1. Background
Stroke ranks first among chronic neurological diseases in adults in terms of importance (1). By 2030, the number of new stroke cases is projected to rise to 23 million (2). The sudden onset of clinical symptoms associated with this disease can lead to complications in multiple bodily systems (3). The impact of stroke often results in significant changes to an individual's mental state, cognition, mobility, self-care ability, body image, activity level, and overall sense of recovery (4).
Family caregiving is common due to the lack of sufficient supportive systems for stroke rehabilitation and care (5). The quality of life (QOL) of family caregivers is at risk, as they bear the mental and physical strain of providing post-discharge care (6).
The QOL of family caregivers is closely linked to their resilience, a crucial trait that facilitates effective adaptation to challenging living conditions and stressful situations (3). Nurses can play a supportive role for stroke survivors and their families by tailoring training to meet their specific needs, thereby improving their QOL (7). A support program has been developed to encourage collaboration between nurses and family caregivers in the care of stroke patients (8). The program's primary goal is to foster a collaborative care approach that promotes responsibility and cooperation among nurses, patients, and family caregivers. This initiative enables home care nurses to provide ongoing support at home with the assistance and training of family caregivers and stroke patients (9).
Nursing theories can enhance the comprehensiveness of nursing interventions. One valuable model for the care of stroke patients is Orem's self-care model (10). The self-care deficit theory, a core component of Orem's model, provides a foundation for nursing interventions and care plans aimed at supporting family caregivers of stroke patients (11).
The primary target group for stroke patient care is family caregivers, as stroke often leaves patients unable to care for themselves. The self-care support program (SSP) aims to empower patients and their family caregivers by helping them recognize and address their specific care needs based on their capabilities (12). For patients with debilitating disorders such as stroke, self-care that involves identifying the educational needs of family caregivers is as crucial as medical treatment (13).
The dimensions of self-care for family caregivers of stroke patients include assisting patients with eating, mobility, medication management, physical activities, prevention of acute and chronic complications, care of other bodily systems, and prevention of wounds and other health deviations (14).
The use of self-care programs based on Orem's model is a well-established approach for supporting family caregivers. These programs provide safe, non-pharmacological, non-invasive, and cost-effective methods for delivering care. Family caregivers are a cornerstone of stroke patient care, and Orem’s model offers a structured framework to guide their efforts (15).
This study focuses on a SSP designed for stroke patients and their family caregivers. The program includes components such as assessing caregivers' self-care needs, implementing nursing diagnoses, and evaluating the program's effectiveness. Stroke can significantly affect the physical, mental, and social well-being of patients, leading to a loss of independence and an increased care burden. This study was conducted with the hypothesis that the SSP, based on Orem's model, positively impacts the QOL of stroke patients, enhances the QOL of their family caregivers, and improves caregivers' resilience.
2. Objectives
This study aims to investigate the effectiveness of SSPs on the QOL and resilience of family caregivers of stroke patients.
3. Methods
3.1. Study Design
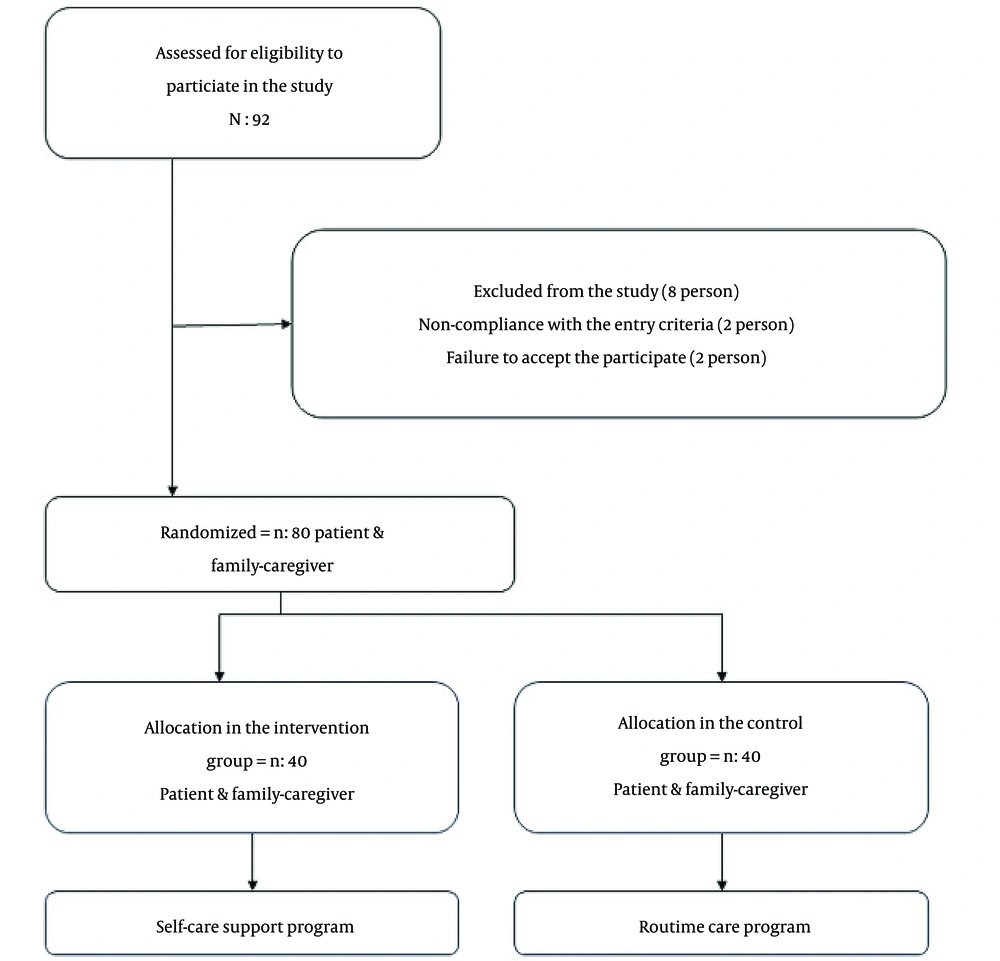
The present study was a clinical trial with a two-group pre-test-post-test design conducted at Besat Hospital of Hamadan in Iran from May to September of 2022. The sample size, under the supervision of the statistics professor, including 10% sample loss, 95% test power, and type 1 error and type 2 error, resulted in a total sample of 80 patients and 80 family caregivers who were placed in two groups of 40 intervention and control (16).
The intervention and control groups who met the inclusion and exclusion criteria were divided into intervention and control groups through 3-block randomization (Figure 1).
3.2. Inclusion Criteria
The inclusion criteria for this study were: (1) Family caregivers who have completed at least primary education, are over 18 years old, and have a family relationship with the patient (daughter, son, sister, brother, father, mother, or spouse); (2) caregivers must be the primary caregivers for the patient in the family, providing care for at least four days a week for a minimum of 2 months; (3) caregivers should not have a history of specific psychiatric disorders and should not be employed or associated with medical centers; (4) the family caregivers must remain the same in the hospital and at home and have access to a mobile phone; (5) patients who have experienced a stroke for the first time have a moderate level of dependency according to the Barthel criteria (including the ability to speak); (6) patients should currently be hospitalized in the neurology department; (7) patients should not have a history of mental illness based on medical documentation; (8) patients should not receive home care from a nurse other than the family caregiver; (9) at least two months must have passed since the use of the tissue plasminogen activator and the acute phase of the stroke.
3.3. Exclusion Criteria
The exclusion criteria for this study were as follows: (1) Any problem that leads to the termination of participation from the study at any time (such as death or transfer to another city); (2) lack of desire to continue participating in the study.
3.4. Data Collection
In this study, patients diagnosed with stroke and their family caregivers were admitted to the neurology department. The purpose and method of participation were explained to the participants to ensure their privacy. A questionnaire was used to collect demographic information and evaluate the functional abilities of patients and caregivers. After two months, Follow-Up Questionnaires were completed to assess the QOL of patients and caregivers, as well as caregivers' resilience. Self-care examinations were also performed.
The participants were divided into two groups: (1) An intervention group, and (2) a control group, based on their scores in the Barthel Index. The intervention group received face-to-face sessions at the neurology clinic to assess and support caregivers and patients in self-care. The control group followed the routine care program of the neurology ward. A total of 160 questionnaires were distributed, with a 100% response rate (Table 1).
| The Self-care Support Program | Context |
|---|---|
| Assessment | In this study phase, the self-care needs of stroke patients and family caregivers were investigated. The findings from the evaluation were used to prepare a plan for the self-care program (17). |
| Design | The self-care program is designed as an education plan, which includes selecting the appropriate type of education and nursing care (17). |
| Implementation | Depending on the patient's condition, after discharge, two training sessions were held at the time of visiting the clinic or at home. These 30-minute sessions were conducted based on the needs of patients and family caregivers (17). |
| Evaluation | Based on the achievement of goals in the field of reducing needs and increasing abilities, scoring was done, and re-completion of quality of life and resilience questionnaires was done for the target group based on their desire, face to face or by phone (17). |
3.5. Instruments
3.5.1. Barthel Index
The first part of the study focused on the patients, including demographic information and a questionnaire based on the Barthel Index, which evaluates ten basic activities of daily living (3). The scoring range for the Barthel Index is from 0 to 100, with 100 indicating complete independence. Scores between 100 and 60 suggest partial dependence, scores from 55 to 40 indicate moderate dependence, scores from 35 to 20 indicate severe dependence, and scores below 20 indicate total dependence.
Participants selected for this study were those with moderate dependence scores and the ability to speak. This questionnaire was completed upon the patient's entry into the study, prior to randomization. The validity and reliability of the Barthel Index have been confirmed in previous research by Tagharrobi et al. The agreement coefficient between evaluators for each item was above 0.6 (kappa) . The internal consistency coefficient of the tool was calculated to range from 0.96 to 0.99, and reliability was also confirmed through correlation methods with the Overall Scale (17, 18).
3.5.2. Stroke Specific Quality of Life Scale
Stroke patients completed the SS-QOL Questionnaire, which uses a Likert Scale ranging from 1 to 5. The total score is calculated by summing the scores from all 12 dimensions and 49 items, yielding a range of 49 to 245. Patients completed this questionnaire upon entering the study and before random allocation. The validity of the SS-QOL was confirmed by Ewert et al. in a 2007 study conducted in America. Additionally, Pedersen et al. in Norway evaluated the internal consistency of the questionnaire using Cronbach's alpha, which resulted in a coefficient of 0.89 (19, 20). In Iran, Azimi et al. assessed the reliability of the questionnaire, reporting a Cronbach's alpha coefficient of 0.95 and a retest correlation rate of 0.68 after three weeks (21).
3.5.3. SF-12 Quality of Life
This questionnaire consists of 8 subscales. The overall QOL score is categorized as good (37 - 48), average (25 - 36), or poor (12 - 24) based on the total score. Kontodimopoulos et al. confirmed the construct validity and reliability of the SF-12 in Greece, reporting Cronbach's alpha coefficients of 0.85 and 0.75, respectively (22). In Iran, Montazeri et al. also validated the questionnaire, with the test-retest method confirming its desirable reliability (23).
3.5.4. Family Caregivers’ Resilience Scale
The Resilience Questionnaire consists of 66 items that assess family resilience across three areas: Communication and problem-solving, social and religious resources, and acceptance. This tool uses a Four-Point Likert Scale ranging from strongly disagree (1) to strongly agree (4). The total score, summing all dimensions, ranges from 66 to 264. Sadat Hosseini and Hosseinchari standardized this scale in Iran, reporting a Cronbach's alpha coefficient of 0.93 for the entire scale and subscale alpha coefficients ranging from 0.76 to 0.93 (24). Before the study commenced, the questionnaires were reviewed by faculty members, and their validity was confirmed by 10 nursing faculty members. The reliability of the questionnaires was tested by calculating the correlation coefficient, which was α > 0.9 in all cases.
3.6. Ethical Statement
This study is part of an approved thesis with the code 140106014209 at Hamadan University of Medical Sciences. Ethical approval was obtained from the Research Deputy Ethics Committee of Hamadan University of Medical Sciences (code: IR.UMSHA.REC.1401.240). Additionally, approval was secured from the Iranian Clinical Trials Center (registration number: IRCT20220903055859N1) before any intervention began.
3.7. Statistical Analysis
A database was created using Excel, and statistical analyses were performed with SPSS version 16. Mean and standard deviation were used to describe quantitative variables, while frequency and percentage were used for qualitative variables. Chi-square and Fisher's exact tests were employed to compare qualitative variables between groups. For data with a normal distribution, independent t-tests were used to compare means between the two groups, and paired t-tests were used to compare pre- and post-intervention means within each group. A homogeneity of variance test was also conducted due to the lack of significant differences in pre-test scores between the two groups.
4. Results
4.1. Participant General Information
The two study groups showed no statistically significant differences in terms of age, gender distribution, marital status, income, co-morbidities, and disabilities among patients. Similarly, there were no significant differences in gender, relationship with the patient, income, care days, and education level among family caregivers (P > 0.05). Specific data are presented in Table 2.
| Variables and Groups | Intervention | Control | Chi-square Test | P-Value a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | ||||
| Sex | 2.212 | 0.263 | ||
| Male | 23 (57.5) | 18 (45) | ||
| Female | 17 (42.5) | 22 (55) | ||
| Marital status | 2.354 | 0.154 | ||
| Married | 33 (82.5) | 38 (95) | ||
| Single | 7 (17.5) | 2 (5) | ||
| Income | 2.412 | 0.372 | ||
| Low | 14 (35) | 20 (50) | ||
| Medium | 5 (12.5) | 3 (7.5) | ||
| Much | 21 (52.5) | 17 (42.5) | ||
| Disease along | 2.520 | 0.392 | ||
| HTN | 10 (25) | 7 (17.5) | ||
| DM | 2 (5) | 4 (10) | ||
| HPL | 6 (15) | 10 (25) | ||
| HF | 3 (7.5) | 3 (7.5) | ||
| Multiple disease | 18 (45) | 12 (30) | ||
| Non-disease | 1 (2.5) | 4 (10) | ||
| Disabilities | 3.413 | 0.881 | ||
| Right hemiplegia | 7 (17.5) | 6 (15) | ||
| Left hemiplegia | 7 (17.5) | 6 (15) | ||
| Visual disorder | 5 (12.5) | 7 (17.5) | ||
| Mobility disorder | 6 (15) | 7 (17.5) | ||
| Urinary disorder | 6 (15) | 3 (7.5) | ||
| Multiple disorder | 9 (22.5) | 11 (27.5) | ||
| Family caregivers | ||||
| Sex | 1.251 | 0.371 | ||
| Male | 22 (55) | 17 (42.5) | ||
| Female | 18 (45) | 23 (57.5) | ||
| Family relationship | 2.546 | 0.770 | ||
| Spouse | 8 (20) | 8 (20) | ||
| Brother | 1 (2.5) | 0 | ||
| Sister | 1 (2.5) | 0 | ||
| Parents | 1 (2.5) | 1 (2.5) | ||
| Children | 23 (57.5) | 26 (65) | ||
| Others | 6 (15) | 7 (17.5) | ||
| Education level | 2.654 | 0.265 | ||
| High school | 26 (65) | 22 (55) | ||
| Diploma | 3 (7.5) | 8 (20) | ||
| Master's & bachelor's degree | 11 (27.5) | 10 (25) | ||
| Income | 3.738 | 0.154 | ||
| Low | 10 (25) | 10 (25) | ||
| Medium | 20 (50) | 21 (52.5) | ||
| Much | 10 (25) | 9 (22.5) | ||
| Care days | 2.421 | 0.930 | ||
| < 2 days in week | 4 (10) | 6 (15) | ||
| 2 - 5 days in week | 1 (2.5) | 6 (15) | ||
| > 5 days in week | 35 (87.5) | 28 (70) |
Abbreviations: HTN, hypertension; DM, diabetes mellitus; HPL, hyperlipidemia; HF, heart failure.
a Significant: P < 0.05.
4.2. Scores of Stroke Specific Quality of Life, SF-12, and Resilience
In the control group, certain aspects of the patients' QOL improved before and after the intervention; however, these improvements were not statistically significant. A decrease was observed in various dimensions, including personality, self-care, and social roles. The total QOL score in the control group before and after the intervention was 83.77 ± 3.39 and 86.70 ± 8.25, respectively, with no statistically significant difference (P = 0.065). Conversely, the intervention group experienced significant improvements across all quality-of-life dimensions. The total QOL score in the intervention group before and after the intervention was 83.95 ± 1.43 and 119.72 ± 4.54, respectively (P < 0.0001). Detailed data are shown in Table 3.
| Variables | Intervention | Control | P-Value | F a | Statistical-Test b | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Intervention | After Intervention | Before Intervention | After Intervention | Intervention | Control | |||
| Energy | 5.42 ± 0.54 | 7.00 ± 1.10 | 5.42 ± 0.67 | 5.67 ± 0.82 | < 0.0001 | 0.057 | 1.312 | 48.162 |
| Family role | 5.02 ± 0.89 | 7.02 ± 1.04 | 5.17 ± 0.95 | 5.32 ± 1.04 | < 0.0001 | 0.061 | ||
| Speaking | 8.72 ± 0.81 | 12.80 ± 1.28 | 8.82 ± 1.05 | 8.87 ± 1.11 | < 0.0001 | 0.076 | ||
| Mobility | 10.35 ± 0.62 | 15.65 ± 1.40 | 10.27 ± 0.64 | 11.10 ± 1.15 | < 0.0001 | 0.081 | ||
| Creation | 8.40 ± 0.49 | 12.67 ± 1.34 | 8.15 ± 0.69 | 8.15 ± 0.92 | < 0.0001 | 0.077 | ||
| Personality | 4.87 ± 0.51 | 7.25 ± 1.12 | 5.15 ± 0.86 | 4.5 ± 1.19 | < 0.0001 | 0.056 | ||
| The self-care | 8.62 ± 0.74 | 11.57 ± 1.33 | 8.35 ± 0.80 | 7.55 ± 1.19 | < 0.0001 | 0.069 | ||
| Social role | 10.37 ± 0.62 | 15.02 ± 1.40 | 10.45 ± 0.93 | 9.72 ± 1.39 | < 0.0001 | 0.051 | ||
| Thinking | 8.62 ± 0.80 | 12.27 ± 0.93 | 8.45 ± 0.84 | 11.10 ± 1.42 | < 0.0001 | 0.082 | ||
| Upper limb function | 4.82 ± 0.67 | 7.90 ± 1.00 | 4.90 ± 0.63 | 5.52 ± 1.35 | < 0.0001 | 0.059 | ||
| Visual | 4.72 ± 0.45 | 7.92 ± 1.07 | 4.70 ± 0.51 | 5.20 ± 0.93 | < 0.0001 | 0.078 | ||
| Working power | 3.97 ± 0.15 | 5.62 ± 0.92 | 3.92 ± 0.26 | 3.97 ± 0.27 | < 0.0001 | 0.056 | ||
| Total score | 83.95 ± 1.43 | 119.72 ± 4.54 | 83.77 ± 3.39 | 86.70 ± 8.25 | < 0.0001 | 0/065 | ||
a Homogeneity of variance test.
b Independent t-test.
As shown in Table 4, there were no statistically significant differences in the quality-of-life dimensions for family caregivers in the control group. For instance, emotional problems and mental health showed a decline, and the total QOL score before and after the intervention was 17.30 ± 1.60 and 18.17 ± 2.45, respectively (P = 0.096). However, in the intervention group, all quality-of-life dimensions improved significantly. The total QOL score before and after the intervention in this group was 17.70 ± 1.11 and 25.37 ± 2.31, respectively (P < 0.0001).
| Variables | Intervention | Control | P-Value | F a | Statistical-Test b | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Intervention | After Intervention | Before Intervention | After Intervention | Intervention | Control | |||
| General understanding of your health | 1.62 ± 0.49 | 2.20 ± 0.66 | 1.52 ± 0.50 | 1.62 ± 0.49 | < 0.0001 | 0.074 | 46.841 | 46.841 |
| Physical performance | 2.50 ± 0.87 | 4.10 ± 1.27 | 2.60 ± 1.03 | 3.10 ± 1.35 | < 0.0001 | 0.053 | ||
| Physical health | 3.00 ± 0.90 | 3.45 ± 0.56 | 2.87 ± 0.85 | 3.05 ± 0.84 | < 0.0001 | 0.068 | ||
| Emotional problems | 3.12 ± 0.64 | 3.65 ± 0.50 | 3.00 ± 0.78 | 2.97 ± 0.65 | < 0.0001 | 0.071 | ||
| Physical pain | 1.45 ± 0.50 | 2.55 ± 0.51 | 1.42 ± 0.50 | 1.50 ± 0.50 | < 0.0001 | 0.082 | ||
| Social performance | 1.15 ± 0.36 | 2.12 ± 0.57 | 1.12 ± 0.33 | 1.22 ± 0.42 | < 0.0001 | 0.069 | ||
| Vitality and vital energy | 1.52 ± 0.50 | 2.22 ± 0.61 | 1.47 ± 0.50 | 1.50 ± 0.50 | < 0.0001 | 0.323 | ||
| Mental health | 3.32 ± 0.52 | 4.95 ± 1.01 | 3.27 ± 0.50 | 3.20 ± 0.82 | < 0.0001 | 0.520 | ||
| Total score | 17.70 ± 1.11 | 25.37 ± 3.31 | 17.30 ± 1.60 | 18.17 ± 2.45 | < 0.0001 | 0.096 | ||
a Homogeneity of variance test.
b Independent t-test.
As shown in Table 5, a decrease was observed in the control group of family caregivers in dimensions such as communication, problem-solving, and religious and social resources.
| Variables | Intervention | Control | P-Value | F a | Statistical-Test b | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Intervention | After Intervention | Before Intervention | After Intervention | Intervention | Control | |||
| Communication and problem-solving | 87.37 ± 2.28 | 132.3 ± 6.70 | 86.97 ± 2.55 | 81.30 ± 3.42 | < 0.0001 | 0.078 | 1.436 | 47.758 |
| Social religious resources | 25.75 ± 1.56 | 44.2 ± 1.86 | 25.35 ± 1.58 | 25.92 ± 2.45 | < 0.0001 | 0.063 | ||
| Accepting the problem | 17.12 ± 0.82 | 27.7 ± 1.99 | 16.82 ± 1.11 | 17.02 ± 1.21 | < 0.0001 | 0.059 | ||
| Total score | 130.25 ± 2.81 | 194.20 ± 9.15 | 129.15 ± 3.40 | 124.25 ± 5.31 | < 0.0001 | 0.12 | ||
a Homogeneity of variance test.
b Independent t-test.
Additionally, the total resilience score in the control group decreased from 129.15 ± 3.40 to 124.25 ± 5.31 after the intervention (P = 0.12). However, in the intervention group of family caregivers, all dimensions of resilience, including the total score, showed significant improvement. The resilience score in this group increased from 130.25 ± 2.81 before the intervention to 194.20 ± 2.15 after the intervention (P < 0.0001).
5. Discussion
The results of this study showed that QOL scores for patients in the control group exhibited no statistically significant difference before and after routine care. However, in the intervention group, QOL scores significantly improved across all dimensions, enhancing the patients' overall QOL. Family caregivers’ QOL scores did not show a statistically significant difference in the control group, with declines observed in aspects like emotional problems and mental health. Conversely, in the intervention group, QOL scores significantly improved across all dimensions, suggesting that the SSP effectively enhanced caregivers' overall QOL.
In terms of resilience, family caregivers in the control group exhibited no significant changes in resilience scores before and after the intervention, with some decline observed. In contrast, resilience scores significantly improved in the intervention group, demonstrating the effectiveness of the SSP in enhancing caregivers' resilience.
These findings are consistent with those of Zangbari et al., who reported a statistically significant improvement in QOL scores following SSP intervention (P < 0.001) in the intervention group, while no significant differences were observed in the control group (25). Similarly, Yadegarfar demonstrated that proper education significantly improved QOL in stroke patients (26).
Pitthayapong et al. supported the idea that family caregivers participating in post-stroke care intervention programs acquired essential caregiving skills, improving work efficiency and reducing stroke complications in patients (9). Amraei et al. also found that educational programs for hemiplegic stroke patients reduced caregiver stress, anxiety, and depression, increasing their awareness and ability to adapt to caregiving roles (27). This enhanced their communication with patients and improved their QOL.
Behzadi et al. noted that caregiver resilience improves after support program interventions, influenced by factors like knowledge, social support, and family structure (28). Similar supportive programs for chronic conditions like mental disorders and heart failure have demonstrated improved long-term resilience for caregivers, reducing caregiving pressure and enhancing QOL. Fathani's study also confirmed that SSP interventions improve QOL for caregivers of heart patients (29).
The independent variable in this study was the SSP, with QOL as the dependent variable and resilience as an intermediate variable. A structural equation model was established to analyze and verify the causal relationships between these three variables. The results showed that family QOL had a direct positive effect on caregivers’ QOL and could also indirectly affect it through resilience. Resilience itself had a direct positive effect on caregivers’ QOL. Acting as an intermediary variable, resilience played a significant dual role by mediating the relationship between family QOL and caregiver QOL. In the process of adaptation and acceptance among stroke patients, resilience played a positive role during the self-psychological adjustment stage, serving as a source of strength for psychological transformation (30). Resilience, recognized as a protective factor for individual psychological well-being, has been identified as a mediating variable in numerous research studies (31, 32). This study further demonstrated that resilience had a practical intermediary effect, reinforcing its potential as a focus for nursing interventions.
The limitations of this research include non-cooperation from some caregivers and stroke patients during data collection, personal challenges when answering the questionnaire, unconscious biases in responses, and insufficient attention to cultural conditions. Despite these challenges, this study concludes that SSP significantly improves resilience and QOL for family caregivers, offering a practical framework for better caregiving outcomes.
5.1. Implications
This randomized controlled trial demonstrates SSP effectiveness for caregivers of stroke patients, with implications for nursing practice, research, policy, and education. The program improves QOL, resilience, and outcomes for patients while reducing caregiver burden. The findings highlight the need for resource investment and SSP integration into nursing practice.
The study recommends conducting additional clinical trials to evaluate SSP's impact on caregivers of other chronic diseases. Strategies such as practical training sessions and psychological support should be developed to foster family caregiver involvement, enhance their awareness, and ensure attention to cultural contexts. Healthcare managers should use these findings to design effective caregiver support strategies. The program developed in this study should be applied to patients and caregivers with similar conditions to maximize its benefits.
5.2. Conclusions
The findings indicate that implementing an SSP for family caregivers of stroke patients is effective in enhancing the well-being of both caregivers and patients. The program provides essential support, training, and guidance, enabling caregivers to manage daily activities and address mental, emotional, physical, and psychological challenges effectively. This study emphasizes the importance of family participation in patient care and underscores the value of nursing theories like Orem's self-care theory.