1. Introduction
Gastrointestinal symptoms including nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea, and poor appetite have been reported in up to 39% of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)-infected patients (1). These findings have been confirmed in other studies (2, 3). Recently, new evidence suggests a link between gastrointestinal symptoms and complications such as coagulopathy in COVID-19-infected patients (4-6). New studies have shown that venous and arterial thromboembolic disease may occur in COVID-19 patients due to excessive inflammation, hypoxia, and immobilization, and Diffuse Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) (7-9).
In this study, clinical features, lab tests, and CT scan findings of acute and massive aortic thrombosis were reported in a 73-year-old patient who was infected by COVID-19 and referred to the hospital with gastrointestinal symptoms.
2. Case Presentation
A 73-year-old man with a history of ischemic heart disease (IHD) was referred to the Emergent Department (ED) because of generalized abdominal pain with anorexia starting one day ago. Two weeks ago, he presented to the hospital with a complaint of fever and acute dyspnea, and after doing a chest CT scan and PCR, the diagnosis of COVID-19 was made for him. After control of his respiratory symptoms, he was discharged without any anticoagulation drug.
Initially, when he returned with abdominal pain, the hemodynamic status was stable (BP: 145/90 mm Hg and pulse rate was 95 bpm), and the patient showed symptoms of acute respiratory insufficiency (RR: 21, O2Sat: 88%). Laboratory tests showed increased C-reactive protein (110 mg/L) and severe leukocytosis (WBC count 28.2 × 1000/mm3), but prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), international normalized ratio (INR) and platelet count were within the normal limits. Blood gas analysis showed no acidosis. The patient's alanine transaminase (ALT) enzyme was excessively increased, but aspartate transaminase (AST) was within the normal range. The PCR test for COVID-19 was still positive on this admission (Table 1). Electrocardiography (ECG) was normal with sinusoidal rhythm and no evidence of atrial fibrillation (AF) rhythm. Also, echocardiography was performed, with no evidence of clot in the heart, and ejection fraction was in the normal range (50%).
| Admission (May 20, 2020) | Discharge (May 31, 2020) | |
|---|---|---|
| White blood cell count (per mm3) | 28200 | 13000 |
| Red blood cell count (per mm3) | 5.54 | 4.68 |
| Fasting blood sugar (mg/L) | 263 | 156 |
| Urea | 33 | 43 |
| Total neutrophils | 67.7 | 56.5 |
| Total lymphocytes | 27.9 | 39.7 |
| Platelet count (per mm3) | 251 | 361 |
| Hemoglobin (g/L) | 15.4 | 12.5 |
| Alanine aminotransferase (U/L) | 237 | 34 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (U/L) | 34 | 21 |
| Creatinine (μmol/L) | 0.8 | 0.7 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 110 | - |
| Na | 134 | 140 |
| K | 3.8 | 3.6 |
| Bill-direct | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Bill-indirect | 0.6 | 0.3 |
| ESR | 59 | - |
| pH | 7.52 | - |
| PaO2 | 133.4 | - |
| PaCO2 | 22.4 | - |
| HCO3 | 18.3 | - |
| Amylase | 81 | - |
| Lipase | 35 | - |
| TPI | 8/4 (nl) | - |
| Prothrombin time (PT) (s) | 14.7 | 26.5 |
| Activated partial-thromboplastin time (PTT) (s) | 26 | 39 |
| INR | 1.28 | 2.3 |
| PCR quality for COVID-19 | Positive | - |
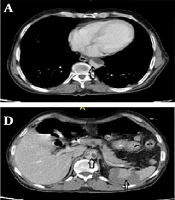
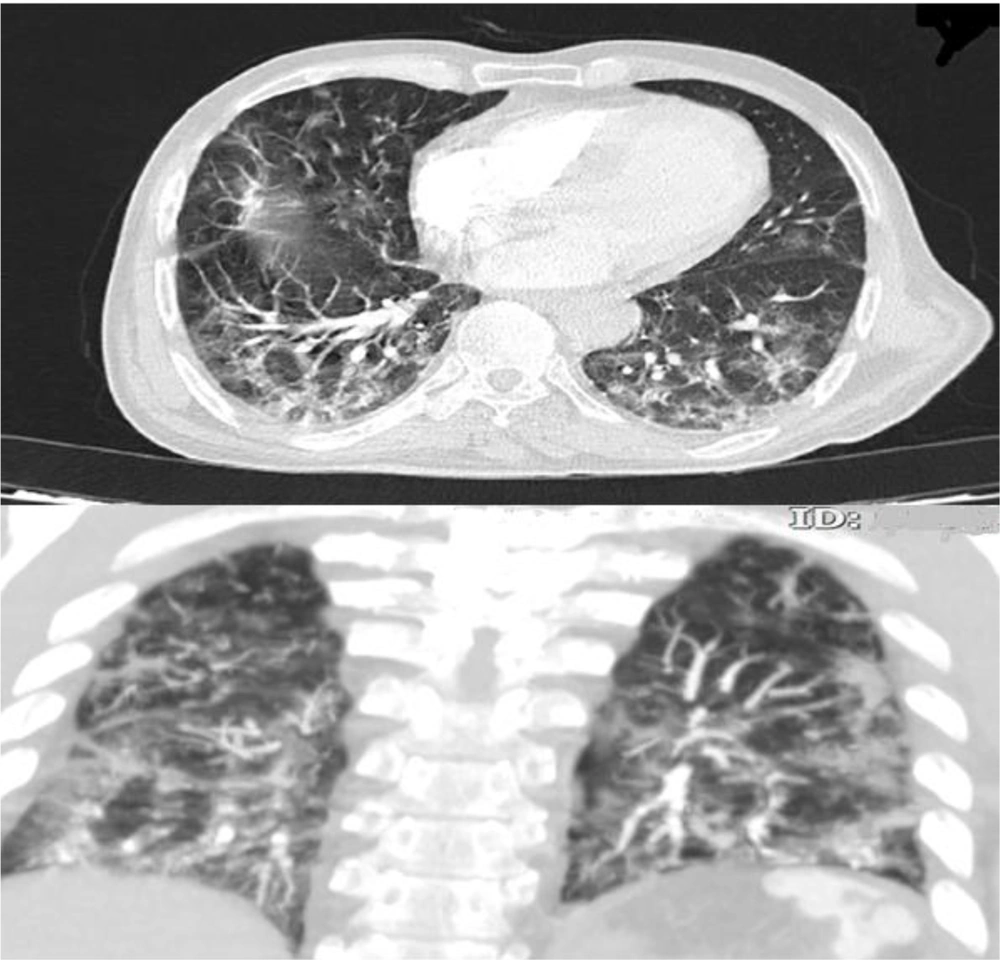
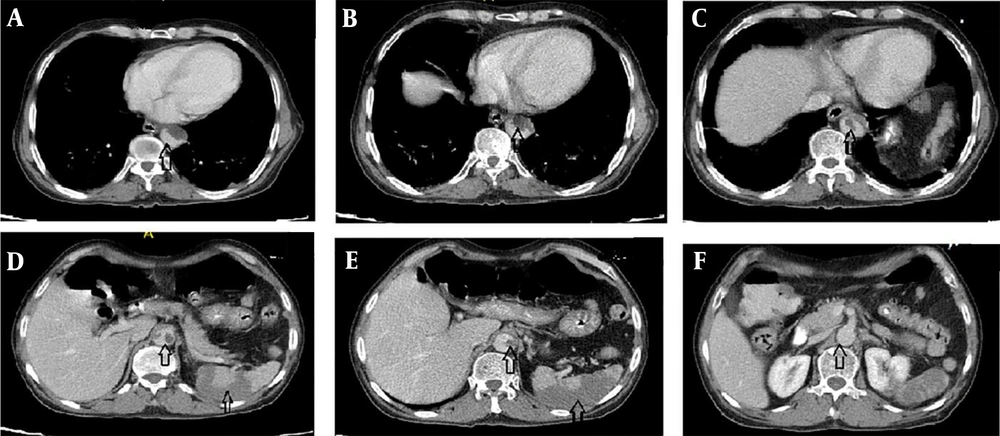
high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) was performed for him due to respiratory symptoms, which displayed typical signs of COVID-19 pneumonia (Figure 1). Due to the generalized abdominal pain, the patient underwent spiral abdominal, and pelvic CT scans with and without intravenous injection and oral contrast agent. The CT scan report showed an irregular and free-floating aortic thrombosis from the carina site to the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) detachment site (Figures 2A, B, C, and F) indicative of acute and life-threatening thrombosis because of the high possibility of systemic embolization. No sign of significant atherosclerosis was seen in the aorta. Filling defects were seen in the middle and distal part of the splenic artery, indicating embolic occlusion of the splenic artery (Figures 2D and E). Also, multiple wedge-shaped low-density areas of the spleen were evident (classic appearance of massive splenic infarct). There were evident embolic filling defects of the left renal artery and the right renal arterial branches, along with heterogeneous contrast enhancement of both kidneys with triangular parenchymal areas of lower attenuation because of renal ischemia. After doing the CT scan, the patient was admitted to the Intensive Care Unit (ICU). A vascular surgery consult was applied, which showed the patient was a candidate for conservative treatment. Based on the vascular surgeon’s opinion, surgery was not possible for him because of massive aortic thrombosis. Also, a hematologic consult was performed for the evaluation of the causes of the hyper-coagulative state. We checked tumor markers (CEA, CA19-9, and PSA), all of which were normal. Because of the patient's condition, which was in the inflammatory phase due to COVID-19 infection, hyper-coagulative state tests were not reliable, and we were recommended to do these tests after the patient's recovery. After about two weeks of conservative management with anticoagulant therapy and remission of respiratory symptoms, the patient was discharged with oral anticoagulants (warfarin 5 mg daily) and good general condition. After discharge, he did not return to the clinic for follow-up; so, we called him after two months and asked about his condition. He was in a good condition with no problem.
3. Discussion
As known, COVID-19 has misleading symptoms, and it is associated with a wide range of symptoms (10) and complications, including severe distress (11), sepsis (12), septic shock (12), and coagulopathy (8). Coagulopathy commonly happens in sepsis, and it may be a side effect of COVID-19 (13). This coagulopathy can lead to outcomes including pulmonary thromboembolism (4, 14). Ignat et al. reported small bowel ischemia because of mesenteric and portal vein thrombosis in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 (15). Similarly, Vulliamy et al. reported acute aorto-iliac mesenteric arterial thrombosis in patients infected with COVID-19 (6). Also, de Barry et al. reported arterial and venous abdominal thrombosis in a 79-year-old woman with COVID-19 pneumonia (16). The unique feature of our case was acute and massive aortic thrombosis with embolic occlusion of the splenic artery, the left renal artery, and the right renal arterial branches, which may be due to coronavirus infection and its side effects.
3.1. Conclusions
The present and previous studies show that the side effects of COVID-19 infection are arterial and venous abdominal thrombosis. Therefore, COVID-19 patients who present with gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, diarrhea, poor appetite, and abdominal pain should be paid more attention to concerning arterial and venous abdominal thrombosis.