1. Context
Moral distress is a common phenomenon in the nursing profession (1). It is the emotional and mental pain and discomfort, which is morally inevitable while having the required knowledge and ability to make moral judgments, due to actual or mental limitations (2). Today, since nurses are correlated with many moral issues in their working shifts and patient care is always associated with ethics and ethical considerations, moral distress is of great importance (3, 4).
Insult, mistrust, and conflicting demands of the patient and his family from the therapy team (5, 6), shortage of manpower in clinical environments, negligence and medical errors, lack of time, poor communication of doctors and nurses (7), opposition to superiors, medical limitations, institutional policies and personal or ideological ethical considerations, and incompetence of some medical personnel can be the reasons for the emergence of moral distress (8, 9). It causes a negative impact on personal and professional lives of nurses (10), physical and psychological stress, low efficiency, quality of care, and increase in the cost of nursing care (11-15).
As Corley, a pioneer in the field of nurses’ moral distress, stated moral distress can cause nurses to experience conflict in caring and avoid facing with the patient and providing high-quality care. It involves absence from work and leaving the profession that leads to a defect in improvement and increasing the duration of hospitalization and it also affects other medical professionals’ services. It can also act as a deterrent and destructive factor for nurses to provide caring (11, 16-18). Effects of moral distress in nurses can lead to wrath, depression, disability and frustration, anger and physiological or psychological problems (7).
Moral distress is examined by two intensity and frequency dimensions: intensity means the perceived amount of moral distress but the frequency is the number of times nurses face with it in a limited interval. As Hamric Said “questionnaire contains 21 question and each of the 21 items scored by participants in terms of the how often the situation arises (frequency) and how disturbing the situation is when it arises (“intensity”)”. The scale ranges never to very frequently, and none to great extent for frequency and intensity, respectively (11, 19-21).
1.1. Objectives
Increasing sample size due to the increasing number of relevant studies, reducing difference in existing parameters and confidence interval are the main goals of meta-analysis studies. In fact, these studies are a vital link between research studies and decision making at the bedside (22). Due to the controversy in reporting the moral distress there is a lack of access to the global community to this factor in Iranian nurses, on the other hand, review of several studies cannot lead to final conclusions for policymaking to planning the proper preventive management at the national level. Therefore, a systematic review of all documents and their combination through meta-analysis can create a complete viewpoint (22) of the dimensions of moral distress in Iranian nurses. This first international study was done aiming to investigate the “Intensity and Frequency of Moral Distress in Iranian Nurses”.
2. Evidence Acquisition
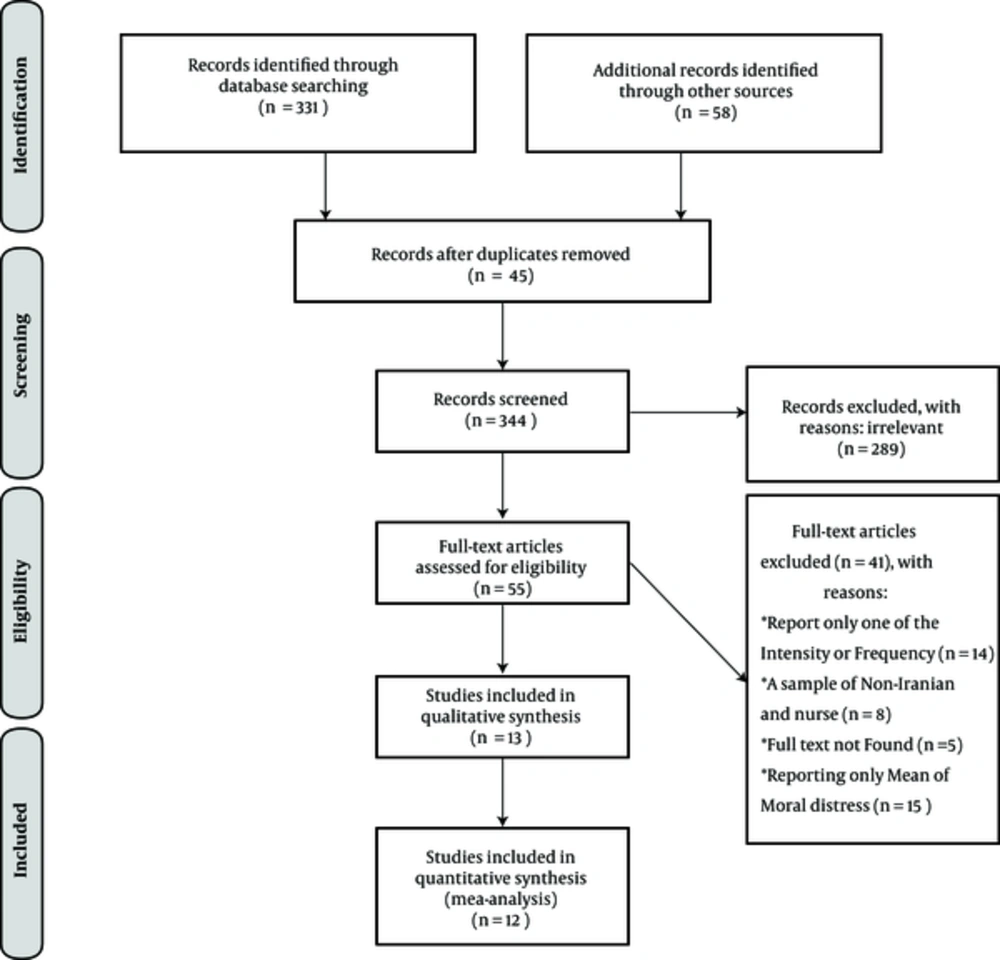
This is the first systematic and meta-analysis review study aiming to evaluate the intensity and frequency of moral distress in Iranian nurses by 2016. The present meta-analysis study was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA guideline (23). To avoid publication bias, the entire processes of research including search, selection of studies, qualitative evaluation of studies, and data extracting were independently done by 2 researchers. Any additional encounters was assessed by a third researcher.
2.1. Study Selection
2.1.1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
The main criteria for inclusion in the study were an evaluation of the frequency and intensity of moral distress in Iranian nurses. The exclusion criteria included: 1. Non-Iranian sample, 2. non-nurse sample, 3. poor information like failing to report just one of the items “intensity and frequency”, 4. unrelated to the research subject, 5. non-random sample, 6. letters to the editor, and 7. duplicate articles.
2.1.2. Search Strategy and Study Selection
Results of this study are based on all papers published in national and international journals, dissertations, and reference websites. Related English and Persian literature were reviewed in national databases like SID, Magiran, Irandoc, IranMedex, and international banks such as Madlib and Web of Sciences, Scopus, PubMed, Direct-Science, Cochrane, Embase, Springer, Online Library Wiley, Ebsco, CEBM, CINHAL, SAGE, and Google Scholar search engine. Searching articles was done using Persian keywords and their English equivalents in accordance with their Mesh: “Moral”, “Morale”, “Distress”, “Iran”, “Frequency”, “intensity”, “Ethics”, “Nurse”, and all possible combinations of words using “Boolean operators” in combination for English databases. The manual search to find more articles was also done through reviewing references of identified articles.
What is noticeable in searching databases, is “High Sensitive Searching”. Searching was performed by a researcher and master familiar with searching databases. To avoid bias, the search was separately done by 2 researchers (“M.H. YK” and “M. A”) any encounters was assessed by a third researcher. As soon as the search ended, titles of the collected articles were entered into EndNote™, resource management software, to find similar articles. Manual searching was also done through reviewing the reference list of relevant articles.
2.1.3. Quality Assessment
In the next step, using STROBE (24) checklist, which has 22 sections, researchers evaluated the selected articles from methodological aspects, including sampling method, measurement of variables, statistical analysis, and study objectives, independently and any encounters were assessed by a third researcher. Articles, which obtained a minimum score of 16 based on the checklist, were selected for meta-analysis (Figure 1).
2.2. Data Extraction
At first, a checklist was designed based on objectives and by studying other available resources. The designed checklist included items such as authors, year, place, sample size, questionnaire, score of scale, mean intensity (± SD), mean frequency (± SD), mean age (± SD), and Job Experience, which was extracted independently by 2 researchers (Table 1). All documents were assessed and date extracted by 2 researchers independently and all extracted data were rechecked after they were finished by the third researcher who is an expert in this field (M.E-B).
| Authors | Year | Place | Sample Size | Questionnaire | Score Scale | Mean Intensity | Mean Frequency | Mean Age | Job Experience (Lowest-Highest) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Borhani et al. (25) | 2015 | Tehran | 153 | Corely1995 | 4 | 1.8667 ± 0.6950 | 1.9417 ± 0.6854 | 32.9 ± 6.52 | 9.23 ± 6.43 (1 - 35) |
| Shafei et al. (15) | 2015 | BorazJan | 91 | Corely1995 | 4 | 2.2329 ± 0.4742 | 1.9829 ± 0.5921 | 33.91 ± 7.08 | 10.5 ± 6.78 (1 - 26) |
| Borhani et al. (26) | 2015 | Kerman | 300 | Corely2001 | 5 | 3.54 ± 0.3 | 3.11 ± 0.6 | 32 ± 3.1 | 14 ± 4 (2 - 25) |
| Mohammadi et al. (5) | 2014 | Kerman | 260 | Corely1995 | 5 | 3.5 ± 0.8 | 3.9 ± 0.55 | 37 ± 2.46 | 14 (2 - 25) |
| Mohammadi et al. (27) | 2014 | Kerman | 330 | Corely1995 | 5 | 3.5 ± 0.9 | 3.7 ± 1.2 | - | 16 (1 - 28) |
| Borhani et al. (28) | 2014 | Birjand | 220 | Corely2001 | 5 | 2.25 ± 0.6 | 2.11 ± 0.56 | 31.12 ± 5.13 | 6.54 ± 4.4 (1 - 24) |
| Borhani et al. (14) | 2013 | Kerman | 110 | Corely1995 | 6 | 3.5 ± 1.2 | 2.7 ± 1.1 | - | (1 - 27) |
| AbbasZadeh et al. (29) | 2013 | Sirjan | 184 | Corely2002 | 4 | 1.92 ± 0.77 | 1.5 ± 0.7 | 32.7 ± 5.49 | 10 |
| AbbasZadeh et al. (30) | 2013 | Birjand | 220 | Corely2001 | 5 | 2.25 ± 0.6 | 2.11 ± 0.56 | - | (1 - 24) |
| Mohammadi-Nafchi et al. (31) | 2013 | Kerman | 300 | Corely2001 | 5 | 2.7 ± 0.57 | 3.24 ± 0.43 | 28 ± - | 16 (1 - 28) |
| AbbasZadeh et al. (32) | 2012 | Shiraz | 117 | Corely2005 | 4 | 2.5475 ± 0.0558 | 2.2642 ± 0.0475 | 31.38 ± 5.65 | 5.59 ± 4.64 |
Specifications Studies Entered Into Meta-Analysis (Sorted by Year)
2.3. Statistical Analysis
In any study, after taking into account the intensity and frequency of moral distress as a binomial probability distribution, its variance was calculated through binomial distribution and Cochran test (Q) and I2 index were used to evaluate the heterogeneity of the studies. Due to the heterogeneity of studies, random effects model was used to combine the results of both studies. Data was analyzed using the Meta-analysis specialized software of “The Cochrane Collaboration Co.”, called Review Manager Ver. 5.3.5 and comprehensive Meta-Analysis V.2 a significance level less than 0.05 was considered.
3. Results
In this systematic study, based on performed searches, 389 article were identified and after review and final assessment in accordance with checklist, 12 (3.08%) titles were included in the list with a total of 2655 nurses with a mean age of 32.3 ± 15.265 and work experience (1 - 25 years) (Table 1 and Figure 2). The results of the systematic review and meta-analysis, are divided into 2 parts: Intensity and frequency.
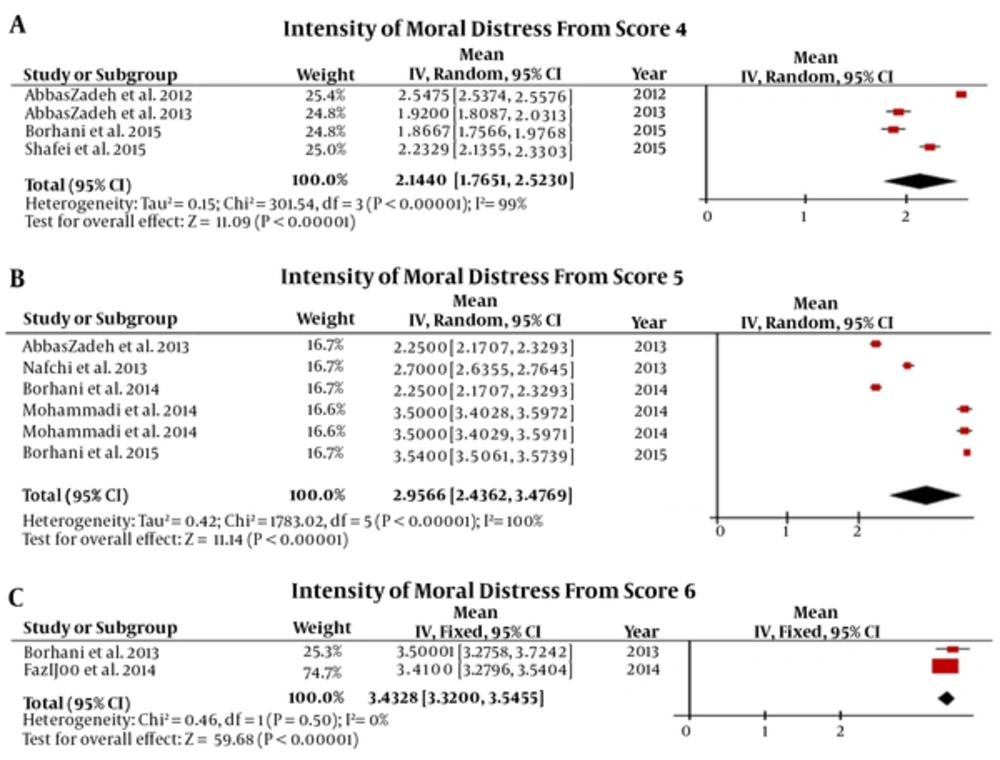
Results of the meta-analysis of the mean intensity of moral distress in Iranian nurses are 2.2329 [CI95%: 1.7651, 2.5230] out of 4, 2.9566 [CI95%: 2.4362, 3.4769] out of 5, and 3.4328 [CI95%: 3.3200, 3.5455] out of 6 (Figure 3).
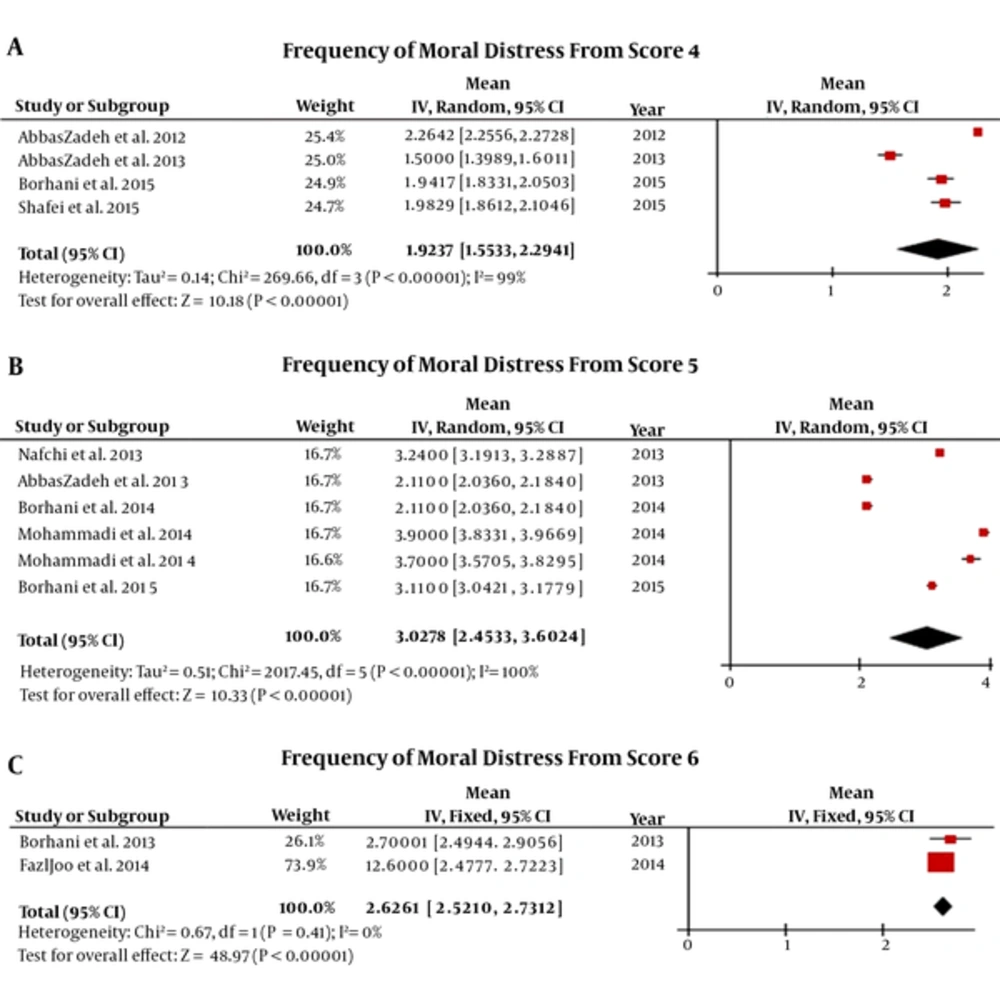
Results of the meta-analysis of mean frequency of moral distress in Iranian nurses are 1.9237 [CI95%: 1.5533, 2.2941] out of 4, 3.0278 [CI95%: 2.4533, 3.6024] out of 5, and 2.6261 [CI95%: 2.5210, 2.7312] out of 6 (Figure 4).
The heterogeneity rate in the study was 66.33%, which is in the midrange (I2 index less than 25% is low heterogeneity, between 25% and 75% is midrange, and more than 75% is high heterogeneity).
Also, the probability of publication bias was not statistically significant by using Begg and Egger tests and was determined as P = 0.6457 and P = 0.8632, respectively.
4. Discussion
This systematic review and meta-analysis study was carried on 12 academic papers, and has provided basic and enough information regarding morale distress among Iranian nurses. This study revealed the frequency and intensity of morale distress, which can be used by policy makers and nursing managers.
Results of this study can give a more accurate understanding of moral distress in the clinical environments to researchers and nurses. What is understood from Iranian studies is that, nurses as the key individuals in the health system the have most direct contact with patients, thus, 50% - 80% of health care is done by nurses (33). There is a consensus on the concept of moral distress by Andrew Jameton (1984) that the nurse knows what is correct, however, the organizational restrictions makes it impossible to do the right thing (26, 32, 34). In Iranian studies, no tool is generated to assess the distress specific to Iranian society and culture, and studies are mainly conducted based on Jameson tools 1992 (35), Corley edited the version of 1995 (19, 25), 2001 (21, 26), 2002 (20, 29), and 2005 (11, 32). These tools were adjusted by Iranian researchers for Iranian culture in years (1, 3, 5, 11, 14, 15, 25-32, 34-41). Studies in Iran have manipulated the number of Likert scales and in Likert 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7, they have reported that this makes it difficult to compare the results (Table 1). According to the aim of this study, intensity and frequency of moral distress have been reported in the range of moderate to intense.
Iranian studies suggest that most nurses are in moral stressful situations and this can jeopardize their health or have a negative impact on their professional performance (42). Iranian studies expressed the most common side effects of moral distress as qualm, pain, and discomfort, lack of job satisfaction, turnover (26), and it seems that each of the side effects is worse than the moral distress.
Iranian studies suggest that moral distress is a serious challenge in nursing and requires special attention (18, 34). Nafechi (31) and Abbaszadeh (32) also expressed distress was high in nursing staff and moral distress reduction strategies should be planned and implemented. It is always stressed that organizational and nursing managers should develop mechanisms to reduce moral distress and support nurses (43, 44). However, since care in Iran is not based on evidence, the results of these studies have never been used. Everyone believes that further studies should be performed in this regard, and basically it is unclear when and how the nursing community will deal with this moral issue in practice. These structures must be developed properly, impartially and, naturally by nurses.
Trisha states that more studies need to be done by all members of the treatment team on why we cannot apply more effective interventions against the phenomenon of moral distress (44). Before studying the definitions of moral distress, we should focus more on the issue of what we should do to reduce the effects of moral distress, especially in nurses.
The heterogeneity rate (I2) has been calculated to 66%. Observed differences are due to different sampling. In addition, differences in measured parameters in different populations can be the reasons of heterogeneity in this study (45-47).
Overall, to avoid personal, organizational, and professional effects of moral distress in the clinical setting, a standard tool based on Iranian health care culture should be developed. The frequency and intensity of moral distress and related factors on nurses across the country should be evaluated. In the next step, the solutions of dealing with each of these factors should be provided according to Iranian health care background. Results of this study, our knowledge, and experiences show that because of terrible disruptive effects of moral distress on nurses, management, and preventative strategies should only be developed and run by nurses.
Limitation: The number of men was very low so it was not possible to express the distressing rate based on gender. In addition, lack of focus onwards made it impossible to detect the rate of distress in each ward and comparison between the ward and other wards. It is recommended to conduct further studies to assess distressing rate based on gender and onwards (e.g. Emergency, Internal, ICU/CCU/NICU).