Dear Editor
Child abuse, malicious and deliberate intention of harming or killing a child, is well-documented in history and is more hideous in infants due to their disability to communicate and defend, making them more susceptible victims for such a crime.
Embedding sewing needle(s) into brain through natural openings and soft parts of the cranium has been reported for infanticide purpose (1). The relative small number of reported cases in medical literature does not match the real number of cases due to missed-detections, lack of physician referral or infant death before disclosure of respective cause (1, 2).
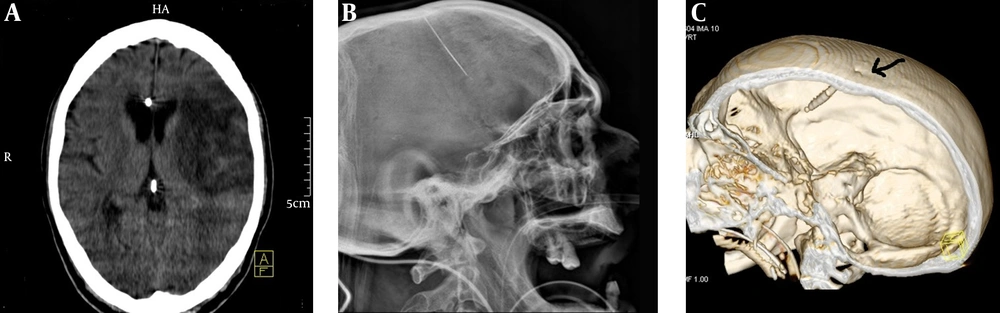
A 57-year-old man presented with symptoms of an ischemic cerebrovascular accident (CVA). Brain CT scan revealed a left middle cerebral artery territory infarct and surprisingly a metallic foreign body embedded in mid-frontal region slightly deviated to the right (Figure 1 A) that proved to be artifacts of a sewing needle on plain X-rays (Figure 1 B). The site of entry seemed to be anterior fontanel showed as a dimple on 3D CT reconstruction of the skull (Figure 1 C).
There was no record or sign of previous trauma or any surgical procedures on the scalp, skull or brain. The family denied any unusual childhood or infancy background including non-parental babysitter or stepmother. Past medical history lacked of any relevant symptoms attributable to the presence of foreign body in the brain. Finally, we came to conclusion that this was an accidental finding.
Convenient brain penetration sites for sharp small-caliber objects are non-ossified regions including fontanels, cranial sutures, ear canal and orbits during infancy (4, 5), with anterior fontanel as the most primeval and particular site due to its width and noticeability. Therefore, it was commonly used by non-medical offenders.
Proper healing and concealing make the introduction site unnoticed and if the patient survives from the acute and subacute complications, metallic object would sink deeper into brain; probably as its higher specific gravity and also impact of cerebral pulsations (6).
Metallic foreign bodies, especially iron-made needles, are usually well-tolerated in brain, as lack of air exposure and irregular iron phosphate spots on the needle play protective roles against the corrosive process (4). Thus, its size and shape will retain for decades.
The usual approaches to such patients have ranged from follow-up observations to surgical interventions with a variety of outcomes (1, 5).
Unless a definite relationship between patient’s clinical manifestations and presence of sharp object is established, intention of a surgical intervention should be either avoided or carefully weighed against the possible complications of such an approach.
A, Brain CT scan on admission confirms infarction in left middle cerebral artery territory and presence of a metallic foreign body in mid-frontal region with slight right deviation. B, Three dimensional skull CT scan showing a sharp thin object in frontal region with length of 42 mm and a dimple in frontal bone proposing the entry site of sharp object (black arrow). C, Lateral view of skull X-ray confirms the presence of a sharp thin metallic object in frontal region.