1. Context
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a neurological disease in which the CNS-covering myelin is damaged. Based on the data obtained from the Iranian MS Association, around 50,000 patients, i.e. 60 to 70 patients per every 100,000 people in Iran's population have this disease (1).
Persons with MS (PwMS) in addition to losing motor, sensory, and cognitive functions, also experience associated symptoms including depression, anxiety, stress, fatigue, and pain (2, 3). Thus, PwMS confront numerous physical, mental, and emotional problems on a daily basis (4). Although in the initial stages of the disease, the physical problems are usually limited, patients experience anxiety and psychological distress (5, 6). Based on different studies, 48% of patients experience stress, anxiety, and depression within the first year following diagnosis (7, 8). Depression with prevalence of 50% is another common comorbid disease among PwMS (9). Fatigue is another common symptom of this disease (10) which is experienced by around 80% of patients in its early stages (11). In a large epidemiological study based on a semi-structured interview, it was reported that 43% of PwMS experience at least one type of pain (12). The symptoms can be controlled to some extent by pharmacotherapy, though considering the problems and side effects resulting from drugs, use of nonpharmacological methods that can mitigate the negative symptoms seems logical. In recent years, nonpharmacological methods such as cognitive behavioral therapy, mindfulness, as well as acceptance and commitment (ACT) therapy have gained the interest of patients including PwMS, and are known as complementary treatment. These treatments have a holistic nature which are used for enhancing the psychological and physical welfare of patients.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is used for management of symptoms and increase of psychosocial consequences for individuals suffering from chronic diseases (13, 14). The goal of CBT is to correct wrong interpretations, giving a sense of control over life, increasing positive as well as constructive self-talks, and improving coping strategies (15). There is evidence suggesting that CBT may be useful in mitigating depression, anxiety, fatigue, disability, problems related to cognition, in addition to improving the quality of life of PwMS (13, 16). Meanwhile, other therapies of this field which are called third wave therapies are mindfulness plus acceptance and commitment therapy. Mindfulness refers to "attention to a special targeted method at the present with no judgment" (17). Studies have shown that training mindfulness is associated with decreased anxiety, depression, stress, pain, as well as enhanced positive psychological functions (17, 18). Acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT) refers to improving psychological flexibility and is defined as the ability of facing challenging experiences in an open and informed way as well as changing the individual behaviors for participation in valuable activities (19). In acceptance-based therapies, unlike many other treatments, no special value or lifestyle is imposed to the person; rather in these treatments the clients make decisions about change based on their own system of values (20). The effectiveness of ACT has been confirmed for mitigating the depression, anxiety, stress, fatigue, and pain in PwMS (21-23). Previous meta-analyses for PwMS have been performed with a limited range of mindfulness-based interventions (24), which have not covered different forms of interventions including CBT, mindfulness-based stress mitigation approach, ACT, or a wide range of symptoms. Meanwhile, this meta-analysis is only specific to the interventions performed for PwMS in Iraq and so far no systematic review covering meta-analyses has been performed on PwMS in Iran.
2. Objectives
The aim of this study is to summarize, evaluate, and quantify the findings of controlled clinical trials on psychological interventions that are based on CBT, mindfulness, and ACT for the symptoms of PwMS in Iran.
3. Methods
3.1. Sources of Information and Search Methods
This is a meta-analysis of randomized trials involving the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral, mindfulness and acceptance and commitment (CMAC) on psychological syndrome of pwMS in Iran. In order to find the relevant published studies, search was performed from the beginning of 20 November 2021 across both Iranian databases (Sid, Magiran, Irandoc, Civilica, Iranmedex) and foreign ones (Web of Sciences, PubMed Cochrane Library Scopus, Google Scholar). The key search terms associated with interventions and the population (MS) were combined to identify the relevant literature. The search was done through both Persian and English keywords including cognitive behavioral therapy, acceptance and commitment therapy, mindfulness, dialectical behavioral therapy, clinical trial, multiple sclerosis, MS, anxiety, depression, stress, pain, fatigue, and systematic review. Search and investigation of the eligible studies were performed by two independent researchers in terms of the inclusion criteria along with methodological quality assessment of the chosen studies.
3.2. The Selection Criteria of Studies
Initially, the abstract of papers was examined. Then, based on the inclusion criteria, the full text of the papers was inspected. The papers with these features were chosen for this meta-analysis: (1) the study should have been a randomized clinical trial (RCT) with pretest and posttest with control group; (2) the participants in the study should have had MS regardless of age, gender, types, and intensity of symptoms; (3) the study should have had reported pretest and posttest results in symptoms including depression, anxiety, stress, fatigue, or pain among PwMS; (4) the outcomes should have been evaluated using criteria with tested or reported psychometric features; (5) the study should have been done in Iran and published in a credible journal.
3.3. Measuring the Effect
The reported mean, standard deviation (SD), and sample size of the intervention plus control groups in studies were introduced in an Excel file and then inputted into RevMan 5.4.1 software for meta-analysis. The standardized mean difference (SMD) with confidence interval of 95% was used as a summary statistic for measuring the effect of intervention to calculate the outcomes measured by various assessment tools (25). In order to incorporate the heterogeneity of studies resulting from the variety in participants and interventions, weighting of studies was done based on the sample size and experimental errors, random effects model with inverse variance method (26).
4. Results
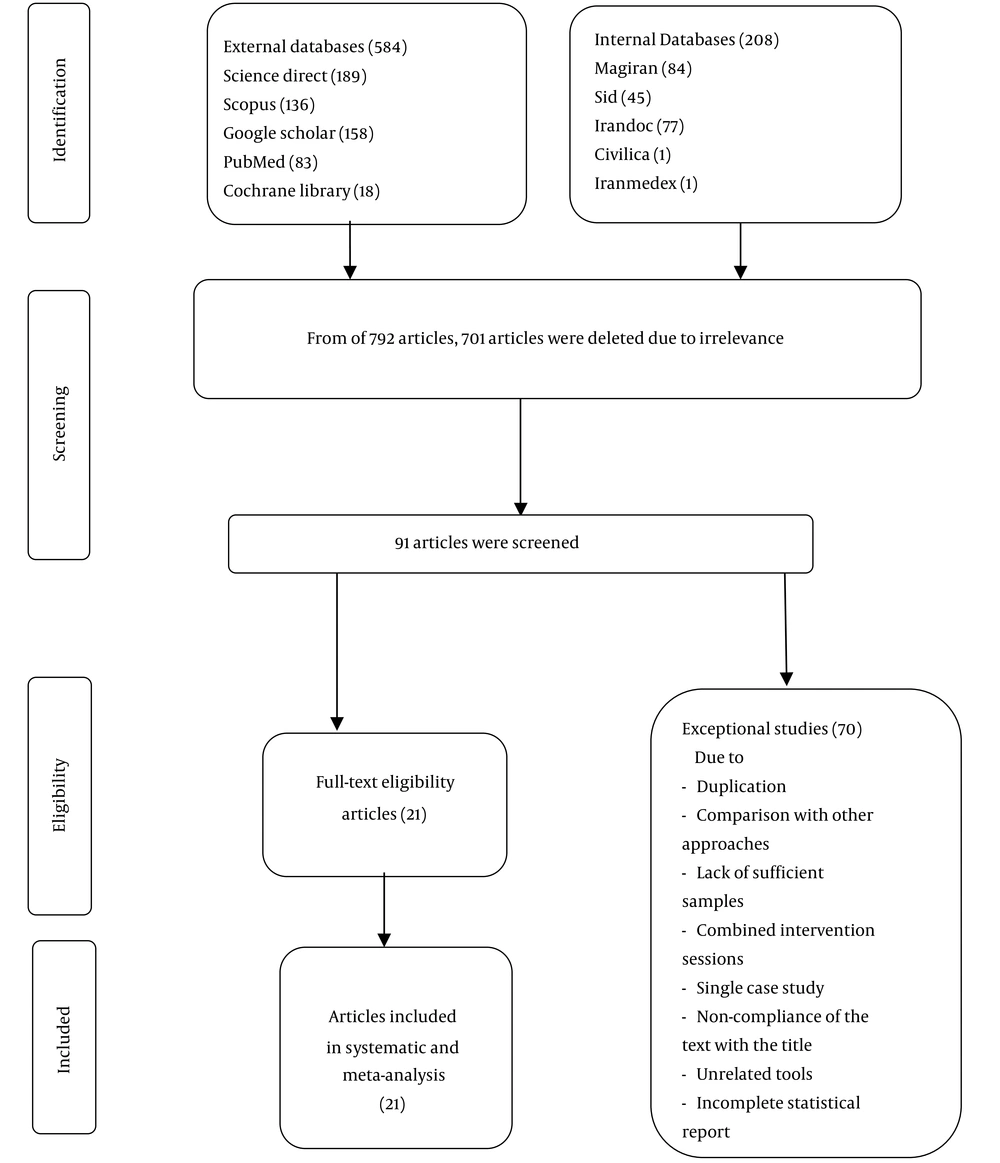
Overall, 792 papers were identified across databases (Figure 1). The search results of different databases were merged using EndNote software and similar studies were removed. After eliminating 701 irrelevant studies, 91 papers were screened based on the title and abstract. After reading the full text, other papers were excluded because of the reasons mentioned in Figure 1. Eventually, 21 papers fulfilling the inclusion criteria were chosen for the present review.
4.1. The Characteristics of Included Studies
The main characteristics of 21 eligible RCTs are summarized in Table 1. The included interventions were as follows: mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) four studies (27-30), ACT five studies (22, 23, 31-33), CBT eight studies (31, 34-38), MBSR and CBT four studies (39-44). Out of 21 studies, in 20 of them the sessions had been held as in person (21-23, 27-41, 43), and in one study it had been done using Telegram application (42). Fifteen studies had been done as 8-session, four as 10-session, and three as 9-session studies. The minimum sample size was 20 and maximum was 70 with the mean of 36.72. Four studies had been conducted in Tehran (33, 35, 42, 43), four in Isfahan (22, 23, 36, 45), and others in different cities of Iran. Out of the studies, in seven of them, the gender of patients was unspecified (22, 27, 30, 34, 35, 40, 41). In six studies, the age of patients had not been mentioned (32, 34, 36, 40, 42, 44), and in other studies the mean age of the patients was 35.06 years. The type of MS had not been mentioned in any of the studies.
| Authors (City) | Study Design | Study Period | Sample Size; Mean Age; Female (%); MS Types | Intervention/Treatment | Outcomes | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pouyanfard, et al. (Kerman) (44) | Semi-experimenl research with pretest posttest design and control group | Two-hour 8 sessions | 20; NR; 60%; NR | Mindfulness-integrated cognitive behavior (MICBT) | Anxiety and depression | MICBT significantly decreased depression and anxiety |
| Farhadi and Pasandideh (Rasht) (28) | Semi-experimenl research with pretest posttest design and control group | Two-hour 8 sessions | 30; NR, 100%; NR | Mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) | Depression, anxiety and stress | MBSR significantly decreased depression, anxiety and stress |
| Khalifeh-Soltani and Borhani (Isfahan) (22) | Semi-experimental research with pretest posttest design and control group | 8 sessions | 60; 53.40; NR; NR | Acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT) | Pain and stress | ACT significantly reduction pain and stress |
| Ensan et al. (Neyshabur) (27) | Semi-experimental research with pretest posttest design and control group | 8 sessions | 47; 38.8; NR; NR | Mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) | Fatigue | MBSR significantly improved fatigue |
| Mehraban et al. (Tehran) (43) | Semi-experimental research with pretest posttest design and control group | 10 sessions (1 session per week, each 120 minute) | 30; 29.20, 100%; NR | Cognitive-behavioral-based stress management | Anxiety | Cognitive-behavioral-based stress management training effective anxiety reduction |
| Zamani et al. (Tehran) (33) | Quasi-experimental research with pretest posttest design and control group | 8 sessions (twice a week) | 30; 31.36; 83%, NR | ACT | Anxiety | ACT significantly reduction anxiety |
| Mami et al. (Arak) (32) | Semi-experimental research with pretest posttest design and control group | 8 sessions | 29; NR; 62%; NR | ACT | Pain | ACT significantly reduction Pain |
| Ghodspour et al. (Semnan) (41) | Quasi-experimental research with pretest-postes and control group | 8 two-hour sessions | 30;36; NR; NR | Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) | Depression, anxiety, and stress | MBCT significantly decreased depression, anxiety and stress |
| Rajabi and Yazdkhasti (Isfahan) (23) | Quasi-experimental with pre-test, post-test and control group | Two-hour 8 sessions | 20; 34; 100%; NR | ACT | Anxiety and depression | ACT significantly reduction anxiety and depression |
| Karimi et al. (Tehran) (35) | Semi-experimental research with pretest posttest design and control group | 10 sessions | 30; NR; 100%; NR | CBT | Fatigue | CBT had effect on reducing the severity of fatigue |
| Kolahkaj and Zargar (Ahvaz) (29) | Semi-experimental research with pretest posttest design and control group | Two-hour 8 sessions | 48; 25.3; 100%; NR | MBSR | Anxiety, depression and stress | MBSR significantly reduction anxiety, depression and stress |
| Pahlavanzadeh et al. (Isfahan) (36) | Quasi-experimental research with pretest-postes and control group | 8 90-minute group sessions (a session per week) | 70; NR; 100%; NR | CBT | Stress, Anxiety, and depression | CBT significantly reduction stress and anxiety, depression |
| Purbahrami et al. (Urmia) (38) | Quasi-experimental research with pretest-postes and control group | Nine sessions of one and a half hours | 30; 30; 72%; NR | CBT | Stress, anxiety, and depression | CBT decreased stress, anxiety, and depression |
| Khazaeili et al. (Tehran and Qom) (42) | Quasi-experimental with pre-test, post-test and control group | Eight 2-h sessions | 30; NR; 100%; NR | Mindfulness based internet intervention (MBI) | Anxiety, depression, and fatigue | MBI reducing anxiety, depression, and fatigue |
| Shareh and Robati (Razavi Khorasan) (31) | Quasi-experimental with pre-test, post-test and control group | Ten 2-hour sessions | 68; 35.22; 32%; NR | CBT | Fatigue, and depression | CBT reducing fatigue and depression |
| Rezaeinasab et al. (Karaj) (37) | Semi-experimental research with pretest posttest design and control group | 8 sessions of one and a half hours | 30;40; 100%; NR | CBT | Pain | CBT significantly reduction pain |
| Namvar et al. (Bojnourd) (30) | Semi-experimental research with pretest posttest design and control group | Eight 2-hour sessions | 22; 39.5; NR; NR | MBSR | Anxiety, depression | MBSR significantly reduction anxiety, depression |
| Davoodi et al. (Ahvaz) (21) | Quasi-experimental with pre-test, post-test and control group | Eight 2-hour sessions | 30; 34.95; 66%; NR | ACT | Fatigue and Pain | ACT significantly reduction fatigue and pain |
| Ghaffarzadeh and Aghdasi (Tehran) (34) | Quasi-experimental with pre-test, post-test and control group | 10 sessions | 20; NR; NR; NR | CBT | Stress and anxiety | CBT decreased stress and anxiety |
| Asadnia et al. (Urmia) (40) | Quasi-experimental with pre-test, post-test and control group | Fourteen 60-minute weekly sessions | 32; NR; NR; NR | CBT | Anxiety and depression | CBT decreased anxiety and depression |
| Abbasi et al. (Isfahan) (39) | Semi-experimental research with pretest posttest design and control group | Eight 90-minute group sessions | 66; 33.47; 100%; ; NR | CBT | Fatigue | CBT decreased fatigue |
Characteristics of the Included Studies
4.2. The Results of Risk of Bias (ROB) Assessment
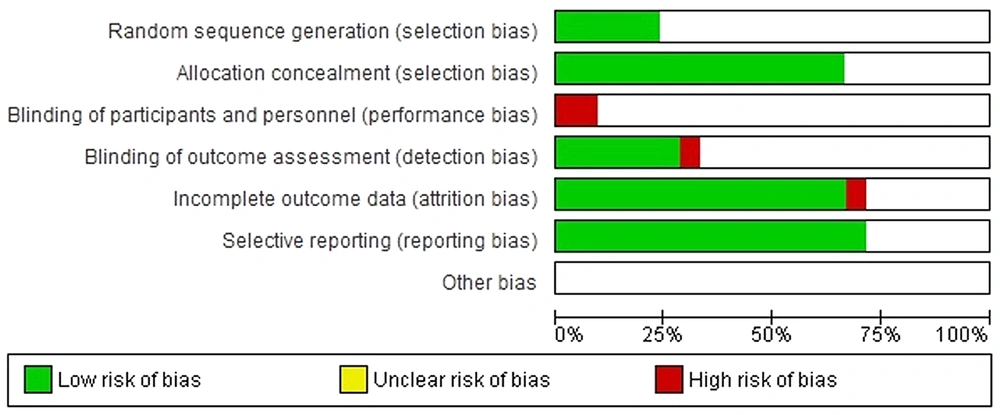
Two authors separately evaluated the risk of bias based on Cochrane guideline. Assignment concealment and bias of reporting were evaluated as low risk in 70% of studies, and unknown bias in 30%. In all studies out of seven domains, the domain related to blinding of participants and personnel in about 90% of the included clinical trials was evaluated as unknown risk of bias (RoB), as these studies had not reported sufficient information for judgment about blinding of participants and personnel. The bias of random sequence generation was evaluated as low risk in 20% of studies (23, 29, 31, 33, 44), and as unknown risk in 75% of studies (Figures 1 and 2).
4.3. The Results of Meta-analysis of Effects
4.3.1. Effects of CMAC on Depression
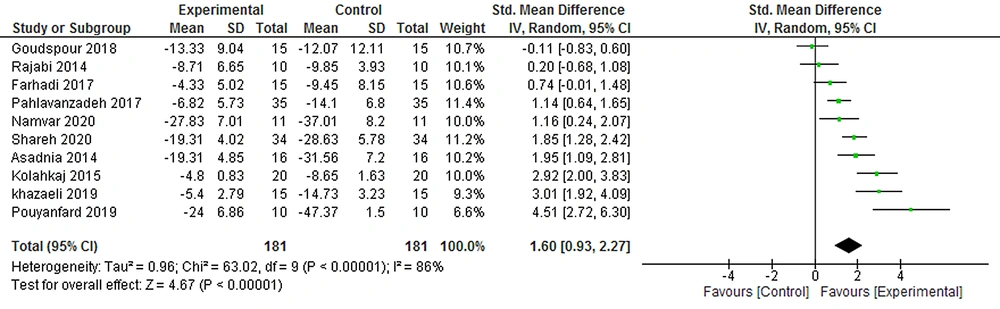
The first meta-analysis in which 10 clinical trials (181 participants) was investigated, SMD using the random effects model was 1.60 with confidence interval 95% (0.93, 2.27). Since the confidence interval did not cover zero, it suggests strong evidence of the positive effect of the therapy. I2 which is a criterion of heterogeneity representing the percentage of variance across studies (25) was 86%, indicating that 86% variance in estimating the effect of therapy was due to real differences of studies (heterogeneity) and only 14% was because of chance (Figure 3).
4.3.2. Effects of CMAC on Anxiety
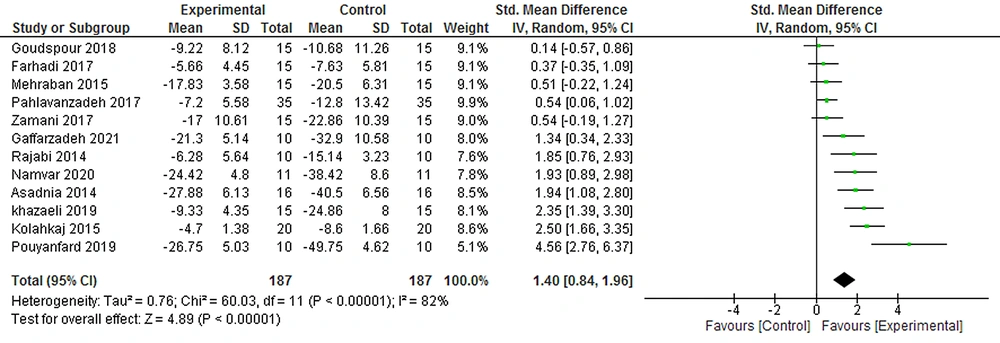
The meta-analysis on 12 studies and the largest sample size (187 participants) showed the effect of CMAC on anxiety reducing in the posttest in comparison to control groups (SMD = 0.49, 95% CI = [0.19, 0.80]) (Figure 4).
4.3.3. Effects of CMAC on Stress
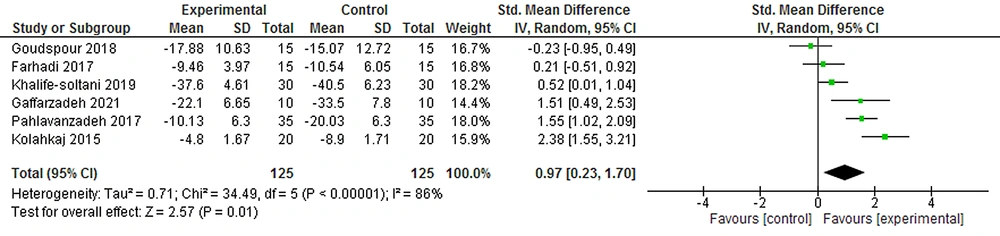
The meta-analysis on six clinical trials (125 participants) indicated that the overall effect of CMAC on stress reducing in the posttest (SMD = 0.97, 95% CI = [0.23, 1.70]) was statistically significant in comparison to the control groups (Figure 5).
4.3.4. Effects of CMAC on Fatigue
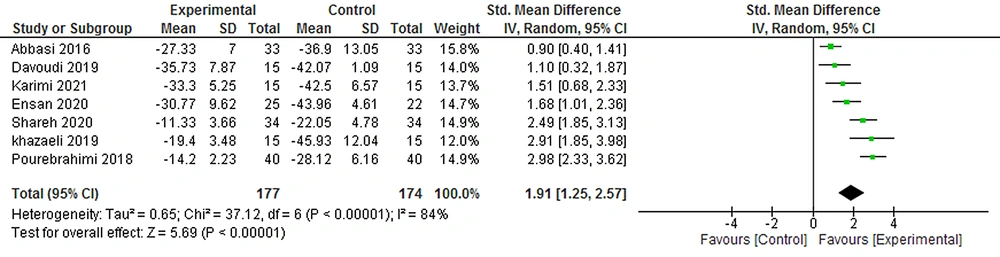
The effects of CMAC on reducing the fatigue symptoms were examined in seven studies (177 participants). This meta-analysis revealed the effect of CMAC on reducing fatigue in the posttest in comparison to the control groups (SMD = 0.19, 95% CI = [1.25, 2.57]) (Figure 6).
4.3.5. The Effects of CMAC on Pain
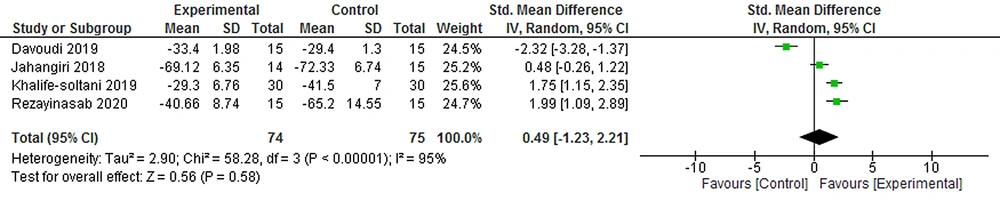
The meta-analysis on four clinical trials (75 participants) showed that the total effect of CMAC on pain reducing was not statistically significant in the posttest (SMD = 0.49, 95% CI = [1.23, 2.21]) compared to the control groups (Figure 7).
5. Discussion
This systematic review and meta-analysis evaluated 21 clinical trials evaluating the effects of CMAC on depression, anxiety, stress, fatigue, and pain of PwMS. The meta-analysis in the posttest showed that the effects of CMAC were considerable on reducing depression, anxiety, stress, and fatigue, but the effects were not notable for pain mitigation. The findings of this meta-analysis have been in line with previous meta-analysis findings for other populations, as they also reported the effects of CMAC on alleviating the symptoms of depression, anxiety, stress, fatigue, and pain. A meta-analysis on seven clinical trials showed considerable effect of CBT on mitigating the depression symptoms of PwMS posttest (46). Van Kessel et al. (47) compared CBT and relaxation therapies, and found that CBT lead to more significant improvement in the extent of fatigue, depression, anxiety, and stress of PwMS.
In interpreting the effectiveness of CBT, it can be stated that with increasing the awareness of patients about negative thoughts, cognitive errors, and with emphasis on active coping strategies such as attempts for doing tasks, in spite of presence of symptoms and ignoring them, the severity of psychological symptoms would diminish. This approach by correcting cognitive errors of the patient allows them to liberate themselves from do's and don’ts as well as idealistic thoughts. Further, existence of behavioral strategies which are a step for activating the patient helps them not to drown in patient role and get engaged with daily activities as much as possible (48).
Studies performed over the past two decades have provided massive data on supporting the usefulness and efficiency of mindfulness-based therapies on mitigating stress, depression symptoms, improving cognitive executive functioning of PwMS brains, and even other physical diseases such as chronic pain and cancer (49).
Han (24) in a meta-analysis by investigating 23 clinical trials reported the effects of mindfulness and acceptance-based therapies as significant on mitigating the symptoms of depression, anxiety, stress, and fatigue, but the effects for pain mitigation were not significant. Simpson et al. (50) observed the effect of mindfulness-based intervention on mitigating the symptoms of depression and anxiety from eight clinical trials, moderate effect on reducing stress from six clinical trials, and small effect on alleviating fatigue from seven clinical trials.
Carletto et al. (51) included 10 controlled clinical trials in meta-analyses, and found moderate effects of mindfulness-based interventions on mitigating the symptoms of depression and anxiety. In immediate posttest (nine studies for depression symptoms and eight studies for anxiety) as well as follow-up (seven studies for depression symptoms and six studies for anxiety), they observed large effects on stress mitigation in immediate posttest (five studies) and follow-up (four studies) as well as moderate effect on mitigating fatigue in the immediate posttest (eight studies) which diminished in the follow-up (six studies).
Training mindfulness is helpful in reducing mental preoccupations of individuals with negative self-assessment which leads to increased negative symptoms of patients. This technique trains patients to steer away from their self-critical cognitions, and observe them only with awareness with no judgment, without any need to separate from them, they would attach to them, and modify or control them (52).
Similar to and in line with the results of meta-analysis of efficacy of ACT on improving the PwMS symptoms, meta-analysis of Li et al. (53) also found that ACT had moderate to considerable effects on mitigating anxiety, depression, and stress, as well as improving hope in patients with cancer. Hughes et al. (54) also reported the effectiveness of ACT therapy on pain as trivial. ACT therapy is a therapeutic method in which individuals are trained to instead of mental and practical avoidance from disturbing thoughts and situations, have active and effective coping with thoughts and emotions, refrain from avoidance, and by establishing accessible goals and commitment to them, they cope with the condition (55). In explaining the findings of the present meta-analysis regarding the effectiveness of ACT therapy on mitigating the symptoms of PwMS, it can be stated that implementation of these therapeutic approach leads to development of psychological flexibility in PwMS, and this brings about changes in the suffering and mood of patients.
The studies included in the present meta-analysis were similar to previous studies of meta-analysis about CMAC for other populations in terms of types, duration, and form of CMAC intervention (24, 47, 53, 54). Similar to the studies incorporated in the present paper, CMAC was presented mostly in group and in eight weekly sessions in the previous meta-analysis papers. However, the difference of this meta-analysis with previous meta-analysis was in assessment of CBT, ACT, and MBSR for reducing the symptoms of PwMS; in previous studies, only one of the mentioned therapies had been examined but in our review involved more studies compared with previous meta-analyses for individuals with MS. Another difference of this study with previous meta-analysis was in the region of conducting the included studies. These studies had been performed in Iran. Generally, no larger effects were found in the current study.
5.1. Strengths and Limitations
Nevertheless, several strengths and limitations have taken into account in this review. The strong point of this study was that it has been the first meta-analysis on the effectiveness of CMAC on mitigating the symptoms of PwMS in Iran. One limitation was use of available sampling, small sample size, and not having follow-up test in the assessed studies, which would affect its generalizability. Another limitation was that the studies were only limited to Iran. None of the studies had specified the type of MS. In this study, the effectiveness of three therapeutic methods was evaluated, which can impair data collection because of considerable scattering. A meta-analysis (24) on four clinical trials also showed that MBSR therapy for mitigating the pain symptoms in PwMS was not significant in comparison to the control group. The reason of this similarity can be small sample size and limited studies. Most of the studies chosen for the meta-analysis had no follow-up stage. The available studies include different types of MBSR, ACT, and CBT. It is suggested that future studies deal with examining the effects of DBT as well.
5.2. Implications for Clinical Practice and Future Research
This review found evidence for the effects of CMAC on the mood of patients with multiple sclerosis. It is recommended that these treatments be applied to improve the quality of life of pwMS. We recommended to investigate the effectiveness of each treatment approach separately in future meta-analysis studies. Also Future studies should ensure that rigorous of methodology, mainly adequate randomization, allocation concealment, intention-to-treat analysis, and blinding of at least outcome assessors.
5.3. Conclusions
Current evidence suggests that CMAC showed efficacious on depression, anxiety, stress and fatigue in pwMS, however, no significant effect was found in the meta-analysis for effectiveness in reducing pain. Given the high prevalence and often associated mood symptoms in pwMS, the low cost of CMAC makes it a self-management option for reducing mood symptoms in pwMS. Future high-quality studies with follow-up evaluations are needed to support effects of CMAC on reducing symptoms common to pwMS and to examine intervention features that increase and maintain intervention effects.