1. Background
The emerging disease of COVID- 19 was caused by coronaviruses. It was first seen in Wuhan, China in late 2019. The disease was zoonotic and had signs and symptoms similar to those of acute respiratory syndrome. The disease could not be treated with routine medications. COVID-19 was transmitted by droplets. The disease was reported shortly afterward in Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan (1-5). The World Health Organization approved a pandemic of the disease in early March 2020 (6). This disease is one of the most important threats to human health today due to its high infectivity and case fatality rate (7). According to epidemiological models, several million deaths have been estimated in some of the most populous countries due to COVID-19 (7).
2. Objectives
This study aims to describe the epidemiological features of COVID-19 in continental Europe.
3. Methods
In this ecological study, the characteristics of COVID-19 in continental Europe were examined. Preliminary data of this study, which included information about the total definitive cases identified, total definitive cases of death due to COVID-19, and the population of countries, were extracted from the reports of the World Health Organization from the beginning to March 8, 2021, and transferred to Excel version 2016. Final calculations were performed using SPSS version 24 (8, 9). The case fatality rates were also obtained using the following formula (10).
Case- fatality rates (percent)=((No of individuals dying during a specified period after disease onset or diagnosis)/(No of the individuals with the specified disease)) ×100
4. Results
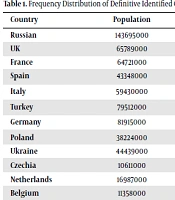
The total number of countries on the continent, according to the World Health Organization, is 52 countries, the most populous of which is Russia with 146,695,000, and the least populated is San Marino with 33000. The highest number of confirmed cases of COVID-19 is related to Russia with 4,333,029 cases, and the lowest belongs to Monaco with 2023 cases. The United Kingdom had the highest number of confirmed deaths due to COVID-19 with 124,419 cases, and the lowest number of deaths due to this disease was in Monaco, with 26 deaths. The highest case fatality rate was in Bulgaria with 4.08%, and the lowest was in Iceland with 0.48% (Table 1).
| Country | Population | Total Case COVID-19 | Total Death COVID-19 | Case Fatality Rates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Russian | 143695000 | 4333029 | 89473 | 2.06 |
| UK | 65789000 | 4218524 | 124419 | 2.95 |
| France | 64721000 | 3836480 | 88099 | 2.30 |
| Spain | 43348000 | 3142358 | 70501 | 2.24 |
| Italy | 59430000 | 3067489 | 99785 | 3.25 |
| Turkey | 79512000 | 2780417 | 29030 | 1.04 |
| Germany | 81915000 | 2505193 | 71934 | 2.78 |
| Poland | 38224000 | 1801083 | 45317 | 2.52 |
| Ukraine | 44439000 | 1406800 | 27128 | 1.93 |
| Czechia | 10611000 | 1325291 | 21882 | 1.65 |
| Netherlands | 16987000 | 1120075 | 16540 | 2.04 |
| Belgium | 11358000 | 787891 | 22891 | 2.91 |
| Sweden | 9838000 | 684961 | 13003 | 1.90 |
| Switzerland | 8402000 | 559627 | 9278 | 1.66 |
| Serbia | 8820000 | 458439 | 4562 | 1.00 |
| Austria | 8712000 | 471820 | 8538 | 1.81 |
| Hungary | 9753000 | 468713 | 15988 | 3.41 |
| Kazakhstan | 17988000 | 268327 | 3389 | 1.26 |
| Bulgaria | 7131000 | 260308 | 10614 | 4.08 |
| Georgia | 3925000 | 272998 | 3591 | 1.32 |
| Belarus | 9480000 | 295511 | 2038 | 0.69 |
| Armenia | 2925000 | 175016 | 3225 | 1.84 |
| Croatia | 4213000 | 246514 | 5590 | 2.27 |
| Azerbaijan | 9725000 | 236768 | 3241 | 1.37 |
| Moldova | 406000 | 195252 | 4111 | 2.11 |
| Greece | 11184000 | 203978 | 6705 | 3.29 |
| Slovakia | 5444000 | 195468 | 4169 | 2.13 |
| Bosnia | 3517000 | 136898 | 5259 | 3.84 |
| Denmark | 5712000 | 214839 | 2379 | 1.11 |
| Kyrgyzstan | 2078000 | 195468 | 4169 | 2.13 |
| Uzbekistan | 31447000 | 214839 | 622 | 0.78 |
| Ireland | 4726000 | 223219 | 4422 | 1.98 |
| Lithuania | 2908000 | 202430 | 3336 | 1.65 |
| Romania | 19778000 | 107163 | 3195 | 2.98 |
| Portugal | 10372000 | 810094 | 16540 | 2.04 |
| Albania | 2926000 | 39014 | 822 | 2.11 |
| Norway | 5255000 | 73493 | 632 | 0.86 |
| Montenegro | 629000 | 79771 | 1059 | 1.33 |
| Luxembourg | 602005 | 56646 | 622 | 1.17 |
| Finland | 5503000 | 60904 | 767 | 1.26 |
| Lativia | 1971000 | 90331 | 1695 | 1.88 |
| Estonia | 1312000 | 76183 | 667 | 0.88 |
| Tajikistan | 7835000 | 13714 | 91 | 0.66 |
| Cyprus | 1170000 | 36878 | 233 | 0.63 |
| Malta | 429000 | 24398 | 334 | 1.37 |
| Andorra | 77000 | 11042 | 112 | 1.01 |
| San Marino | 33000 | 3922 | 76 | 1.94 |
| Iceland | 33200 | 6064 | 29 | 0.48 |
| Liechtenstein | 2908000 | 2663 | 53 | 1.99 |
| Monaco | 3800 | 2023 | 26 | 1.29 |
5. Discussion
The largest number of definitive cases of COVID-19 detected in continental Europe belonged to Russia, England, and France, respectively. The results of a study by Zemtsov and Baburin, which examined the risk factors for mortality and morbidity from COVID-19 in Russia, showed that the increase in definitive diagnosis of COVID-19 in Russia was due to the addition of private laboratories to diagnose the disease and the use of public transportation system, such as buses and city trains. These vehicles had poor ventilation, which was effective in transmitting the disease from healthy carriers to others. Other important factors involved in the transmission of the disease were seasonal workers moving from the northern regions to industrial and densely-populated cities. The return of these workers, who were mostly young and possibly healthy and asymptomatic carriers, transmitted the disease from them to family members and relatives, especially the elderly and the chronically ill, and the disease was more severe and fatal in these people (11).
According to a study by Brandily et al., the spread of the disease was different in various regions and cities of France. Poor economic conditions and poor environmental conditions, including living in slums, played a major role in the disease transmission and mortality from COVID-19 (12). The results of a study by Pollán et al. in Spain showed that the central regions of the country were at high risk for COVID-19, and that social gatherings in these areas were effective in transmitting the disease (13).
The highest case fatality rates of COVID-19 occurred in Bulgaria, Bosnia, and Greece, respectively. In a study by Sudharsanan et al., comparing the fatality of COVID-19 in ten countries, the highest case fatality rate was reported in Italy and the lowest in South Korea, which was almost inconsistent with the results of this study (14). However, the high case fatality rate in some countries may be due to the lack of definitive diagnosis of COVID-19. Adherence to health protocols, such as the use of masks and social distancing, is still the only way to prevent the disease transmission.