1. Context
Orofacial clefts, including cleft lip (CL), cleft palate (CP), or cleft lip and palate (CL/P) together, are the most common heterogeneous craniofacial malformations in the oral cavity characterized by environmental and genetic factors (1). These clefts may be unilateral or bilateral. Maxillary retrognathism, greater anterior facial heights, and retroclined maxillary incisors are the main clinical factors in patients with unilateral CL/P (2, 3). The disease prevalence is 1 to 2 in 1,000 live births worldwide. The highest and lowest incidences of CL/P are reported among Indian and Afro-Caribbean populations, respectively (4-7). The main aspects that should be considered for these patients are the modification of facial malformation, optimization of the quality of speech, and maintenance or restoration of middle ear function (8).
CL/P patients are regarded as less intelligent and social with fewer professional opportunities than normal children (9-12). In this regard, the most important protective factor for children with CL/P is a healthy family environment. The parents of special children with intellectual disabilities are prone to experience emotional disorders, especially depression, and have higher child-related stress than parents of normal children (13, 14). There are some reports on the experience of CL/P patients, intellectual and social development of CL/P subjects, and reactions of CL/P cases to their unique environments; however, limited studies have assessed the psychological status of parents with CL/P children. Due to the effect of the mental status of parents on children, the assessment of psychological aspects of this problem and associated effects on the patients and their parents is critical and can help optimize their quality of life (QoL). However, there have not been sufficient data on the mental condition of parents of children with CL/P. Therefore, this study aimed to determine the QoL and emotional problems, including anxiety and depression, in the mothers of CL/P children. In this regard, the following issues were assessed by the present review: (1) QoL in caregivers of children with CL/P; (2) anxiety status of caregivers of children with CL/P; (3) depression status of caregivers of children with CL/P.
2. Evidence Aquisition
This systematic review assessed the QoL, stress, and depression in parents or caregivers of children with CL/P. The guidelines of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, including eligibility criteria investigation, an extensive search for data collection, unrelated papers removal, risk of bias assessment, data extraction, and discussion, were used in this study (15).
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
The inclusion and exclusion criteria were selected based on the participants-intervention-comparison-outcome-study design. All the studies comparing the QoL, depression, and anxiety in parents of children with CL/P were included in the present study. All the papers were published in English and conducted on human subjects. Since the present study aimed to assess the QoL, depression, and anxiety in parents of children with CL/P, the papers focusing on patients with CL/P were excluded from the study. Parent reports on the psychological conditions of their children, social and emotional experiences, and care services for CL/P patients were omitted from the study. Moreover, exploratory, qualitative, and phenomenological studies, articles with a sample size of lower than 30, retrospective chart reviews, and papers not examining children and parents separately were removed from the study. In addition, in vitro and animal studies, editorial letters or short communications, books, reviews and narrative articles, case reports, and unavailable full-texts were excluded from this study. The current review only included prospective case-control studies with descriptive, comparative, or inventive processes in nature to assess the QoL, stress, and depression in parents of children with CL/P.
2.2. Literature Search
All the published studies were searched in three electronic databases, including MEDLINE, PubMed, and Web of Science, from December 1 to December 30 in 2020 using the keyword, namely “Orofacial Clefts” and “Cleft Lip and Palate” in combination with “Anxiety," "Stress," "Depression," and "Quality of Life” in addition to “Parents," "Mothers," "Fathers," and "Caregivers."
2.3. Study Design and Data Extraction
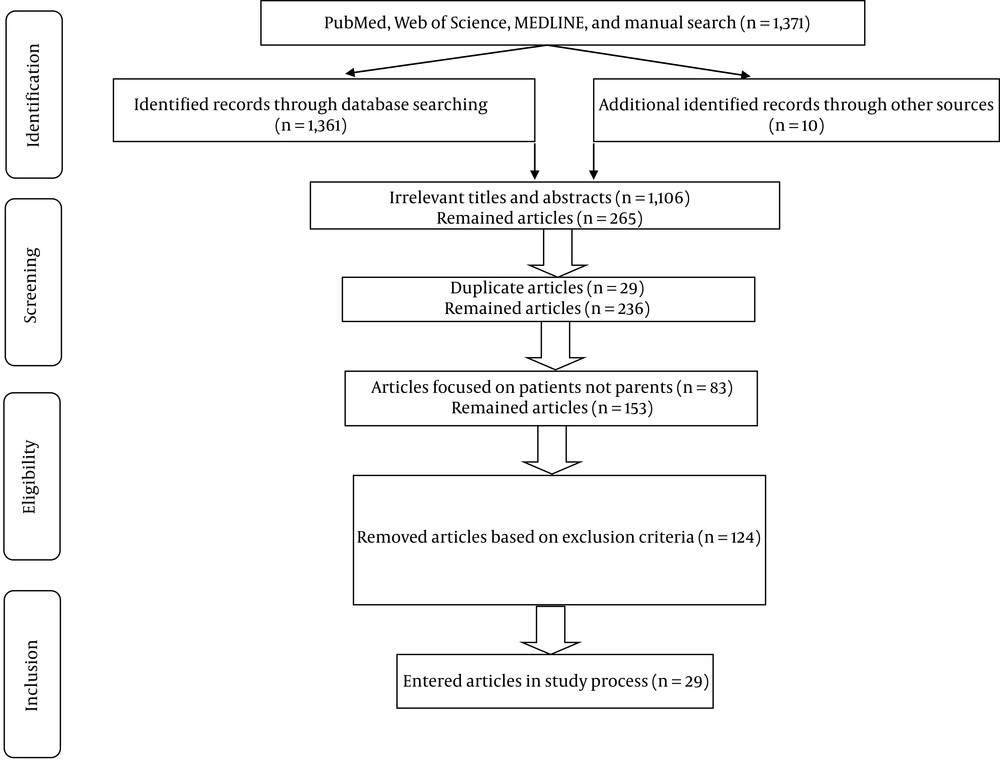
This systematic review focused on the QoL, stress, and depression in parents or caregivers of children with CL/P. In the first stage, three selected electronic databases were searched on December 30, 2020. In the first research process, the titles and abstracts of the identified papers were studied, and unrelated articles were removed. In the next step, duplicate papers were excluded from the study. After completing the search process and removing irrelevant and duplicate articles, the full-text versions of the selected papers that were consistent with the objective of the current study were obtained for final evaluation. Subsequently, the studies were reviewed, and the eligible articles were screened for relevancy. Papers with insufficient data were excluded from the study. Two researchers performed all the research processes in contact with each other, and they separately reviewed the titles and abstracts of all the articles. They discussed the determination of papers, selection of articles, removal of studies, and extraction of data. All the extracted data were recorded in a researcher-made checklist. The PRISMA flowchart represents the stages of article selection (Figure 1).
2.4. Risk of Bias and Quality Assessment
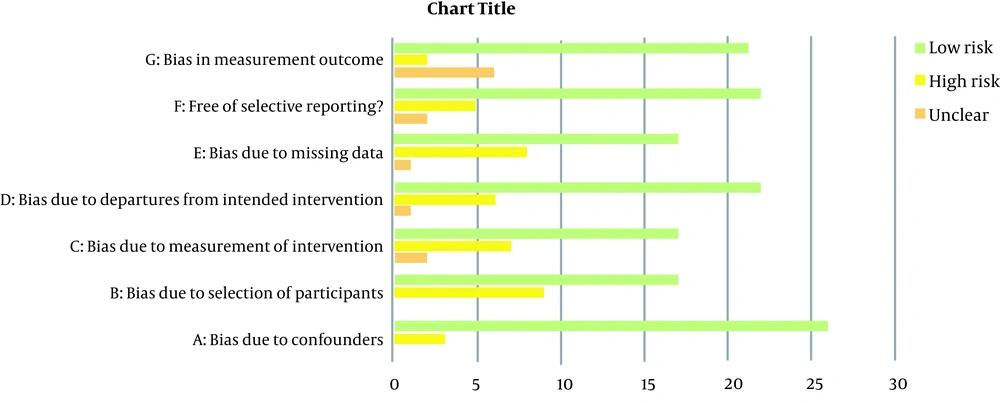
Cochrane’s risk of bias tool was used to determine the risk of bias. In this study, the researchers assessed the quality of each study by evaluating the risk of bias in seven domains, including bias due to confounders, bias due to the selection of participants, bias due to the measurement, bias due to missing data, incomplete outcome data, selective reporting, and other sources of bias (16). The options were chosen based on the nature of the selected studies. In total, 29 papers were reviewed in the present study based on the seven domains of the Cochrane guidelines to determine the risk of bias. The low, high, and unknown risks of bias were marked as "Yes," "No," and "Unclear," respectively (Table 1) (Figure 2).
| Author and Reference | Bias Due to Confounders | Bias Due to Selection of Participants | Bias Due to Measurement of Intervention | Bias Due to Missing Data | Incomplete Outcome Data | Free of Selective Reporting | Other Sources of Bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weigl et al. (8) | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No |
| Kramer et al. (17) | No | Yes | No | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Unclear |
| Baker et al. (18) | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Gowda et al. (19) | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| Onah and Achor (20) | No | Yes | No | Yes | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear |
| Hasanzadeh et al. (21) | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| Oshodi and Adeyemo (22) | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes |
| Thamilselvan et al. (23) | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| Sischo et al. (24) | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Awoyale et al. (25) | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Unclear |
| Rosenberg et al. (26) | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No |
| Bos et al. (27) | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No |
| Hemati et al. (28) | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Emeka et al. (29) | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No |
| Macho et al. (30) | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No |
| Boonplia et al. (31) | No | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Aslan et al. (32) | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No |
| Beluci et al. (33) | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Unclear |
| Khanchezar et al. (34) | No | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | Unclear |
| Nur Yilmaz et al. (35) | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | Unclear |
| Yilmaz et al. (36) | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No |
| Kumar et al. (37) | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No |
| Boztepe et al. (38) | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No |
| Grollemund et al. (39) | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No |
| Scheller et al. (40) | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No |
| Stock et al. (41) | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No |
| Dissaux et al. (42) | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No |
| Gbolahan et al. (43) | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No |
| van Dale et al. (44) | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No |
3. Results
A total of 1,371 papers were identified in the first step of the research process, of which 1,106 irrelevant articles were excluded. Out of 265 remaining studies, two articles were duplicated and were excluded from the review. Furthermore, the articles (n = 83) focusing on the QoL, stress, and depression among patients with CP/L were removed from the study. In the next step, the articles that did not meet the inclusion criteria or were not consistent with the objectives of the current study were omitted from the review. In this regard, the studies in which parents reported on the psychological conditions of their children (n = 31), social and emotional experiences (n = 12), care services for CL/P patients (n = 4), exploratory, qualitative, and phenomenological studies (n = 14), articles with a sample size of lower than 30 (n = 9), retrospective chart reviews (n = 19), and studies in which children and parents were not separately examined (n = 3) were excluded from this study. Moreover, the papers published in languages other than English (n = 5) were removed from the study. In addition, in vitro and animal studies (n = 0), editorial letters or short communications (n = 4), books (n = 1), reviews and narrative articles (n = 17), case reports (n = 4), and unavailable full-texts (n = 1) were excluded from this study. Finally, 29 articles were included in this review. The PRISMA flowchart represents the process of study selection (Figure 1).
All the papers were prospective studies. The majority of the studies were analytic, 17.2% (n = 5), 10.3% (n = 3), and 6.9% (n = 2) of which were case-control, cohort, and pilot studies, respectively. Furthermore, 20% of the articles were interventional (n = 6). About 48.2% of the studies were descriptive, including questionnaire (n = 4), cross-sectional (n = 9), and longitudinal (n = 1) studies. The included studies were performed in seven regions, mostly (38%) Asia (Turkey n = 4, India n = 3, Iran n = 3, and Thailand n = 1). Moreover, 10 studies (34.5%) were performed in Europe (UK n = 3, Germany n = 2, Slovakia n = 1, Netherlands n = 2, and France n = 2). Two studies (6.9%) were conducted in North America, and one study (3.4%) was carried out in South America (Brazil). In addition, five studies (17.2%) were performed in Africa (Table 2).
In general, the included articles were performed on 3,825 parents (including mothers, fathers, and other caregivers) of 3,235 patients (children and adolescents) with CL/P. The mean age of the subjects (caregivers) was within the range of 23.6 - 40.3 years. Moreover, the mean age of the children varied widely (from 5.7 months to 12.1 years). The male/female ratio of patients with CL/P was 1/1.06 (881 females and 824 males). The majority (62%) of the studies were conducted on both mothers and fathers. Eight studies (27.5%) were carried out only on mothers of children with CL/P. In three studies (10.3%), other caregivers were studied in addition to mothers and fathers. The type of deformity was determined in 12 studies (1,134 patients). The CL/P was observed in 4.7 - 55% of the patients. Moreover, CP and CL were reported in 10.6 - 43% and 10 - 58% of the patients, respectively.
Various tools were used for assessing QoL, stress, and depression in parents of CL/P children. The World Health Organization quality of life questionnaire, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS), Impact on Family Scale, General Health Questionnaire, and 36-item Short-form Survey (SF-36) were the most commonly used tools. Surgical correction was used in the majority of interventional studies. Nasoalveolar Molding (NAM) and traditional cleft treatment were used in two studies (24, 35).
Moreover, a happiness training and teamwork program was applied to improve the psychological status of mothers of patients with CL/P (28, 34). The depression status of mothers with CL/P children was assessed in eleven studies (8, 20, 22-24, 35, 37, 39, 41, 42, 44). Among the studies mentioned above, 54% showed that depression was higher among mothers with CL/P children than in the normal or general population (8, 24, 37, 39, 41, 42). Moreover, two studies showed that most mothers were screened positive for depression (20, 22). Based on a study, NAM therapy and lip surgery decreased maternal and paternal depression levels (35). A study showed a higher level of depression among mothers than in other caregivers (35). Furthermore, another study demonstrated a correlation between depression and behavioral problems (23).
Anxiety in mothers with CL/P children was assessed in 19 studies, among which six (33%) studies confirmed a high level of parental stress and anxiety among individuals with CL/P children (20-22, 24, 40, 43). In addition, 31.5% of the studies showed a higher anxiety level among mothers with CL/P children than in the normal or general population (8, 18, 24, 37, 38, 41). However, two studies demonstrated that mothers of children with CL/P experienced the same stress level as the mothers of normal children (27, 44). Two studies indicated a higher level of depression among mothers than among other caregivers (24, 35); nevertheless, another study rejected this finding (36). A correlation between anxiety and behavioral problems and child pain scores was confirmed (22, 26). Based on the results of a study, a happiness training program decreased maternal anxiety levels (28).
The QoL in mothers with CL/P children was assessed in 14 studies. Based on some studies, orofacial clefts in children significantly affect the quality of their family life (19, 30). In addition, another study demonstrated that the social, physical, and psychological aspects of QoL were lower in the parents of cleft children than in the general population (32); however, the previous finding was rejected by another study (8). On the other hand, another study demonstrated that mothers with CL/P children gained better scores than normal individuals on the Health-related Quality of Life (HRQoL), family functioning, emotional status, daily activities, and family relationships subscales and a less favorable score on cognitive functioning. Moreover, fathers with CL/P children achieved better scores than normal individuals on all the scales of the Pediatric Quality of Life Family Impact Module (PedsQL-FIM) (41).
Some studies indicated that the QoL of parents with CL/P children is affected by psychiatric morbidity, family income, poor access to specific information, and lack of professionals' empathy (20, 23, 25, 33). Moreover, there is an inverse correlation between the QoL and burden in physical health, psychological status, social relationships, and environment domains (33). Another study showed no relationship between the QoL and the extent of malformation, initial diagnosis time, and reconstructive surgery frequency (17).
Two studies demonstrated that surgical correction and lip surgery increased the maternal level of QoL (29, 31). Another study reported the effectiveness of teamwork in improving the QoL of mothers with CL/P children compared to individual treatment or non-teamwork therapy (34). Finally, although more severe depressing conditions and higher stress levels are reported among mothers of CL/P children (37), no difference is observed in satisfaction with motherhood among mothers with CL/P children (27)). In this regard, the role of support from friends and family in less negative family impact and lower psychological distress should be considered (18, 26).
| Author (Year) Reference | Country | Type of Study | Sample Size of Children | Sample Size of Parents | Age of Children | Age of Parents (Year) | Male/Female Ratio | Participants | Type of Deformity | Tool | Intervention | Depression | Anxiety | QoL and Main Condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weigl et al. 2005) (8) | Germany | Case-control study | 50 | 50 | 12 months to 10 years | - | 27/23 | Only mothers | CL/P: 25 (50%) CP: 20 (40%) CL: 5 (10%) | HADS 36-item Short-Form Health Survey | No | CL/P: 6% Control: 2.5% P > 0.05 | CL/P: 8% Control: 9.6% P > 0.05 | There was no difference between the QOL of CL/P patients and the control group in VT, SF, RE, MH, and RP subscales; however, a difference was observed in PF, BP, and GH subscales between the two groups. |
| Kramer et al. (2007) (17) | Germany | Questionnaire study | 130 | 130 | 14 months (6 - 24) | Mothers: 28.5 Fathers: 30.6 | 74/56 | Both mothers and fathers | CL/P: 46 (35%) CP: 36 (28%) CL: 48 (37%) | IOFS | No | - | - | The extent of malformation (type of cleft), initial diagnosis time, and reconstructive surgery frequency did not affect QoL. |
| Baker et al. (2009) (18) | UK | Case-control study | 100 | 100 | 8.9 (0 - 18) years | 37.92 | 50/53 | Mothers: 86 Fathers: 17 | CL/P: 48 (46.6%)CP: 33 (32%) CL: 22 (21.4%) | Coping Response Inventory GHQ | No | - | High levels of stress-related growth as a result of child’s condition | Association between support from friends and family and less negative family impact, lower psychological distress, and better adjustment |
| Gowda et al. (2013) (19) | India | Pilot study | 79 | 79 | - | - | 36/43 | Mothers, fathers, and other caregivers | - | GHQ World Health Organization quality of life questionnaire | No | - | - | Half of the caregivers suffered from poor mental health and reduced QoL |
| Onah and Achor (2014) (20) | Nigeria | Questionnaire study | 48 | 48 | - | 30 | 21/27 | Only mothers | - | Brief Screen for Depression EUROHIS-QOL 8-item Index Self-reporting Questionnaire | - | 62.5% screened positive for depression | - | Lower QoL in mothers positive for psychiatric morbidity than in those without morbidity |
| Hasanzadeh et al. (2014) (21) | Iran | Cross-sectional study | 55 | 55 | 12.1 years | 35.98 | 23/32 | Only mothers | Unilateral CL/P: 32 (58.2%)mBilateral CL/P: 23 (41.8%) | IOFS GHQ Coping Response Inventory | No | - | Psychological distress: 38% | Mothers relied more on the use of approach-oriented rather than avoidance-oriented coping strategies. Psychological distress: 38% Psychological problems: 23% |
| Oshodi and Adeyemo (2015) (22) | Nigeria | Cross-sectional study | 52 | 52 | - | 31.2 | 21/31 | Only mothers | - | Causal beliefs questionnaire GHQmPerceived Stress Scale | - | Subjective feelings of misery and depression: 73% | About 18% of the mothers had the perception of more than average stress. | - |
| Kumar et al. (2015) (23) | India | Cross-sectional exploratory study | 50 | 50 | 3.06 years (1 - 5) | 31/19 | Both mothers and fathers | - | Depression, Anxiety, Stress Scale Child behavior checklist | No | Correlated with behavioral problems | Correlated with behavioral problems | QoL of parents and behavioral problems in parents of children with CL/P | |
| Sischo et al. (2016) (24) | USA | A mixed-method multicenter longitudinal study | 114 | 118 | - | 30.3 (17 - 45) | 11/109 | Both mothers and fathers | - | Generalized Anxiety and Depressive symptom scales Parenting Stress Index Life Orientation Test Family Environment Scale Coping Health Inventory for Parents | NAM therapy and traditional cleft treatment | Higher levels of depression in parents than in normal individuals | Caregivers had average elevated levels of anxiety but lower than average levels of parental stress | Caregivers of NAM-treated neonates experienced a faster decrease in anxiety and depressive symptoms and better coping skills over time than caregivers whose newborns had traditional care |
| Awoyale et al. (2016) (25) | Nigeria | Mixed-method study | 107 | 107 | - | 15-31 | Mothers: 101 Fathers: 6 | CL/P: 52 (50%) CL: 30 (28%) CP: 25 (23.4%) | IOFS | - | - | - | QoL and delivery of family-centered care were affected by poor access to specific information and lack of empathy of professionals. | |
| Rosenberg et al. (2017) (26) | USA | Cohort study | CL/P: 59 Cranial vault repair: 13 | 71 | 6.6 months | 34.2 | Mothers: 64 (90%) Fathers: 7 (10%) | - | HADS | Craniofacial surgery | - | High anxiety correlated with child pain scores. | Maladaptive coping, low parental self-efficacy, and external locus of control were independently associated with high parental anxiety. | |
| Bos et al. (2017) (27) | Netherlands | Case-control study | 76 | Case: 76 Control: 52 | 34.6 months | 33.8 | 45/31 | Only mothers | Isolated CP: 26 34%) CL/P: 37 (48%) Isolated CL: 13 (17%) | Motherhood Satisfaction Nijmeegse Ouderlijke Stress Index | - | - | Mothers of children with clefts experienced the same stress level as mothers of normal children. | Mothers of children with clefts did not differ in their satisfaction with motherhood. |
| Hemati et al. (2017) (28) | Iran | Quasi-experimental study | 32 | 32 | 0 - 12 years | 33.3 | 20/12 | Only mothers | - | Cohen Perceived Stress Questionnaire | Happiness training program (10 sessions) | - | Before intervention < 0.05 After intervention > 0.05 | - |
| Emeka et al. (2017) (29) | Nigeria | Longitudinal study | 95 | 95 | 5.7 months (1 - 48) | - | 54/40 | Both mothers and fathers and other caregivers | CL/P: 22 (23.4%) CP: 10 (10.6%) Unilateral CL: 49 (52.1%) Bilateral CL: 13 (13.8%) | IOFS Health-related quality of life questionnaire | Surgery | - | - | Before intervention < 0.05 After intervention > 0.05 |
| Macho et al. (2017) (30) | Slovakia | Interventional study | 40 | 40 | - | - | - | Both mothers and fathers | CL: 20 (50%) CL/P: 20 (50%) | Researcher-made | Surgical correction | - | - | Orofacial clefts in children significantly affected family QoL. |
| Boonplia et al. (2017) (31) | Thailand | Case-control study | 44 | 44 | 31 - 45 | Mothers: 37 Fathers: 7 | CL: 24 (55.8%) CP: 17 (39.5%) CL/P: 2 (4.7%) | The Thai version of the World Health Organization quality of life questionnaire | Surgical correction | - | - | A significant improvement was observed in all dimensions of the QoL. | ||
| Aslan et al. (2018) (32) | Turkey | Questionnaire study | 74 | 148 | 9.2 years | Mothers: 34.5 Fathers: 38.7 | 44/30 | Both mothers and fathers | - | Family Assessment Scale Short form of World Health Organization quality of life | - | - | - | Levels of social, physical, and psychological aspects of life quality were lower in cleft parents than in the control group. |
| Beluci et al. (2019) (33) | Brazil | Exploratory cross-sectional study | 77 | 77 | - | 28.8 | - | Mothers: 74 Other caregivers: 3 | - | World Health Organization quality of life questionnaire Burden Interview Scale | - | - | - | Positive correlation between QoL and family income; an inverse correlation between QoL and burden in the physical health, psychological health, social relationships, and environment domains |
| Khanchezar et al. (2019) (34) | Iran | Analytical epidemiology study | 101 | 101 | 2 - 7 years | 32 | 51/50 | Only mothers | CP: 44 CL: 11 CL/P: 44 | Quality of Life Questionnaire 36-item Short-Form Health Survey | Teamwork | - | - | QoL was better in mothers in a multidisciplinary team than in individual providers. |
| Nur Yilmaz et al. (2019) (35) | Turkey | Interventional study | 80 | 80 | - | 23.61 (8 - 36) | - | Mothers: 40 Fathers: 40 | - | Beck Depression Inventory Beck Anxiety Inventory | NAM therapy and lip surgery | Different maternal and paternal depression levels in different times of intervention; higher maternal depression than paternal one | Maternal anxiety levels were higher than the paternal ones in all periods. | - |
| Yilmaz et al. (2020) (36) | Turkey | Case-control study | 80 | 80 | > 14 days | Mothers: 31.9 Fathers: 34.6 | 22/18 | Mothers: 40 Fathers: 40 | - | Amsterdam Preoperative Anxiety and Information Scale Spielberger’s State-Trait Anxiety | Lip surgery | - | No differences between the parents | - |
| Kumar et al. (2020) (37) | India | Case-control study | 240 | A a: 72 B b: 70 c: 98 | - | - | - | - | - | GHQ Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Scale | - | A difference was observed in depression among the three groups. | A difference was observed in anxiety and stress among the three groups. | The severely depressed state of mind and moderate to severe levels of stress were reported in most parents. |
| Boztepe et al. (2020) (38) | Turkey | Cross-sectional observational study | Case: 90 Control: 90 | 90 | 0 to 12 months | 29.6 | 50/40 | Mothers: 69 Fathers: 1 Both: 20 | CL: 30 (33%) CP: 30 (33%) CL/P: 30 (33%) | Parenting Stress Index-Short Form Multidimensional Scale of Perceived Social Support | No | - | Higher mean stress score in mothers of neonates born with CL/P than in control mothers | Parenting stress was higher and social support was lower in mothers of neonates with a cleft. |
| Grollemund et al. (2020) (39) | France | Cohort study | 156 | 156 | - | - | 109/47 | Both | CP: 66 (42%) CL/P: 90 (58%) | Parenting Stress Index Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale IOFS | Surgical correction | Higher postpartum depression in both parents than in the general population | Early intervention decreased maternal stress. | Much better preparation to accept the waiting time between birth and first surgical intervention was reported in parents for whom it had been possible to give a prenatal diagnosis. |
| Scheller et al. (2020) (40) | UK | Pilot study | 84 | 84 | - | - | 39/45 | Only mothers | - | Researcher-made | Surgical correction | - | High parental stress | High parental stress and physical and emotional strains among mothers |
| Stock et al. (2020) (41) | UK | Questionnaire study | 791 | 1,163 | - | - | - | Mothers: 644 Fathers: 519 | - | Pediatric Quality of Life family impact module Perceived Stress Scale HADS | No | Higher depression levels in parents than in normal individuals | Higher anxiety levels in parents than in normal individuals | Mothers reported better scores than normal individuals on health-related QoL, family functioning, emotional status, daily activities, and family relationship subscales and less favorable scores on cognitive functioning; fathers of CL/P children achieved better scores than normal individuals on all the scales of the Pediatric Quality of Life family impact module |
| Dissaux et al. (2020) (42) | France | Multicenter prospective cohort | 158 | 158 | 0 to 4 months | - | - | Both mothers and fathers | CLP | IOFS EPDS PSI | Surgical correction | Intervention decreased maternal stress at four months. | Intervention decreased maternal stress at four months. | - |
| Gbolahan et al. (2020) (43) | Nigeria | Cross-sectional | 90 | 90 | 1 - 252 months | 32.4 | 57/33 | Mothers: 84 Fathers: 4 | CL: 29(32.2%) CP: 31 (34%) CL/P: 30(33.3%) | Zarit burden interview score | - | - | Caregiver burden stress Severe: 4.4% Moderate to severe: 21.1% Mild to moderate: 40% Little or none: 34.5% | - |
| van Dale et al. (2021) (44) | Netherlands | Cross-sectional study | 181 | 309 | 2 - 12 years | 40.3 | 118/63 | Mothers: 136 Fathers: 173 | - | PSI SCL-90 | Surgical correction | No difference between parents of children with CL+P and normal group | Lower anxiety in parents of children with CL+P than in normal group | - |
Abbreviations: CL/P: cleft lip and palate; CP, cleft palate; CL, cleft lip; QOL, quality of life; VT, vitality; SF, social functioning; RE, role emotional; MH, mental health, RP, role physical; PF, physical functioning; BP, bodily pain; GH, general health; NAM, nasoalveolar molding; HADS, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale; IOFS, Impact on Family Scale; GHQ, General Health Questionnaire; EPDS, Edinburgh Postpartum Depression Scale; PSI, parenting stress index; SCL-90, Dutch translation of the symptom checklist-90
a Parents (mother or father) of cleft lip and palate children under 10 years of age.
b Parents of cleft lip and palate children over 10 years of age.
c Parents of children with no cleft lip and palate or any other genetic disorder.
4. Discussion
4.1. QoL in Caregivers of Children with CL/P
The mental status of mothers of CL/P children is an essential protective factor for the child. The effectiveness of HRQoL as a significant parameter has been proven in the diagnosis and determination of therapeutic procedures (8). There have been data on lower QoL in caregivers of children with physical or mental disorders than in the general population (22, 45, 46). The HRQoL is an international classification system, which is considered a multidimensional construct, including physical, mental, and social aspects of life. The SF-36 covers all the aspects; therefore, some studies applied the questionnaire to achieve their purposes.
In a study by Stock et al., the overall levels of HRQoL and family functioning were higher in both mothers and fathers of CL/P children than in normal individuals. Mothers of CL/P children reported better scores than normal individuals on the HRQoL, family functioning, emotional status, daily activities, and family relationships subscales and a less favorable score on cognitive functioning. Fathers of CL/P children achieved better scores than normal individuals on all the scales of the PedsQL-FIM. They showed a correlation between the positive life orientation and less overall impact on the family for parents (41). Positive outcomes associated with CL/P are warranted. The recent approaches emphasize the systemic developmental approach; accordingly, the family unit is regarded as a whole with multilevel capacity (47).
In another study y Weigl et al., the QoL, anxiety, and depression of 50 mothers with CL/P children were assessed using the SF-36 and HADS. No significant difference was observed between mothers with CL/P children and normal controls. Therefore, Weigl et al. concluded that mothers with CL/P children do not require psychological screening (8). It should be considered that only mothers of children older than one year of age participated in the study mentioned above. The majority of mothers emphasized that they experienced emotional distress immediately after childbirth. There has been evidence showing that the QoL decreased in families with CL/P children, especially during the very early life stage of the cleft patient (48).
The assessment of the factors affecting the QoL of families with CL/P children helps the affected families cope with particular conditions and provide adequate care for the individual. A study by Kramer et al. identified factors influencing the QoL of families having children with orofacial cleft within the age range of 6-24 months. A self-administered questionnaire was used in the study mentioned above (17). Kramer et al. carried out a study only on children under two years of age. At this age, families are confronted with the birth of the cleft patient and most of the operations required for reconstruction. In addition to the birth of the cleft patient, families are confronted with problems, such as financial issues, and require operations for reconstruction in the early stage of CL/P. They demonstrated a relationship between the parental levels of satisfaction and treatment outcomes. They showed that the economic and social effects were reduced in families with isolated CL children than in families with CL/P or isolated CP children; nevertheless, coping problems increased. It is probably due to later surgery for reconstruction.
Social impact is affected by the prenatal diagnosis of orofacial cleft; however, it did not decrease the general impact on the affected families. More tailored support of affected families with distinct types of cleft may improve their QoL. They indicated that the extent of malformation (the type of cleft), time of initial diagnosis, and frequency of reconstructive surgery do not affect the QoL. Families with CP children are usually visited less frequently by the cleft team during the first year of life. It may result in more incredible difficulty in coping with the problem (17). It has been proven that the self-perception of mothers with CL/P children changes over time (10-12, 49, 50); moreover, it may be affected by other variables, such as the gender of the child.
The impairment of children is differently experienced by their parents (13). In this regard, identifying caregiver burdens and providing better support for them is essential because the QoL of caregivers is affected by the burden imposed on them (23). The parents of disabled children show overinvolvement in the protection of such children. Moreover, assessing the main pattern of behavioral problems in younger children and its effect on behavioral problems and negative emotions in parents is very important. Wu et al. reported more behavioral problems in children with CL/P than normal controls (51). In another study by Kumar et al., a correlation was reported between the QoL of parents and behavioral problems of children with CL/P. In addition, children’s internalizing and externalizing problems correlated with parental QoL. Kumar et al. observed a relationship between some children’s behavioral problems and negative emotions in parents (i.e., depression and stress) (23). As an essential aspect of developing a child-parent relationship, the quality of parents' relationships is another factor that could be affected by involving emotional expression (52).
Commonly, significant responsibilities associated with these children are taken by the mothers (14). Some mothers of children with impairment have to give up their occupation to care for their children, making them unable to pursue their interests. It may lead them to focus on disabled children, which continually increases the mother's stress (53). Therefore, multidisciplinary care should be provided for patients with CL/P. Surgical correction of the facial disfigurement and rehabilitation of functional deficits are the primary therapeutics provided for developing the communicational competence of these patients.
Training parents with disabled children to express positive emotions and use adjustment strategies could help parents decrease their stress and improve their QoL. Based on a study by Murthy, there is a direct relationship between QoL improvement and better patient care (52). Moreover, a positive relationship was observed between children's externalizing problems and parental negative emotions. This finding was confirmed by similar studies (54, 55).
Since the QoL of families with CL/P children may decrease due to the pressure caused by extra financial costs of nutritional and medical management of the children (56), the assessment of the approaches reducing the concerns and stress of parents through other ways is critical. The teamwork treatment is suggested as a standard approach for patients with CP in most regions of the world (56, 57). This approach can help parents receive more information on their children’s health conditions. Therefore, the parents can decrease their parental concerns regarding their children's health by establishing a close relationship with an interdisciplinary team of specialists (58). A study by Khanchezar et al. assessed the effect of teamwork treatment on the QoL of mothers with CL/P children in Iran. In the study mentioned above, higher scores were shown in five subscales of the QoL in mothers of the teamwork group than in the control group (34).
Social support is considered a protective factor against the adverse effects of chronic stress, playing an essential role in helping families adjust to chronic illness (18, 47). Close friendship could help mothers with CL/P children against depressive symptoms. Consideration of national and local culture plays a vital role in providing successful care for neonates with CL/P (59). Due to the differences in health care and culture in various geographic regions, controversial findings are obtained on the QoL of parents with CL/P children. Moreover, social support plays a vital role in the prevention, resolution, and treatment of psychological problems of parents with disabled children and can help parents cope with difficult situations (18, 60).
4.2. Anxiety Status of Caregivers of Children with CL/P
Parents often report anxiety and feelings, such as fear, guilt, and self-blame, especially mothers of children with congenital malformations (17, 61). Previous studies reported conflicting emotions experienced by parents of CL/P children. These conflicts are highlighted, especially in the period from the CL/P diagnosis to primary surgery. Mothers may be affected by the feelings of social exclusion and stigmatizing reactions of others, which may increase anxiety for their children’s future (62). On the other hand, there is evidence of the interactive effect of stress and risk of CL/P. The experience of psychological symptoms during pregnancy in some mothers with CL/P neonates was reported by Boztepe et al. (38). A higher risk of orofacial cleft due to maternal stress during pregnancy was reported in another study (63).
Grollemund et al. observed that children's social withdrawal is related to the level of stress and distress of the mothers, not the severity of the medical condition (39). This finding emphasizes the importance of the psychological status of parents in social withdrawal behaviors in children with CL/P. A study by Scheller et al. showed high parental stress and physical and emotional strains among mothers with CL/P children (40). In addition, Stock et al. reported a higher stress level in both parents (mothers and fathers) with CL/P children than in normal individuals. Furthermore, mothers' worry about the condition's impact on their children and family was more remarkable than normal individuals'. Stock et al. demonstrated a correlation between positive life orientation and lower anxiety levels among both mothers and fathers (41).
In a study by Boztepe et al., a higher stress score was reported for mothers of neonates born with CL/P than mothers with healthy children (38). They showed an association between the high mean parenting stress scores of mothers with CL/P newborns and low mean social support scores (38), confirmed by other studies (64, 65). Social support is essential for effectively coping with stress (64). However, it should be considered that the psychological conditions of parents, including well-being, attitude, stress, and coping, are affected by individual cultural and belief systems influencing parental perceived social support (27, 66). One study showed that receiving substantial support from family and friends by mothers of CL/P newborns decreased the psychological problems and increased the rate of adaptation to the situation (18).
It has been reported that the stress of caring for an impaired child can decrease via self-realization and partnership emotional support (13, 67). Probability, mothers are more vulnerable than fathers when exposed to problems in the parenting domain (24). Based on the obtained results of some studies, the depression scores of fathers of disabled children are lower than those of mothers (13, 68). Anxiety disorders and depression are the most common emotional disorders affecting women higher than men (69, 70), although it seems that fathers with disabled children report fewer symptoms of psychological distress than mothers (71). However, similar challenges regarding these children were reported by mothers and fathers in some exploratory qualitative studies (72).
Some factors play essential roles in increasing parents' stress with CL/P children. Parental reactions are different depending on the time of CL/P diagnosis; accordingly, mothers who learned of the diagnosis at birth have higher stress than those who learned of the diagnosis before birth (38). Kramer et al. showed that parents who were aware of the neonates' problem before birth had lower anxiety and stress levels and could cope better with this situation than mothers who were unaware of this situation (17). Difficulty in feeding is the main problem of mothers with CL/P children, leading to inadequate nutrition, malnutrition, and mortality in some cases (73). Moreover, a higher level of parenting stress was reported in mothers who could not breastfeed their newborns than in mothers who could (38). Mothers who have difficulties feeding their neonates may experience unpleasant feelings, including inadequacy, guilt, stress, and anxiety (74).
Surgical correction of the facial disfigurement and rehabilitation of functional deficits are the primary therapeutics provided for patients with CL/P. Boztepe et al. reported higher stress scores among mothers of newborns who had not yet undergone any surgery than those whose neonates had undergone surgery (38). The considerable effect of parental anxiety on attachment representations and longer-term child development is undeniable. These findings emphasize the necessity of psychological screening in the first few months following the diagnosis to facilitate providing appropriate psychological support for parents with CL/P children (71).
4.3. Depression Status of Caregivers of Children with CL/P
In a study carried out by Stock et al., higher levels of depression were reported among mothers with CL/P children than in normal individuals. The result mentioned above was not confirmed for fathers. Moreover, Stock et al. showed a correlation between positive life orientation and lower levels of depression for both mothers and fathers (41). Higher levels of depression in mothers with CL/P children than in normal individuals were confirmed by other similar studies (24, 37).
Weigl et al. showed a higher score of depression in mothers with CL/P children than in those with normal children (8). Other studies demonstrated that most mothers with CL/P children were screened positive for depression (20, 22). In another study by Kumar et al., there was a correlation between behavioral problems of CL/P children and depression of their parents (both mothers and fathers) (23). Moreover, Yilmaz et al. showed higher maternal depression than paternal one (35).
In a study by Grollemund et al., socioemotional problems of these children were related to postpartum depression of parents. In the study mentioned above, the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale, Parenting Stress Index, and Impact on Family Scale were used to evaluate the psychological status of parents. However, the depression of parents decreased after surgical correction of their children (39). This finding showed that the depression and stress of parents with CL/P children are not stable and probably are temporary ssues. In this regard, the resilience of both children and parents is essential (75).
Parents with CL/P children have many challenges, including accepting and observing this cleft mouth for the first time at birth, nutritional problems, and coping with the child's discomfort after surgery and stress of the first anesthesia. This issue may increase the stress of mothers, thereby increasing depression. In this regard, the screening of the parents for the symptoms of depression at the time of their children's first evaluation is essential. However, it seems that there is no sufficient information on the topic.
4.4. Risk of Bias
Although the study provides valuable data on the mental health of caregivers of children with CLP, some limitations are reported in reviewed studies. Moreover, although all studies were prospective, a bias due to the selection of participants was observed in two-thirds of them because the samples were randomly selected. This issue could be described due to the limited population of patients with CLP, which could reduce the reliability of our study. On the other hand, bias due to the measurement of intervention, bias due to confounders, and selective reporting were reported in a few studies. Bias due to missing data and incomplete outcome data were observed in less than 30% of studies. Based on the information mentioned above, the risk of bias in the present study is low with a good quality assessment.
5. Conclusions
Due to the differences in health care and culture, controversial findings were obtained on the QoL of parents with CL/P children. Social support plays a vital role in the prevention, resolution, and treatment of psychological problems of parents with CL/P children. The majority of studies confirmed the higher levels of anxiety and depression in caregivers of children with CL/P. These findings emphasize the necessity of psychological screening in the first few months following the diagnosis to facilitate providing appropriate psychological support for parents with CL/P children.