1. Background
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS), also known as runner’s knee or jumper’s knee, is one of the most common diagnoses made for patients referred to physical/rehabilitation and orthopedic clinics. Diffused pain in one or both of the knees is the most common symptom of PFPS. In most cases, the pain is exacerbated by intense activity, kneeling, squatting, climbing, and weakness of quadriceps muscle. However, the symptoms can be controlled by resting the knee as much as possible, decreasing activity level, and physical therapy (1-5).
While the exact cause of PFPS is unclear, it’s believed to be caused by changes in the patellofemoral joint biomechanics due to over-use and damage to the joint such as internal rotation of the femur, genu varum, tibial torsion, subtalar joint pronation, muscle imbalance, previous knee trauma, declined muscle flexibility, and quadriceps muscle strength.
Patients suffering from PFPS may experience major physical disabilities, which significantly declines the quality of life (QoL) (1, 3, 6). Therefore, determining the most plausible pain mechanism is of crucial importance to develop proper treatments with the highest efficacy and lowest possible complications. In this context, various methods have been used to determine the plausible mechanisms of knee pain, including clinical examination, medical imaging, as well as arthroscopy, each with their own specificity and sensitivity (7).
The lumbosacral manipulation and knee exercises are the most widely used treatment in physical medicine to treat PFPS that carry no major side effects (8-11). Manipulative therapy was first introduced in Europe back in the 4th century. Since the 19th century, this technique has been rapidly expanding around the world, particularly in the fields of osteopathy and chiropractic (12, 13). The science of manipulation is based on the fact that even minor disorders of the central nervous system, particularly the peripheral nerves, can cause severe vague pain in lower extremities (14).
Although the main mechanisms of manipulation techniques are not clear yet, it’s believed that they may lead to neuroplastic changes by the biomechanical recovery of the corresponding joint (13). Physicians readjust the vertebrae to the correct position by subtle movements, which dramatically reduces the pain from nerve impingement (15, 16). Lumbosacral manipulation, which has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration, is reported to be beneficial for some patients with acute and chronic pain such as lumbar disc diseases (15, 17). Only a trained professional should provide Lumbosacral manipulation.
2. Objectives
3. Methods
In this randomized controlled clinical trial, all patients diagnosed with PFPS admitted to the Emam Reza hospital in Tehran (Iran) between 2017 and 2019 were included. After receiving the study approval by the Institutional Review Board at the AJA University of Medical Sciences and obtaining written informed consent from all participants, eligible patients were divided into two groups of study or control. Data were collected using a checklist and questionnaire. The inclusion criterion was referring to the physical medicine and rehabilitation clinics of the Emam Reza Hospital with PFPS diagnosis. Exclusion criteria were being diagnosed with radiculopathy, tibiofemoral degenerative joint diseases (grade 2 and above based on the Kellgren-Lawrence radiographic grading), existing pes planus, and history of lumbar disc herniation, surgery, and knee trauma. The eligible patients were divided into two groups, each with 15 subjects. The study group received the lumbosacral manipulation with the knee exercises, and the control group received the knee exercises alone.
Radiographic examinations, including anterior-posterior, lateral, and patellar views of the knee, were performed for all participants at the beginning of the study. Anterior-posterior and lateral views of the lumbosacral were also obtained for all participants.
All individuals in the study group received a single bilateral lumbosacral manipulation after ruling out any contraindication for lumbosacral manipulation by lumbosacral radiography. The manual movements were performed by a trained professional at the level of L2 to S1 (the quadriceps and hamstrings muscles’ neuronal levels). Then, both groups participated in the therapeutic strengthening knee exercise program (included the straight leg raise, quadriceps isometric, cuff, and hamstring stretching exercises) for 4 weeks (twice a day, every day of the week). It should be noted that individuals were not allowed to perform activities that could trigger knee pain during the program. All exercise techniques were based on Therapeutic Exercise, Foundations, and Techniques by Carolyn Kinser (22).
Gait analysis (including cadence, foot pressure, single support time, and double support time), measuring the range of motion of the knee, assessment of quadriceps muscle strength by superficial electromyography, Visual Analog Scale (VAS), and the Knee injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS) questionnaires were used to collect information before providing the interventions, during the second session, and four weeks after knee strengthening exercises.
To assess improvement in pain severity, VAS was used in two measurement sessions (23). To assess the knee pain, symptoms, function in daily living, function in sport and recreation, and knee-related quality of life, the KOOS worldwide questionnaire was completed in two measurement sessions by all participants. The KOOS includes 42 patient-centered items on five patient-related subscales: Pain (9 items), symptoms (stiffness, etc.) related to the disease (7 items), daily activities (climbing the stairs, standing, etc.) (17 items), sports and recreational activities (jumping and running) (5 items), and knee-related QoL (4 items). Each item has five possible answers on a Likert scale. The score of each subscale ranges from zero to 4. Therefore, the total score of KOOS ranges from zero (“No Problems”) to 100 (Extreme Problems) (24).
The Kellgren-Lawrence radiographic grading system uses radiological evidence of osteophytes presence and reduction of articular space to categorize patients into five groups based on the severity of the pain, as follows: grade 0 (none); grade 1 (doubtful narrowing of the joint space with possible osteophyte formation); grade 2 (possible narrowing of the joint space with definite osteophyte formation); grade 3 (definite narrowing of joint space, moderate osteophyte formation, some sclerosis, and possible deformity of bony ends); grade 4 (osteophyte formation, severe narrowing of the joint space with marked sclerosis, and definite deformity of the bone end) (25). Most of the recent osteoarthritis-related studies have used this grading system to diagnose osteoarthritis or to determine the severity of joint involvement.
3.1. Data Analysis
Data analysis was performed using SPSS version 24. Quantitative data are described using mean and standard deviation. While frequency was used to describe qualitative data. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test was applied to test for a normal distribution. Quantitative variables were analyzed using t-test and ANOVA. Categorical variables were compared using the Chi-square test. Statistical significance was considered when P value < 0.05.
4. Results
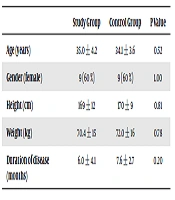
In total 37 patients enrolled to participate in the present study, that seven were excluded due to the insufficiency of data. The remaining 30 patients [18 females and 12 males] had a mean age of 34 ± 5 years. There was no significant difference concerning the variables of age, gender, height, weight, and duration of the disease in both groups. The demographic characteristics of the participants are described in Table 1.
| Study Group | Control Group | P Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 35.0 ± 4.2 | 34.1 ± 3.6 | 0.52 |
| Gender (female) | 9 (60 %) | 9 (60 %) | 1.00 |
| Height (cm) | 169 ± 12 | 170 ± 9 | 0.81 |
| Weight (kg) | 70.4 ± 15 | 72.0 ± 16 | 0.78 |
| Duration of disease (months) | 6.0 ± 4.1 | 7.6 ± 2.7 | 0.20 |
No significant difference was observed concerning the VAS and KOOS indexes of participants in both groups, before and 4 weeks after providing the intervention (Table 2).
| Study Group | Control Group | P Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beginning of the Study | After 4 Weeks | Beginning of the Study | After 4 Weeks | ||
| VAS score index | 5 ± 1.1 | 3.6 ± 1.2 | 5 ± 1.3 | 3.7 ± 1.2 | 0.39 |
| KOOS score index for the knee pain | 65 ± 12 | 76 ± 13 | 65 ± 14 | 73 ± 10 | 0.97 |
| KOOS score index for symptoms | 79 ± 16 | 81 ± 11 | 77 ± 13 | 82 ± 10 | 0.68 |
| KOOS score index for function in daily living | 68 ± 11 | 77 ± 4 | 72 ± 12 | 80 ± 13 | 0.42 |
| KOOS score index for function in sport and recreation | 56 ± 15 | 67 ± 13 | 59 ± 4 | 68 ± 2 | 0.53 |
| KOOS score index for knee-related quality of life | 59 ± 14 | 60 ± 10 | 60 ± 13 | 65 ± 10 | 0.51 |
Abbreviations: VAS, Visual Analog Scale; KOOS, Knee injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score.
Based on the results of the gait analysis, a significant difference was observed in the swing phase of walking between the two groups four weeks after providing the intervention. Also, an association was observed between foot pressure and the method of lumbosacral manipulation (Table 3).
| Study Group | Control Group | P Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beginning of the Study | After 4 Weeks | Beginning of the Study | After 4 Weeks | ||
| Swing phase of walking (%) | 33.4 ± 3 | 33 ± 2 | 33.6 ± 2 | 31 ± 3 | 0.03 |
| Stance phase of walking (%) | 66 ± 3 | 66 ± 2.5 | 65.4 ± 1.6 | 68.1 ± 2.8 | 0.61 |
| Index of cadence (step/min) | 52 ± 4 | 54 ± 4 | 50 ± 4 | 52 ± 4 | 0.45 |
| Foot pressure (n/cm2) | 28 ± 1.6 | 27 ± 1.1 | 29.6 ± 2.6 | 29.6 ± 2.5 | 0.05 |
| Single support time (second) | 0.33 ± 0.03 | 0.33 ± 0.02 | 0.32 ± 0.02 | 0.32 ± 0.02 | 0.23 |
| Double support time (second) | 0.33 ± 0.05 | 0.32 ± 0.03 | 0.34 ± 0.03 | 0.33 ± 0.05 | 0.56 |
No significant difference was found concerning the knee range of motions. However, quadriceps muscle strength was increased in the study group (Table 4).
| Study group | Control group | P Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beginning of the Study | Week 4 | Beginning of the Study | Week 4 | ||
| Extension rang of motion (degree) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.6 ± 2.5 | 2.3 ± 4.9 | 0.32 |
| Flexion range of motion (degree) | 108 ± 5 | 108 ± 5 | 112 ± 6 | 112 ± 6 | 0.11 |
| Quadriceps muscle strength (mV) | 596 ± 139 | 873 ± 119 | 606 ± 133 | 720 ± 138 | 0.003 |
5. Discussion
Various risk factors are suggested for PFPS, including gender, existing pes plan us, and extreme activities. Adolescents and young people are at greater risk of PFPS, however, the elderly also may experience PFPS. It’s more common among females than males, probably due to weaker muscles and wider pelvic angle. Also, those with pes planus are more vulnerable to PFPS syndrome because of the additional pressure on their knees. Also, overuse of knees (e.g. running and jumping sports) put repetitive stress on the joints, which enhances the risk of developing PFPS following a knee injury (26, 27).
There was no difference between the participants of the present study concerning the demographic characteristics. Moreover, each group comprised of six males and nine females, as we expected. Nevertheless, there was no statistically significant gender difference between the two groups (P = 1.00).
Findings about the efficacy of lumbosacral manipulation therapy are controversial (1, 18-21, 28-30). Miller et al., in a study on 18 PFPS patients, reported that Kinesio taping was more effective than lumbosacral manipulation (18). This dissimilarity can be attributed to the differences caused by the second method used in the treatment of patients. Grindstaff et al., in a study on 48 PFPS patients, showed that lumbosacral manipulation didn’t have any immediate effect on quadriceps muscle strength (19). However, in the present study, a statistically significant difference was observed in quadriceps muscle strength based on the surface electromyography and swing phase of walking after 4 weeks in the study group compared to the control group. This finding is consistent with previous reports. Crowell et al. (1) and Iveronet al., reported that Lumbopelvic manipulation was effective in 57% and 45% of PFPS patients, respectively (1, 20). Although previous studies reported some complications and risks after providing Lumbopelvic manipulation, in the present study no complication was observed among participants (11, 31).
In conclusion, this study demonstrated that using manipulation caused significant improvements in PFPS patients compared to the sole therapeutic exercise. Accordingly, incorporating this method can improve the functions of PFPS patients.