1. Context
According to a World Health Organization (WHO) report, one in four families has at least one member with a mental disorder and, by 2020, mental illnesses are estimated to make up the greatest portion of the world’s total burden of disease. Mental disorder is assessed in terms of the degree of deviation from normal behavior. The reported mortality rate among mentally ill patients is significantly higher compared to the normal population (1).
Psychological health problems encompass a wide range of different disorders. Yet, they share a common feature in that they can potentially affect the personality, mentality, and social interactions of an individual. They are also more complicated to accurately measure and diagnose, as opposed to physical illnesses (2).
Psychiatric disorders play a role in the prediction and development of medical illnesses. Research unanimously indicates that a large portion of patients with physical health issues simultaneously suffer from psychiatric disorders of one kind or another, which delays the recovery process for both conditions (3, 4). Comorbidity of medical illnesses and psychiatric disorders results in the following: increases symptom load, disrupts functioning, lower quality of life and increasing treatment costs., diminishes responsiveness to treatment, increases hospitalization period, and increases mortality rate (5-7).
“Consultation-liaison psychiatry” is a term used for the first time by Billings (8). The rapid growth of psychiatric disorders requires psychiatric consultations to be provided on a wider scale, particularly for hospitalized patients. Specifically, an early psychiatric referral can have a profound effect on the rate of recovery from other physical illnesses. In their study of the effects of prompt referral on hospitalization period, Wood et al. found that timely requests for consultation, particularly in younger patients, effectively shortened hospitalization period (9).
Several research studies have shown that only a small number of hospitalized patients seek psychiatric services, including psychiatric consultations (10). Attending to psychiatric disorders helps improve overall recovery time, which shortens the hospitalization period and, ultimately, lowers treatment costs. The relationship between psychiatric and medical illnesses is scarcely studied worldwide. Meanwhile, not a great deal of information is available on consultation-liaison psychiatry.
By virtue of its boundless nature in terms of study selection and study quality, a scoping review can prove an unchallenged approach to determining the value of new topics and expanding on their analyses. Scoping reviews can also prove useful in detecting existing gaps in the literature and helping researchers identify areas needing further investigation and consideration. With this in mind, the current scoping review carries out an inquiry on the extent of requests made for psychiatric consultations by patients admitted at general hospitals.
2. Objectives
We aim to examine the available research evidence in order to identify the knowledge gaps in the literature.
3. Methods
The present scoping review follows an established objective based on a defined title, which was designed with due respect to the sine qua nons of PRISMA guidelines (11). The structural framework is consistent with what Arksey & O’Malley introduced for the first time in January 2005, and Levac et al. further contributed to it at a later time (12, 13). The different stages of this foundation will be discussed throughout.
3.1. Question Set Up
Research questions are as follows:
- What do the academic research articles investigating psychiatric consultations suggest about general hospitals?
- Is psychiatric consultation necessary in every hospital department?
- Which wards have shown more demand for psychiatric consultation?
- What is the extent of psychiatric disorders in hospitals and which types are more prevalent?
- What are the obstacles preventing psychiatric consultation requests?
3.2. Relevant Literature Search
Literature was searched in Web of Science, Scopus, PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane (up to December 2019) databases; using English keywords, namely “psychiatric disorder”, “psychiatric”, “general”, “hospital”, “consultation liaison”, and “consultation”. The data was collected manually and examined. We did not use other sources of evidence such as expert opinion, policy documents, abstract proceeding bibliographic databases, social media platforms, or qualitative studies.
3.3. Study Selection
The collected literature was closely examined prior to selecting the related studies by means of peer review. Titles and abstracts were independently studied. Both inclusion and exclusion criteria were set in order to simplify the process. Only complete and original research articles, including descriptive and analytic studies were included. Moreover, only articles investigating the prevalence of psychiatric disorders in hospitals, as well as the extent of overall and department-based requests made in these centers for psychiatric consultations were included. Studies with an irrelevant title, repetitive topic, or defective content were excluded. In addition, different types of evidence or data sources (e.g., qualitative research, expert opinion, policy documents, and abstract proceedings) were excluded.
3.4. Data Classification
Two reviewers independently assessed the titles and abstracts of all the articles found by the abovementioned search strategy. Data was summarized within a framework of themes comprised of psychiatric consultation, prevalence of psychiatric disorders, hospital departments, diagnosis of psychiatric disorders, and nature of research prior to theoretical classification and tabulation.
4. Results
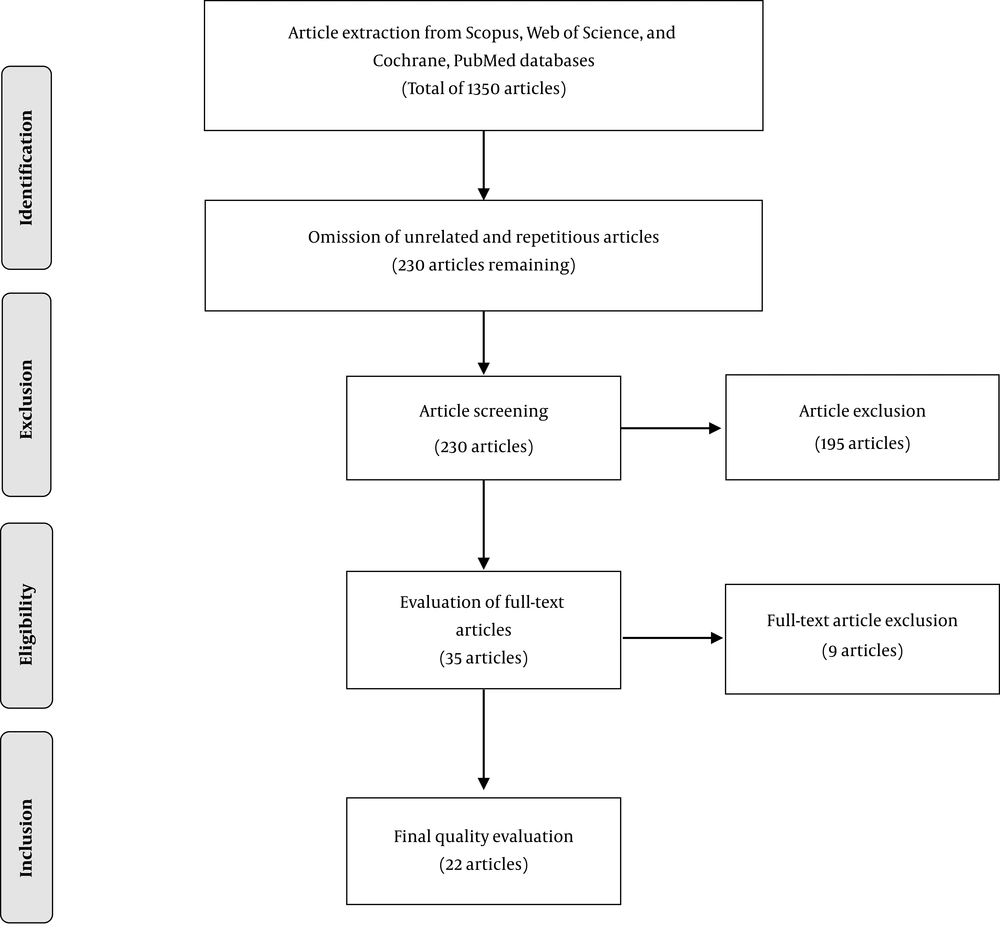
1350 studies were identified in the initial search, after screening and removing unrelated and duplicate articles, 230 articles remained. Of those, articles not written in English or with incomplete information were eliminated. The remaining 35 articles were evaluated and 9 were excluded, as they did not include information about the different wards in the hospital. Ultimately, 22 full-text articles were appraised as principal references and included in this review. The article selection process is outlined in the form of a flowchart in Figure 1.
Studies were selected from 11 countries, with the United States of America (USA) (36%), and Italy (13.6%) contributing the majority of published articles (Table 1). Age grouping was different in each study, with categories generally including “children”, “youth”, “adult”, and “elderly”. DSM-III-R and ICD-10 were the diagnostic systems most commonly used (preferred by 22.7% of the studies). Studies were conducted in general hospitals, training hospitals affiliated with medical science institutes (academic), and military hospitals. The highest sample size belonged to the Diefenbacher and Strain study conducted in the USA with 4429 samples; and the lowest sample size belonged to the Ramchandani et al. study with 50 samples (14, 15). The maximum requests for psychiatric consultations were made in Austria and Italy with 22.6% and 0.8% of cases, respectively (16, 17). The articles used in this review were from 1977 to Dec 2019 (Table 2).
| Study Information | Number of Studies | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Country | ||
| USA | 8 | 36 |
| Iran | 2 | 9 |
| Italy | 3 | 13.6 |
| Australia | 2 | 9 |
| Canada | 1 | 4.5 |
| India | 1 | 4.5 |
| China | 1 | 4.5 |
| Japan | 1 | 4.5 |
| Saudi Arabia | 1 | 4.5 |
| Israel | 1 | 4.5 |
| Ireland | 1 | 4.5 |
| Diagnostic criteria | ||
| DSM-IV-TR | 2 | 9.1 |
| DSM-IV | 3 | 13.6 |
| DSM-III-R | 4 | 18.2 |
| DSM-III | 1 | 4.5 |
| DSM-II | 2 | 9.1 |
| ICD-10 | 4 | 18.2 |
| ICD-9 | 2 | 9.1 |
| Unknown | 4 | 18.2 |
| Type of hospital | ||
| General | 11 | 50 |
| Academic | 10 | 45.5 |
| Military | 1 | 4.5 |
Comparison of Studies Investigated (by Quantity and Details)
| Author | Year | Country (City) | Study Design | Diagnostic Criteria | Type of Hospital | Sample Size | Male/Female% | Percentage of Counseling | Duration of Study (Month) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Karasu (18) | 1977 | USA (new york) | Cross-sectional | - | academic | 151 | - | 2.7 | 3 |
| Craig (19) | 1982 | USA | Cross-sectional | DSM-II | academic | 308 | - | 1.9 | 12 |
| Pérez (20) | 1983 | Canada | Cross-sectional | DSM-III | General | 255 | 39/61 | 2 | 12 |
| Malhotra (4) | 1984 | India | Cross-sectional | DSM-II | Academic | 366 | - | 2.5 | 12 |
| Hales (21) | 1986 | USA | Cross-sectional | ICD-9 | Military | 1065 | 53.4/46.6 | 5.8 | 12 |
| Sobel (22) | 1988 | Israel | Cross-sectional | - | General | 479 | 39.9/60.1 | - | 12 |
| Clarke (23) | 1995 | Australia | Cross-sectional | DSM-III-R | Academic | 165 | 35.8/64.2 | 4.2 | 12 |
| Ramchandani (15) | 1997 | USA (newyork) | Cross-sectional | DSM-III-R | Academic | 50 | - | - | 12 |
| Schofield (17) | 1986 | Ireland | Cross-sectional | ICD-9 | General | 370 | - | 1.6 | 9 |
| Gala (24) | 1999 | Italy | Cross-sectional | ICD-10 | General | 4182 | 39.9/60.1 | 0.8 | 12 |
| Wallen (25) | 1987 | USA | Cross-sectional | - | General | 2374 | 59.2/40.8 | 0.9 | 24 |
| Diefenbacher (14) | 2002 | USA | Cross-sectional | DSM-III-R | Academic | 4429 | 45.9/54.1 | 1.3 | 120 |
| Kishi (26) | 2004 | USA | Cross-sectional | DSM-IV | General | 541 | 47.3/52.7 | 1.3 | 12 |
| Bourgeois (27) | 2005 | USA (California) | Cross-sectional | DSM-IV | Academic | 901 | 52/48 | 4.2 | 12 |
| Krautgartner (3) | 2006 | Australia (Vienna) | Cross-sectional | DSM-III-R | General | 728 | - | 22.6 | 12 |
| Alhuthail (28) | 2007 | Saudi Arabia (Riyadh) | Cross-sectional | DSM-IV | General | 264 | 35.2/64.8 | - | 12 |
| Arbabi (29) | 2012 | Iran (Tehran) | Cross-sectional | DSM-IV-TR | Academic | 503 | 39.8/54.3 | 1.19 | 12 |
| Wong (30) | 2014 | China (Hong Kong) | Cross-sectional | - | General | 1392 | 36/64 | - | - |
| De Giorgio (31) | 2015 | Italy | Cross-sectional | ICD-10 | General | 1098 | 39.2/60.8 | 2.52 | 12 |
| Shiraishi (32) | 2018 | Japan | Retrospective | ICD-10 | Academic | 343 | 58/42 | 20 | 36 |
| Elyasi (33) | 2018 | Iran (Sari) | Cross-sectional | DSM-IV-TR | Academic | 1688 | 44.1/55.4 | 5.1 | 12 |
| Porcellana (34) | 2019 | Italy (Milan) | Cross-sectional | ICD-10 | General | 511 | 41.3/58.4 | 7 | - |
Psychiatric Consultation Related Studies
The frequency of requested consultations was higher for female compared to male patients (Table 2). Of the total number of studies investigated, in 10 studies, the medical wards that requested counseling, were classified separately. The request for psychiatric consultation was greater in the internal and surgical wards and lowest in the Otorhinolaryngology (ENT) ward (Table 3).
| Author | Internal Medicine | Cardiology | Neurology | Endocrinology | ENT | Surgery | OBGYN | Orthopedy | Emergency | Intensive Care Unit (ICU) | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Karasu (18) | 70 (40.4) | - | 14 (9.3) | - | 3 (2) | 25 (15.9) | 8 (5.3) | 5 (3.3) | - | - | 26 (17.2) |
| Pérez (20) | - (65) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Hales (21) | - | - | 131 (12.6) | - | - | 419 (40.3) | 26 (2.5) | - | - | - | 463 (44.5) |
| Sobel (22) | 156 (32.6) | - | 8 (1.7) | - | - | 25 (5.2) | 26 (5.4) | - | 22.8 (47.6) | - | 36 (7.5) |
| Gala (24) | 524 (12.5) | 554 (13.2) | 197 (4.7) | 282 (6.7) | - | - | - | 110 (2.6) | - | - | 2515 (60.1) |
| Krautgartner (3) | 229 (31.5) | - | - | - | - | 124 (17) | 238 (32.7) | - | - | - | 138 (18.8) |
| Alhuthail (28) | 119 (45.1) | - | - | - | - | 67 (25.3) | 56 (21.3) | - | - | 15 (5.7) | 7 (2.6) |
| Wong (30) | 587 (42) | - | - | - | - | )37 (3) | 1 (0.1) | 40 (3) | 695 (50) | 2 (0.1) | 30 (2) |
| De Giorgio (31) | - (51.3) | - | - | - | - | - (8.8) | - | - | - | - | - (30.1) |
| Elyasi (33) | 241 (14.2) | - | 240 (14.2) | - | 23 (1.3) | 140 (8.8) | 80 (5.3) | 121 (7.2) | 568 (34) | 58 (3.4) | 100 (5.9) |
Requests for Psychiatric Consultation in Different Wardsa
Table 4 notes the common reasons for requesting psychiatric consultations and the result of post-consultation diagnoses based on the facts and figures reported in all 22 studies. The diagnosed psychiatric disorders included mood disorders (e.g. depression, bipolar disorder, etc.), personality disorders, cognitive disorders (e.g. delirium, dementia, etc.), adjustment disorder, schizophrenia, and substance use disorders (e.g. drugs and alcohol use disorder, etc.) (Table 4). As illustrated, the most frequent diagnostic groups were mood and substance use disorders. Delirium and Bipolar disorder were the least frequent diagnoses (Table 4).
| Author | History of Psychiatric Disorder | Suicide | Organic Mental Disorder | Delirium | Cognitive Disorder | Anxiety Disorder | Bipolar Disorder | Mood Disoder | Substance Use Disorder | Depression | Personality Disorder | Psychotic Disorder | Brain Injury | Adjusment Disorder |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Karasu (18) | 19.2 | 13.9 | 15.9 | - | 20.5 | 4 | - | 21.2 | 11.2 | 21.2 | 9.3 | 12.6 | - | 3.3 |
| Craig (19) | 7.7 | 12 | - | - | 21.8 | - | - | 28.6 | 8.1 | 28.2 | - | 10 | 21.4 | - |
| Pérez (20) | 6.8 | - | 15.2 | - | 18.8 | - | - | 36.4 | 7.2 | 27.2 | 8 | 3.2 | 18.8 | 15.6 |
| Malhotra (4) | 3.2 | - | 16.6 | - | 19.3 | - | - | 31.3 | 1.8 | - | 0.89 | 6.8 | - | - |
| Hales (21) | - | - | 0.9 | - | 17.1 | 1.3 | - | 14.4 | 4 | - | - | 1.1 | - | 18.7 |
| Sobel (22) | 8.5 | 24.7 | - | - | 10.3 | 6.6 | 1 | 15.9 | 1.5 | 14.9 | 8.6 | 7.9 | - | 3.9 |
| Clarke (23) | 10 | 21 | - | - | 35 | - | - | 55 | 4.2 | - | 15 | - | 24 | 19 |
| Ramchandani (15) | 16 | - | 4 | - | 14 | - | - | 10 | 10 | - | 18 | 16 | - | 24 |
| Wallen (25) | - | - | - | - | 8.8 | - | 51.3 | 11.8 | - | - | 12.8 | - | - | |
| Gala (24) | 3.1 | - | - | - | 10.7 | 12.6 | - | 3.1 | 6.3 | 15.5 | - | 5.6 | - | 14.4 |
| Schofield (17) | - | - | - | - | 4 | - | - | 44 | 10.4 | - | - | 7 | - | - |
| Diefenbacher (14) | - | - | - | - | 40.1 | - | - | 29.8 | 8.5 | 28.1 | - | -- | - | - |
| Kishi (26) | 6.1 | 11.5 | 3.9 | 19.1 | - | 13.5 | 6.6 | - | 37.1 | 54.8 | 5 | - | - | 8.5 |
| Bourgeois (27) | - | - | - | 21.1 | 32 | 9 | - | 40.7 | 18.6 | - | - | 11.2 | - | 10.8 |
| Krautgartner (3) | - | - | 18.9 | - | - | 5.3 | - | 50 | 32.7 | - | 19 | - | - | - |
| Alhuthail (28) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.1 | 33.3 | - | - | - | - |
| Arbabi (29) | - | - | - | 7 | 7.6 | 8.6 | 5.8 | 43.5 | 6.1 | 23.8 | - | 2.4 | - | 9.1 |
| Wong (30) | - | - | - | 4.3 | 25 | - | 3.3 | 18 | 9 | 12.7 | 3 | 9.8 | 4 | 15 |
| De Giorgi o (31) | 14.4 | 11.2 | 11.2 | - | - | 18.9 | 13.4 | - | - | 18.2 | - | - | - | - |
| Shiraishi (32) | 5.2 | 44.6 | - | - | - | 3.8 | - | 31.4 | - | - | - | 16.3 | - | - |
| Elyasi (33) | - | - | - | 5.3 | - | 7.6 | - | 22.3 | 12.3 | - | 3.4 | 3.1 | - | 9.5 |
| Porcellana (34) | - | - | - | - | 1.4 | - | - | - | 3.8 | - | 6.8 | 6.2 | - | - |
Reasons for Psychiatric Consultation and Prevalence of Psychiatric Disorders (%)
5. Discussion
The present study was carried out to investigate the scope of psychiatric consultation demands made for patients in multiple hospital departments worldwide. Twenty-two original full-text articles were examined in the course of this scoping review. Generally, psychiatric consultation requests in hospitals are rarely studied and information on this topic is scarce. The majority of the published literature belonged to the USA and several countries did not have any publications available.
The sample size and duration of the study were highly heterogeneous in different studies. For instance, Ramchandani et al. (15) took into consideration a population of 50 individuals, while in the research conducted by Diefenbacher and Strain (14) the sample examined consisted of 4429 individuals (Table 2). Although, this may have been due to the longer duration of the Diefenbacher and Strain (14) study. Coming to a firm conclusion in the presence of such disparity was a complicated task. This concern was present throughout the review process. As the duration of studies available in the literature varied from 3 (18) to 120 months (14). However, most articles included in this review extended for 12 months (Table 2).
It is also important to note that the rate of consultation requests differed widely, from 0.8% by Gala et al. (24) to 22.6% reported by Krautgartner et al. (3) in the USA (Table 2). The strength of the Krautgartner et al.’s study was that all 728 inpatients were interviewed by research psychiatrists, using the Clinical Interview Schedule set forth in the DSM-IV-TR (3). Assessment of the need for consultation can be difficult to judge, as this important issue is based on the clinical judgment of the physician.
There is a high degree of disparity in this field of research. The different procedures used to evaluate psychiatric disorders, the disparity in the size of populations studied, duration of the study, cultural issues, stigma associated with psychiatric disorders, socioeconomic differences of communities, and the degree of importance placed on patient mental health by medical staff may contribute to differences in the literature. Nevertheless, further comparative investigation is needed based on more homogenous diagnostic criteria in order to identify the influential factors involved. Another potentially significant factor influencing the mental health of patients is age. For example, delirium is more prevalent in older patients.
Psychiatric disorders are increasing rapidly worldwide. Based on a WHO report, the prevalence is expected to reach its peak by the year 2020. According to the literature, the rate of mortality is significantly higher among populations with psychiatric disorders (1). With the high prevalence of psychological disorders in different parts of the world becoming a critical public health concern and with due attention to their detrimental consequences for patients and societies at large- psychiatric consultation, prompt diagnosis, and appropriate use of medication can prove helpful in relieving the pressure and burden from patients, their dependants, and societies (35). It is also important to highlight that psychiatric disorders are connected to medical illnesses (36).
Delay in the diagnosis and treatment of psychiatric disorders in patients with concomitant medical conditions and mental disorders,
The hospital stay is longer.
The DSM-III-R and ICD-10 were the preferred diagnostic method across the studies reviewed (Table 1). The diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM) classifies mental disorders according to their descriptions and symptoms; it serves as a guide for clinicians. However, there are both advantages and disadvantages associated with the DSM. The DSM-II was introduced in 1968 with 182 diagnoses, followed by the DSM-III in 1980 with 265 diagnoses, DSM-III-R in 1987 with 292 diagnoses, DSM-IV in 1994 with 297 diagnoses, and DSM-IV-TR in the year 2000. The latest revised DSM-5 was not used in any of the reviewed articles. A number of reviewed studies used the ICD-9 and ICD-10. Since the selected studies spanned over a wide period of time (1977 - 2019), it is not surprising to observe a large variation in the diagnostic methods.
The medical centers included in the selected research studies were restricted to general, training and military hospitals. On a departmental-basis, most requests were made for internal, surgical, emergency, and maternity departments, respectively. The least number of requests came from the endocrinology, ENT, cardiology, ICU, and orthopedic departments. Factors affecting request-related data include the variation in type and number of departments in different centers, the overall capacity of each hospital, the presence of full-time fellowship and psychiatric residents, as well as the psychiatric consultation schedule (full-time every day of the week or part-time on specific days).
Hospitalization is a stressful process that can affect the clinical condition of patients and make the situation more critical for those with psychiatric issues (37). This is where psychiatric consultations can prove tremendously helpful by improving depression and anxiety-related symptoms, particularly in patients with a longer hospital stay (38). The majority of requests in this study were from the internal department. The reason could be due to the large-scale illness variation, high patient population, and the abundance of subspecialists in the internal medicine unit. One of the main limitations of the studies reviewed was that in many instances, despite the presence of separate departments for children and the elderly, issues related to these departments were not independently considered. It is also important to note that a number of articles specifically targeted military hospitals; this is potentially problematic as the prevalence of psychiatric disorders among this group of patients is significantly different than among the general public owing to occupational features.
In the present scoping review, mood and substance use disorders made the highest count of all the disorders reported in the literature. In studies conducted by Karasu et al., Clarke et al., Grant et al., and Arbabi et al., mood disorders were more frequently reported (18, 23, 29, 39). Mood and anxiety disorders are the most common forms of mental health conditions in Canada and the world at large. It is estimated that 12.6 % of Canadians, over the age of 15, will develop mood disorders in the course of their life (40). We found that delirium was the least prevalent diagnosis in requested consultations. This may be due to the classification of delirium as a cognitive disorder in some of the studies. Cognitive disorders were the most common diagnosis after mood disorders in some studies (4, 18, 19). Before the publication of DSM-IV, delirium was categorized as an “organic mental disorder” and this could be the reason for the least diagnostic reported in the consultations prior of DSM-IV. In the Krautgartner et al.’s study (3), dementia and other organic mental illnesses formed 18.9% of consultations, and delirium was not listed separately. In some studies, only cognitive disorders were listed in their reports (14, 19, 22) (Table 4).
In conclusion, taking into account the prevalence of psychiatric disorders in patients suffering from physical illnesses, the expected referral rate was considerably low. However, this was not entirely due to poor detection. In a study considering the attitudes and practice of physicians regarding consultation-liaison (CL) psychiatry, the following were the most common reasons listed by doctors for not requesting psychiatric consultation: lack of time, forgetfulness, lack of access to a psychiatrist, and lack of belief in the need for psychiatric consultation (41). since the psychiatric disorder is associated with social stigma in most societies and mental health care in all societies is not a policy priority, it is challenging to consider the psychiatric disorders of patients admitted to general hospitals and to request psychiatric counseling. Therefore, in the future, more effort needs to be directed towards identifying the main obstacles hindering the adoption of measures that provide more care and respect for the mental health of individuals. In addition, restructuring traditional CL services and faster active liaison can provide an opportunity for better treatment services, as well as better education for students in teaching hospitals.
Psychiatric disorders are the result of complex interactions between various biological, genetic, economic, social, and psychocognitive factors (42). Investigation of the prevalence of psychiatric disorders in hospitalized patients requires extensive and accurate research, taking into consideration the factors outlined above. In the present scoping review, we have weighed the related literature in an attempt to shed light on the existing gaps and shortages that need to be addressed in the future by broader and more conclusive research.
Future investigations are recommended to consider the effectual presence of CL psychiatry, psychophysical fellowship programs, and related issues. In the studies that were reviewed in this paper, the diagnosis was carried out using a wide range of criteria that, in effect, caused significant diversity and inconsistency in the results.
6. Conclusion
The frequency of psychiatric consultation reports vary widely between countries. As we studied only English articles, this may be due to selection bias. The key points that limit definitive statistical comparison between studies are methodological differences and the use of different diagnostic criteria. Owing to the vast prevalence of psychiatric disorders and their relation with other medical conditions, future investigations are recommended. In conclusion, considering the prevalence of psychiatric disorders in patients suffering from physical illnesses, expected referral rate was considerably low.