1. Background
With the rising demand for travel and tourism, and the transformation of the tourism industry into one of the largest industries in the world, countries aiming to attract potential tourists must align their efforts with socio-economic development and infrastructural growth. Marketing performance, as a tool for evaluating the status of a system, is essential in this industry because marketing plays a fundamental role in the long-term success of businesses. Therefore, assessing marketing performance is considered crucial for management (1).
The intensification of competition in the regional and global business environment, rapid changes, and increasing environmental uncertainty forces organizations to seek solutions to survive under these conditions (2). Many countries are implementing practical and legal service plans aimed at developing this industry. However, the affordability of medical services in Iran, compared to other countries, along with the high quality and alignment with the latest medical advancements worldwide, are significant factors that can boost medical tourism in Iran (3). Military hospitals, due to their higher discipline, more modern facilities, better pharmaceutical and logistical support, and superior strategic treatment choices, exhibit high therapeutic performance and significant potential to attract health tourists (4).
Health tourism is a type of travel that includes health and medical care in addition to recreation, leisure, and comfort. This industry is rapidly becoming a global phenomenon. Medical advancements and high-level healthcare facilities in Iran have created new tourism opportunities, particularly in attracting health tourists (5). As the medical tourism industry grows rapidly on a global scale, competition among countries to increase their market share has intensified significantly. The success of this industry largely depends on proper market segmentation and the accurate selection of target segments (6).
Marketing is one of the most essential activities organizations undertake throughout their operations. Over time, technological advancements have altered how organizations operate, their product or service markets, and their interactions with customers. In marketing, organizations must be aware of the best methods to connect with their customers and establish strong relationships to increase engagement and market value. Researchers have identified the best approach to achieving maximum customer engagement, emphasizing communication as the core structure. With technological advancements in many aspects of life, communication now encompasses more than one method; it can be conducted via the Internet and other communication media (7).
The emergence of new marketing trends is influenced by ongoing development, innovations, and changes in the market environment. As global markets evolve, companies must adapt to these phenomena (8). With increasing competition, attracting potential customers requires not only quality products and services but also modern marketing strategies. Consumers now demand more than ever easy access to products and services (9).
Today, the urban tourism market is highly competitive. Many cities around the world are working to create a better urban image to attract potential tourists and achieve sustainable tourism development (10). Meanwhile, consumer habits and behaviors are undergoing fundamental changes, with a growing shift toward digital consumption (11).
With the advancement and expansion of technology, the tourism industry has embraced innovations to enhance customer experiences and reduce operational costs (12).
Amid the growing importance of understanding technological transformation in the tourism industry, researchers are encountering the third wave of the internet era, which introduces the metaverse (13). The metaverse, also known as the metaworld, is the next generation of the Internet, consisting of decentralized, persistent online 3D virtual environments where users play an active role in activities like digital market investments. This virtual world will be accessible through headsets, augmented reality glasses, smartphones, personal computers, and gaming consoles (14).
The term "metaverse" was first coined by author Neal Stephenson in his 1992 science fiction novel Snow Crash, referring to a fully immersive, collective, and virtual shared space created by the convergence of augmented physical reality and persistent virtual reality. It represents an evolutionary leap for the Internet—an integrated physical and digital world where users can naturally interact with a computer-generated environment (15).
Metaverse marketing offers businesses and brands a unique opportunity to enter the global market. Some of the world’s largest brands have already started integrating and solidifying their digital presence in the metaverse. Similarly, some of the biggest technology companies are working on creating an official version of the metaverse that will be accessible anytime and from anywhere. Given these factors, more and more brands are quickly realizing that the best way to reach consumers is through the metaverse. As a result, the term "metaverse marketing" has recently emerged, creating a new style of business interaction in technology-driven environments (16).
The metaverse has the potential to change how people interact and perform daily tasks. It is a virtual, digital, and three-dimensional world formed by integrating various technologies and virtual spaces (17). The metaverse tourism ecosystem encompasses an immersive 3D virtual space that offers new opportunities for making tourism products tangible and serves as a source of inspiration for the creative economy. This ecosystem facilitates interactions among tourists, travel agents, and other stakeholders, enabling the execution of tourism processes at different stages (18).
Today, developing metaverse applications for marketing requires augmented reality (AR). AR and virtual reality (VR) technologies, combined with experiential marketing principles, aim to create positive experiences that engage users both physically and emotionally (19). As Buhalis et al. demonstrated in their study, metaverse marketing strategies using virtual reality can create immersive customer experiences. This advanced technology provides a clear, realistic picture, making customers feel like they are physically present in the situation, which differs from the experience of watching a regular 2D screen (20).
Some experts have raised essential concerns in the health sector arising from the development and implementation of metaverse technology (17). The metaverse and virtual reality are growing technologies that create distinctive experiences for users. In a study, 62% of consumers claimed to be more engaged with a brand through these media than through traditional physical marketing. Furthermore, over 71% of consumers perceive brands that use virtual reality marketing more favorably (19). For example, Tang et al. researched the importance of virtual reality technology in the spa (health and beauty services) industry in China. The findings revealed that spa users quickly recognized the benefits of augmented reality technology in waiting rooms, which aided specialists, owners, and spa doctors in providing superior services (21).
The rapid expansion of the metaverse has sparked numerous debates about its potential to transform society. Proponents describe the metaverse as an innovation that will have significant long-term impacts on people's lives, much like the Internet did previously (22).
2. Objectives
This article aims to explore the marketing opportunities of the metaverse in the health tourism industry within military and civilian hospitals in Iran.
3. Methods
This research was conducted in May and June 2024 using a qualitative research method with a contractual content analysis approach. The statistical population included professors and experts in new technologies and tourism from Semnan Province who were thoroughly familiar with health tourism. This included professors from Semnan University, Semnan University of Medical Sciences, Shahrud University of Medical Sciences, Shahrud Azad University, Payam Noor University of Semnan, Payam Noor University of Garmsar, and Payam Noor University of Majn (with a background in Tourism Management and IT Engineering). Additionally, professors from Shahrud University of Technology and Damghan University (with degrees in Computer Engineering and IT) were also included, as well as experts familiar with health tourism and modern marketing science from all travel and tourism agencies in Semnan Province. The sampling methods employed were purposive and snowball sampling.
The main criteria for selecting the sample members included a comprehensive knowledge of the IT industry, expertise in modern marketing and health tourism, and a master's degree or higher. Sampling continued until theoretical saturation was reached (23). The saturation point is when no new topics emerge, and researchers, after reviewing all scenarios, determine that sufficient data are available to complete the information (24).
The data collection tool was in-depth and semi-structured interviews, which were recorded and coded after obtaining permission from the interviewees. Initially, key ethical issues such as goals, outcomes, satisfaction, identity, relationships, confidentiality, and protection were shared and communicated with the interviewees. The interview questions focused on marketing through the metaverse and health tourism. The interviews began with demographic questions about the interviewee and continued with semi-structured questions related to marketing through the metaverse and health tourism.
After a thorough review of the literature on "metaverse technology" and "health tourism," the interview questions were designed and developed in collaboration with experts, including professors and specialists in new technologies and tourism who were thoroughly familiar with health tourism.
The reliability of the questions was assessed using two methods. In the first method, the research results were shared with experts, and their approval was obtained. In the second method, to calculate test-retest reliability, three interviews were selected, and each was coded by the researcher at 15-day intervals. The reliability between the two coders for the conducted interviews was calculated using the following formula:
Reliability = (Number of agreed codes/between two coders total number of codes) × 100%
This resulted in a reliability score of 0.77. Since the reliability was above 60%, the coding trustworthiness was confirmed, and it can be concluded that the current interview analysis has suitable reliability. The semi-structured interview questions included:
(1) What are the advantages of using metaverse marketing in the health tourism industry in military and civilian hospitals?
(2) What are the benefits of employing metaverse technology specialists in health tourism marketing?
(3) What opportunities can metaverse marketing offer in developing health tourism services in military and civilian hospitals?
(4) What challenges can metaverse marketing pose in developing health tourism services in military and civilian hospitals?
(5) How can metaverse technology in the health tourism marketing industry reduce the high costs of advertising and related expenses?
(6) What factors influence metaverse marketing in health tourism in military and civilian hospitals?
(7) How can the benefits and hospital services within the country be introduced to foreign health tourists using metaverse technology?
(8) How can the advantages of using metaverse technology be communicated to travel and tourism companies to attract health service seekers?
All interviews were conducted in person at the workplace. Each interview lasted about 45 minutes. At the end of each interview, after thanking the interviewees, they were asked to elaborate on any remaining topics. In total, eleven interviews were conducted.
In addition to the interviews, published texts and articles on "metaverse technology," "health tourism," and "marketing" from various scientific databases were reviewed and analyzed. The data from the semi-structured interviews were analyzed using the content analysis method of Graneheim and Lundman (25).
For data analysis, each interview was recorded, transcribed, and listened to by the researcher. The entire text was transcribed line by line. After transcribing the interviews and conducting multiple reviews and comparisons, open codes were extracted and categorized. Irrelevant information was removed, and the final categories and dimensions were refined. The criteria for categorizing topics were based on the main stakeholders in the metaverse marketing process in the health tourism sector.
The main categories were identified, weighted, and ranked using the Shannon entropy method in the quantitative phase. According to experts, the Shannon entropy method is considered more robust and valid for data analysis. In the Shannon entropy method, categories are first counted based on their frequency. Then, based on the frequency table, the following steps are performed:
(1) Normalizing the frequency matrix using the formula:
Where:
F is the category frequency, p is the normalized frequency matrix, i is the interviewee number, n is the number of categories, m is the number of interviewees, and, j is the category number., Calculating the information load of each category and placing it in the relevant column using the formula:
Where
This study is derived from a research project approved by the Research and Technology Deputy of Semnan University of Medical Sciences, with the ethics code IR.SEMUMS.REC.1403.021 in 2024.
4. Results
The interview process began with one of the active participants in the metaverse technology field, and other subjects were subsequently introduced. Gradually, the number of participants increased until data saturation was reached. Data collection continued after 11 interviews, reaching the point of saturation, meaning that new interviews did not provide additional insights.
In this study, metaverse marketing opportunities refer to conditions where metaverse technology is used to drive the growth and development of marketing in the health tourism sector. Based on content analysis, 215 open codes, 3 main categories, and 3 subcategories were identified from the interview texts. The main categories include:
- Opportunities related to health tourism businesses (66 codes),
- Opportunities related to health tourists (82 codes),
- Opportunities related to health tourism service providers (71 codes).
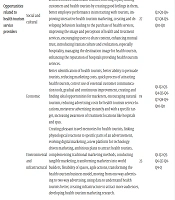
The subcategories include social, cultural, economic, environmental, and infrastructural aspects. Table 1 presents the extracted codes, main categories, subcategories, and interviewee numbers. It is important to note that to maintain the confidentiality of the participants, each interviewee is represented by the letter "QI." "Q" represents the interview, and "I" indicates the interviewee's number.
| Main Categories | Subcategories | Open Codes | Frequency of Open Codes | Reference to Interviews |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opportunities related to health tourism businesses | Social and cultural | Conducting various activities to introduce community culture like health food festivals, comprehensive introduction of native medicinal plants used in nature therapy with virtual tourism, virtual entertainment events, or creating mental relaxation, suitable opportunity to introduce medical services, creating an experience of presence in domestic hospitals, reducing the gap between real-world interactions and virtual interactions. | 11 | Q1-Q2-Q4-Q7-Q8-Q9-Q10-Q11 |
| Economic | Dynamic and continuous value, introduction and employment of skilled human resources in technology and medicine, providing health tourism services without limitation of tourist numbers, revenue generation from data, optimal use of devices and forms, creating more digital participation opportunities in daily life, creating an independent and new economy, facilitating trade of medical equipment, opportunity to enter the global medical technology market, gaining competitive advantage, long-term profitability, investment in health tourism businesses, opportunity to enter global medical markets, critical role in the future of the health tourism industry, opportunity to introduce brands of medical products to consumers, revenue generation opportunity for travel agencies, fast and easy results, opportunity to attract skilled individuals in health and medicine, reducing repetitive costs, reducing transportation costs, introducing health tourism services at any time and place, providing higher quality customized services, improving the position of health tourism companies in the business market, continuous improvement, driving sales of health tourism services and products, creating financial incentives like tax, customs, and insurance cost reductions. | 35 | Q1-Q2-Q3-Q4-Q5-Q6-Q7-Q8-Q9-Q10-Q11 | |
| Environmental and infrastructural | Creating advanced virtual hospitals like Metaverse Hospital in the UAE, monitoring and scanning users, creating new borderless cyberspace, using virtual reality, blockchain, and digital currency technologies, utilizing interconnected virtual worlds, new resource combinations, using cutting-edge technologies like NFTs, leading in new technologies, continuous development of the metaverse, partnering with startups and knowledge-based companies, aligning technologies with business goals, aligning with the global market, smartening the tourism market, making smart contracts on the blockchain with developers, attracting investors to develop internet bandwidth. | 20 | Q1-Q2-Q3-Q4-Q6-Q8-Q9-Q11 | |
| Opportunities related to health tourists | Social and cultural | Conducting various activities like receiving health and medical consultations, creating a better health tourism experience, creating excitement and motivation in tourists, helping health tourists behave appropriately when encountering actual service providers, gaining real experiences in the form of avatars, inspiring health tourists, making travel experiences memorable and recalling for health tourists, interacting with doctors from different countries, joining various global medical communities, public education on health tourism, understanding tastes and preferences, learning about health services in other regions, overcoming some limitations for those interested in health tourism like people with disabilities, participating in health festivals without location constraints, finding countries with similar religious beliefs for health tourism. | 22 | Q1-Q2-Q3-Q5-Q7-Q8-Q10-Q11 |
| Economic | Connecting to the most relevant health service provider in the shortest possible time, making foreign health tourists aware of low treatment costs in the country, traveling to different locations for mental and physical health like hot springs or well-equipped hospitals, better meeting health tourists' needs, providing superior value to health tourists, creating new travel and tourism opportunities, facilitating travel during epidemics like COVID-19, replacing some unnecessary physical travel, experiencing activities not possible in the real world, better decision-making for health tourism areas, gaining new ideas for treatment from tourists, trial before arrival at destinations and attractions for health tourists, choosing the best option according to needs and interests, creating comprehensive and valuable experiences, receiving timely and appropriate medical services, diverse medical services, reducing search costs, reducing approval costs, reducing transportation costs, reducing tracking costs, receiving high-quality customized medical services, tourism enjoyment for all social groups, no need for visa issuance. | 40 | Q1-Q2-Q3-Q4-Q5-Q6-Q7-Q8-Q9-Q10-Q11 | |
| Environmental and infrastructural | Entering the screen as an avatar and creating a digital twin for each tourist, an entirely realistic and simulated construction of the natural world, enjoying travel with security and peace at home, accessible health tourism, creating suitable infrastructure for the tourism of disabled and elderly people, marketers pursuing their interests, saving time, public security. | 16 | Q3-Q4-Q5-Q6-Q7-Q9-Q11 | |
| Opportunities related to health tourism service providers | Social and cultural | Better market segmentation for health tourism, more interventionist than digital advertising, compatibility with the modern world, enhancing audience interaction, gaining market knowledge, benefiting from change agents as employees, better interaction with users and health tourists, fostering loyalty among customers and health tourists by creating good feelings in them, better employee performance in interacting with tourists, improving interactive health tourism marketing, creating and developing behaviors leading to the purchase of health services, improving the image and perception of health and treatment services, encouraging users to share content, enhancing mutual trust, introducing Iranian culture and civilization, especially hospitality, managing the destination image for health tourists, enhancing the reputation of hospitals providing health tourism services. | 27 | Q2-Q3-Q6-Q7-Q8-Q9-Q10-Q11 |
| Economic | Better identification of health tourists, better ability to persuade tourists, reducing marketing costs, quick process of attracting health tourists, correct use of essential customer communication tools, gradual and continuous improvement, creating and finding ideal opportunities for marketers, encouraging natural tourism, reducing advertising costs for health tourism service locations, metaverse advertising instantly and with a specific target, increasing awareness of treatment locations like hospitals and spas. | 19 | Q1-Q2-Q3-Q4-Q5-Q6-Q7-Q8-Q9-Q10-Q11 | |
| Environmental and infrastructural | Creating pleasant travel memories for health tourists, linking physiological reactions to specific parts of an advertisement, evolving digital marketing, a new platform for technology-driven marketing, ambitious plans to attract health tourists, complementing traditional marketing methods, conducting tangible marketing, transforming marketers into world builders, flexibility of spaces, agile actions, transforming the health tourism business model, moving from one-way advertising to two-way advertising, using data to understand health tourists better, creating infrastructure to attract more audiences, developing health tourism marketing research. | 25 | Q1-Q2-Q5-Q6-Q7-Q8-Q9-Q |
Coding of Main and Subcategories of Metaverse Marketing Opportunities in Attracting Health Tourists
The prioritization of the main categories of metaverse marketing opportunities in health tourism, derived from Shannon entropy, is as follows:
- Opportunities related to health tourism service providers,
- Opportunities related to health tourism businesses,
- Opportunities related to health tourists.
5. Discussion
This study aimed to identify and rank the opportunities for metaverse marketing in attracting health tourists to military and civilian hospitals in Iran. Analyzing interviews and reviewing theoretical foundations and past research revealed additional opportunities to attract health tourists using advanced metaverse technology.
The most significant strength is the alignment of Iran's medical services with current global science and technology, as well as the availability of modern medical equipment. In contrast, the lack of an efficient health tourism information system is the primary challenge in Iran's health tourism sector (27). Therefore, it is crucial to leverage advanced technologies, such as the metaverse, to inform and market health tourism services. As expert number seven stated, "Metaverse marketing can serve as a factor and parameter in improving the current state of health tourism in modern marketing. Given the large scale of the tourism industry, it can reduce costs, increase revenues, offer new services, provide better sustainable services, diagnose issues in traditional health tourism processes, enhance the tangible experience for tourists, and better analyze health tourists' behavior in military and civilian hospitals." This finding aligns with Potjanajaruwit's research in Thailand, which aimed to promote health tourism marketing using metaverse technology and VR glasses, studying 372 health tourists. The medical tourism standards data were analyzed using multiple regression analysis, and the results showed that developing metaverse technology applications for health tourism marketing, including sensory and perceptual aspects, had an R² value of 0.509, indicating impactful and creative marketing (19).
Given today’s highly competitive tourism market and the rapid pace of changes in the business environment, companies must take actions aligned with these changes to achieve optimal performance. Since marketing is a core business component, innovative and creative actions can be an effective solution (28). As expert number ten mentioned, "Metaverse technologies are used to create communications and align technologies with business goals. One of the main aspects of metaverse marketing is transforming the health tourism business model. We need to reconsider targeting and move toward agility using metaverse marketing tools. Metaverse marketing focuses on providing fast, desirable, and diverse services." These findings align with Suanpang et al.'s research, which aimed to design and develop an open metaverse platform for tourism called the "Extended Metaverse" in Thailand, involving 428 users. The research analyzed requirements, then designed and implemented the system architecture, followed by system evaluation. The results showed that the extended metaverse was divided into three layers: Creating tags, characters, and virtual objects. The satisfaction results from the metaverse, the created tourism experience, and overall satisfaction with the metaverse usage diversity were 86%, 79.7%, and 92.9%, respectively (29).
Buhalis et al. demonstrated in their study that the metaverse creates many exciting opportunities for tourism. Tourism organizations that use metaverse strategies to create hybrid virtual and physical experiences for customers enable communication before, during, and after the trip with both customers and other stakeholders, providing a platform for implementing metaverse research opportunities (30).
The following table details the main and subcategories and open codes:
5.1. Expert Perspectives Analyzed Using Shannon Entropy Approach
The results of the Shannon entropy analysis for the main categories of opportunities related to health tourism businesses, health tourists, and health tourism service providers are presented in Table 2 below:
| Main Categories | Importance Coefficient (Ej) | Weight (Wj) | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|
| Opportunities related to health tourism businesses | 0.954 | 0.333 | 2 |
| Opportunities related to health tourists | 0.951 | 0.332 | 3 |
| Opportunities related to health tourism service providers | 0.957 | 0.334 | 1 |
Ranking of Main Categories of Metaverse Marketing Opportunities in Attracting Health Tourists in Military and Civilian Hospitals
As the results indicate, the ranking of the main categories in order of priority is as follows:
- Opportunities related to health tourism service providers,
- Opportunities related to health tourism businesses,
- Opportunities related to health tourists.
The rapid expansion of technologies has empowered customers and facilitated communication between companies and customers. Therefore, marketers must adapt by altering previous customer purchase pathways for products and services and create new paths aligned with these changes. Individuals and businesses can explore rapidly developing technologies that bring unimaginable opportunities. The metaverse is a new platform for digital marketing, enhancing the way businesses interact with their audience. Marketing in the metaverse presents unique opportunities (31).
Health tourism service providers can establish better interactions with patients using this technology. Patients can meet and chat with doctors in the form of avatars. Additionally, to attract more tourists, health tourism service providers can offer virtual tours of the different sections of the hospital before travel, allowing patients and tourists to preview the services they are likely to receive in the future. This virtual experience helps individuals get a sense of the services they will receive, which can be a critical factor in attracting health tourists and influencing their decision to choose a particular service provider (32).
It is recommended that businesses and health tourism service providers in military and civilian hospitals adopt innovative metaverse technology in their marketing strategies to offer diverse services to health tourists and gain a competitive edge.
One of the limitations of this study is the existence of filtering within the country, which restricts the implementation of this technology in Iran compared to other countries.