1. Introduction
Emotional problems are prevalent amongst the most common causes of disability. National institute of mental health (NIMH) reported that 13 million American adults (approximately 1 in 17) have a serious mental illness (1). Mental health disorders cause severe problems in life. People with high levels of depressive symptoms or depressive disorders are at risk of having academic and interpersonal difficulties. It is expected for these students to become cigarette smokers, use other substances and make an effort for suicide (2, 3). In the United States and Canada, accounting for 25% of all years of life lost to disability and premature mortality (4). Moreover, suicide is the 11th leading cause of death in the United States, accounting for deaths of approximately 30000 Americans each year (WISQARS, 2010). Iranian student population is also affected by depression, anxiety and stress. For example, the study of Najafikolyani et al. showed that 76% of students had stress, while 56% and 53% had depression and anxiety, respectively (5).
Mental disorders, such as depression and anxiety, have an effect upon people’s capacity to join and become involved in health-promoting behaviors. In turn, mental health arises prosperous performance of mental function, resulting in productive activates, fulfilling relationships with other people, and the ability to adapt to change and deal successfully with demanding or stimulating situations. Mental health is dependent on many factors, such as family and individual factors. Thus, attachment security plays an important role in emotional regulation and mental health (6). Bowlby underlined that loosing an attachment figure extends the likelihood of depression in adulthood (7, 8). Attachment researchers insist that the parental emotional negligence provides a basis for anxiety disorder (9).
Previous studies showed that adolescent attachment organization was a predictor of the antagonism (10), social competence (11-13), illicit drug use (14), depression (15), eating disorders (16), affective disorder, obsessive-compulsive, histrionic, borderline or schizotypal personality disorders, and self-reported avoidant, anxious and dysthymic personality traits (12). Keating, Tasca and Hill found that there was a negative relationship between anxious attachment and body esteem. They also concluded that attachment avoidance had an indirect negative relationship with body esteem through alexithymia (17).
Lee and Hakins (18) showed that anxious and avoidant attachment predicted depression and anxiety, therefore quality of attachment is an important factor in improving the power or capacity of individuals to tolerate unfavorable environmental conditions and enduring mental health (19). Also insecure attachment during puerility is a strong predictor of adulthood depression (20). Haddadi Koohsar and Ghobary Bonab (21) found that anxiety and depression of Iranian college students could be predicted by quality of attachment. Studies showed that depression and anxiety exists in students with anxious attachment more than individuals with dependent attachment (dependability of others). Meta-analysis of 100 studies indicated that there was a negative association between a secure attachment and anxiety and depression (22).
Clarifying the mechanisms by which attachment dimensions cause clinical symptoms such as depression, anxiety and interpersonal problems, has increasingly become a subject of interest (22). Dewitte, Houwer, Goubert and Buysse declared that the attachment of the internal working models influences strategies of emotion regulation (23). Maternal characteristics such as sensitivity, availability (e.g. the quality of being at hand when needed) and responsiveness make a secure basis for children. Having a secure basis prepares the person to experience and cope with difficulties. Also Bowlby, Roque and Verissimo, and Vallotton and Ayoub stated that the main source of variation in emotion regulation strategies was explained by sensitivity, availability and responsiveness (7, 24).
A number of studies have identified mediators between psychological distress and attachment. For example, Wei and colleagues (15) determine that affect regulation perform as mediator between attachment dimensions and negative mood in a sample of college students. In another research declared that emotion focused coping mediate in the relationship between attachment anxiety and body image disturbances, depression and problem eating, hence can assert that affect regulation strategies has role in mediating the relationship between attachment dimensions and both depressive and eating disorder (ED) symptoms (25, 26). Hilbert and Tuschen-Caffier (27) also found that binge eating was preceded by difficulty in regulating affect in females with Bulimia nervosa. Besharat and Shahidi confirmed the mediating role of positive and negative cognitive emotion regulation strategies on the relationship between attachment styles and alexithymia (28).
Therefore, we can propose that attachment insecurity is a rational motive for the development of maladaptive regulation, which leads to emotional problems (stress, anxiety and depressive symptoms). For instance, anxious individuals with attachment anxiety may experience maladaptive emotion regulation that may produce symptoms like arousal behavior.
Cognitive emotion regulation strategies are cognitive responses to emotion-eliciting special set of circumstances that consciously or unconsciously endeavor to make the individuals’ emotional experience or the event itself less severe or harsh or extreme (29-33). In the recent years, firm work has been done to describe the relationships between tendency to use certain strategies and a variety of disorders, including depression (29, 30), mania (31), generalized anxiety disorder (32), post-traumatic stress disorder (33), social anxiety disorder (34), and eating disorders (30, 35).
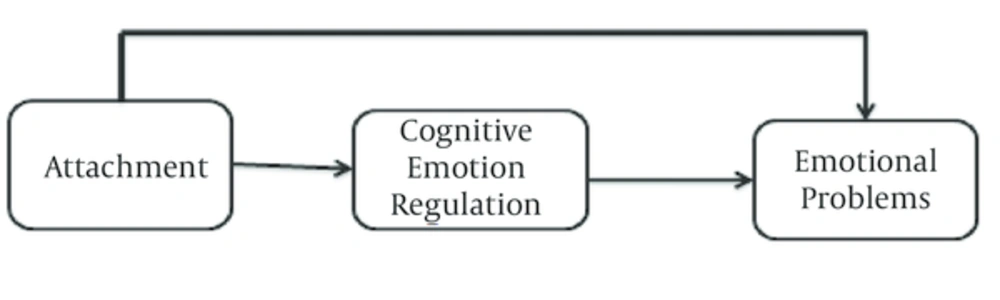
In this context, there is a wide variety of cognitive emotion regulation strategies that can be used to cope with emotionally arousing thoughts elicited by the experience of threatening or stressful life events. These strategies range from theoretically more adaptive strategies (e.g., positive refocusing, acceptance and positive reappraisal) to more maladaptive strategies (e.g., self-blame, ruminative thinking and catastrophizing). When investigating complex mechanisms such as the activation of inefficient attitudes and depressive symptoms under stress, it has been suggested to consider classes of strategies instead of focusing on one single cognitive strategy (36). No studies have examined the mediating role of cognitive emotion regulation to explain the relationship between attachment insecurity and emotional problems. The purpose of this study was to examine the mediating role of cognitive emotion regulation. We hypothesized that the association between attachment dimensions and emotional is mediated by cognitive emotion regulation (see Figure 1).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
The population in the current study consisted of college students in Tabriz University of Iran. Overall, 285 students aged between 22 and 26 years were selected randomly by multi-stage cluster sampling. In this study 64% of the participants were female and 36% were male; all of them were single and Shia Muslims. After preparation of assessment devices, questionnaires were administered to college students by a trained research assistant. Permission of instructors was sought to distribute questionnaires at the end of their classes. All contacted instructors showed good cooperation. In general, 285 students completed the questionnaires.
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. Cognitive Emotion Regulation Questionnaire (CERQ)
This questionnaire was constructed for people who have experienced negative events or situations. The cognitive emotion regulation questionnaire (CERQ) is a 36-item questionnaire consisting of the following nine conceptually distinct subscales, each consisting of four items and each referring to what someone thinks after the experience of threatening or stressful life event: self-blame, blaming others, rumination, catastrophizing, putting into perspective, positive refocusing, positive reappraisal, acceptance, and planning. Cognitive emotion regulation strategies were measured on a five-point Likert scale ranging from one (almost never) to five (almost always). Individual subscale scores were obtained by summing the scores belonging to the particular subscale (ranging from 4 to 20). Previous research showed that all subscales have good internal consistencies ranging from 0.68 to 0.86 (36). Numerous researchers have considered psychometric properties of this questionnaire in the Iranian population. For example Abdia, Tabanb and Ghaemian investigated the Persian translation of the CERQ questionnaire in students and found adequate construct validity (37). Dadkhah and Shirinbayan during year 2012 and Hasani during year 2010 reported that CERQ is an appropriate instrument for research and clinical purposes in Iran. Briefly, principal component analysis provided the original CERQ nine-factor model, which explained 74% of the variance. The degree of interrelations among the subscales was high (0/32 to 0/67) (38, 39). The internal consistency for the reappraisal subscale in this sample was satisfied (Cronbach’s alpha between 0.91 and 0.96).
2.2.2. Revised Adult Attachment Scale (RAAS)
Revised adult attachment scale was developed By Collins and Read (40). They provided the material of their questionnaire on the basis of Hazan and Shaver’ scale (1987). The revised adult attachment scale (RAAS) self-report assesses prototypes of adult attachment and their interpersonal skills. It consists of 18 statements on the basis of five-point Likert scale. The sub-scales extracted by factor analysis were dependency (measures how individuals trust and depend on each other and how they are accessible when it’s necessary), closeness (measures participant’s comfort about their intimacy with others) and anxiety (it assesses the rate of fear when subjects interact with others). The scale measures were secure, avoidant and ambivalent styles. Closeness accords with secure attachment, dependency conforms to avoidance style and also anxiety correlates with ambivalence attachment style. The test-retest reliability after two mounts of execution for three sub-scales (C, A and D) was 0.68, 0.71 and 0.52, respectively, and its validity was 0.95. Previous research on RAAS has shown that all subscales have good internal consistencies ranging from 0.80 to 0.83. Najarian normalized the scale in Iran. Factor analysis determined three subscales. Also, alpha coefficient for Iranian sub-scales was from 0.77 to 0.93 (41). In this study, internal consistency by Cronbach’s alpha turned out to be very satisfying between 0.86 and 0.88.
2.2.3. Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Scale (DASS 21)
Depression, anxiety and stress scale (DASS 21) was designed by Lovibond and Lovibond in 1995 to measure emotional distress in three sub categories of depression (e.g. loss of self-esteem/incentives and depressed mood), anxiety (e.g. fear and anticipation of negative events) and stress (e.g. persistent state of over arousal and low frustration tolerance) (39). It was a self-reporting questionnaire with 21 items (seven items for each category) based on a four-point rating scale. To calculate comparable scores with full DASS, each seven-item scale was multiplied by two. Items included, “I found it hard to wind down”, “I was aware of dryness of my month” and “I couldn’t seem to experience any positive feeling at all”. Participants were asked to rate how many of each of the items (in the form of statements) applied to them over the past week, from “0 = did not apply to me at all” to “3 = applied to me very much, or most of the time”. The higher the score meant the more severe the emotional distress. Internal consistency for each subscale was 0.91 for depression, 0.81 for anxiety and 0.90 for stress (42).
Much of the evidence of the research supported that the Persian version of the DASS-21 had satisfactory psychometric properties among the Iranian adult population. Asghari, Saed and Dibajnia tested the psychometric properties by using factor structure, reliability, convergent validity and discriminant validity of the DASS-21 Persian version among a non-clinical population. In another research, Sahebi, Asgari and Salari considered the validity of this scale in an Iranian sample. Results of these studies confirmed that it is a useful and beneficial inventory for Iranian psychological research and clinical settings (43, 44).
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive data and correlations were computed using SPSS 22. Means, standard deviations and correlation among the main variables are shown in Table 1. All attachment dimensions, cognitive emotion regulation and emotional problems were highly correlated. However, there were no significant correlations between positive regulation and attachment avoidance.
aP < 01.
3.2. Path Analysis
To test the hypothesized model, the Amos software (version 16) was used. To compare the hypothesized model to a null model, the comparative fit index (CFI) was used (45). Comparative fit index values greater than 0.95 were indicative of adequate fit (46). To assess the discrepancy between the estimated and population parameters, the root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA) was used. Root mean square error of approximation values below 0.05 indicate close fit, between 0.05 and 0.08 indicate fair fit, between 0.08 and 0.10 indicate mediocre fit, and above 0.10 indicate poor fit (47, 48).
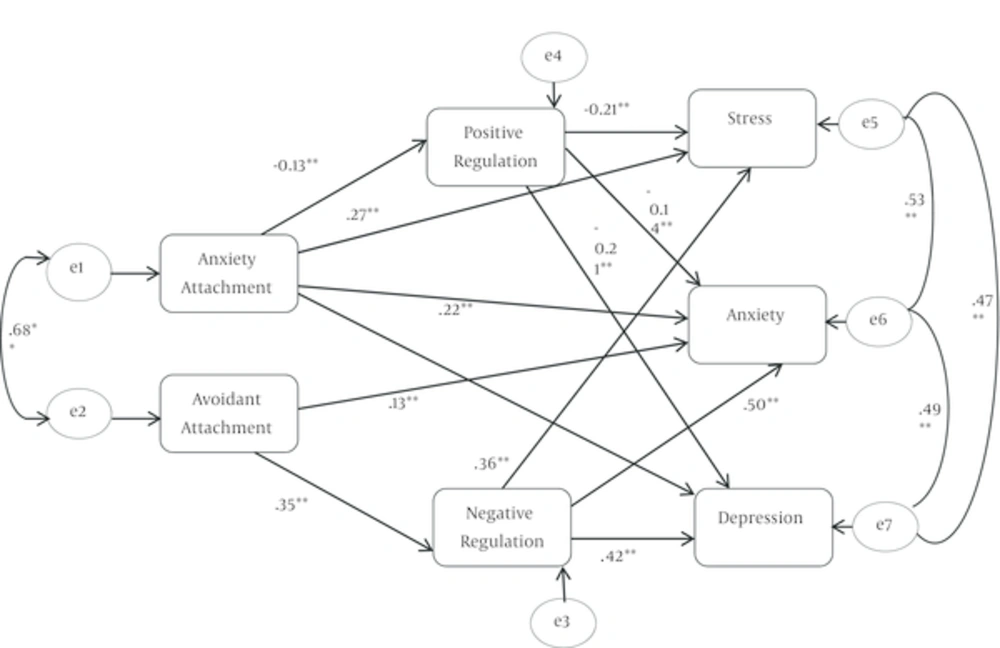
The model produced a fair fit with a significant chi square χ2 (29, N = 285) = 93.23, p b 0.001, CFI = 0.97, and RMSEA = 0.10. The CFI value suggested an adequate fit. However, the RMSEA indicated a mediocre fit. Table 2 shows the factor loadings from the final measurement model. Figure 2 demonstrates all the standardized path coefficients of the Model
| CMIN/df | P | df | CFI | TLI | IFI | RFI | NFI | RMSEA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.04 | 0.001 | 7 | 0.97 | 0.88 | 0.97 | 0.85 | 0.96 | 0.10 |
3.3. Indirect Effects
Consistent with the findings that attachment anxiety was a significant predictor of cognitive emotion regulation and emotional problems, the mean indirect effect from attachment anxiety through cognitive emotion regulation to emotional problems in the Model was significant, depression (b = 0.15), anxiety (b = 0.17) and stress (b = 0.09). The mean indirect effect from attachment avoidance through cognitive emotion regulation to emotional problems in the Model was significant depression (b = 0.03) and anxiety (b = 0.02).
4. Discussion
This study was designed to accomplish two goals, including, first determining the relationship between attachment styles and stress, anxiety and depression, second testing the mediating role of the cognitive emotion regulation strategies in relationship with attachment styles and emotional problems. The results of the study indicated that the relationship between attachment dimensions and stress, anxiety and depressive symptoms was significant. The outcomes are consistent with studies that provide evidence that attachment insecurity plays a role in clinically relevant indicators of distress, such as depression and interpersonal problems, through mediating psychological processes (15, 22, 49). Also, in line with the findings of the study, numerous studies show the mediating role of positive and negative cognitive emotion regulation strategies in the relationship between attachment styles and other emotional problems (28, 50).
In several studies, it has been found that attachment relationships interact with the development of stress-related psychopathology (51-53). One explanation may exist for the importance of attachment dimensions on cognitive emotion regulation and emotional problems. Secure attachment seems to be a protective factor. Protective factors are traits that decrease a future potential of growing an undesirable or negative psychosocial consequence later in life (54). The positive outcomes of many protective factors may not be clear; they may be apparent only under a state at a particular time, in a stressful condition (55).
In attachment theory, the mental constructs that guide attachment-behavior are internal working models. Internal models are an elaborated concept of representations of the self and others in relationships (56-58). The model of self represents beliefs about the chance that the self has to call forth (emotions, feelings, and responses) care from others and the model of other represents beliefs about the availability of others to supply feeling of freedom from worry or disappointment when needed (7) Greenberg (55) declared that attachment security may foster a protective factor against the development of negative psychosocial and emotional outcomes (stress, anxiety and depression). Earl and Burns suggested that attachment security acts as a protective factor against the development of anxious and aggressive behaviors at school age (59).
Indeed as results revealed, emotional responses in the context of attachment anxiety were correlated with emotional disorder symptoms. According to these results, attachment dimensions promote the use of adaptive strategies (e.g., positive refocusing, acceptance and positive reappraisal) or maladaptive strategies (e.g., self-blame, ruminative thinking and catastrophizing). Alternatively, the interpersonal aspect of insecure attachment causes uncontrollable feeling and so using maladaptive strategies. This tendency may exacerbate emotional problems. Certainly, emotion regulation has a key role in most theories of emotion (60-65). It serves as a reason behind how individuals experience, modulate, and organize emotion, and how such management has an effect upon human behavior (66).
For further explanation of this process, we can discuss that attachment system active against perceived threats and fear to regulate stress response (22). Attachment system promotes processes include primary attachment behaviors such as separation distress and subsequent proximity seeking (67). Experimental and naturalistic studies have demonstrated this in children, adolescents and adults (22, 68).
Bowlby (7), Bretherton and Munholland (68) believed that individuals become increasingly capable of effectively regulating their stress-responses by calling upon mental representations of internalized attachment figures so-called internal working models. A secure attachment is gained through experiences including having an attachment figure with a faithful manner, giving close and thoughtful attention, and responsive. Experiences of reassurance, a sense of safety and, ultimately, effective affect regulation are characteristics of a secure attachment. These experiences recur and are generalized as experience-expectant predictions of interactions and lead to a reduced reliance on external cues of safety (21). Thus, securely attached individuals have an efficient manner in dealing with stress and anxiety, either by seeking proximity to a reliable attachment figure in their actual environment or by mentally drawing upon past experiences in which stress was effectively co-regulated (52, 69). On the other hand, unsecure attachment promotes dysfunctional stress regulation, and the development of anxiety disorders, as indicated by the current study. Indeed, emotion regulation strategies play a mediator role between attachment and disorders.
Some limitations of the present study were as follows, first, the path analysis and modeling results imply the possibility of causality, but the design was cross sectional and correlational in nature. Also, all of the data was gathered by self-report measures that reflect consciously available self-evaluations, whereas, attachment interviews assess less consciously available states of mind (70). Replication of these results with other methods of data collection, such as interview would make stronger results (71).
The results suggest that attachment dimensions and cognitive emotion regulation are useful avenues for comprehending emotional problems. Improving security can be a worthy goal to inform the design and delivery of tailored clinical interventions to people with emotional problems. Clinicians may act better if they assess attachment style among their patients. Treatment of patients, who experience insecure attachment, needs consideration of negative cognitive emotion regulation, and on interpersonal connectedness in a therapeutic relationship.