1. Context
Breast cancer (BC) is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in women, making it the second most prevalent type of cancer worldwide (1, 2). The incidence of BC has been increasing in recent decades. This suggests that BC may soon become one of the leading causes of mortality among women of childbearing age, particularly in low- and middle-income countries (3). According to GLOBOCAN, an online database that predicts the worldwide incidence and death of cancer, 34.2% of all new cases of cancer in 2018 were BC cases (4). Furthermore, a significant number of women are diagnosed with BC at an advanced stage at a young age, where the disease is largely destructive and needs mastectomy (3). Due to the long-term exposure to the disease and its fatal nature, BC imposes a significant psychological burden on patients (5-7). Evidence affirms that BC women are more likely to develop depression, particularly during the first year of diagnosis (8, 9). In fact, the reduced physical capability, adverse effects of treatment, pain, stress, and fear of death, as well as financial problems and lack of social support, lead to destructive mental disorders in cancer patients (7).
Depression (as one of the most common psychiatric symptoms in BC patients) negatively affects the quality of life and puts patients at higher risk of evolving severe anxiety and stress (10). A review conducted by Wong-Kim and Bloom revealed that 11% of newly-diagnosed BC women struggled with severe depressive disorders (11). Relatively, Tegethoff et al. found that 10% to 32% of BC patients at a young age usually develop depression (12). In a study in China, the prevalence of depression was reported to be 26% in BC women (13). Also, another study in India estimated that 22% of BC women suffered from depression symptoms (14). Overall, nearly 30% of BC patients feel anxiety, depression, reduced functional capacity, and low self-esteem after the disease diagnosis. In recent years, the fast-increasing prevalence of psychiatric disorders in BC patients has been considered an important issue to take immediate action to eliminate these mental disorders to improve the overall well-being and quality of life in BC patients (15).
Several studies have found associated factors with developing depression among BC patients, including the long-term and painful process of chemotherapy treatment, mastectomy surgery, lack of family or social support, and lower educational level. Based on the literature, being correctly informed about BC diagnosis and the disease progression could improve patient quality of life and reduce the risk of depression (16, 17). Thus, it is essential to adopt appropriate strategies to control the psychological problems in BC patients and consequently provide more positive results for the physical health status of patients. Accordingly, this systematic review was conducted to determine the incidence of depression and its risk factors among women with BC in Middle Eastern countries.
2. Evidence Acquisition
A comprehensive literature search was conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) Statement 2009 (18).
2.1. Databases and Search Terms
We searched for English-language primary sources in Embase, Scopus, PubMed, and Web of Science databases from January 2000 to November 2021 using the following terms: (“Depressions” [Title] OR “Depression” [Title] OR “Depressive Symptoms” [Title] OR “Depressive Symptom” [Title] OR “Emotional Depressions” [Title] OR “Emotional Depression” [Title]) AND (“Breast Neoplasm” [Title] OR “Breast Tumors” [Title] OR “Breast Tumor” [Title] OR “Breast Cancer” [Title] OR “Mammary Cancer” [Title] OR “Mammary Cancers” [Title] OR “Malignant Neoplasm of Breast” [Title] OR “Breast Malignant Neoplasm” [Title] OR “Breast Malignant Neoplasms” [Title] OR “Malignant Tumor of Breast” [Title] OR “Breast Malignant Tumor” [Title] OR “Breast Malignant Tumors” [Title] OR “Cancer of Breast” [Title] OR “Cancer of the Breast” [Title] OR “Human Mammary Carcinomas” [Title] OR “Human Mammary Neoplasm” [Title] OR “Human Mammary Neoplasms” [Title] OR “Breast Carcinoma” [Title] OR “Breast Carcinomas” [Title]). Also, all the Middle East countries were included in our search.
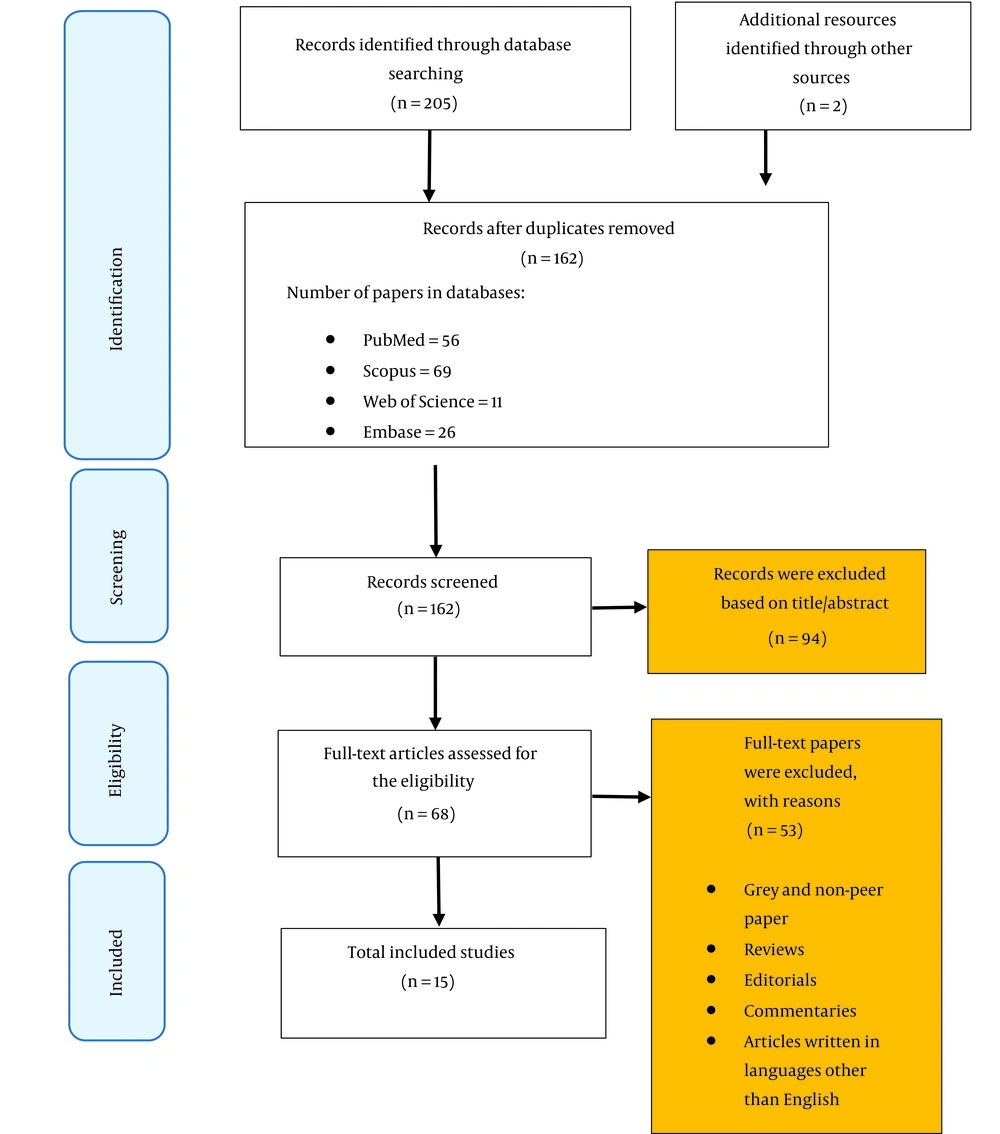
After the search, a total of 207 articles were identified. Duplicates were removed after importing the searched documents to EndNote software, and consequently, the number of remaining papers was reduced to 162. The paper titles and abstracts were screened by 2 independent research team members to check the data relevancy, which accordingly resulted in 68 articles. Thus, the evaluation procedure included papers that offered information on the prevalence of depression among women with BC or characteristics related to this condition. Conference abstracts and the cited works of the featured publications served as supplementary sources. The final number of papers included in the analysis was 15 after applying inclusion/exclusion criteria (Figure 1).
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
We analyzed quantitative data on the incidence of depression and associated factors among BC patients. Various study designs were considered, including cross-sectional, prospective, case-study, case-series, and cohort studies. In addition, we considered all publications that had complete English texts accessible between January 2000 and November 2021. Studies conducted in Middle Eastern countries were also included. However, interventional studies, case-control studies, reviews, letters to the editor, short reports, reports, and comments were not included. Inadequate research question data, as well as studies that primarily addressed diagnostic or therapeutic strategies or drug use, were also excluded from this analysis.
2.3. Quality Assessment
The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS), which is a standardized tool for assessing the quality of observational studies, was used to evaluate the quality of papers; 2 independent research members evaluated the quality of the included papers (19). In case of any discrepancy between the 2 reviewers, the consensus was achieved by consulting with a third party. Ascertaining exposure and outcomes, selecting research groups, and ensuring that they are comparable were the 3 basic categories under which the NOS elements fell. Each paper has a possible range from 0 to 10, with 0 being the lowest and 10 the highest. As a result, a score of 4 or less indicated a poor-quality article, while a score of 4 or more indicated a high-quality article.
2.4. Data Extraction
Two independent investigators entered the data achieved from the included studies into a data extraction form. The form items incorporated the author/authors’ name, publication date, study setting, study design, sample size, data collection tool, age, country, WHO region, quality of study, prevalence of depression, and quantitative data on its determinants (Table 1).
| No. | First Author, Year | Year | Type of Sample | Study Design | Total Sample | Prevalence (Depression) | Country | Age (Mean) | Questionnaire | Quality of Study | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Okati-Aliabad et al., 2022 | 2021 | Under treatment | Cross-sectional | 120 | 45 | Iran | 47.35 | HADS | High | (16) |
| 2 | Nazlican et al., 2012 | 2012 | Under treatment | Cross-sectional | 125 | 65 | Turkey | 49.2 | BDI | High | (17) |
| 3 | Alacacioglu et al., 2009 | 2009 | Under treatment | Cross-sectional | 55 | 9 | Turkey | 48.2 | BDI | High | (20) |
| 4 | Alagizy et al., 2020 | 2020 | Under treatment | Cross-sectional | 64 | 32 | Egypt | 52.29 | BDI | High | (21) |
| 5 | Alcalar et al., 2012 | 2012 | Under treatment | Cross-sectional | 110 | 34 | Turkey | 48.32 | BDI | High | (22) |
| 6 | Alquraan et al., 2020 | 2020 | Under treatment | Cross-sectional | 169 | 51 | Jordan | 49.12 | BDI | High | (23) |
| 7 | Bener et al., 2017 | 2017 | Under treatment | Meta-analysis | 678 | 320 | Qatar | 47.7 | BDI | High | (24) |
| 8 | Shakeri et al., 2016 | 2016 | Under treatment | Double-blind clinical trial | 98 | 86 | Iran | 47.60 | BDI | High | (25) |
| 9 | Slovacek et al., 2010 | 2010 | Under treatment | Prospective and cross-sectional | 41 | 15 | Turkey | 58 | The Czech version of the Zung self-rating depression scale | High | (26) |
| 10 | Hajian-Tilaki and Hajian-Tilaki, 2020 | 2020 | Treated | Cross-sectional | 305 | 202 | Iran | 49.5 | HADS | High | (27) |
| 11 | Hajj et al., 2021 | 2021 | Under treatment | Cross-sectional | 112 | 48 | Lebanon | 56.04 | HADS | High | (28) |
| 12 | Geyikci et al., 2018 | 2018 | Under treatment | Cross-sectional | 94 | 16 | Turkey | 50 | BDI | High | (29) |
| 13 | Hashemi et al., 2020 | 2020 | Under treatment | Cross-sectional | 190 | 19 | Iran | 46.3 | DASS-21 | High | (30) |
| 14 | Karakoyun-Celik et al., 2010 | 2010 | Treated | Cross-sectional | 120 | 23 | Turkey | 55 | BDI | Medium | (31) |
| 15 | Khan et al., 2016 | 2016 | Treated | Cross-sectional | 88 | 73 | Pakistan | 52.3 | A self-made questionnaire with 20 questions related to anxiety and depression, focusing on a mixture of psychological and physiological symptoms | Low | (32) |
Abbreviations: HADS, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale; BDI, Beck Depression Inventory; DASS-21, Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Scale, 21 Items.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
A meta-analysis as a statistical analysis was used to combine the quantitative results of different studies. Accordingly, aggregate data were obtained from the literature, which generally represented a summary of effect measures. However, due to heterogeneous studies that were planned to be synthesized, the random effects model of the meta-analysis was applied. This method calculated the sum of the weighted effect sizes of studies and divided it by the sum of the weightings. The statistical heterogeneity was calculated by the I2 test, and publication bias was assessed by the Egger test. Furthermore, due to the variability of estimates derived from different study settings and patients’ socio-demographic characteristics, the subgroup analysis was used. Accordingly, the study samples were divided into different subsets of participants based on the country, stage of treatment, questionnaire used for assessing depression, and quality of the study. Data were analyzed by a comprehensive meta-analysis and R software.
Furthermore, to determine the eligibility of studies for each synthesis, we tabulated the characteristics of different studies to facilitate the comparison of population, intervention, comparison, outcome (PICO) factors across them, synthesize related characteristics, and finally, categorize them for statistical synthesis purposes. This also allows us to perform the assessment of studies dealing with a certain meta-analysis more easily.
3. Results
A total of 207 articles were found during the initial search process. Afterward, the records were entered into EndNote software, and 45 duplicates were excluded. In the phase of screening, 162 articles were reviewed according to their titles/abstracts by 2 research team members, of which 56 articles were retrieved from PubMed, 69 from SCOPUS, 11 from Web of Science, and 26 from Embase databases. After the screening process, 68 relevant records remained and entered the assessment phase based on the eligibility criteria. Finally, after considering inclusion/exclusion criteria, 15 articles remained.
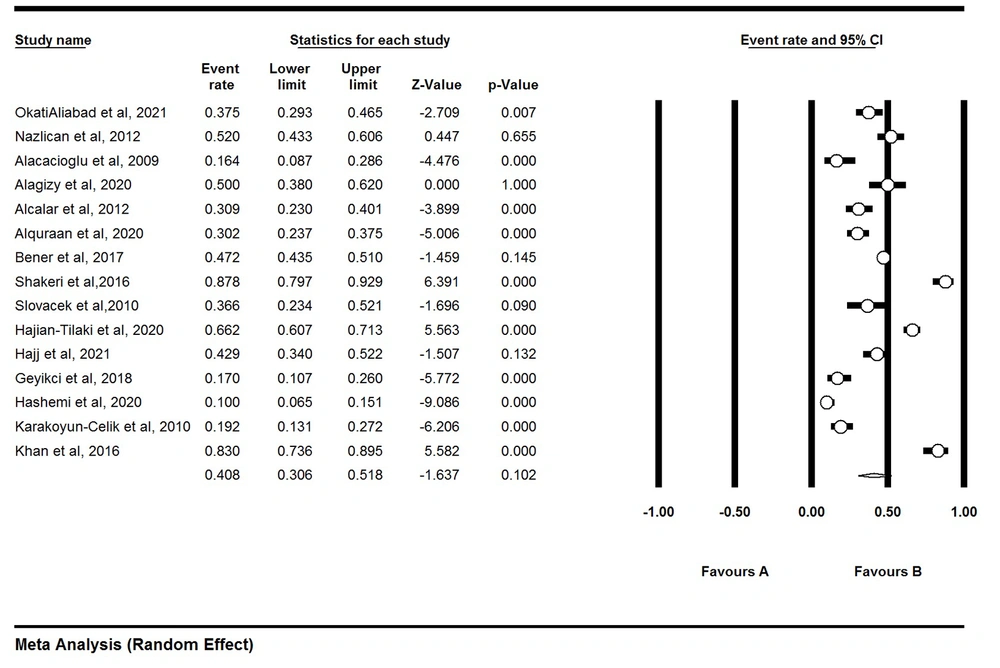
The findings of this study were provided based on the items of PRISMA. After reviewing the remaining 15 articles published from January 2000 to November 2021, the prevalence of depression was estimated at 40.8% for a total of 2369 women with BC (Figure 2).
3.1. Meta-analysis Based on the Country
The findings based on the analysis of countries revealed that the highest depression rate (83.9%) was among Pakistani women with BC (95% CI, 73.6 - 89.5), while the lowest depression rate (27.5%) was among Turkish women (95% CI, 17.2 - 40.9; Table 2).
| Countries | Effect Size and 95% Interval | Test of Null (2-Tail) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Point Estimate | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | Z Value | P-Value | |
| Egypt | 0.500 | 0.380 | 0.620 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| Iran | 0.494 | 0.191 | 0.801 | -0.031 | 0.975 |
| Jordan | 0.302 | 0.237 | 0.375 | -5.006 | 0.000 |
| Lebanon | 0.429 | 0.340 | 0.522 | -1.507 | 0.132 |
| Pakistan | 0.830 | 0.736 | 0.895 | 5.582 | 0.000 |
| Qatar | 0.472 | 0.435 | 0.510 | -1.459 | 0.145 |
| Turkey | 0.275 | 0.172 | 0.409 | -3.155 | 0.002 |
3.2. Meta-analysis Based on the Stage of Treatment
To enrich the systematic review, we divided study participants into patients who were under treatment and those who had completed their course of treatment. According to analysis, the latter group of patients had a lower prevalence of depression at 37% (95% CI, 27.3 - 47.7), while those who were under treatment revealed a greater rate of depression at 56.7% (95% CI, 22.2 - 85.7; Table 3).
| Groups | Number of Studies | Effect Size and 95% Interval | Test of Null (2-Tail) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Point Estimate | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | Z-Value | P-Value | ||
| Treated | 3 | 0.370 | 0.273 | 0.477 | -2.359 | 0.018 |
| Under treatment | 12 | 0.567 | 0.222 | 0.857 | 0.346 | 0.729 |
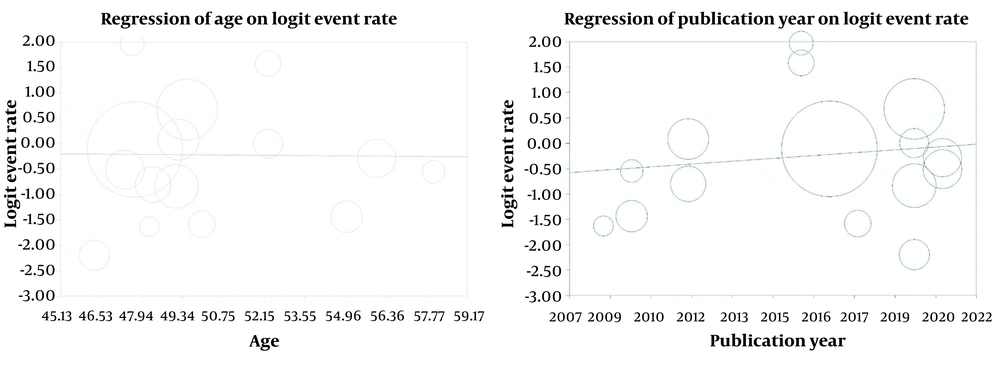
3.3. Meta-regression Based on the Year of the Publication and Age
A meta-analysis affirmed a significant direct relationship between depression in BC patients and the year of the study publication (P < 0.05); thus, a unit of increase in the study year resulted in an increase in patients’ depression scores. Furthermore, an indirect association between the patient’s age and depression prevalence was found, which was not statistically significant (Figure 3).
3.4. Meta-analysis Based on Tools and Quality of the Study
According to the data collection tools used in the included studies, almost 90% of the previous studies used Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) and Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) questionnaires, with a prevalence rate of 49.2% (95% CI, 30.5 - 68.2) and 38.2% (95% CI, 26.8 - 51.1), respectively (Table 4). During the assessment of study quality, it was found that 13 studies were of high quality, 1 study was of medium quality, and 1 study was of low quality (Table 4).
| Groups | Number of Studies | Effect Size and 95% Interval | Test of Null (2-Tailed) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Point Estimate | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | Z Value | P Value | ||
| Tool | ||||||
| BDI | 9 | 0.382 | 0.268 | 0.511 | -1.790 | 0.073 |
| DASS-21 | 1 | 0.100 | 0.065 | 0.151 | -9.086 | 0.000 |
| HADS | 3 | 0.492 | 0.305 | 0.682 | -0.077 | 0.938 |
| The Czech version of the Zung self-rating depression scale, a self-made questionnaire | 2 | 0.228 | 0.173 | 0.932 | 0.490 | 0.624 |
| Quality of the Study | ||||||
| High | 13 | 0.393 | 0.293 | 0.502 | -1.918 | 0.055 |
| Low | 1 | 0.830 | 0.736 | 0.895 | 5.582 | 0.000 |
| Medium | 1 | 0.192 | 0.131 | 0.272 | -6.206 | 0.000 |
Abbreviations: BDI, Beck Depression Inventory; DASS-21, Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Scale, 21 Items; HADS, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale.
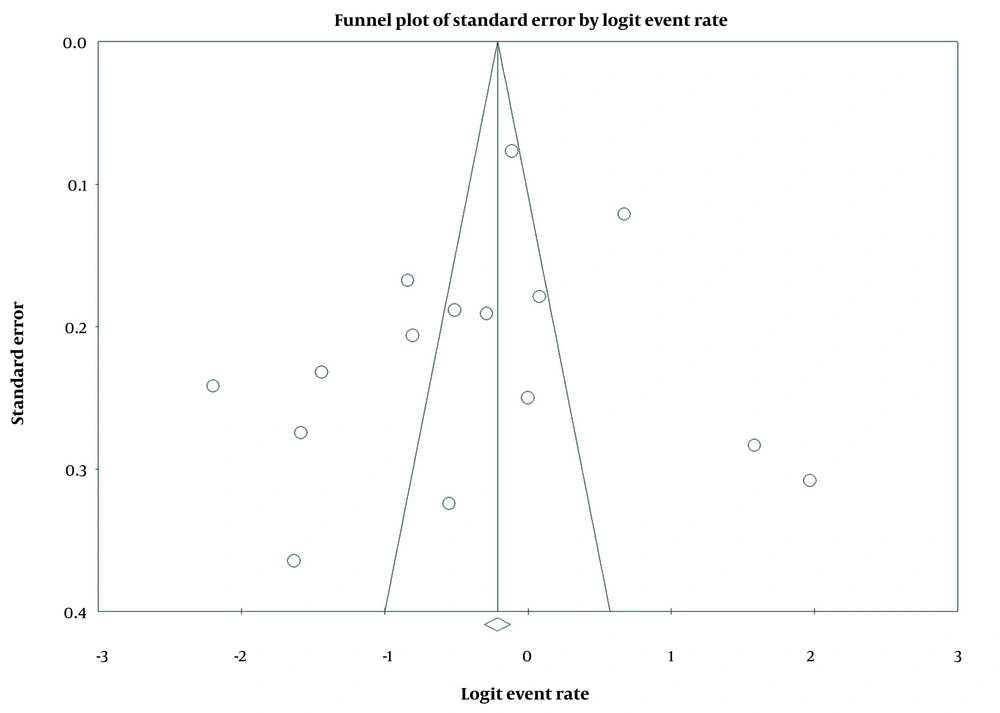
3.5. Publication Bias
According to Figure 4, the Egger statistical test showed that the P value was 0.87 (2-tailed), affirming the insignificance of the results, which proves the existence of no publication bias in the study.
4. Discussion
The main objective of this study was to systematically review the results of the existing literature to identify the depression prevalence among BC patients and explore its associated factors in Middle Eastern countries. After the review, we identified 15 articles that met our inclusion criteria. The vast majority of them used HADS and BDI questionnaires to calculate depression. Several factors associated with depression were found, including place of residence, stage of the disease treatment, and year of the study publication. These findings could facilitate the provision of scientific evidence and lead to a practical therapy plan that simultaneously considers psychological factors in treating BC survivors.
The average total score of depression reported in our review was 40.8%, which was higher than the rates estimated in both Indian and Malaysian studies, where it was reported to be 22% (24, 33). Similarly, Vahdaninia et al. found that 22.2% of BC patients experienced severe depression (34). Comparing the depression prevalence in different Middle Eastern countries confirmed that the prevalence rate in Egypt was 68.6%, which was much higher compared to other countries in the region, followed by Palestine (35.4%), Jordan (30.2%), and Lebanon (24.7%) (26, 27, 35).
In a systematic review of observational studies, Zainal et al. found that the prevalence of depression in Asian countries was much lower compared with the upper limit reported in Western countries, ranging from 1% to 56% (33). Related findings explain differences between geographical areas due to multi-factorial causes, including diversity in socioeconomic status, educational level, and difficulties in terms of access to health care and hospital referrals (35). Furthermore, cultural beliefs and women’s attention to their physical appearance might vary between different countries with diverse cultures. For example, the psychological impact of chemotherapy-induced alopecia in Middle Eastern populations was reported to be lower than their Western counterparts, which could be explained by the fact that many women living in Middle Eastern countries cover their hair and body; this can diminish the negative mental effects of mastectomy or alopecia (35). Another reason might be referred to religiosity and spirituality, which have been affirmed to be significantly associated with depressive symptoms (35). A study conducted by Hammoudeh et al. revealed that cancer patients with high levels of religiosity were less likely to suffer from depression (36). These results are consistent with a study that analyzed the impact of religion or spirituality on the emotional well-being of Jordanian and Palestinian cancer patients. Findings from a Palestinian study suggested that religious practice mitigated psychiatric illnesses in BC women (36). Similarly, a Jordanian study found that faith and a sense of reliance could help cancer patients endure painful treatments (36).
In our review, the prevalence of depression was not significantly different between various age groups. This finding is consistent with Haj Sadeghi et al., finding no statistical relationship between depression prevalence and patient’s age (35). On the other hand, the study by Hortobagyi revealed that younger women were at a higher risk of developing depression and other psychological disorders (37). The disparities in the samples and the variety of the persons included might account for the discrepancies. More research is needed to determine whether there is a correlation between age and depression.
According to our findings, the rate of depression was lower among patients who had finished therapy compared to those who were newly diagnosed or susceptible individuals during treatment. This finding is supported by a study that also pointed to the progression of the illness as a significant contributor to the onset of depression (38). Such results are also consistent with Naser et al., affirming that patients in advanced disease stages were more susceptible to developing depression (39). Similarly, Khan et al. emphasized that the disease stage was a significant predictor of mental health among BC patients; thus, patients who were at stage IV of the disease were more susceptible to anxiety, depression, and lower levels of quality of life (40). As confirmed by psychiatrist Elisabeth Kübler-Ross in 1969, there are 5 stages of grief after a BC diagnosis, including rejection, irritation, bargaining, depression, and acceptance. These emotions come up as the result of distractions of social roles, changes in life plans and activities, changes in body image, end-of-life challenges, and even financial problems imposed on patients due to the disease (41). Such findings were also discussed in similar studies, showing that patients undergoing radiotherapy had lower physical and mental well-being, probably due to the side effects of the treatment regimen. However, Al-Natour et al. in Yemen found that women who completed radiotherapy and received necessary care had better quality of life scores compared with those who faced challenges during the therapy process (42). These findings emphasize the need for therapeutic strategies, such as sustainable clinical monitoring and treatment of depression, in the treatment protocol for BC patients.
DASS-21, BDI, and HADS have been mentioned as useful screening tools for depression in cancer patients (23, 43). In our study, HADS and BDI revealed a similar prevalence of depression among patients, while DASS-21 revealed a lower prevalence. However, these scales can identify disease symptoms rather than diagnose major depression; thus, the applicability of mentioned instruments in screening programs has been confirmed (44). Alexander et al. also showed that at the cutoff score of 10, HADS had a sensitivity and specificity of 50% and 97% for depression, respectively (44). To sum up, the study revealed the reliability of HADS as a screening instrument for depression.
4.1. Limitations
This study has some limitations. First, we may miss some important studies since our search was restricted to papers written and published only in English. Second, we were unable to expand the generalizability of the results to all Middle Eastern countries due to a lack of data for some of the countries. Third, there was a gap in our data about the comparison of the depression prevalence in BC women by illness duration or treatment phase. Further, the article failed to discuss how various treatments affected the patients’ depression. Fourth, in our systematic review, we mentioned studies that used BDI, DASS-21, and HADS as screening tools for depressive symptoms, which mainly dealt with symptom scales rather than diagnosing major depression. Additionally, we did not take into account the positive past psychiatric history of the patients.
4.2. Conclusions
This systematic analysis discovered various characteristics that impact depression in women with BC in Middle Eastern countries, including Egypt, Iran, Jordan, Lebanon, Pakistan, Qatar, and Turkey; these findings have important clinical implications. One of the study implications for practice and policy is that there is an important need for the development of personalized interventions to manage the disease and treatment-related symptoms in a more proper manner through applying mental support activities that aim to promote both the psychological and physical health of patients with BC. To align appropriate services with patients’ needs, more attention should be given to geographical differences/consequent cultural disparities and the stage of the disease. Furthermore, it is recommended to consider the symptoms of depression among patients during a clinical treatment process; this can provide accurate assessments of the mental and social well-being of patients and consequently, inform them about their own care. Therefore, it is essential for cancer treatment facilities to include the evaluation and provision of mental health services as integral components of the treatment regimen, with the aim of preventing and managing depression in breast cancer patients.