1. Background
Pyrimidine derivatives have a variety of biological properties, explained by their similar structure to endogenous substances making them promising substances as medicinal compounds (1-4). Among the derivatives of pyrimidine-4-one and their related compounds, a compound with a tetrahydrobenzothieno fragment can be distinguished. For instance, compounds tetrahydrobenzo[4’,5’]thieno[3’,2’:5,6]pyrimido[1,2-b]isoquinoline were tested in vitro against a panel of two human tumor cell lines, namely, hepatocellular carcinoma (liver) HepG2 and mammary gland breast MCF-7. Almost all the tested compounds showed satisfactory activity (5). Some of the tetrahydrobenzothienopyrimidine derivatives exhibited pronounced antimicrobial activity (6). Most of the 5,6,7,8-tetrahydro[1]benzothieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one derivatives bearing a hydroxamic acid, 2-aminoanilide, and hydrazide moieties displayed moderate to strong histone deacetylase inhibitory activity. Some of these compounds showed potent anti-proliferative activity against human HepG2, MCF-7, and HCT-116 cell lines (7). The results of a study indicate that tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine scaffolds may serve as models for the development of antimalarial agents (8).
The synthesis of new representatives of this series and the optimization of methods for their preparation will expand the arsenal of potential active pharmaceutical substances (APS) and medicines.
Hyperpigmentation of the skin occurs due to the diffuse deposition of melanin in the subcutaneous structures, leading to the staining of certain areas of the skin in a light brown or brown color. This phenomenon can be a symptom of quite dangerous skin lesions. In chronic poisoning with dioxin and dioxin-like substances (polychloro-organic toxicants), aryl–carbohydrate receptors of melanocytes are activated, and the melanous deposits are formed by the early and reliable signs of melanoma (9). It has been established that the activation of melanocytes is possible as a result of intoxication with drugs, including fluoroquinolones, tetracyclines, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or antiarrhythmic drugs (10). In addition to the lack of aesthetics, hyperpigmentation of the skin has a significant impact on the psycho-emotional state of a person and his social adaptation. Thus, scientists in 2017 found that 78% of respondents who had hyperpigmentation of the facial skin were not able to establish proper social contact, 22% noted a deterioration in the quality of life, and 10% needed qualified psychological assistance (11). Also, abnormally elevated melanogenesis can be a predisposing factor for dermatological diseases, such as black acanthosis, cervical poikiloderma, melasma, periorbital hyperpigmentation, lentigines, skin cancer, or a consequence of neurodegeneration in the case of Parkinson disease.
The existing methods of synthesis of 2-substituted tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine-4(3H)-one from 2-amino-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1-benzothiophene-3-carboxamide consist mainly in its interaction with the aldehydes in different conditions. A method for the synthesis of these pyrimidines is known by suspending the parent compounds with a catalytic amount of concentrated hydrochloric acid for 12 hours at a temperature of 80°C (12) or with the addition of dimethylformamide (DMF) and piperidine (13). Another method for the preparation of 2-substituted tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine-4(3H)-one is based on the use of the ZnO-CeO2 nanocomposite as a catalyst (14). A method for obtaining these pyrimidine derivatives is proposed by adding nitrile saturated with hydrogen chloride gas to a solution of 2-amino-3-carbethoxytiophene in anhydrous dioxane (15) or by adding a solution of hydrochloric acid (16).
Thus, the available methods for the synthesis of 2-substituted tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine-4(3H)-one require the use of special synthesis conditions and toxic and expensive solvents and catalysts. Optimization of the conditions for obtaining the studied pyrimidines, as well as the synthesis of new biologically active compounds, is a promising direction for pharmaceutical science.
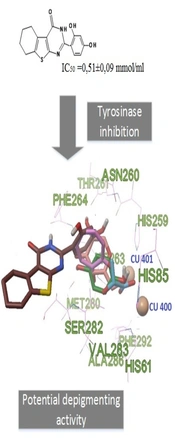
Phenolic compounds have the greatest ability to inhibit tyrosinase, which can be in the form of small molecular structures or conjugated forms with sugars or organic acids (17). It has been established, for example, that such simple phenols as hydroquinone, resorcinol, vanillin, kojic acid, and their derivatives can have an inhibitory effect on tyrosinase. At the same time, hydroquinone, resorcinol, and vanillin have pronounced toxic properties on the human organism (18). Synthesis of new organic compounds with phenolic substituents will expand the class of potential tyrosinase inhibitors. We propose to use the tetrahydrobenzothienopyrimidine core as the scaffold of the designed compounds by analogy with known structures with anticancer activity (15, 19, 20). Designed compounds in this way may be effective for the treatment of melanoma; therefore, such structures have an anticancer scaffold and anti-tyrosinase phenolic fragments. In the first stage, it is advisable to select the most active tyrosinase inhibitors and then investigate their therapeutic ability against melanoma. Pyrimidine derivatives, due to their proximity to endogenous nitrogenous bases, are characterized by low toxicity and, with phenyl, hydroxyphenyl, and heteryl fragments (as a rule), exhibit high biological activity (21, 22). By carrying out the molecular design by introducing phenyl fragments into the second position of the heterocyclic nucleus of tetrahydrobenzothienopyrimidine-4(3H)-one, it is possible to predict structures that presumably have anti-tyrosinase activity in combination with low toxicity (Figure 1).
2. Methods
2.1. Molecular Modeling
The target of molecular docking is the tyrosinase of the fungus Agaricus bisporus. This enzyme was studied by X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, and its 3-dimensional model are given in the Protein Data Bank (PDB; rcsb.org) with identification number 2Y9X (23). The virtual complex of 2Y9X contains its inhibitor (tropolone), allowing for a qualitative assessment of the conformational complex of the simulated compounds with the enzyme obtained in silico. It is also possible to propose a mechanism for the amino acid interaction of the ligand with the active site of tyrosinase in the course of a computational experiment with a high degree of probability.
The 3-dimensional structures of the studied compounds were constructed using HyperChem version 8.0.4 and then geometrically optimized by the molecular mechanics method using the MM+ method (24). The final geometry optimization of the virtual structures was calculated by ORCA version 4.1 using the density functional theory (UB3LYP) method and the 6-311G** basis set. The conversion of the HIN format to the PDB required for molecular modeling was carried out using Open Babel version 2.4.1.
The docking study was performed using AutoDock version 4.0 (25). Molecular modeling was performed subject to the conformational flexibility of the ligands. The charges of all the atoms of the simulated system are calculated by the Gasteiger algorithm. The charge for the 2 copper atoms in the simulation zone is manually specified +2. The area of the computational experiment is a cube. The center of a box is located (x = -9.985; y = -27.898; z = -40.690). The spacing is 0.375 angstrom. The number of points in x-, y-, and z-dimension is 44. The program was set to search for 200 energetically favorable conformations of the ligand-enzyme complex formation using the Lamarckian GA 4.2 scoring function for calculating the energy of the ligand-enzyme interaction.
Root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) for validation docking was done using the location of the tropolone at complex 2Y9X (XRD analysis) and its location according to the molecular docking data. Calculating RMSD was made according to the following equation:
Where RMSD is a root-mean-square deviation, Å; N is a number of atoms; ri is a distance between the corresponding atoms i, Å.
2.2. Chemistry
All chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA), Carl Roth (Carl Roth, Karlsruhe, Germany), and Merck Chemicals (Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany). Melting points (mp) were recorded using the PMP-M1 melting point apparatus (Himlaborpribor, Klin, Russia). All reactions were monitored by thin-layer chromatography (TLC) using silica gel 60 F254 TLC plates (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany). Spectroscopic data were registered with the following instruments: IR, IR-Fourier FSM 1201 spectrophotometer (Spectrum, Moscow, Russia); UV, SF-2000 device (Spectrum, Moscow, Russia); and 1H NMR and 13C NMR Bruker Avance III 400 МHz spectrometer (Bruker, Germany) in DMSO-d6 and Chloroform-d6, using tetramethylsilane as the internal standard. The 13C NMR spectrum of compounds 4f and 4h could not be detected due to its poor solubility in deuterated DMSO-d6 and Chloroform-d6, even with the addition of trifluoroacetic acid (TFA). Coupling constant (J) values are measured in hertz (Hz), and spin multiples are given as s (singlet), d (doublet), t (triplet), q (quartet), m (multiplet).
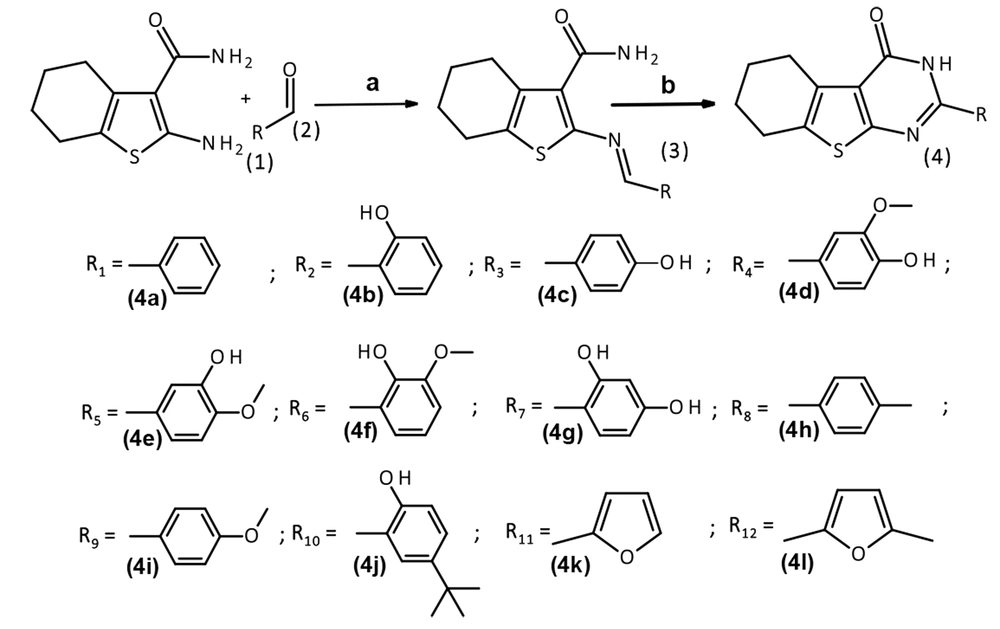
2.3. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Azomethine Derivatives of 2-Amino-4,5,6,7-Tetrahydro-1-Benzothiophene-3-Carboxamide (3a-3m)
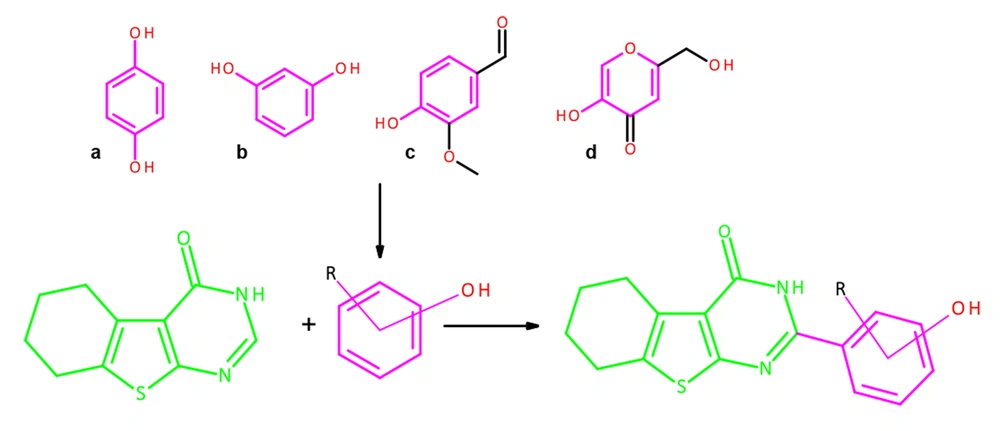
A mixture of 0.01 mol (1.92 g) of compound 1 and an equimolar amount of the corresponding aldehyde 2 (in the case of compound 3e, 0.012 mol) was refluxed for 30 - 60 minutes. After cooling, the precipitated compound was filtered and recrystallized from ethanol. The target product of the reaction with vanillin was additionally precipitated with water (26).
2.4. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 2-Substituted Tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]Thieno[2,3-d]Pyrimidine-4(3H)-One (4a-4m)
Azomethine 3 (0.08 mol) was refluxed for 30-60 minutes in the glacial acetic acid. Then, 1 - 2 mL DMSO was added, and the reaction mixture was refluxed for 60 minutes. After cooling, the formed precipitate was filtered. In the filtrate, the remaining target product was precipitated with a 0.1 М cold water solution of sodium chloride. Precipitations were combined. Recrystallization of the obtained compounds was carried out from acetic acid.
2.5. Evaluation of Anti-tyrosinase Activity
The test compounds were dissolved in DMSO until a solution with a final concentration of 1000 µg/mL. Next, a series of double dilutions of the initial solution was prepared with a concentration range of the test compounds of 500 µg/mL, 250 µg/mL, 125 µg/mL, and 62.5 µg/mL. Kojic acid, hydroquinone, and lactic acid in a similar concentration range were used as reference compounds. The choice of referents was based on a different mechanism of tyrosinase inhibition, as well as different clinical efficacy and toxicity of compounds.
Hydroquinone and kojic acid were obtained from Hunan Warrant Pharmaceuticals (China), and lactic acid was provided by Sigma-Aldrich (Germany).
2.6. Analysis Progress
The study was performed using micro-analysis, where 70 µL of each serial dilution was added to a 96-well plate, and 30 µL of a tyrosinase (Sigma-Aldrich) solution in a phosphate buffer with an activity of 333 U/mL was added to the reaction medium. The reaction mixtur e was incubated at room temperature for 5 minutes, after which 110 µL of the substrate (2mM L-tyrosine solution) was added to each well and re-incubated in a similar mode. The absorbance of the samples was recorded at 492 nm using an Infinite F50 reader (Tecan) (27). The tests were performed in the triplet version. Half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) mmol/mL was calculated by the probit analysis method. The results were presented as mean ± SEM, and inter-group comparisons were performed by single-factor analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Newman-Keuls post-processing.
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis
A new cyclocondensation condition was used to make 2-substituted tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine-4(3H)-one with high yields. As shown in Figure 2, 2-amino2-amino-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1-benzothiophene-3-carboxamide 1 and aldehydes 2 were refluxed in ethanol to obtain azomethine derivatives of 2-amino-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1-benzothiophene-3-carboxamide 3, and then heterocyclization reaction was performed using glacial acetic acid and DMSO to afford the 2-substituted tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine-4(3H)-one 4.
The compounds were characterized by nuclear magnetic resonance and infrared spectroscopy.
3.2. 2-Phenyl-5,6,7,8-Tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]Thieno[2,3-d]Pyrimidine-4(3H)-One (4a)
The light yellow crystals were obtained. Yield: 96%. Mp: 265 - 268°C. UV spectrum (ethanol), λmax (nm): 203, 331. IR spectrum (Vaseline oil). ν (cm-1): 1659 (C = O). 1H NMR spectrum (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 1.80 (m, 4H, CH2); 2.75 (t, J = 6.4 Hz, 2H, CH2); 2.92 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, CH2); 7.63 - 7.40 (m, 3H, ArH); 8.12 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H, ArH); 12.53 (s, 1H, NH). 13C NMR spectrum (100,6 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 22.23; 22.95; 25.02; 25.79; 121.35; 128.10; 129.15; 131.33; 131.84; 132.39; 132.96; 152.56; 159.29; 163.47.
3.3. 2-(2-Hydroxyphenyl-5,6,7,8-Tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]Thieno[2,3d]Pyrimidine-4(3H)-One (4b)
The brown crystals were obtained. Yield: 86%. Mp: 311 - 314°C. UV spectrum (ethanol), λmax (nm): 213, 356. IR spectrum (Vaseline oil). ν (cm-1): 1655 (C = O). 1H NMR spectrum (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 1.85 - 1.66 (m, 4H, CH2); 2.83 (dt, J = 55.5, 6.2 Hz, 4H, CH2); 7.09 - 6.84 (m, 2H, ArH); 7.42 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, ArH); 8.11 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H, ArH); 12.04 (s, 1H, NH). 13C NMR spectrum (100,6 MHz, DMSO-d6 with the addition of TFA), δ (ppm): 22.17; 22.92; 24.95; 25.72; 111.32; 117.07; 117.92; 119.95; 129.30; 131.34; 132.87; 133.57; 157.98; 158.21; 158.97; 159.34.
3.4. 2-(4-Hydroxyphenyl-5,6,7,8-Tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]Thieno[2,3-d]Pyrimidine-4(3H)-One (4c)
The light yellow crystals were obtained. Yield: 83%. Mp: 297 - 300°C. UV spectrum (ethanol), λmax (nm): 204, 338. IR spectrum (KBr). ν (cm-1): 3415 (OH), 1643 (C = O). 1H NMR spectrum (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 1.79 (dt, J = 13.9, 7.3 Hz, 4H, CH2); 2.73 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, CH2); 2.89 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, CH2); 6.87 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H, ArH); 8.01 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H, ArH); 10.17 (s, 1H, OH); 12.26 (s, 1H, NH). 13C NMR spectrum (100,6 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 22.26; 22.98; 24.96; 25.80; 115.88; 120.48; 122.92; 129.93; 131.19; 131.86; 152.54; 159.35; 160.97; 163.93.
3.5. 2-(4-Hydroxy-3-Methoxyphenyl-5,6,7,8-Tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]Thieno[2,3-d]Pyrimidine-4(3H)-One (4d)
The brown crystals were obtained. Yield: 72%. Mp: 278 - 281°C. UV spectrum (ethanol), λmax (nm): 206, 341. IR spectrum (KBr). ν (cm-1): 3462 (OH), 1643 (C = O). 1H NMR spectrum (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 1.79 (dt, J = 13.4, 7.1 Hz, 4H, CH2); 2.73 (t, J = 5.8 Hz, 2H, CH2); 2.90 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, CH2); 3.87 (s, 3H, CH3); 6.87 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H, ArH); 7.67 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, ArH); 7.73 (s, 1H, ArH); 9.77 (s, 1H, OH); 12.30 (s, 1H, NH). 13C NMR spectrum (100,6 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 22.25; 22.98; 24.97; 25.81; 56.22; 111.53; 115.89; 120.51; 121.81; 123.08; 131.21; 131.92; 148.01; 150.38; 152.44; 159.40; 163.91.
3.6. 2-(3-Hydroxy-4-Methoxyphenyl-5,6,7,8-Tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]Thieno[2,3-d]Pyrimidine-4(3H)-One (4e)
The light yellow crystals were obtained. Yield: 75%. Mp: 293 - 295°C. UV spectrum (ethanol), λmax, nm: 207, 341. IR spectrum (KBr). ν (cm-1): 3457 (OH), 1646 (C = O). 1H NMR spectrum (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 1.90 - 1.63 (m, 4H, CH2); 2.73 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, CH2); 2.90 (t, J = 6.2 Hz, 2H, CH2); 3.84 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 3H, CH3); 7.02 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, ArH); 7.70 - 7.56 (m, 2H, ArH); 9.34 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H, OH); 12.28 (s, 1H, NH). 13C NMR spectrum (100,6 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 22.25; 22.98; 24.97; 25.79; 56.13; 112.03; 115.00; 119.72; 120.68; 124.71; 131.24; 132.08; 146.94; 151.11; 152.38; 159.31; 163.77.
3.7. 2-(2-Hydroxy-3-Methoxyphenyl-5,6,7,8-Tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]Thieno[2,3-d]Pyrimidine-4(3H)-One (4f)
The brown crystals were obtained. Yield: 80%. Mp: 297 - 301°C. UV spectrum (ethanol), λmax (nm): 205, 357. IR spectrum (KBr). ν (cm-1): 3468 (OH), 1664 (C = O). 1H NMR spectrum (400 MHz, DMSO-d6 with the addition of TFA), δ (ppm): 1.98 - 1.62 (m, 4H, CH2), 2.91 - 2.78 (m, 4H, CH2), 3.86 - 3.68 (m, 3H, CH3), 6.92 (t, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.16 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.70 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 1H, ArH), 11.68 (s, 1H, OH), 12.16 (s, 1H, NH).
3.8. 2-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-5,6,7,8-Tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]Thieno[2,3-d]Pyrimidine-4(3H)-One (4g)
The dark brown crystals were obtained. Yield: 88%. Mp: 265 - 268°C. UV spectrum (ethanol), λmax (nm): 215, 357. IR spectrum (KBr). ν (cm-1): 3421 (OH), 1646 (C = O). 1H NMR spectrum (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 1.77 (dt, J = 13.3, 7.0 Hz, 4H, CH2); 2.79 (dt, J = 58.2, 6.2 Hz, 4H, CH2); 6.39 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 2H, ArH); 8.03 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H, ArH); 10.23 (s, 1H, OH); 11.96 - 11.80 (m, 1H, OH); 12.39 (s, 1H, NH). 13C NMR spectrum (100,6 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 22.18; 22.95; 24.90; 25.74; 103.65; 106.68; 108.69; 120.26; 130.42; 131.30; 131.77; 152.98; 158.20; 160.45; 161.71; 162.62.
3.9. 2-(p-Tolyl)-5,6,7,8-Tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]Thieno[2,3-d]Pyrimidine-4(3H)-One (4h)
The light yellow crystals were obtained. Yield: 90 %. Mp: 274 - 278°C. UV spectrum (ethanol), λmax (nm): 207, 336. IR spectrum (Vaseline oil). ν (cm-1): 1647 (C = O). 1H NMR spectrum (400 MHz, Chloroform-d6 with the addition of TFA), δ (ppm): 1.88 (s, 4H, CH2); 2.46 (s, 3H, CH3); 2.83 (t, J = 5.7 Hz, 2H, CH2), 3.00 (t, J = 6.3 Hz, 2H, CH2), 7.41 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 2H, ArH); 7.91 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 2H, ArH); 12.34 (s, 1H, NH).
3.10. 2-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-5,6,7,8-Tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]Thieno[2,3 d]Pyrimidine-4(3H)-One (4i)
The brown crystals were obtained. Yield: 85%. Mp: 269 - 272°C. UV spectrum (ethanol), λmax (nm): 203, 339. IR spectrum (Vaseline oil). ν (cm-1): 1659 (C = O). 1H NMR spectrum (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 1.85 (d, J = 46.9 Hz, 4H, CH2); 2.82 (d, J = 60.5 Hz, 4H, CH2); 3.94 - 3.72 (m, 3H, CH3); 7.06 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H, ArH); 8.12 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H, ArH); 12.38 (s, 1H, NH). 13C NMR spectrum (100,6 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 22.25; 22.98; 24.98; 25.80; 55.94; 114.54; 120.74; 124.52; 129.82; 131.23; 132.21; 152.25; 159.33; 162.28; 163.77.
3.11. 2-(5-Tret-Butyl-2-Hydroxyphenyl)-5,6,7,8-Tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]Thieno[2,3-d]Pyrimidine-4(3H)-One (4j)
The light yellow crystals were obtained. Yield: 89 %. Mp: 284 - 286°C. UV spectrum (ethanol), λmax (nm): 214, 356. IR spectrum (KBr). ν (cm-1): 3486 (OH), 1647 (C = O). 1H NMR spectrum (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 1.31 (c, 9H, CH3); 1.88 - 1.70 (m, 4H, CH2); 2.76 (t, J = 5.8 Hz, 2H, CH2); 2.90 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, CH2); 6.95 (d, J = 8.6, 1H, ArH); 7.47 (dd, J = 8.7, 2.1 Hz, 1H, ArH); 8.10 (s, 1H, ArH); 12.05 (s, 1H, OH); 12.38 (s, 1H, NH). 13C NMR spectrum (100,6 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 19.03; 22.19; 22.94; 24.98; 25.77; 31.72; 34.59; 56.59; 114.79; 117.64; 121.19; 125.26; 130.95; 131.42; 132.78; 142.17; 153.19; 156.29; 158.46; 161.53.
3.12. 2-(2-Furyl)-5,6,7,8-Tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]Thieno[2,3-d]Pyrimidine-4(3H)-One (4k)
The dark brown crystals were obtained. Yield: 90%. Mp: 256 - 259°C. UV spectrum (ethanol), λmax (nm): 218, 264, 345. IR spectrum (Vaseline oil). ν (cm-1): 1659 (C = O). 1H NMR spectrum (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 1.86 - 1.62 (m, 4H, CH2); 2.82 (dt, J = 56.8, 6.3 Hz, 4H, CH2); 6.74 (d, J = 3.5 Hz, 1H, ArH); 7.59 (d, J = 3.5 Hz, 1H, ArH); 7.98 (s, 1H, ArH); 12.51 (s, 1H, NH). 13C NMR spectrum (100,6 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 22.21; 22.91; 25.00; 25.78; 113.12; 114.80; 121.32; 131.49; 132.88; 144.25; 146.04; 146.97; 158.64; 163.06.
3.13. 2-(5-Methyl-2-Furyl)-5,6,7,8-Tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]Thieno[2,3-d]Pyrimidine-4(3H) - One (4l)
The brown crystals were obtained. Yield: 92%. Mp: 259 - 262°C. UV spectrum (ethanol), λmax (nm): 216, 280, 348. IR spectrum (Vaseline oil). ν (cm-1): 1644 (C = O). 1H NMR spectrum (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 1.86 - 1.64 (m, 4H, CH2); 2.37 (s, 3H, CH3); 2.80 (dt, J = 57.4, 6.2 Hz, 4H, CH2); 6.35 (d, J = 3.5 Hz, 1H, CH); 7.49 (d, J = 3.5 Hz, 1H, CH); 12.35 (s, 1H, NH). 13C NMR spectrum (100,6 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 13.98; 22.22; 22.93; 24.98; 25.79; 109.54; 116.15; 120.93; 131.44; 132.45; 144.24; 144.38; 156.52; 158.69; 163.27.
3.14. Docking Studies
In the course of the in silico calculation of the ligand-enzyme interaction, the most energetically favorable locations of the simulated compounds at the active site of the enzyme were selected.
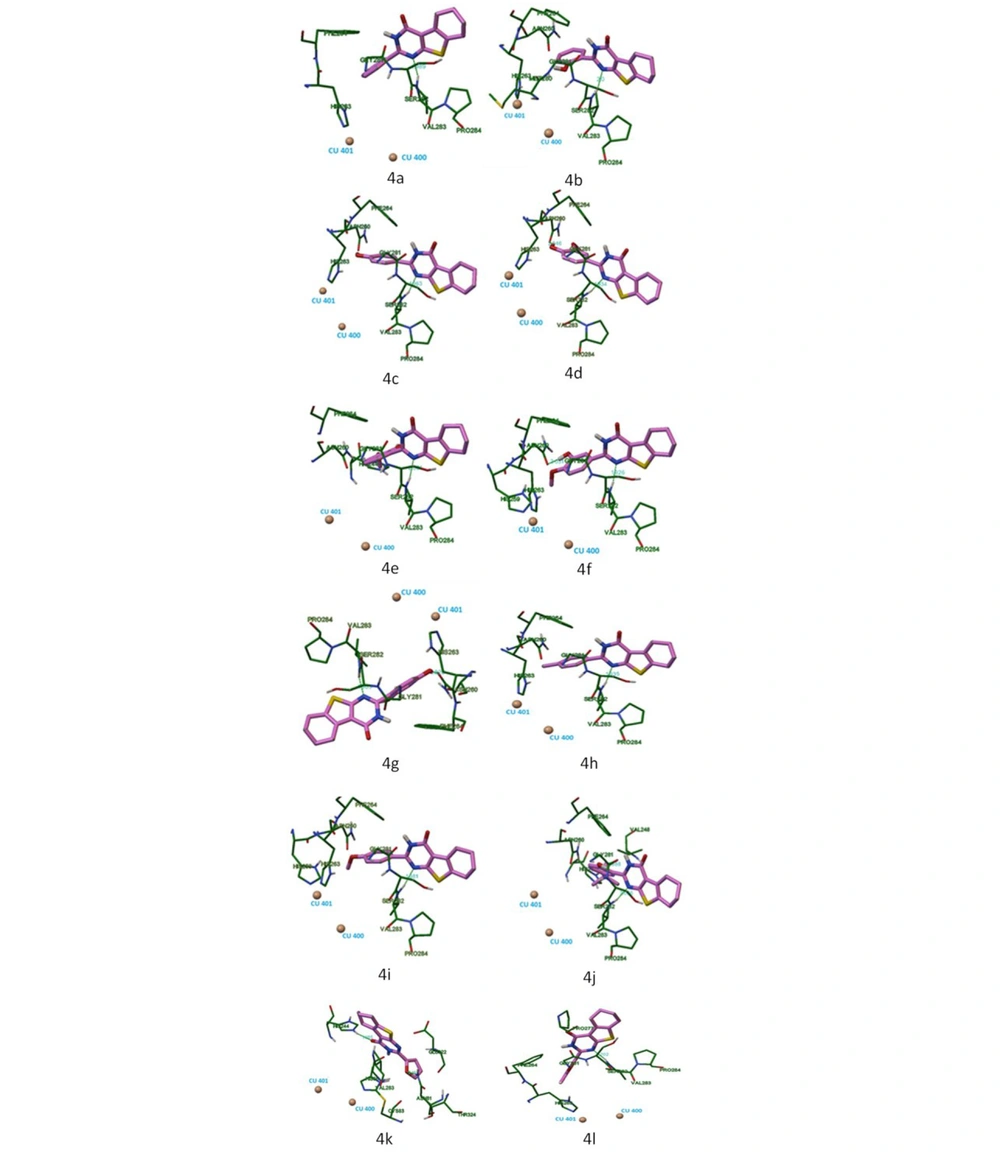
According to the results of molecular docking, 2-substituted tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-th]pyrimidine-4(3H)-one forms bonds with the following amino acid residues of the active tyrosinase site: His 259, Asn 260, His 263, Phe 264, Met 280, Gly 281, Ser 282, Val 283, and Pro 284.
Table 1 shows the minimum energies for the formation of ligand complexes with the active site of tyrosinase and hydrogen bonds.
| Compounds | AutoDock Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | Residue | Ligand Atoms | Distance (Å) | Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4a | -5.97 | Val 283 | -N = | 1.989 | Hydrogen bond |
| 4b | -5.91 | Val 283 | -N = | 2.000 | Hydrogen bond |
| 4c | -6.30 | Val 283 | -N = | 1.963 | Hydrogen bond |
| 4d | -6.24 | Val 283 | -N = | 1.934 | Hydrogen bond |
| Asn 260 | OH | 2.046 | Hydrogen bond | ||
| 4e | -6.12 | Ser 282 | -N = | 1.926 | Hydrogen bond |
| Asn 260 | OH | 2.051 | Hydrogen bond | ||
| 4f | -6.16 | Val 283 | -N = | 2.031 | Hydrogen bond |
| 4g | -6.19 | Val 283 | -N = | 1.963 | Hydrogen bond |
| Asn 260 | OH | 1.828 | Hydrogen bond | ||
| 4h | -6.28 | Val 283 | -N = | 1.935 | Hydrogen bond |
| 4i | -5.84 | Val 283 | -N = | 1.981 | Hydrogen bond |
| 4j | -6.52 | Ser 282 | -N = | 2.036 | Hydrogen bond |
| Gly 281 | OH | 1.988 | Hydrogen bond | ||
| 4k | -5.19 | Asn 81 | Furyl (C-O-C) | 2.159 | Hydrogen bond |
| His 244 | C = O | 1.985 | Hydrogen bond | ||
| 4l | -5.57 | Val 283 | -N = | 2.202 | Hydrogen bond |
| Hydroquinone | -3.7 | Met 280 | OH | 2.134 | Hydrogen bond |
| Kojic acid | -4.46 | Asn 260 | OH | 2.117 | Hydrogen bond |
| Lactic acid | -7.22 | - | - | - | - |
The nitrogen atom in the first position of the pyrimidine heterocycle of compounds 4a-4d, 4f-4i, and 4l made hydrogen bonds with Val 283, and 4e could form hydrogen bonds with Ser 282, the same structural fragment. Hydroxyl groups of compounds 4d, 4e, and 4g made hydrogen bonds with Asn 260. Compound 4j made hydrogen bonds with Gly 281, its hydroxyl group. The furyl fragment of 4k could form hydrogen bonds with Asn 81; also, for this compound, a hydrogen bond was formed between His 244 and its carboxyl group.
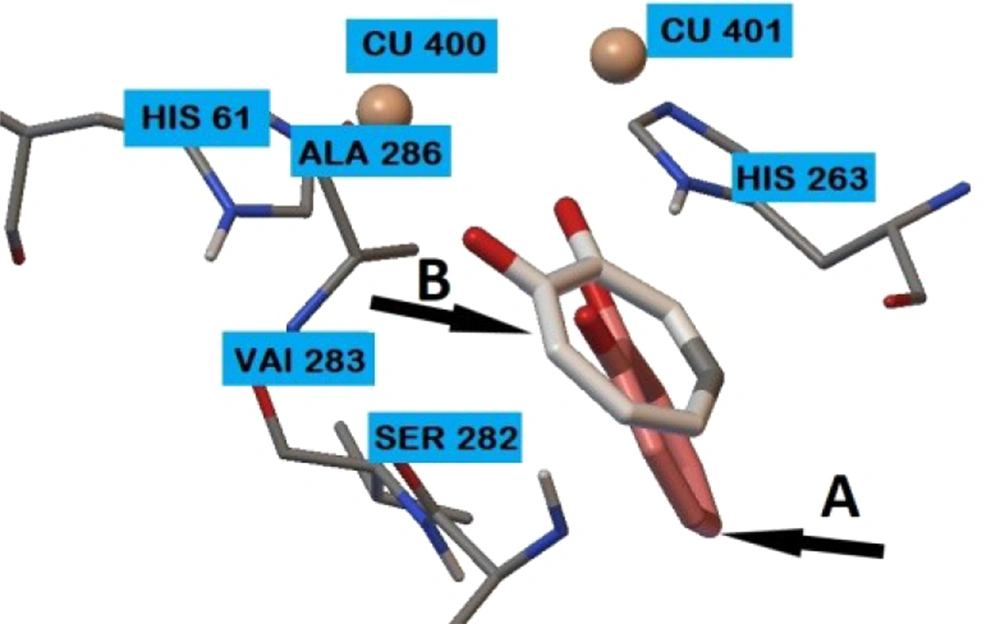
The spatial structure of the stable conformational model of compound 4g in the active site of the enzyme based on the results of molecular docking and the location of tropolone determined by XRD analysis are shown in Figure 3. It can be seen that in compound 4g, the 2,4-dihydroxyphenyl fragment is located next to the tropolone molecule, suggesting a similar molecular mechanism for tyrosinase inhibition. Thus, it is possible to select the hydroxyphenyl residue and assume its significant effect on tyrosinase inhibition.
RMSD between the location of the tropolone at complex 2Y9X (XRD analysis) and its location according to the molecular docking data is 2.89 angstrom (Figure 4).
Figure 5 shows the locations of compounds 4a-4l at the tyrosinase binding site.
3.15. Anti-tyrosinase Activity Evaluation
The results of the study of the anti-tyrosinase activity of the synthesized compounds are presented in Table 2. As can be seen from the results obtained, among the studied substances, the most pronounced anti-tyrosinase activity was possessed by compound 4g, which in terms of activity was comparable to lactic acid; however, it was less than hydroquinone and kojic acid (P < 0.05). Compound 4c showed slightly lower efficiency. The rest of the studied objects showed no significant anti-tyrosinase properties (IC50 was significantly and statistically higher in relation to the reference subjects). Given that the use of hydroquinone and kojic acid in practical medicine is limited to a large number of undesirable side effects, the most affordable and safe depigmenting agent is lactic acid (28). In this regard, compounds 4g and 4c, which showed comparable activity with lactate, can be considered promising objects for further study and development of drugs for the treatment of hypermelanogenic conditions.
| Compound | IC50 ± SEM (mmol/mL) |
|---|---|
| 4a | 1.11 ± 0.15 a, b, c |
| 4b | 0.87 ± 0.06 a, b, c |
| 4c | 0.7 ± 0.04 a, b |
| 4d | 2.04 ± 0.15 a, b, c |
| 4e | 2.45 ± 0.11 a, b, c |
| 4f | 1.57 ± 0.05 a, b, c |
| 4g | 0.51 ± 0.09 a |
| 4h | 2.25 ± 0.11 a, b, c |
| 4i | 2.34 ± 0.17 a, b, c |
| 4j | 2.11 ± 0.08 a, b, c |
| 4k | 3.03 ± 0.15 a, b, c |
| 4l | 2.1 ± 0.1 a, b, c |
| Hydroquinone | 0.15 ± 0.007 |
| Kojic acid | 0.32 ± 0.005 |
| Lactic acid | 0.46 ± 0.031 |
a Statistically significant relative to hydroquinone (P < 0.05).
b Statistically significant relative to kojic acid (P < 0.05).
c Statistically significant relative to lactic acid (P < 0.05).
4. Discussion
According to the minimum binding energy of ligands with the active tyrosinase site, the leading compounds are 4j, 4h, and 4c, but this is not exactly consistent with in vitro data. The greatest anti-tyrosinase activity was shown by compounds 4g, 4c, and 4b. Based on this, it can be assumed that metal-ligands interactions with 2 copper atoms in the tyrosinase binding site play an important role in inhibiting the enzyme. The presence of a hydroxy group of a compound increases the probability of the presence of anti-tyrosinase activity. Meanwhile, the fragment of the molecule with hydroxy groups should not contain large substituents, as in the case of compound 4j, hindering the penetration of the aryl fragment of 2-substituted tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine-4(3H)-one toward the copper atoms. According to the results of molecular docking, it is clear that the reference compounds hydroquinone, kojic acid, and lactic acid have a low molecular weight and hydroxy and/or carboxyl groups, allowing them to be located close to the copper atoms of the tyrosinase binding site and form metal-ligands interactions. The introduction of only hydroxy groups into the aryl substituent significantly increases the inhibitory activity of the compounds (4b, 4c, and 4g). Compound 4g with the 2,4-dihydroxyphenyl fragment showed the maximum anti-tyrosinase activity in 2-substituted tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine-4(3H)-one, which was comparable to lactic acid in terms of activity; however, it was less than hydroquinone and kojic acid. Compounds containing 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl 4d, 3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl 4e, 2-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl 4f fragments did not show anti-tyrosinase activity, although they contain a hydroxy group in their structure.
Also, the presence of anti-tyrosinase properties in the studied compounds can significantly expand the range of depigmenting substances. The reason is that it is currently established that hyperpigmentation of the skin is a process of diffuse deposition of melanin in subcutaneous structures, leading to the staining of certain areas of the skin in light brown or brown. Hyperpigmentation can be a symptom of quite dangerous skin lesions. Thus, chronic poisoning with dioxin and dioxin-like substances (polychloro-organic toxicants) leads to the activation of aryl–carbohydrate receptors of melanocytes and the formation of melanous deposits, one of the early and reliable signs of melanoma (29). Also, the activation of melanocytes can occur as a result of intoxication with drugs, including fluoroquinolones, tetracyclines, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), or antiarrhythmic drugs (10). In addition to being unaesthetic, hyperpigmentation of the skin (especially open areas of the body) has a significant impact on the psycho-emotional state of a person and his social adaptation. França and Keri found that 78% of respondents with hyperpigmentation of the facial skin were unable to establish proper social contact, 22% noted a deterioration in the quality of life, and 10% needed qualified psychological assistance (11).
Melanogenesis is a complicated procedure characterized by a complex cascade of enzymatic events, with proteins linked to tyrosinase TYRP1 and TYRP2-polyfunctional copper-containing metalloenzymes playing a determining role in catalyzing a reaction that restricts the rate of melanin synthesis. As a result, tyrosinase inhibition may be one of the methods to treat skin hyperpigmentation. The most well-known tyrosinase inhibitors are kojic acid and hydroquinone, the use of which in clinical practice is limited due to a substantial number of adverse effects. As a result, hydroquinone should only be administered in conjunction with isotretinoin (as a gel), which considerably increases the drug load on the patient (30). Kojic acid is a fungi-produced natural metabolite that inhibits tyrosinase. Although kojic acid has high biocompatibility, it does not increase efficacy or help reduce toxicity (31).
4.1. Conclusion
The method of synthesis of 2-substituted tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine-4(3H)-one was suggested, which is technologically simple and environmentally and economically feasible. A number of thienopyrimidine derivatives obtained have a pronounced property of inhibiting tyrosinase. The computational experiment made it possible to predict the structures that inhibit tyrosinase, as well as to simulate the interaction of the constructed compounds with the tyrosinase binding site. In vitro studies have shown that 4g compounds have the greatest anti-tyrosinase activity.
![Location according to molecular docking: 4g ([A] brown color), kojic acid ([B] beige color), hydroquinone ([C] green color), lactic acid ([D] blue color), and the location of tropolone determined by XRD analysis ([E] pink color). Location according to molecular docking: 4g ([A] brown color), kojic acid ([B] beige color), hydroquinone ([C] green color), lactic acid ([D] blue color), and the location of tropolone determined by XRD analysis ([E] pink color).](https://services.brieflands.com/cdn/serve/3170b/a6b022888596f75846ae9fafe0b55e7773cdec50/ijpr-126557-g003-F3-preview.webp)