1. Background
Chronic renal failure refers to an irreversible impairment of renal function; when the function of the kidney reaches less than 50%, and its capacity reaches less than 10 - 15%, it is considered to end-stage renal disease (ESRD) (1). According to previous studies, about 10% of the adult population in the United States suffers from chronic renal failure, and the prevalence of this disease is reported to be 20% in Iran (2).
Patients with ESRD require alternative therapies, including hemodialysis or kidney transplantation. Hemodialysis is the most common treatment for these patients, which, despite prolonging their life expectancy, causes significant psychological, social, and physical problems (3, 4). The results of many studies indicate a high prevalence of psychosocial disorders, including stress, anxiety, and depression, in these patients (5-8). About 34.5% of patients undergoing hemodialysis suffer from depression (9). In some studies, about 19 - 60% of the patients have been reported to suffer these problems (10). Moreover, 12 - 52% of these patients have anxiety (4), as the rate of hospitalization of hemodialysis patients in psychiatric wards is 1.5 to 3 times that of other chronic patients (11). Stress, anxiety, and depression are also very influential factors in the quality of life of these patients (5, 12). Physical and dietary restrictions weaken their social roles and responsibilities due to physical problems, impotence, financial burden, muscular weakness, fatigue, insomnia, sleep disorders, and frequent hospitalizations due to underlying diseases. All of these factors, along with stress, anxiety, and depression, impair the quality of life of these patients (13-15). Quality of life is a broad and multidimensional mental concept that encompasses a person's physical, mental, social, and spiritual functioning and is an understanding of the current state of his/her life according to the cultural context and value systems in which he/she lives (16, 17). Studies showed that the quality of life of hemodialysis patients who receive training, especially in the fields of physics, psychology, and social relations, was significantly better than that of untrained patients (18). Today, education is considered one of the most important dimensions of health care in order to prevent, protect, cure, and control diseases (19). One of the best strategies for promoting mental health in patients is resilience training, which allows them to better understand and respond appropriately to challenging situations (20). By improving resilience, these patients can resist and overcome the stressors, anxiety, and factors that cause many of their psychological problems (21). According to some review and meta-analysis studies, interest in resilience training programs is on the increase today (22). Numerous studies have confirmed the important role of resilience in people's health and development so that according to some studies, high resilience levels are associated with anxiety, depression, and other mental disorders and play a protective role against these factors (21).
2. Objectives
Owing to the fact that not much research has been done on the psychological interventions of these patients, including stress, anxiety, and depression, and to improve the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions in these patients. This study evaluated the effect of resilience training on stress, anxiety, depression and the quality of life in patients undergoing hemodialysis.
3. Methods
3.1. Design
This is a controlled clinical trial study with a parallel design, which was conducted in the south of Iran from October to December 2019.
3.2. Sample
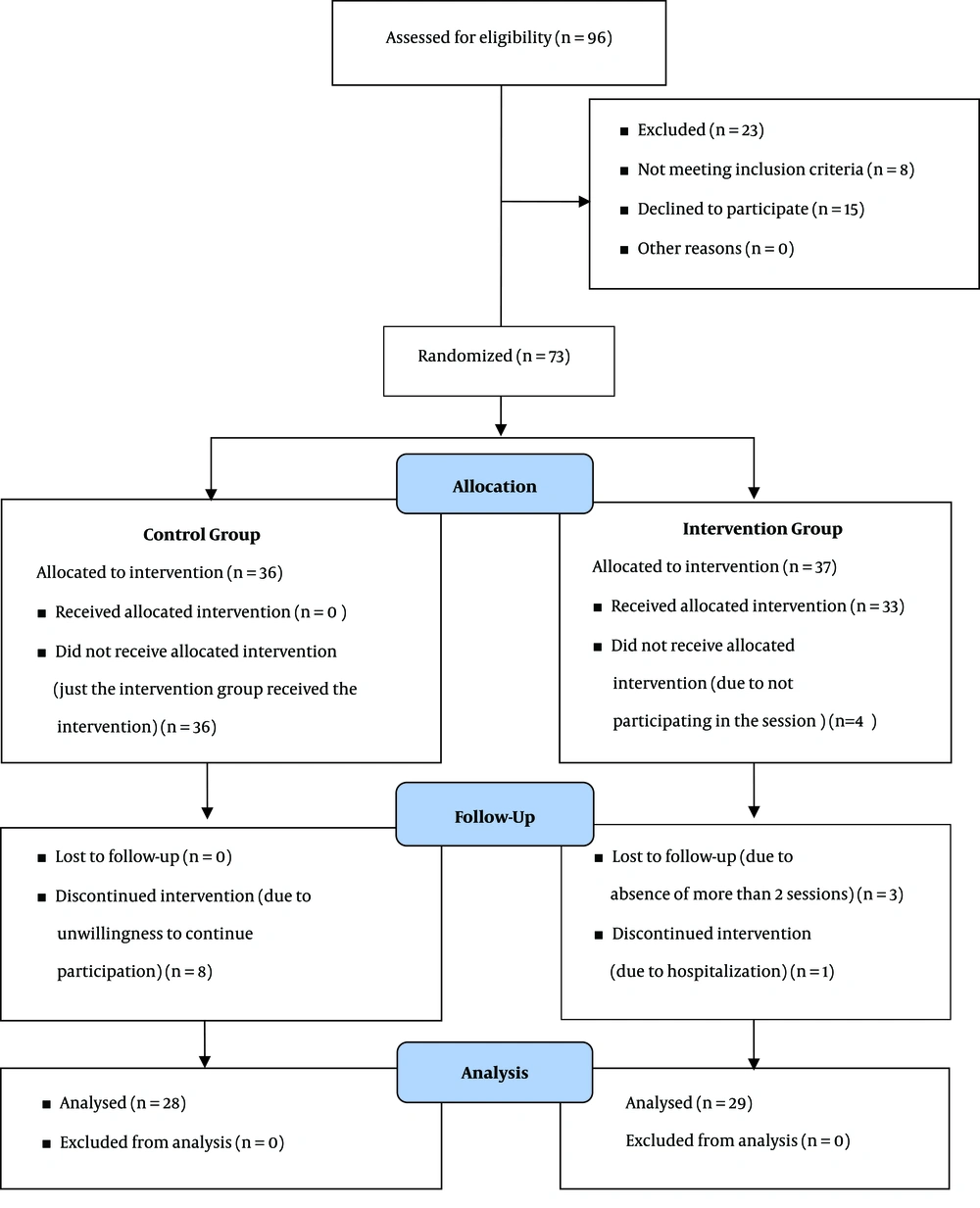
The statistical population of this study included hemodialysis patients referred to educational and medical centers affiliated to Fasa University of Medical Sciences (FUMS), Fasa, Iran. The sample size was calculated using the formula below using α = 0.05, β = 0.10, and the mean (mean1 = 7.46, mean2 = 14.93) and standard deviation (S1 = 8.20, S2 = 8.20) based on the results of a previous study (23). At least a 54-subject sample size (27 subjects in each group) was determined for the study. By considering a 30% attrition rate, the final sample size for both groups was about 70 subjects (35 subjects in each group). The blocking randomization (block size = 4) method was used to randomly divide the participants, who met the inclusion criteria, into the intervention and control groups (Figure 1).
3.3. Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria
The inclusion criteria for the study were as follows: willingness to participate in the study, age 18 - 70 years, ESRD and under hemodialysis, a history of hemodialysis for at least 12 months or more, the lack of participation in other training courses at the same time, no history of resilience training, and the lack of treatment with psychotropic drugs (24). Patients who refused to continue their participation for any reason or were absent for more than two sessions were excluded.
3.4. Data Collection
Data collection tools included a demographic information form, SF-36 quality of life questionnaire, and DASS-21 anxiety, stress, and depression questionnaire.
3.4.1. Quality of Life Short Form-36 (SF-36)
This questionnaire is one of the most common and comprehensive standard tools in the field of quality of life related to public health, which is used internationally and has two dimensions of physical and mental health (25). The validity and reliability of the Persian translation of the questionnaire were confirmed in the study of Montazeri et al., and its alpha Cronbach coefficient was reported 0.77 - 0.90.(26).
3.4.2. Anxiety, Stress, and Depression Questionnaire DASS-21
Depression, anxiety, and stress-21 scale was designed in 1995 by Lovibond and Lovibond (27). The test contains 21 questions, each with a share of 7 subscales of depression, anxiety, and stress, and more scores on the test showed high severity of the disorder (28). This scale was first validated in Iran by Sahebi and his colleagues, and the test subscales were matched through Cronbach's alpha, and its values were 77% for depression, 79% for anxiety, and 78% for stress (29).
3.5. The Intervention
In order to develop a resilience education program, we reviewed research and resilience enhancement programs that had previously been conducted for different groups, as well as internal and external studies on resilience (30-34). Then, it was approved by the teachers of Fars University of Medical Sciences, who had academic and clinical experience in this field. The intervention group received 12 sessions of training workshops on resilience skills. The control group did not receive any training during the research, but after completing it, in order to observe the principles of ethics in research, they were taught resilience content in the form of a 2-day workshop. To hold workshops, the intervention groups were divided into smaller groups of 10 people. Training sessions were held by a clinical psychologist through lectures, discussions and group participation, modeling and role-playing, intellectual challenge, staging, and homework. At the end of each session, the participants' questions were answered, and the beginning of the next sessions was accompanied by a review of the topics of the previous session. In order to ensure proper productivity of the training process, as well as to create diversity in training, the final 10% of all training sessions were used for peer training. Peer groups are better able to encourage their peers to choose appropriate health behaviors, and they can share strengths and weaknesses and common experiences. Peer education is an ongoing approach in which he/she establishes a long-term friendly and intimate relationship with the patient and shares his information with him. In order to use peer education in this study, we randomly selected three hemodialysis patients who were not members of the participating groups. These individuals had at least one level of education with a diploma and appropriate expressiveness, had at least one year of hemodialysis experience, and according to the DASS-21 questionnaire, did not suffer from stress, anxiety, and depression or were at a mild level. The training of the peers was such that in the presence of the instructor of the training program, under her supervision and guidance, they shared their experiences and strengths with the patients. Multimedia facilities such as computers, film, and software players (PowerPoint) were used to provide training and prevent tiredness in the participants. Also, educational videos related to resilience, catering, and short breaks were used. One week after the end of the intervention, stress, anxiety, depression, and quality of life questionnaires were completed by the participants in both groups. The summary of the objectives and contents of the meetings is listed in Table 1.
| Session | Goals | Educational Program Content |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Familiarity with the generalities and content of the program | Introducing the participants and getting to know the workshop facilitators; getting acquainted with the objectives and framework of the program; expressing the rules and regulations of the meetings. |
| 2 | Familiarity with the meaning and concepts of resilience (by providing definition, explanation, example). | Definition of resilience; introducing the characteristics of resilient individuals; explaining the factors related to resilience; familiarity with the ways of creating resilience; presenting group tasks (in groups of 5 people) |
| 3 | Awareness of one's abilities | Assessment of homework, awareness of one's abilities and elimination or reduction of irrational beliefs; facilitating the factors and barriers to self-awareness, expression of the patients' experiences, answers, and questions; group discussion |
| 4 | Strengthen self-esteem | A clear understanding of self-esteem; explaining the causes and factors influencing self-esteem; understanding the importance and impact of self-esteem in life; identifying strengths and weaknesses |
| 5 | Effective social communication | The simple definition of communication; the importance of communication; methods of establishing proper and appropriate communication with others; emphasis on the importance of positive relationships with others and the right attitude toward it; group discussion, practical practice, and role play |
| 6 | Determining the goal and how to achieve it | Simply articulate the concept of purpose; be forward-looking, plan-making and goal-oriented, and hope for the future; ability to plan to achieve your goal |
| 7 | Familiarity with internal support factors | The concept of optimism and the role of optimistic thinking in resilience; teaching positive thinking and discovering positive traits and focusing on positive points; cultivating self-confidence; recognizing talents and interests, emphasizing them, and wanting to use them |
| 8 | Familiarity with external support factors | Social support system; individual responsibility and role acceptance; cognitive reconstruction and modeling of constructive thinking (expressing the role of beliefs and thoughts in behavior and emotions and familiarity with cognitive errors |
| 9 | Problem-solving | Learning problem-solving steps; thinking about problems; self-efficacy problem-solving; questions and answers and group discussion, role-playing |
| 10 | Anger and rage management | Explain the concept of anger and rage; the causes and consequences of anger and rage on the health of body, soul, and life; methods of controlling anger and rage; group discussion |
| 11 | Anxiety and stress management | Define the practical and operational concepts of stress and anxiety; explain the effects of stress and anxiety on physical and mental health; learn operational strategies to deal with it (deep breathing, meditation, mental imagery, muscle relaxation, etc.) and practice, Group discussion |
| 12 | Thinking style | Familiarity with thinking styles and creating a model of constructive thinking, changing pessimistic to optimistic style; familiarity with individual differences in perception, emphasizing the importance of the role of thoughts and self-talk; summarizing previous sessions, appreciation, and closing |
3.6. Ethical Considerations
The study was approved by the ethics committee of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences (code: IR.SUMS.REC.1399.132) and obtaining written permission from the university and medical centers. The objectives and research processes were explained to the patients, and written informed consent were obtained from them, ensuring that their information would remain confidential and anonymous; also, they were assured that they could withdraw at any stage of the study willingly.
3.7. Statistical Analysis
Data were analyzed using SPSS-20 software. Descriptive statistics (percentage, average, and standard deviation) were used to describe the demographic characteristics of the participants. To compare the mean scores of stress, anxiety, depression, and quality of life between the two groups before and after the intervention, we used an independent t-test, paired t-test, and chi-square test to compare the mentioned cases in each group before and after the intervention. The significance level was also considered P < 0.05.
4. Results
4.1. Demographic Characteristics of the Participants
Overall, 57 patients participated in the study, of whom 28 patients were included in the control group and 29 patients in the intervention group. The results of the demographic analysis of the study showed that the mean age of the participants in the intervention and control groups was 62.03 ± 7.21 and 58.75 ± 7.70 years, respectively, with a range of 38 to 70 years. Based on the independent t-test, the two groups did not differ significantly in terms of the mean age. Most of the participants in both intervention (72.4%) and control (67.9%) groups were men. According to the chi-square test, there was no significant difference between the two groups in terms of educational status (P = 0.30), marriage status (P = 0.56), gender (P = 0.70), employment (P = 0.51), and duration of dialysis (P = 0.56) (Table 2).
| Demographic Variable | Intervention Group (N = 29) | Control Group (N = 28) | χ2 | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y) | 0.74 | 0.69 | ||
| 20 - 39 | 1 (3.4) | 2 (7.1) | ||
| 40 - 59 | 13 (44.8) | 10 (35.7) | ||
| 60 - 70 | 15 (51.7) | 16 (51.7) | ||
| Gender | 0.14 | 0.70 | ||
| Male | 21 (72.4) | 19 (67.9) | ||
| Female | 8 (27.6) | 9 (32.1) | ||
| Educational status | 2.39 | 0.30 | ||
| High school | 16 (55.2) | 10 (35.7) | ||
| Diploma | 11 (37.9) | 14 (50) | ||
| Associate degree | 2 (6.9) | 4 (14.3) | ||
| Marital Status | 0.33 | 0.56 | ||
| Married | 22 (75.9) | 23 (82.1) | ||
| Single | 7 (24.1) | 5 (17.9) | ||
| Occupation | 0.42 | 0.51 | ||
| Employed | 11 (37.9) | 13 (46.4) | ||
| Unemployed | 18 (62.1) | 15 (53.6) | ||
| Duration of hemodialysis (y) | 1.15 | 0.56 | ||
| < 3 | 4 (13.8) | 7 (25) | ||
| 3 - 6 | 11 (37.9) | (32.1) | ||
| < 6 | 14 (48.3) | 12 (42.9) |
a Values are expressed as No. (%) unless otherwise indicated.
b chi-square test
4.2. The Effect of the Intervention on Stress, Anxiety, and Depression of the Participants
Based on the results of the independent t-test, as shown in Table 3, the mean scores of stress, anxiety, and depression before the intervention were not significantly different between the two groups (P > 0.05). Comparison of the mean score of stress, anxiety, and depression in patients before and after the intervention in the control group did not show a significant difference based on paired t-test (P > 0.05).
| Variable | Pre-test | Post-test | P-Valuea |
|---|---|---|---|
| Depression | |||
| Experimental | 17.58 ± 4.08 | 16.06 ± 3.56 | 0.139 |
| Control | 16.64 ± 3.35 | 17.07 ± 4.16 | 0.696 |
| P-valueb | 0.346 | 0.333 | |
| Anxiety | |||
| Experimental | 16.89 ± 3.56 | 10.62 ± 3.89 | < 0.001 |
| Control | 15.85 ± 4.86 | 17.42 ± 3.80 | 0.133 |
| P-valueb | 0.361 | < 0.001 | |
| Stress | |||
| Experimental | 22.68 ± 3.43 | 15.58 ± 4.67 | < 0.001 |
| Control | 22.07 ± 4.69 | 20.85 ± 3.50 | 0.265 |
| P-valueb | 0.572 | < 0.001 | |
| DASS total | |||
| Experimental | 57.03 ± 7.64 | 42.34 ± 5.92 | < 0.001 |
| Control | 54.35 ± 9.61 | 55.35 ± 6.60 | 0.598 |
| P-valueb | 0.249 | < 0.001 | |
| Quality Of life | |||
| Experimental | 42.06 ± 10.71 | 53.51 ± 7.90 | < 0.001 |
| Control | 42.20 ± 14.35 | 41.85 ± 13.70 | 0.844 |
| P-valueb | 0.967 | <0.001 |
a Paired t-test
b Independent t-test
In the intervention group, the patients’ mean score of stress before and after the intervention was 22.68 ± 3.43 and 15.58 ± 4.67, respectively, likewise, anxiety 16.89 ± 3.56 and 10.62 ± 3.89, which showed a significant effect of the intervention on the mentioned variables. However, the mean score of depression in the intervention group before (17.58 ± 4.08) and after (16.06 ± 3.56) the intervention did not show a significant change (P = 0.13). Also, the mean score of the patients' quality of life before the intervention was not significantly different between the two groups (P > 0.05). Comparison of the mean scores of patients' quality of life before and after the intervention in the control group did not show a significant difference based on the results of paired t-test (P > 0.05). The mean overall score of the patients’ quality of life was 42.06 ± 0.71 and 53.51 ± 7.90 in the intervention group before and after the intervention, respectively, which showed the intervention had a significant effect on the patients' quality of life (P < 0.001).
5. Discussion
The results of the intervention show that resilience training significantly reduces stress (P < 0.001) and anxiety (P < 0.001) in hemodialysis patients, which is consistent with the findings of several studies conducted in this field (35-40).
In the process of resilience training, people learn how to control the stress resulting from illness, and by influencing the thinking processes, it is possible to access resilient strategies. Therefore, they act as a protective shield in the face of stressful life events (41). The results of a study showed that resilience training had an effect on anxiety in burn patients. People with high resilience are more calm and confident in the face of stressful events, so it is easier for them to control these factors (40). The results of another study showed that resilience training, if combined with telephone follow-up courses, could reduce the patients' stress and anxiety and improve their quality of life. In this study, telephone follow-up courses were not conducted (35).
Group training may have a positive effect on reducing stress and anxiety in patients because gathering people in the group and making each individual feel that others have similar problems and using each other's experiences in the group to deal with stress increase the self-confidence and is effective in reducing stress and anxiety. One of the differences between our study and the other studies mentioned in the present research was the use of peer education. Negative emotions and managing stress and anxiety were very effective. On the other hand, the method and type of educational content provided, including familiarity with internal and external support factors, enhancement of self-confidence and self-esteem, improvement of coping skills with anxiety, stress, and anger, as well as the exercises provided, were very effective. However, a comparison of the mean score of depression in the intervention group, before and after resilience training, showed that the intervention did not have a significant effect on the patients' depression, which is not consistent with the results of other studies (42-45). The reason for this can be the differences in the educational methods used in the mentioned studies, subjects under the study, sample size, and study time. On the other hand, given that few studies have been done on the mentioned intervention, especially in relation to hemodialysis patients, definitive judgment is difficult and requires further studies.
In this study, the quality of life of patients before and after the intervention was also measured, which indicated the positive effect of resilience training on the quality of life in these patients. Quality of life is a mental concept that is influenced by people's mental and psychological performance; owing to the positive impact that resilience intervention had on the stress and anxiety of these patients, changes were observed in thinking and attitude, adaptive strategies, and self-confidence and self-esteem in these patients. It seems that improving their quality of life is not unexpected. This result was consistent with those of other studies in this field (46-48).
In this study, the patients' depression in the intervention group decreased after the intervention, but the difference was not significant, which was not consistent with the results of other similar studies (42, 49-51). It seems that the reason for this difference could be the differences in the population under the study, the duration and number of training sessions used in different studies, measuring instruments, sample size, and different training methods used. One of the limitations of this research was the use of self-reporting tools to collect information. The present study was also limited to patients undergoing hemodialysis, so caution should be taken into consideration when generalizing the results to other patients or the statistical population of other cities.
5.1. Conclusion
Resilience intervention programs in the form of group training and peer training can be used as a non-invasive, non-pharmacological method and as a complementary measure along with other methods used for hemodialysis patient care and treatment programs. It is recommended that similar studies should be performed on other chronic diseases with larger sample size.