1. Background
Toxoplasmosis, caused by a well-known intracellular parasite known as Toxoplasma gondii, is considered as one of the main infectious agents during pregnancy (1-4). Cats (Family: Felidae) serve as definitive host (1). The infection is chiefly transmitted through consumption of raw/unwashed vegetables or fruits, ingestion of raw/undercooked meat contaminated with tissue cysts, drinking water contaminated with mature oocysts, vertically from mother to the fetus, and scarcely by blood transfusion and organ transplantation (5-8).
In general, in immunocompetent persons, T. gondii infection is predominantly asymptomatic, while in immunocompromised individuals can cause life-threatening outcomes with poor prognosis (6, 9). Besides, seronegative pregnant mothers are other risk groups for acquiring T. gondii infection (5, 10). Over one-third of the human population are latently seropositive for the parasite worldwide (6, 10, 11). For instance, according to a review study by Pappas et al., the seroprevalence rate of T. gondii infection among pregnant women and those of childbearing age was reported 25.3 - 75.2%, 6.1 - 77.5%, 0.8 - 63.9%, and 8.2 - 63.2% in the Africa, Americas, Asia, and Europe continents, respectively (12). Acute T. gondii infection during pregnancy is oftentimes asymptomatic or may manifest as flu-like signs with fatigue, mild fever, and/or lymphadenopathy. Without prenatal screening programs in a specific region, acute toxoplasmosis in pregnant women will remain overlooked and left untreated (5, 13).
In numerous recent studies, the seroepidemiology of T. gondii during pregnancy period was estimated in different provinces of Iran, including 41.8% in Golestan (14), 62.6% in Mazandaran (15), 43.3% in Isfahan (16), 43.5% in Qom (17), 33.5% in Hamadan (18), 37.8% in Zanjan (19), 34.1% and 21.5% in Khuzestan (20, 21), and 14% and 30.8% in Sistan and Baluchistan (22, 23).
2. Objectives
Since there is lack of epidemiological data regarding seroprevalence rate of T. gondii infection amongst pregnant women in Khorramshahr county, this study was conducted to evaluate the seroprevalence rate of this parasite during pregnancy and its associated risk factors in this region.
3. Methods
3.1. Study Population
This cross-sectional study was performed on 88 pregnant women from Khorramshahr county, Khuzestan province (Southwest Iran). The participants were selected from patients referred to Valiasr hospital from October to December 2019. Following receiving the approval from the Ethical Committee (IR.BHN.REC.1399.007), all pregnant women voluntarily consented to be tested for the specific antibodies (immunoglobulin G (IgG)/immunoglobulin M (IgM)) of T. gondii infection. The inclusion criteria were pregnant women aged 13 - 45 years; T. gondii infection confirmed by both clinical (by an expert physician) and laboratory (positive pregnancy tests) tests, and giving a written informed consent.
3.2. Serology
In order to detect specific IgG and IgM antibodies against T. gondii infection, 5 mL of venous blood was gathered from each subject. As previously described (20, 24), the blood samples were centrifuged at 4000 rpm for five minutes and then stored at -20°C until tested. The IgG and IgM antibodies were detected via a commercially enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit based on the manufacturer's instructions.
3.3. Questionnaire
Each subject filled out a structured questionnaire containing demographic information, including age range, source of drinking water, place of residence, consumption of raw/undercooked meat, education level, contact with cat, reason for referral to hospital, and history of abortion. This questionnaire was developed and accomplished, as earlier described (20, 24, 25).
3.4. Statistical Analysis
All data were imported into the statistical package for the social sciences (SPSS) software (version 21) (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) for more analysis. For statistical analysis, we used the Pearson chi-square and Fisher’s exact tests. The P-value less than 0.05 was defined as the significance level.
4. Results
4.1. Participants
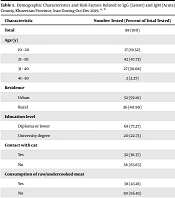
In this study, 88 pregnant women were tested for antibodies to T. gondii and filled out a questionnaire from October to December 2019. In terms of residence, 59.10% (52/88) of the subjects were from urban regions, and 40.90% (36/88) were from rural areas. In terms of education, 77.27% (68/88) had a high school diploma or lower degree, and 22.73% (20/88) had a university degree (Table 1).
| Characteristic | Number Tested (Percent of Total Tested) | IgG Positive | P - Value | IgM Positive | P - Value | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 88 (100) | 34 (38.63) | 2 (2.27) | 36 (40.90) | ||
| Age (y) | 0.642 | 0.079 | ||||
| 10 - 20 | 17 (19.32) | 7 (41.17) | 0 (0) | 7 (41.17) | ||
| 21 - 30 | 42 (47.73) | 19 (45.23) | 1 (2.38) | 20 (47.61) | ||
| 31 - 40 | 27 (30.68) | 8 (29.62) | 1 (3.70) | 9 (33.33) | ||
| 41 - 50 | 2 (2.27) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| Residence | 0.968 | 0.654 | ||||
| Urban | 52 (59.10) | 20 (38.46) | 1 (1.92) | 21 (40.38) | ||
| Rural | 36 (40.90) | 14 (38.88) | 1 (2.77) | 15 (41.66) | ||
| Education level | 0.887 | 0.595 | ||||
| Diploma or lower | 68 (77.27) | 26 (38.23) | 2 (2.94) | 28 (41.17) | ||
| University degree | 20 (22.73) | 8 (40.00) | 0 (0) | 8 (40.00) | ||
| Contact with cat | 0.098 | 0.598 | ||||
| Yes | 32 (36.37) | 16 (50.00) | 1 (3.12) | 17 (53.12) | ||
| No | 56 (63.63) | 18 (32.14) | 1 (1.78) | 19 (33.62) | ||
| Consumption of raw/undercooked meat | 0.888 | 0.68 | ||||
| Yes | 38 (43.18) | 15 (39.47) | 1 (2.63) | 16 (42.10) | ||
| No | 50 (56.82) | 19 (38.00) | 1 (2.00) | 20 (40.00) | ||
| Source of drinking water | 0.015 | 0.538 | ||||
| Purified water | 60 (68.18) | 18 (30.00) | 1 (1.66) | 19 (31.66) | ||
| Unpurified water | 28 (31.82) | 16 (57.14) | 1 (3.57) | 17 (60.71) | ||
| Reason for referral | 0.37 | 0.175 | ||||
| Routine checkup | 80 (90.90) | 30 (37.50) | 1 (1.25) | 31 (38.75) | ||
| Abortion | 8 (9.10) | 4 (50.00) | 1 (12.50) | 5 (62.50) | ||
| History of abortion | 0.267 | 0.369 | ||||
| Yes | 18 (20.45) | 9 (50.00) | 1 (5.55) | 10 (55.55) | ||
| No | 70 (79.55) | 25 (35.71) | 1 (1.42) | 26 (37.14) |
a Values are expressed as No. (%).
b P-value < 0.05 indicates a significant difference in seroprevalence between the categories within each characteristic.
4.2. Seroprevalence of Anti-Toxoplasma gondii Antibodies
The overall seroprevalence of T. gondii infection in pregnant women was 40.90% (36/88). Briefly, 38.63% (34/88) and 2.27% (2/88) of serum samples were detected positive for IgG and IgM antibodies, respectively. No positive sample was found for both IgG and IgM.
4.3. Risk Factors
Among the main risk factors associated with toxoplasmosis, a statistically significant association was found between the seroprevalence of anti-T. gondii IgG and source of drinking water (consumption of unpurified water). The other risk factors showed no significant association (Table 1).
5. Discussion
Acute toxoplasmosis in pregnant women can cause congenital toxoplasmosis. The infection may result in severe and progressive disease with high morbidity and mortality in fetuses and newborns (2, 3, 5). Based on published reports, congenital toxoplasmosis is responsible for approximately 1.2 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) annually (5, 13). According to Torgerson & Mastroiacovo (2013) (13), approximately 190,100 cases (179,300-206,300) with congenital toxoplasmosis happen each year worldwide. Moreover, the authors declared that South America along with some Middle Eastern and low-income countries, had the highest burden for congenital toxoplasmosis (13). In two separate meta-analysis papers with a global perspective, the seroprevalence rate of latent and acute toxoplasmosis during pregnancy was calculated as 33.8% and 1.1%, respectively (5, 10). In a meta-analysis published by Foroutan-Rad et al. (26), the pooled seroprevalence rate of T. gondii infection among Iranian pregnant women from 1990 to 2015 was reviewed. Based on the results, IgG and IgM antibodies were estimated at 38% and 4%, respectively, and the pooled seroprevalence was 41%. Furthermore, the seropositivity for T. gondii infection ranged from 26.6% to 77.2%, with more endemicity in Mazandaran province in northern Iran. The authors highlighted the importance of increasing knowledge about the main transmission routes of T. gondii infection among pregnant women and performing regular screening tests by an appropriate method (26). The seroprevalence rate of pregnant women in the current study was similar to the one reported by Foroutan-Rad et al. (26), and slightly higher than the rate reported by Rostami et al. (10). It is worth mentioning that the IgG seroprevalence of pregnant women drinking unpurified water was higher than those drinking purified water (57.14% vs. 30.00%; P = 0.015). This indicates that contaminated water is considered as a potential source of transmission of T. gondii infection in this region. In our previous study (Abadan county, Khuzestan province), the same results were observed among the general population (24).
5.1. Conclusions
Based on our findings, the overall seroprevalence of 40.90% (36/88) to T. gondii infection was estimated during pregnancy period in Khorramshahr county. Since the risk of acquiring acute T. gondii infection in this susceptible group is clinically significant, improved prevention and control efforts should be strictly performed. Also, the regular screening programs for T. gondii infection into the routine clinical care for pregnant women can be helpful. Finally, increased knowledge of women regarding T. gondii infection and its consequences, the main transmission routes, including source of drinking water, and the related risk factors could reduce the seroprevalence rate, especially in rural communities.