Introduction
Cervicitis is a syndrome of cervical inflammation (1, 2) which is clinically defined as the presence of either mucopurulent discharge or cervical friability (easily bleeding induced by gentle passage of a swab through the Endocervical os) (1-6). More subtle signs of cervicitis include edema of the cervical ectropion (edematous ectopy) and vaginal pain (1, 3, 4, 6). Sacral backache, lower abdominal pain, and dyspareunia are other symptoms of cervicitis (4). Microscopic definitions involving the use of gram stain of cervical secretions includes either more than 10 white blood cells (WBCs) or more than 30 WBCs per high-power field (1, 3, 4, 6). Also, there is an evidence that it is asymptomatic in many cases (1, 2, 4). The incidence of cervicitis is as high as 30–45% in some sexually transmitted infections (STI) among clinic populations (4).
Cervicitis is most often caused by infection (1). Pathogens of Chlamydia trachmatis and Neisseria gonorrhea are the usual culprits (2-4). Less commonly, Mycoplasma genitalium, Mycoplasma hominies, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Trichomona vaginalis, and Herpes simplex Virus are implicated (2, 4). The causes of the rest of the cases remain unknown (3, 4, 7). However, in a few cases it may be attributed to chemical exposure or a foreign body such as a pessary (a device inserted into the vagina to support the uterus), cervical cap (a birth control device), or diaphragm. The condition may also be caused by an allergy to contraceptive spermicides or to latex in condoms (1).
Cervicitis can progress to Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID), ectopic pregnancy, chronic pelvic pain, tuboovarian abscess, damage and adhesion of tubal mucosa, and ultimately infertility (4, 5, 8) even in asymptomatic cases (2).
The initial therapy for cervicitis in conventional system is the use of antibiotics and antifungal therapies either orally and topically (4) leading to an imbalance in gut flora due to prolonged use of antibiotics (8). As a side effect, the increased drug resistance has reduced the therapeutic efficacy (4, 8, 9).
The failure of medical treatment (after two or three attempts) needs further surgical interventions by diathermy, cauterization, cryotherapy, and laser ablation which may cause further complications. None of these treatments not only provides a definite efficacy in spite of their relatively high cost, but also can lead to various adverse events. Due to the nature of these wide-ranging adverse effects, it is important to find effective therapies for genital infections which can be safer, more effective, easily available, and minimal adverse effects.
Complementary and Alternative Medicine (CAM) is progressively accepted and has been interested by the western mainstream medical community because of its less invasive, safer, effective, economical, and convenient therapies. The popularity of CAM has gradually increased, over the last few decades (8). Persian medicine (Iranian traditional medicine (ITM)) with thousands of years of history and hundreds of ancient texts is one of the oldest and richest alternative medicines.
Based on ITM literature, cervicitis is known as ″Qoruh- e- Rahem″, and characterized by pain and mucopurulent or bloody discharge. Qoruh is plural of Qarhah (Qorhah) which means wound in muscle tissue of the uterus and cervix. It can be developed by external causes such as bumps and falls (Sagtah) or internal causes such as dystocia, and flow of caustic humor (Insibab Khilt Hadd-e-Marari) to the uterus (10-14).
In ITM, Qarhah of the cervix can be diagnosed by inspection of cervix and observing the wound with endocervical discharge. Complications of Qoruh-e- Rahem include infertility and adhesion (10-14).
From ITM perspective, the treatment of cervicitis is a package of interventions, including lifestyle modification, medicinal plant therapies with different pharmacological therapeutic effects, and nondrug techniques such as massage (Dalk) and reflex therapy (Ghamz) used individually or in combination with each other.
The aim of the present study was to review the medicinal plants claimed to be effective on cervicitis based on the Iranian traditional medicine manuscripts that may be used as complementary and/or alternative to conventional treatments, based on the classical medicine, to find out more effective and safer treatment strategies.
Experimental
This study is investigated medicinal plants which were used for the treatment of cervicitis/ Qoruhe-e-Rahem with keywords of Qoruh-e-Rahem or Qarhah (Qorhah) in the Iranian Traditional Medicine literature. The herbs were searched and extracted from 7 main traditional medicine reference books including Liber Continent (Al-Havi ) of Rhazes (Abubakr Muhammad ibn Zakariyya al-Razi, 8th century AD), Canon of Medicine (Qanun fi al-Teb) of Avicenna (Ibn Sina,10th and 11th centuries AD) (10), Great Elixir (Exir Azam) of Azam Khan (10th century AD) (11), Treasure of the Khwarazm Shah (Zakhireh Kharazmshahi) of Jorjani (SeyyedIsmaeil Jorjani, 12thcentury AD) (12), Tohfat-ol-Momenin by Hakim Momen Husseini (17th century AD) (15), Storehouse of Medicaments (Makhzan-ol-Advieh) of Aghili Khorasani (18th century AD) (16) and Sharh-ol- Asbab of Nafis-ibn- Evas-e Kermani (15th century AD) (17) as well as other manuscripts written at various times during 10th- 18th centuries in both Arabic or Persian languages. Medicinal plants were categorized in Mofradat (simple ingredient) and Qarabadin (multi-component ingredient) (10, 11). Then, simple herbal drugs (Mofradat) were selected from extracted treatments
To find matches for old names in modern scientific classification, two botany references (16, 18-21) and electronic databases as well as the plantlist.org suggested by the research team were used. Moreover, the opinions of distinguished scholars of ITM were also taken into consideration (Table 1).
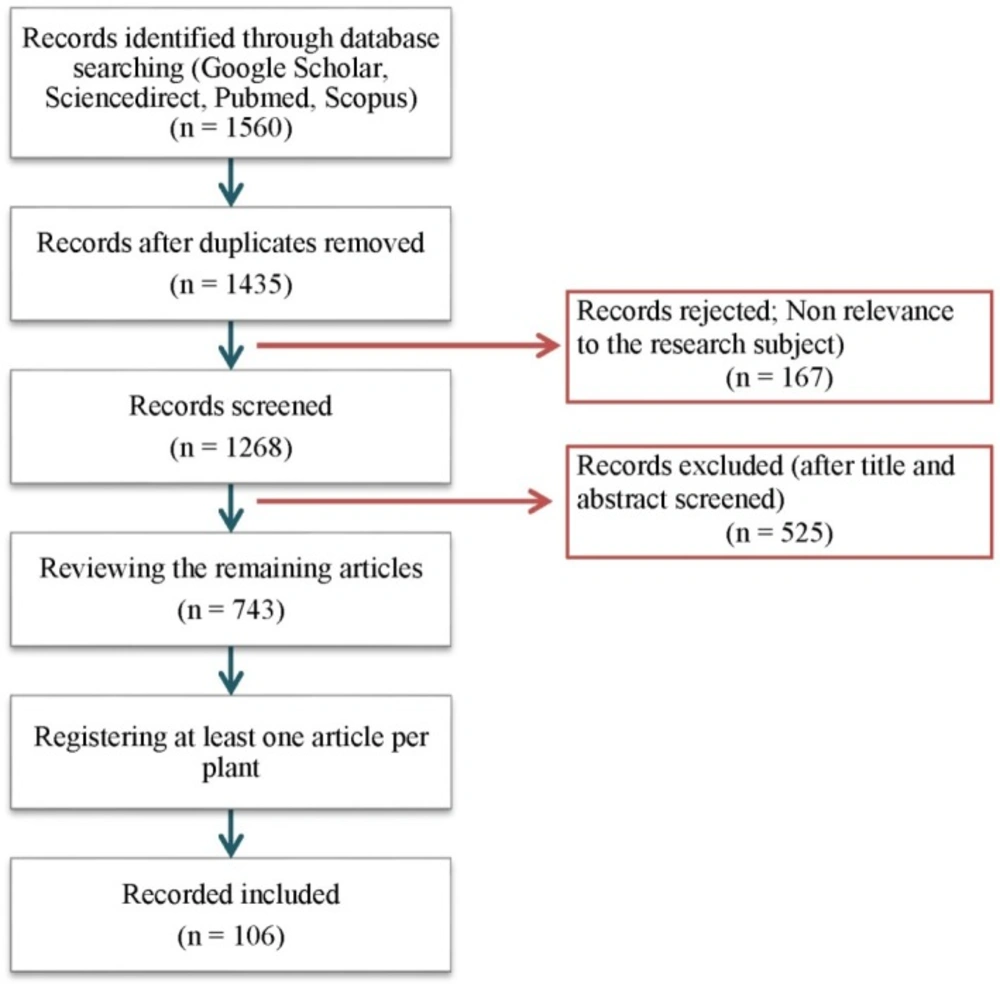
To investigate the pharmacological properties of the medicinal plants, electronic databases including Pub Med, Scopus, Google Scholar, and Sciencedirect were explored for each of these herbs. All retrieved articles which demonstrate the direct efficacy of these medicinal herbs or their mechanisms involved in cervicitis alleviation including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial, antibacterial, antifungal, wound healing and analgesic effects were carefully considered in this study. Bibliography in the electronic databases covered all articles published between years 2000 to 2016. The search terms were ‘‘cervicitis’’, ‘‘cervicitis, uterine’’, ‘‘uterine cervicitis’’, ‘‘cervicitides’’, ‘‘cervicitides, uterine’’ and ‘‘uterine cervicitides’’ in title and abstract as well as the name of each herb in the whole text (Figure 1).
Results and Discussion
After searching for plants effective against cervicitis (Qorohe-Rahem) in the 7 main Iranian Traditional Medicine texts, we reached 31 plants from 21 different families. Table 1, displays the medicinal plants used for the management of cervicitis in Iranian Traditional Medicine and all evidence confirming their efficacy are described individually in Table 2, 3 and 4.
The medicinal plants were categorized into 2 groups; 1) Mofradat which included simple ingredient herbal medicine, 2) Qarabadin which included multi component ingredient herbal medicines (containing 2 or more bioactive pharmaceutical substances) (10, 11, 22). Some routes of administrations for ITM drugs namely oral and topical included intravaginal administration (vaginal suppositories (Ferzajeh/farzaje, Sheiaf, Homoul, Zarour/Zarur), vaginal lavage/enema (Hoghneh)), external therapy (lotion (Tela), balm (Marham), cleansing (Estenja), steaming washing therapy and sitz bath (Abzan)) and rectal administration (retention enema and rectal infusion with liquid herbal medicine) (8, 22),
Ferzajeh and Homoul are two kinds of vaginal suppositories made of components that are kneaded and get dried in shade. Abzan is a traditional remedial sitz bath that is effective in treating gynecology disorders. In this procedure, the patient should sit in a tub filled with water in which a special plant is boiled before. Tela is a kind of lotion used topically. It is used on lower abdominal surface on uterine, pubic, external genitalia, and lumbosacral regions. The other form of drug administration is balm, which is used topically and is named Zemad in Iranian Traditional Medicine, containing some components and suitable liquid part, which makes it pasty. It needs to be dressed with a soft cloth. Cleansing with watery topical preparations is named Estenja (14, 22).
Myrtus communis
Leaves and fruits from Myrtus communis have been claimed to be effective for the management of cervicitis in different references of ITM. Analgesic (24), Antimicrobial (antibacterial, antifungal and antiviral) and antioxidant properties of compounds produced by M. communis have been reported in numerous studies. 1,8-cineole, linalool, eugenol, terpineol and terpinene as myrtle essential oils components have a good antibacterial effects against some gram positive and gram negative bacteria (25).
As demonstrated in several studies, the antioxidant capacity of plant extracts is strongly related to phenolic content.
This activity is not a property of a single phenolic compound, but it is widely attributed to different phenolic phytochemical constituents. Particularly, anthocyanins, flavonoids and phenolic acids seem to be responsible for the antioxidant capacity of Myrtus communis (25). Rossi et al. in their study revealed that M. communis exerts potent anti-inflammatory effects in-vivo and offers a novel therapeutic approach for the management of acute inflammation (26). The effects of the essential oil and methanolic extract of Myrtus communis on Trichomonas vaginalis have been shown in Abdollahy et al. study (27).
Juniperus Sabina
J. Sabina is from Cupressaceae family. Emami et al. have reported antioxidant activity of leaves and fruits of J. Sabina (abhal). Antimicrobial activity of this plant has been confirmed (28, 29).
Peucedanum officinale
Many phytochemical investigations on this genus have confirmed Peucedanum species are rich in essential oils and coumarins. Our review confirmed that some Peucedanum species could have therapeutic effects of anti-inflammatory (30), antioxidant, and antimicrobial (31) .
Commiphora opobalsamum
C. opobalsamum is a small tree (5 m in height) that is found in abundance and widespread on mountains around the holy places such as Makkah Al-Mukarama, Al-Madina Al-Munawara (Al-hijaz area, KSA), and Al-Quds (Palestine). In addition, it is native to other areas such as Oman, Yemen, and Somaliland. Anti- inflammatory, antioxidant, and analgesic effects of C. opobalsamum have been reported by Al-salami et al. (32).
Hyoscyamus sp.
Hyoscyamus niger of Solanaceae family, commonly known as henbane, is widely distributed in Asia and Europe. The pharmacological evaluation of methanolic extract of the seeds of H. niger showed that it possesses potent analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities. The major chemical components, e.g. coumarinolignans specifically cleomiscosin, which is present in the seeds of H. niger is involved in the anti-inflammatory activity of methanolic extract of the seeds (33).
Artemisia vulgaris
Antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory effects of this plant have been reported in the previous studies (34-36).
Polyporus officinalis
Laricifomes officinalis (Polyporus officinalis) is a wood-rotting fungus that grows on different hosts such as conifers. The mushroom is native to Europe, Asia, and North America. It has been used since the ancient times to treat sciatica, weakness of muscles, bronchitis, constipation, stomach and uterus pain, jaundice, fever, and insect bites. It also has diuretic and emmenagogue effects. The biological effects of L. officinalis including anti-viral (especially against smallpox, H5N1 influenza, and hepatitis C virus), anti-tuberculosis, anticoagulant immunomodulatory, and relieving dysmenorrhea, hemorrhoids, cough, and rheumatoid arthritis were confirmed for this fungus by studies performed in the recent decades (37).
Lowsonia inermis
Inhibitory action of henna against both gram negative and gram positive bacteria was proven (38). Chemical components of L. inermis have good antioxidant capacities and this species could be used as a potential source of new natural antioxidants (39).
Trigonella foenum-graecum
Leaves and seeds from Trigonella foenum-graecum has been claimed to be effective for management of cervicitis in different references of ITM. The anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial, analgesic, and wound healing effects of T. foenum-graecum have been reported (40-43). The presence of saponins and flavonoids as the major compounds in T. foenum-graecum may explain the anti- inflammatory activity of this plant (44).
Prangos ferulaceae
Antioxidant effect of P. ferulaceae was reported by Coruh et al. (45).
Apium graveolens
Anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and antioxidant effects of A. graveolens have been reported. Baananou reported essential oil and extracts of A. graveolens aerial parts have antiulcerogenic and antibacterial activities (46-48).
Malva sylvestris
In animal models, M. sylvestris presented antinociceptive effects and anti-inflammatory action (49, 50) in mucous membranes and in carrageenan-induced paw edema when applied topically. The antioxidant and radical scavenger properties of this herb (in-vitro) were presented by a study of Della Greca et al. M. sylvestris is effective as an anti-inflammatory agent when used locally in the skin (50). Antimicrobial effects of this plant also have been reported by Gasparetto et al. (49).
One study evaluated the effect of M. sylvestris topical cream on burn wound healing in the rats. (51).
Descurainia sophia
Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and analgesic activities of Descurainia sophia (flixweed) were attributed to the presence of phenolic compounds (52).
Allium porrum
Antimicrobial and antioxidant effects of A. porrum were reported by Mnayer et al. (53).
Boswellia carteri
The antimicrobial activity of the essential oil of B. carteri was individually evaluated against different microorganisms including fungi, gram-positive, and gram-negative bacteria strains (54). In one study B. carteri was used as a mixture with three plants for diabetic wound healing. The results of this study revealed this treatment is a promising method for wound healing in diabetic mice (55).
Anti-inflammatory, antifungal, antioxidant activities, and analgesic effects of this plant have been reported (56, 57).
Fraxinus excelsior
Antioxidant, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory activities of F. excelsior were shown in the previous reports (58, 59).
Plantago major
The main caffeic acid derivative in P. major is plantamajoside having anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antibacterial activities (60). The wound-healing properties of P. major were evaluated using an ex-vivo porcine wound healing model. Ethanol and water extracts stimulated wound healing in porcine skin (61).
Phaseolus vulgaris
Antimicrobial and antioxidant activity of Ph. Vulgaris have been reported (62-64).
Pistacia lentiscus
Resin of P. lentiscus showed 100% inhibition of inflammation at 800 mg/kg i.p. injection, without any toxicity in mice (65). P. lentiscus virgin fatty oil promotes significantly wound contraction and reduces epithelization period in rabbit model (66). Antifungal and antioxidant effects also have been reported (67).
Commiphora myrha
Pharmacological studies showed that myrrh exhibited analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial activities (57, 68). The analgesic activity of Commiphora extract and pure compounds supported the use of myrrh for wound and pain in indigenous medicines (69).
Trachyspermum copticum
Trachyspermum copticum, an annual plant which grows in Iran, has white flowers and small fruits. Some biological effects of the fruits of T. copticum such as antiviral, anti-inflammatory, antifungal, analgesic, antinociceptive, and antioxidant activity have been confirmed (70-72).
Narcissus tazetta
Ethanol extracts of aerial parts of this plant showed antimicrobial effects. Aerial parts of N. tazetta have flavonoids, terpenoids, and alkaloids (73, 74).
Verbena Officinalis
Casanova et al. reported 50% methanolic extract and caffeoyl derivatives could be potentially considered as excellent and readily available sources of natural antifungal and antioxidant compounds (75). A topical preparation containing at least 3% of V. officinalis methanolic extract showed an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects (76).
Foeniculum vulgare
Antioxidant activity of F .vulgare was demonstrated by various studies. The fruits have shown antioxidant activity in animal models. In a study investigating antioxidant properties of different parts of F. vulgare, the shoots had the highest radical scavenging and lipid peroxidation inhibiting activity. Despite of these positive reports, the results of a study on different fractions of fruit and their major chemical compounds did not show strong antioxidant activities from isolated F. vulgare components (77).
Oral administration of a methanol extract of F. vulgare fruits exhibited inhibitory effects against acute and subacute inflammatory diseases and showed a central analgesic activity in rat and mice (77).
F. vulgare essential oil possesses a strong antifungal activity against different fungal species (78) and aqueous extract of F. vulgare has showed potent antibacterial activity (79).
Cydonia oblonga
Quince is a tree cultivated as a medicinal plant in the Middle East, South Africa, and Central Europe. One study indicates that the mucilage obtained from quince seeds accelerates wound healing in rabbits (80). Polyphenolic compounds of C. oblonga were responsible for the antimicrobial effects of this plant (81).
Branca et al. reported the antioxidant activities of quince. Evaluation of the antioxidant activity of methanolic extract of C. oblonga showed that its peel extract has the highest antioxidant capacity. The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50 values) of quince pulp, peel, and jam extracts were correlated with total content of caffeoylquinic acids (82). Essafi-Benkhadir et al. reported anti-inflammatory effect of polyphenolic extract of the C. blonga (83).
Anethum graveolens
Many studies were done about A. graveolens. In these studies antibacterial, antifungal, and antioxidant activity of A. graveolenshas have been confirmed (84-86).
Ficus carica
Antimicrobial, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of different dosage forms prepared from different parts/extracts of the F.carica are well documented (87, 88).
Rosa damescena
In Shohayeb et al. study, essential oil and different extracts of petals of the R. damascena were evaluated for their antimicrobial activities against three gram- positive and seven gram- negative bacterias, one acid-fast bacterium and three fungi. Rose oil and all tested rose fractions indicated broad spectrum antibacterial activity against all tested bacteria and fungi (89).
The R. damascena similar to many aromatic and medicinal plants exhibits antioxidant properties (41). Hajhashemi et al. showed R. damascena contains active analgesic ingredients acting both centrally and peripherally. Results of one study showed hydroalcoholic extract of this plant relieved inflammatory pain in an animal model (90).
Crocus sativus (Saffron)
Crocus sativus have many pharmacological properties such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial, and wound healing. Extract of pollen of this herb has therapeutic effects on wounds induced by mustard in animals. Chemical constituents of saffron are crocins, crocetin, picrocrocin, β-carotene, and safranal. These compounds have antioxidant activity (91).
Aristolochia longa
Antifungal and antimicrobial effects of this plant have been reported. Aristolochic acids isolated from this plant show antimicrobial activity against some microorganisms (76, 92).
Olea europaea
Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial activities of different parts of O. europaea have been demonstrated in different studies (93-96).
Pereira et al. has reported that low concentrations of olive leaves extract has combined antibacterial and antifungal actions (97). For the first time Koca et al. in 2011 reported wound healing activity of the aqueous extract of O. Europea leaves. Antioxidant and antimicrobial effects of olive leaves might explain their beneficial effects on wound healing (98).
| Scientific name | Part/extract | Active constituent | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Allium porrum | ----- | -------- | ---- |
| 2. | Anethum graveolens | Essential oil | Sabinen | (84) |
| 3. | Apium graveolens | Ethanolic extract of seeds | ----- | (48) |
| 4. | Aristolochia longa Aristolochia rotunda | ----- | ------ | --- |
| 5. | Artemisia vulgaris | Hydroalcoholic extract | Rutin, hydroxybenzoic acid and caffeic | (35) |
| 6. | Boswellia carteri | Aquouse extract | ---- | (57) |
| 7. | Commiphora myrha | Aqeouse extract of resin | sesquiterpene,diterpenen, triterpenic acids | (57) |
| 8. | Commiphora opobalsamum | Petrolatum ether, Chloroform, extract of aerial parts | Triterpens, flavonols, mearnsetin, quersetin, ascorbic acid | (32) |
| 9. | Crocus sativus | Methanolic extract of aerial parts | ----- | (24) |
| 10. | Cydonia oblonga | Polyphenol ectract | polyphenols | (52) |
| 11. | Descurainia sophia | Petrolatom extract of seeds | Coumarins | (83) |
| 12. | Ficus carica | --- | ---- | --- |
| 13. | Foeniculum vulgare | Methanolic extract of fruites | ---- | (77) |
| 14. | Fraxinus excelsior | Ethanolic extract of the bark | coumarins | (59) |
| 15. | Hyoscyamus niger Hyoscyamus albus Hyoscyamus sp. | Methanolic extract of seeds | coumarinolignans | (33) |
| 16. | Juniperus sabina | --- | ---- | --- |
| 17. | Lawsonia inermis | --- | lawsochylin A, lawsonaphthoate | (99) |
| 18. | Malva sylvestris | Ethanolic extract of leaves | malvidin3- glucoside,scopoletin,quercetin | (50) |
| 19. | Myrtus communis | ---- | ---- | (25) |
| 20. | Narcissus tazetta | ---- | ---- | -- |
| 21. | Olea europaea | Chloroformic and methanolic extract of leaves | Iridoids, Flavonoids | (100) |
| 22. | Peucedanum officinale | ---- | ---- | (30) |
| 23. | Phaseolus vulgaris | --- | --- | --- |
| 24. | Pistacia lentiscus | Resin | Flavonoids | (65) |
| 25. | Plantago major | Ethanolic and aquase extract of leaves | Phenolic compounds, Polysaccharides and polyphenolic compounds | (60, 61) |
| 26. | Polyporus officinalis | --- | --- | ---- |
| 27. | Prangos ferulaceae | ---- | ----- | ---- |
| 28. | Rosa damescena | Ethanolic extract of air dried and petals | Phenolic compounds | (90) |
| 29. | Trachyspermum copticum | Ethanolic extract of seeds | Flavonoids and glycosides | (72) |
| 30. | Trigonellafoenum-graecum | Methanolic extract of seeds | Glycoside and steroidal moieties | (44) |
| 31. | Verbena officianalis Verbena sp. | Methanolic extract of leaves | Iridoids and caffeoyl derivatives | (75) |
| Scientific name | Part/extract | Active constituent | Activities | Reference | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Allium porrum | Essential oil | Dipropyl disulfide, dipropyltrisulfide, methyl propyl disulfide, polyphenols | Antibacterial, | (53) | ||||
| 2. | Anethum graveolens | Ethanolic extract of flowers | proanthocyanidins | Antifungal, antibactrial | (85, 86) | ||||
| 3. | Apium graveolens | Essential oil | ---- | Antibacterial | (47) | ||||
| 4. | Aristolochia longa Aristolochia rotunda | Aqueous extract of root, Hexane and benzene extract of dried root | Flavonoides,Saponins/ Aristolochic acid and aristolactam | Antifungal, Antibacterial | (76) | ||||
| 5. | Artemisia vulgaris | Ethanolic Extract of aerial parts | Flavonoids, phenols | Antimicrobial, | (34) | ||||
| 6. | Boswellia carteri | Essential oils | limonene | Antibacterial, antifungal | (54) | ||||
| 7. | Commiphora myrha | Ethanol and ether extracts | ----- | Antimicrobial | (69, 101) | ||||
| 8. | Commiphora opobalsamum | Petrolatum ether | Triterpens, flavonols | Antimicrobial | (102) | ||||
| 9. | Crocus sativus | Methanolic extract of aerial parts | --- | Antimicrobial | (103) | ||||
| 10. | Cydonia oblonga | Fruit aqueous acetone extract | chlorogenicacid | Antimicrobial | (104) | ||||
| 11. | Descurainia sophia | ---- | ---- | ----- | ---- | ||||
| 12. | Ficus carica | Methanol extract | --- | Antibactrial Antifungal | (87) | ||||
| 13. | Foeniculum vulgare | Essential oil, Aquase extract | Anethol | Antimicrobial | (78) | ||||
| 14. | Fraxinus excelsior | dichloromethane of leaves | ---- | Antibacterial | (105) | ||||
| 15. | Hyoscyamus niger Hyoscyamus albus Hyoscyamus sp. | Ethanolic extract of shoot and root | Alkaloids | Antimicrobial | (106) | ||||
| 16. | Juniperus sabina | Essential oil of fruit | Flavonoids | Antimicrobial | (28) | ||||
| 17. | Lawsonia inermis | ---- | ---- | Antimicrobial | (38) | ||||
| 18. | Malva sylvestris | Methanolic extract of aerial parts | ---- | Antibactrial | (104) | ||||
| 19. | Myrtus communis | Essential oil, Ethanolic and methanolic and ethylacetat extract of leaves and berries, Ethanolic extract | Polyphenolic compounds, phenolic acids, tannins, flavonoids | Antimicrobial | (25) | ||||
| 20. | Narcissus tazetta | Ethanol extract of aerial parts | --- | Antimicrobial | (74) | ||||
| 21. | Olea europaea | Aqueous extracts of leaves | Phenolic compounds | Antifungal and antibacterial | (97) | ||||
| 22. | Peucedanum officinale | ---- | ---- | Antimicrobial | (31) | ||||
| 23. | Phaseolus vulgaris | Acetonic extract | Tannins | Antibacterial | (64) | ||||
| 24. | Pistacia lentiscus | Mastic | ---- | Antimicrobial | (67) | ||||
| 25. | Plantago major | Ethanolic and aquase extract of leaves | Phenolic compounds, Polysaccharides and polyphenolic compounds | Antibacterial | (60) | ||||
| Scientific name | Part/extract | Active constituent | Activities | Reference | |||||
| 26. | Polyporus officinalis | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ||||
| 27. | Prangos ferulaceae | Fruit extract | limonene, α-pinen, and | Antibacterial | (45) | ||||
| 28. | Rosa damescena | Essential oil and ethanolic extract | ---- | Antibacterial and Antifungal | (107) | ||||
| 29. | Trachyspermum copticum | Essential oil | Phenols | Antimicrobial | (71) | ||||
| 30. | Trigonellafoenum- graecum | Ethanolic extract of mucilage | --- | Antibacterial | (102) | ||||
| 31. | Verbena officianalis Verbena sp. | Methanolic extract of leaves | Flavonoids and caffeoyl derivatives | Antimicrobial | (75) | ||||
| Scientific name | Part/extract | Active constituent | Reference | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Allium porrum | Essential oil | Dipropyl disulfide, dipropyltrisulfide, methyl propyl disulfide, polyphenols | (53) | |||||
| 2. | Anethum graveolens | Essential oil | Tannins, Flavonoid, Alkaloids | (86) | |||||
| 3. | Apium graveolens | Methanolic and ethanolic extrac of seeds | flavonoids, phenols | (108) | |||||
| 4. | Aristolochia longa Aristolochia rotunda | ------- | ------- | -- | |||||
| 5. | Artemisia vulgaris | Ethanolic Extract of aerial parts | Flavonoids, phenols | (34) | |||||
| 6. | Boswellia carteri | Aquouse extract | ---- | (56) | |||||
| 7. | Commiphora myrha | Ethanol and ether extracts | ---- | (69) | |||||
| 8. | Commiphora opobalsamum | Petrolatum ether, Chloroform, extract of aerial parts | Triterpens, flavonols, mearnsetin, quersetin, ascorbic acid | (102) | |||||
| 9. | Crocus sativus | Methanolic extract of aerial parts | ---- | (103) | |||||
| 10. | Cydonia oblonga | Methanolic extract of pulp and peel and seed and jam | Phenolic compounds | (82) | |||||
| 11. | Descurainia sophia | Ethanolic extract of seeds | Phenols | (109) | |||||
| 12. | Ficus carica | ---- | Polyphenols, Flavonoids, Anthocyanins | (87) | |||||
| 13. | Foeniculum vulgare | Ethanolic extract of fruits | ---- | (77) | |||||
| 14. | Fraxinus excelsior | Ethanolic extract of leaves | Fraxetin, esculetin | (59) | |||||
| 15. | Hyoscyamus niger Hyoscyamus albus Hyoscyamus sp. | ---- | ------ | ||||||
| 16. | Juniperus sabina | Methanolic extract of Leaves and fruits | ---- | (29) | |||||
| 17. | Lawsonia inermis | Ethanolic extract of leaves | ---- | (39) | |||||
| 18. | Malva sylvestris | --- | ---- | (104) | |||||
| 19. | Myrtus communis | Ethanolic extracts of berries | Flavonoids, Tannins, α-tocopherol | (25) | |||||
| 20. | Narcissus tazetta | --- | --- | --- | |||||
| 21. | Olea europaea | leaf extract | Flavonols, Flavans-3-ols, Flavones | (93) | |||||
| 22. | Peucedanum officinale | ---- | ---- | (31) | |||||
| 23. | Phaseolus vulgaris | Methanolic extract of bean | Phenols | (62) | |||||
| 24. | Pistacia lentiscus | Resin | Flavonoids | (67) | |||||
| 25. | Plantago major | Ethanolic and aquase extract of leaves | Phenolic compounds, Polysaccharides and polyphenolic compounds | (60) | |||||
| 26. | Polyporus officinalis | --- | --- | --- | |||||
| 27. | Prangos ferulaceae | --- | Coumarines, Alkaloids, Flavonoids, and Terpenoids | (45) | |||||
| 28. | Rosa damescena | Hydroalcohlic and ethanolic extract, fresh | Phenolic compounds | (41) | |||||
| 29. | Trachyspermum copticum | Ethanolic extract of seeds | Terpenoids and Flavonoids | (70) | |||||
| 30. | Trigonellafoenum-graecum | Ethanolic extract of mucilage | Galactomannan | (110) | |||||
| 31. | Verbena officianalis Verbena sp. | Methanolic extract of leaves | Flavonoids and Caffeoyl derivatives | (75) | |||||
Conclusion
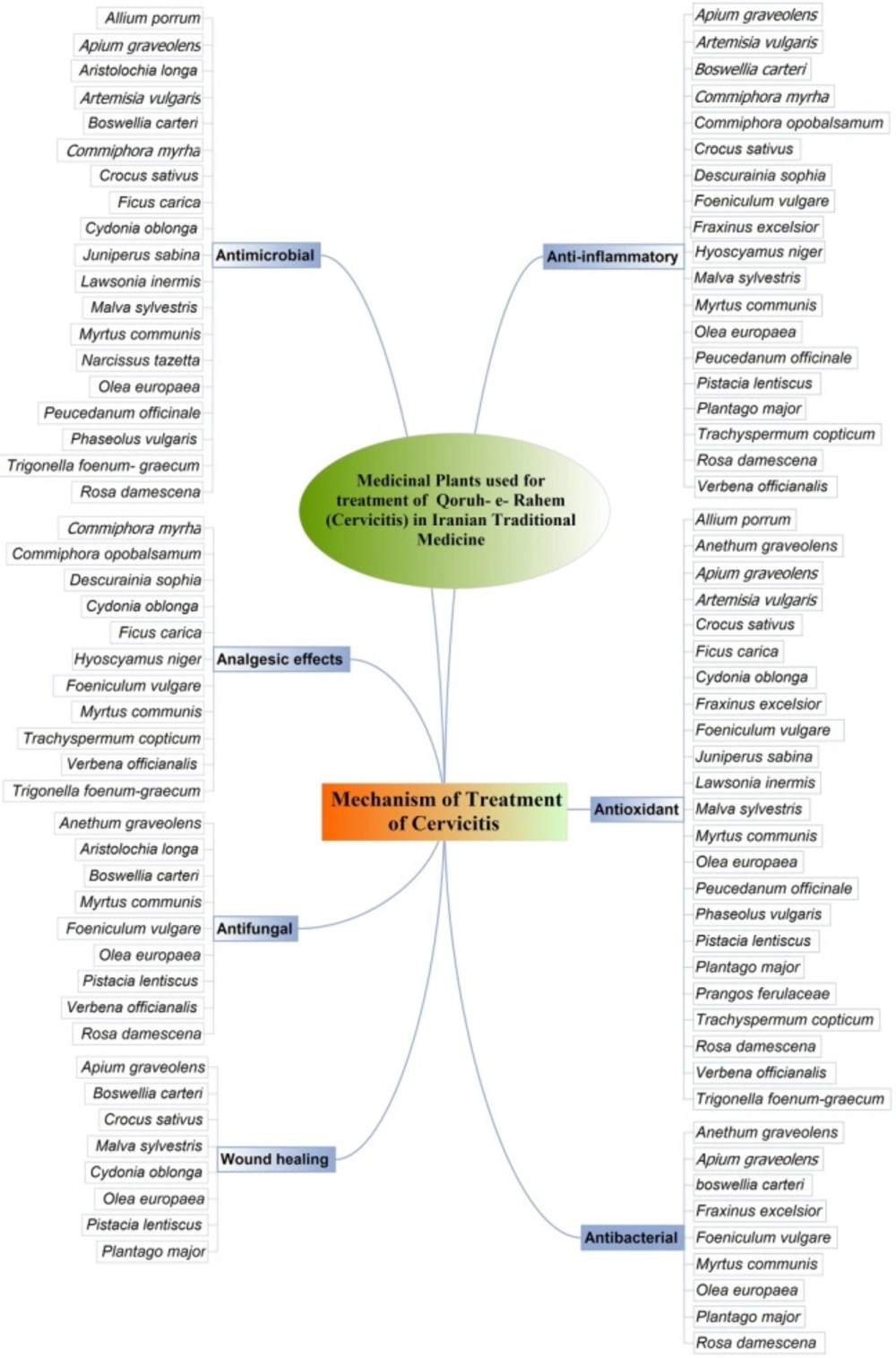
Overall, we found 31 plants from 21 different families cited in the Iranian Traditional Medicine as therapies for cervicitis. Most of these plants had been shown in-vitro and/or in-vivo anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and antioxidant effects (Figure 2).
Treatment with medicinal plants has attracted the attention of scientists and there are throwbacks to the traditional medicine in many countries (111). Medicinal plants used in traditional medicine and ethnopharmacology may be valuable sources for discovering new therapies (112). In Iranian Traditional Medicine manuscripts, various medicinal plants with different pharmacological activities have been introduced. In this article, the medicinal plants claimed to be effective in cervicitis have been collected from Canon of Medicine, Makhzan-Al-advieh, Tohfeh-Al-Momenin, Exire Azam and Sharh-ol- Asbab, Zakhireh Kharazmshahi and their possible efficacy and pharmacodynamics in modern medicine were surveyed. Some of them such as Cydonia oblonga, Olea europaea, Ficus carica, and Allium porrum have nutritional value and are routinely used in human diets.
Cervicitis, presenting as inflammation of the uterine cervix, is a syndrome usually caused by infection (113). Oxidative stress, microbial infections, and inflammation are associated with human uterine cervicitis (4, 7, 113). Different mechanisms of action could be considered for these medicinal plants including anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, analgesic, antioxidant activity, and wound healing activities. Finding the medicinal plants effective on cervicitis based on ITM could suggest a better strategy for relieving and management of cervicitis symptoms especially in recurrent or persistent conditions.
It should be contemplated that even though exploring ITM literature may lead to the identification of effective natural medicines for the management of different ailments such as cervicitis; however, confirming clinical trials or supportive high-quality observational studies needs to be accomplished before routine administration of herbal medicines or treatment regimens (Tadabeer) recommended in traditional medicine texts to affirm efficacy and safety of these treatments.