the amount of consumed energy in the process of droplet formulation, including low (spontaneous) and high (ultrasound-based) energy-consuming methods. The latter method provides nanoscale emulsions by consuming ~ 108 – 1010 Watt per kilogram (W.kg-1) energy (6). It is a safe, easy, fast, and cost-effective method for nano-emulsification. The smallest droplets are the best in biological applications due to their improved absorbency, stability, and solubility (7). Currently, nanoemulsions are produced by encapsulating hydrophobic essential oil in a hydrophilic-continuous phase (8, 9). These types of nanoemulsions are widely used in the pharmaceutical industry as anticancer, antioxidant, and antimicrobial agents (10, 11).
One of the most dangerous bacterial infections is caused by Staphylococcus aureus strains, especially in the skin and respiratory system (12). Different types of antibiotics, such as kanamycin, have been introduced for the treatment of such infections (13). However, several undesirable side effects have been reported for kanamycin consumption, such as ototoxic effects (14). Thus, the search for a less toxic and safe compound seems to be required.
2. Objectives
This study aimed to prepare LSEO Nanoemulsions (LSEO-NE) and characterize it using Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM), Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS), and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). Then, its antioxidant activity was evaluated, utilizing both ABTS and DPPH tests. Finally, the bactericidal activity of LSEO-NE was investigated against S. aureus.
3. Methods
3.1. Material
We obtained Linum usitatissimum seed essential oil (flaxseed oil, commercially available, Dr. Zarghani, Mashhad, Iran). Nonionic surfactant Tween 80, nutrient broth medium, kanamycin, 2,2-azino-bis-3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS), and 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) were supplied from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO). Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 12228) was purchased from the Pasteur Institute of Iran (Tehran, Iran).
3.2. LSEO-NE Preparation
The LSEO-NE was formulated by ultrasonic-based homogenizing of LSE oil and water in the presence of different volumes of nonionic surfactant Tween 80 (3, 6, and 9 mL). The hydrophilic–hydrophobic balance for Tween 80 has been defined at 15. The sonication process was done under 20 kHz frequency and 750 Watt power for 60 min (15, 16).
3.3. LSEO-NE Characterization
The LSEO-NE mean hydrodynamic size (Z-average) was analyzed in three different conditions of surfactant volume (3, 6, and 39 mL), and approved by high-resolution AFM for the smallest LSEO-NE droplets, formed in the presence of 9 mL surfactant. Moreover, the droplets’ morphology was studied by Field Emission Electron Microscopy (FESM) according to the Sun et al. methodology. Briefly, a thin layer of LSEO-NE solution was made by dropping and drying on the microscope slide (gold-coated glass). The prepared slide was used for microscopic studies (17).
3.4. ABTS and DPPH Antioxidant Tests
The ability of LSEO-NE in scavenging oxidants and free radicals was measured by two different antioxidant agents, including ABTS and DPPH, based on measuring the absorbance ratio of ABTS and DPPH free radicals against the LSEO-NE nanoemulsion by UV-vis absorption spectroscopy. Briefly, following the Li et al. methodology, ABTS was detected at 734 nm before and after mixing with LSEO-NE, and according to Kedare et al., DPPH was measured at 517 nm (18, 19). The antioxidant activity (AA%) of LSEO-NE was estimated using the following formula:
In the formula, SA and CA refer to sample absorbance and control absorbance, respectively.
3.5. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing (AST)
The bactericidal activity of LSEO-NE was investigated using the protocol as follows. First, S. aureus ATCC 12228 was inoculated on Mueller-Hinton agar by performing a carpet culture technique. Then, antibiogram discs, including kanamycin, LSEO-NE-smeared, and null discs (6 mm diameter) were preparing and put on the inoculated-culture medium. Finally, culture was done at 37ºC for 24 hours.
3.6. Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 21 software. The one-way ANOVA test was used to check the significant results. The P values of less than 0.001 were defined as statistically significant.
4. Results
4.1. LSEO-NE Characterization
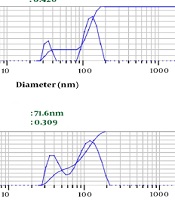
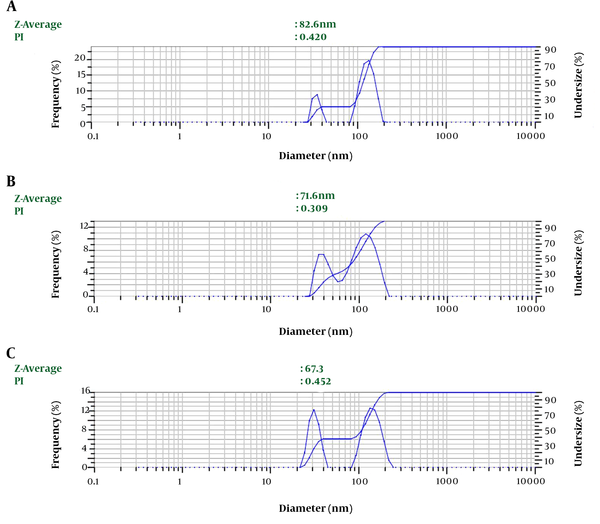
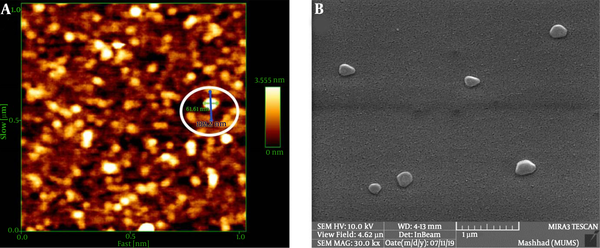
Depending on the amount of consumed surfactant, the droplets’ Z-average ranged from 67.3 nm to 82.6 nm. The results showed a significant relationship between the increasing volume of Tween 80 and decreasing nanoemulsion Z-average (P value ≤ 0.001) (Table 1 and Figure 1). We selected nanoemulsion with the smallest droplet size (67.3 nm) with appropriate PDI (0.452) for further analysis. Regarding Stetefeld et al., the values of less than 0.7 PDI indicate the mono-distribution process. Therefore, the estimated Z-average values were valid and reliable (20). However, further analyses such as AFM and SEM approved the droplet size and revealed the pseudo-spherical morphology of nanodroplets, respectively (Figure 2A and B).
The LSEO-NE size characterization. A: AFM results; the brilliant circle shows the nanoemulsion diameter (61.61 nm) (green line and number) while the blue line and the number indicate the length of the line. B: SEM image of LSEO-NE droplets; pseudo-spherical droplets are detected at the agglomerated size, which may be due to the SEM preparation process. LSEO-NE: L. usitatissimum Seed Essential Oil Nanoemulsion; AFM: Atomic Force Microscopy; SEM: Scanning Electron Microscopy.
| Surfactant Volume (mL) | Z-Average (nm) | Polydispersity Index |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 82.6 | 0.420 |
| 6 | 71.6 | 0.309 |
| 9 | 67.3 | 0.452 |
Droplet Size of LSEO-NE in Three Different Emulsification Conditions; LSEO-NE: Linum usitatissimum Seed Essential Oil Nanoemulsion.
4.2. LSEO-NE Antioxidant Activity
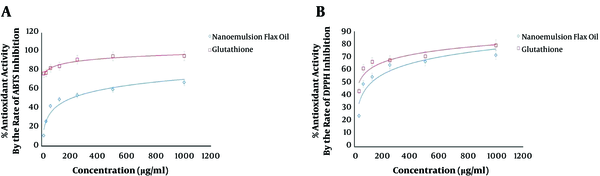
Both ABTS and DPPH tests demonstrated a significant relationship between the increasing doses of LSEO-NE and the decreasing concentrations of ABTS/DPPH free radicals, when compared to glutathione (Figure 3A and B). The estimated IC50 was about 350 µg/mL and 235 μg/mL in the ABTS and DPPH assays, respectively. The results revealed the strong antioxidant activity of LSEO-NE, which seemed to make them safe for even in-vivo applications. However, several types of in-vivo studies need to be designed to verify the toxic potential.
The LSEO-NE antioxidant activity. A: Refers to the % antioxidant activity by the rate of ABTS inhibition, and shows the IC50 of LSEO-NE (350 µg/mL) in the inhibition of ABTS free radicals. B: Refers to the % antioxidant activity by the rate of DPPH inhibition, and shows the IC50 of LSEO-NE (235 µg/mL) in the inhibition of DPPH free radicals. LSEO-NE: L. usitatissimum Seed Essential Oil Nanoemulsion.
4.3. Bactericidal Activity of LSEO-NE
The bacterial growth pattern in the presence of antibiogram discs exhibited a significant antibiotic sensitivity in bacteria around the LSEO-NE-smeared disc compared to negative and positive (kanamycin) discs (Figure 4). It was detectable regarding the presence of an inhibited growth zone around the disc (transparent ring). However, several bacterial strains and further antimicrobial tests such as the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) test is required to define the specificity and strength of its antibiotic activity.
The LSEO-NE bactericidal activity. The image exhibits cultured S. aureus bacteria on Mueller-Hinton agar medium and reveals their sensitivity to the LSEO-NE-smeared disc (A) compared to negative (B) and positive (kanamycin) (C) control antibiogram discs. LSEO-NE: L. usitatissimum Seed Essential Oil Nanoemulsion. The white arrows indicate the bactericidal zone of discs.
5. Discussion
In this study, we used L. usitatissimum essential oil (flaxseed essential oil) to prepare nanoemulsion using ultrasonication. Then, we characterized it for size and assessed its antioxidant and antibacterial efficacies. Linum usitatissimum (flax) has been widely used as an effective natural therapeutic agent for various types of disorders, such as inflammation, blood pressure, and acne (3). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study producing nanoemulsions of flaxseed essential oil for use to evaluate the antioxidant capacity and bactericidal activity against S. aureus strains. We produced nanoemulsion with pseudo-spherical droplets containing L. usitatissimum Seed Essential Oil (LSEO-NE) in 67.3 nm sizes (Figures 1 and 2) and showed their strong antioxidant activity (Figure 3). Moreover, its bactericidal property was measured by the AST method against S. aureus. The results approved the remarkable antibiotic property of LSEO-NE (Figure 4).
Staphylococcus aureus, a Gram-positive facultative anaerobic microbiota member, is often found on the skin and the upper respiratory tract. It can also act as an opportunistic pathogen in skin infections (abscesses), respiratory infections (sinusitis), and poisoned food. Staphylococcal infections are considered as common life-threatening disorders. Most pathogenic S. aureus strains are resistant to antibiotics, such as Methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MSRSA). The prescribed antibiotics such as penicillin, cephalosporin, clindamycin, vancomycin, etc. have potentially various types of side effects. Moreover, there are no vaccines for S. aureus yet to be approved (21-23). Therefore, the investigation of alternative natural and safe antibiotics is ongoing by microbiologists.
Various types of plant essential oils and extracts have been recognized as antioxidants and antibiotics such as Lavandula (Angustifolia), Thymus (Vulgaris), peppermint (Mentha), Cajuput, Cinnamon, Clove, Eucalyptus, Sage (Salvia officinalis), and L. usitatissimum (24-32). The in vivo studies have approved the antibacterial activity of L. usitatissimum nonessential oils against bacterial strains such as S. aureus, E. coli, and Streptococcus agalactiae, and they were effective in bovine mastitis treatment (32). We investigated the bactericidal activity of L. usitatissimum Seed Essential Oil (LSEO) as a nanoemulsion delivery system against S. aureus. The presence of phenols, lignin, and flavonoids has made LSEO an exclusive phytochemical complex affecting cell growth and survival (2). It has the potential to be more efficient if encapsulated with amphiphilic molecules in nanoemulsion. Two main compounds of flaxseed essential oil, including unsaturated fatty acids and lignin are responsible for antibacterial activities (33, 34). Making the essential oils in the form of nanoemulsion causes the oil constitutes to become more stable with better efficiency (35).
Nanoemulsions as suitable drug delivery systems have shown a promising horizon in medicine for prevention and/or treatment purposes because of their ability to be more absorbable and bio-compatible, which are the two main important properties required in pharmaceutical approaches (36). In this regard, depending on their contents, they have been used to deliver their contents more efficiently with fewer possible side effects as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antibacterial compounds (37-39). The eucalyptus, neem, thyme, lemongrass, and clove essential oils are among the plant essential oils used in nanoemulsion delivery systems (37, 40-44).
The lignans repository consists of the main polyphenolic compounds in L. usitatissimum, which are prominent antioxidant compounds due to their potential of free radical scavenging (45). In the current study, this was approved by decreasing ABTS and DPPH free radicals with increasing doses of LSEO-NE (Figure 3). Flavonoids, as natural antibiotics, and phenolic acids of LSEO are the main components responsible for its antibacterial activity (46, 47). Structural heterocyclic N/O, alkylamino chains, and phenyl groups can increase the flavonoids activity and make them efficient in inhibiting the bacterial DNA replication, biofilm formation, energy metabolism, and member porin function. Moreover, flavonoids can lead to a significant alteration in membrane permeability (47). In this regard, the transparent ring around LSEO-NE-smeared antibiogram discs confirmed the induction of LSEO-NE sensitivity in S. aureus, which seemed to be affected by flavonoids and phenolic acids synergistically (Figure 4). However, further complementary studies are required to clarify the bactericidal mechanisms. The antioxidant activity of LSEO-NE makes it safe for treating bacterial infections.
5.1. Conclusion
According to the results, the nanoemulsion of L. usitatissimum seed essential oil can significantly scavenge radicals and induce an inhibitory effect on the S. aureus growth and proliferation cycle. In other words, the antioxidant activity of LSEO-NE, along with its bactericidal property and bio-accessibility makes LSEO-NE a suitable and safe antibiotic. Therefore, it can be used as a safe, natural, and efficient anti-S. aureus agent. However, further in-vivo and in-vitro studies are required to evaluate the LSEO-NE bactericidal efficiency against other pathogenic S. aureus strains.