1. Background
Vitamins are chemically distinct families of organic compounds that are essential in small quantities for normal metabolism. With the exception of vitamin D, humans cannot synthesize vitamins and must obtain them through dietary intake to prevent metabolic disorders. Vitamin D functions as a prohormone for calcium regulation. Approximately 95% of vitamin D is derived from sunlight exposure, while the remaining 5% comes from sources such as egg yolk, fatty fish, cod liver oil, enriched dairy products, fortified cereals, and mushrooms.
2. Methods
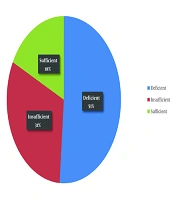
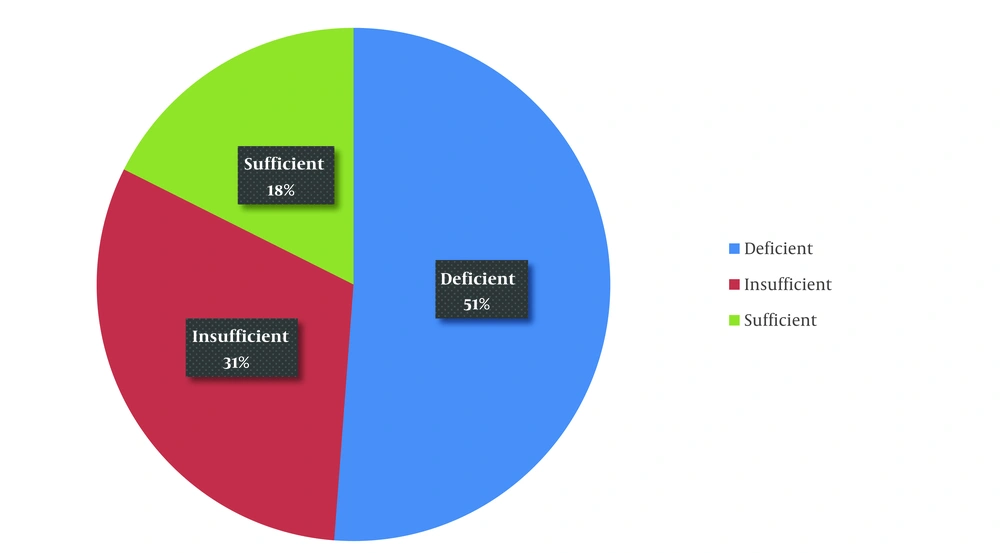
To assess the status of vitamin D efficiency and deficiency in children in the southern part of Iran, subjects were randomly selected from the first author's office referrals, including patients and those visiting for checkups and follow-ups. Over a 5-year study period, 500 children were evaluated for their vitamin D status. These children were otherwise asymptomatic, with their weight and height measured, and their nutritional status assessed. Vitamin D levels were categorized as follows: Levels < 20 ng/mL (50 nmol/L) were considered deficient, levels between 20 - 30 ng/mL (50 - 75 nmol/L) were labeled as insufficient, and levels > 30 ng/mL (> 75 nmol/L) were categorized as sufficient (Table 1 and Figure 1).
3. Results
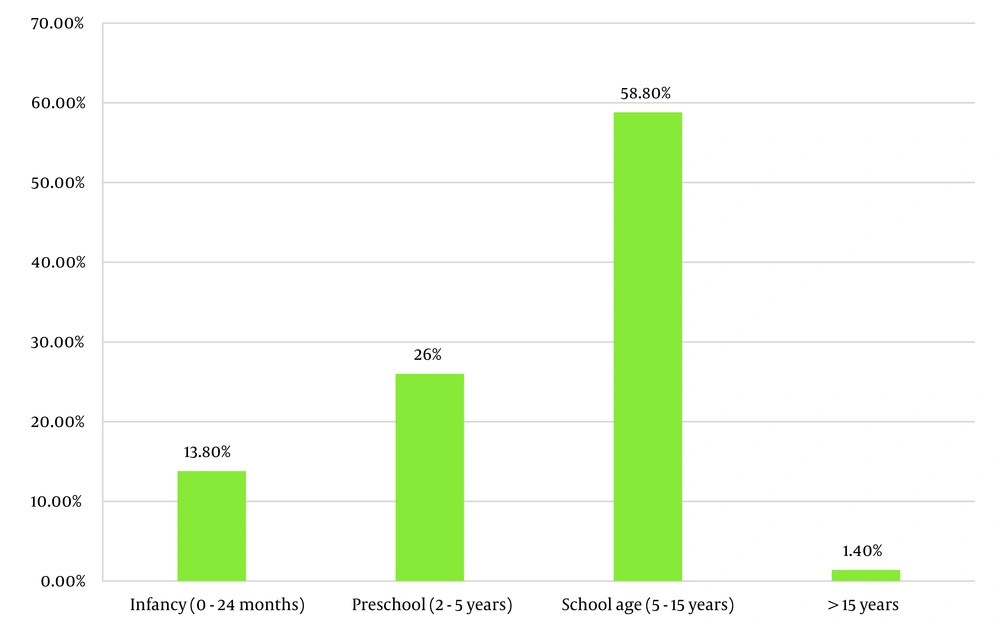
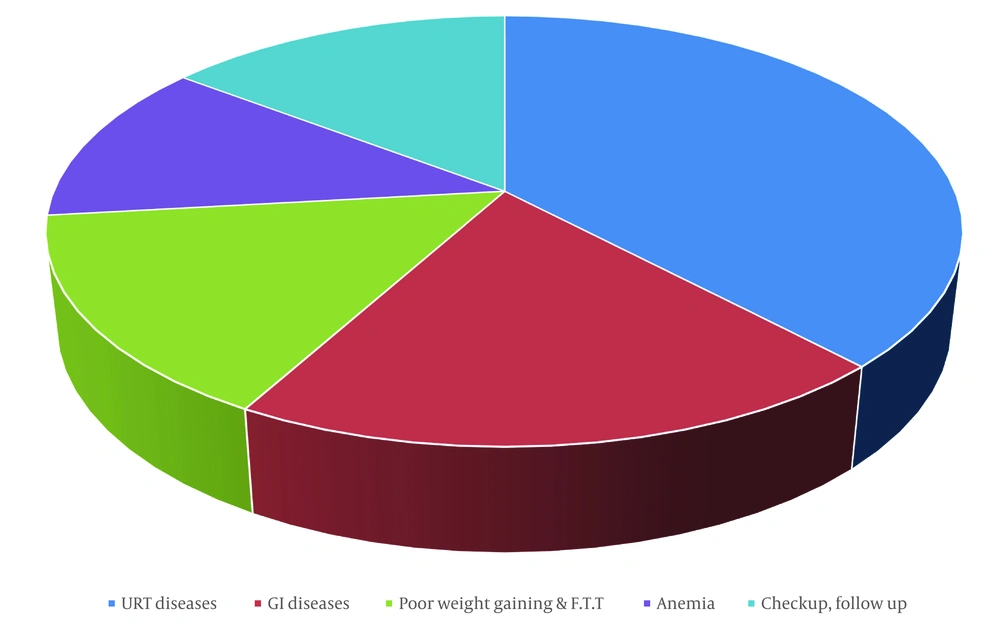
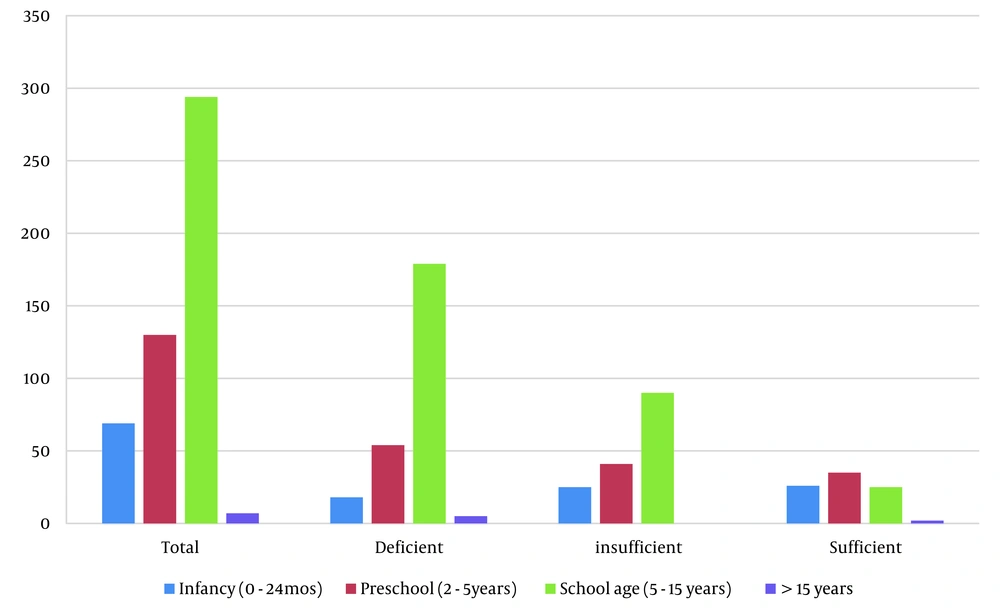
The age and sex distribution of the children is presented in Table 2 and Figure 2. There were 285 males and 215 females, resulting in a male-to-female ratio of 1.3:1. Among the participants, 69 (13.8%) were infants, and 130 (26%) were preschool-aged children. A total of 199 (39.8%) were under 5 years of age, 294 (58.8%) were aged 5 - 15, and 7 (1.4%) were older than 15. Table 3 and Figure 3 illustrate the conditions of patients at the time of referral. The majority of patients had upper respiratory tract diseases — 190 (38%). Gastrointestinal diseases were the second most diagnosed condition, affecting 100 (20%) of the patients. Poor weight gain and failure to thrive were observed in 76 (15.2%) patients, and anemia was present in 61 (12.2%). Seventy-three (14.6%) visited only for checkups and follow-ups. Table 4 and Figure 4 display the status of vitamin D3 deficiency and insufficiency according to age group. School-aged children exhibited the highest vitamin D deficiency at 60.8%, compared to 26% in infants and 41.5% in preschool-aged children (P-value < 0.0001). Infants (2 years and under) had the highest rate of insufficient vitamin D status compared to preschool and school-aged groups. Only 8.5% of school children had sufficient vitamin D levels, indicating significantly lower vitamin D levels in school-aged children compared to preschool (P = 0.37, P-value < 0.0001) and infancy (P = 26.9, P-value < 0.0001). Ensuring adequate vitamin D intake for children, particularly those who are school-aged, is essential and should be pursued regularly.
| Variables | Total | Deficient | Insufficient | Sufficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infancy (0 - 24) (mo) | 69 | 18 (26) | 25 (36.2) | 26 (37.6) |
| Preschool (2 - 5) (y) | 130 | 54 (41.5) | 41 (31.5) | 35 (26.9) |
| School age (5 - 15) (y) | 294 | 179 (60. 8) | 90 (30.6) | 25 (8.5) |
| > 15 (y) | 7 | 5 (71.4) | 0 | 2 (28.5) |
| Total | 500 | 256 (51.2) | 156 (31.2) | 88 (17.6) |
Vitamin D Deficiency/Insufficiency in Subgroups of Age a
The seasonal distribution of cases is presented in Table 5. Deficient and insufficient cases were more prevalent in the summer, accounting for 40%, and generally occurred more frequently during the warm seasons. In contrast, the number of sufficient cases remained consistent across all four seasons.
| Variables | Spring | Summer | Fall | Winter | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deficient | 52 (17) | 120 (39.5) | 84 (27.6) | 48 (15.7) | 304 (100) |
| Insufficient | 24 (14.6) | 64 (39) | 44 (26.8) | 32 (19.7) | 164 (100) |
| Sufficient | 8 (25) | 8 (25) | 8 (25) | 8 (25) | 32 (100) |
| Total | 84 (16.8) | 192 (38.4) | 136 (27.2) | 88 (17.6) | 500 (100) |
| Total | Warm seasons 276 (55.2) | Cold season 224 (44.8) | - | ||
Seasonal Distribution of Vitamin D State Cases a
4. Discussion
In addition to being an essential nutrient for healthy bones and regulating calcium levels in the blood, vitamin D may help prevent other diseases. Vitamin D deficiency can lead to seizures and cardiomyopathy in infants, rickets and poor growth in children, and muscle weakness at any age (1). There are three groups particularly at risk of vitamin D deficiency (2).
4.1. Increased Need
This includes pregnant and breastfeeding women, twins and multiple pregnancies, premature infants, adolescents, and individuals with obesity (3).
4.2. Limited Sun Exposure
This group includes individuals living at northern latitudes or during winter months, those with darker skin, individuals with immobility such as inpatients or those with conditions like cerebral palsy, and those using excessive amounts of sunblock. Although sunshine is the most important source of vitamin D, children in school in the southern part of our country, despite abundant sunshine, do not get enough sun exposure (4).
4.3. Limited Dietary Sources
This includes vegetarians, those with prolonged breastfeeding even if the mother has sufficient vitamin D levels, individuals on exclusion diets (e.g., milk allergy), those with malabsorption, celiac and inflammatory bowel disease, liver and renal diseases, and those using certain drugs (e.g., anticonvulsants, anti-tuberculosis drugs, glucocorticoids, and some antifungal drugs).
The clinical manifestations of vitamin D deficiency primarily include rickets in growing children and osteomalacia in adolescents and adults (5). In our study, 15% of children exhibited poor weight gain and failure to thrive, and 12% had anemia. Only one patient showed clinical evidence of rickets (6). None of these children displayed signs or symptoms related to bone and joint diseases, and nearly 15% came for checkups and follow-ups (7). There were no biochemical changes such as reduced calcium and phosphorus, so no further workup was conducted. Efforts focused on providing sufficient vitamin D intake — 400 IU (10 micrograms) daily for infants and 600 IU (15 micrograms) for those aged 1 - 18 years (8). For high-risk populations, such as those in Mediterranean and Middle Eastern regions, northern latitudes, and children on anticonvulsants, glucocorticoid therapy, and HIV medications, up to 2000 IU/day of vitamin D may be necessary to raise 25(OH)D levels to > 30 ng/mL (75 nmol/L) (9).
In Shiraz, a very warm city with plenty of sunshine year-round, children are less likely to go outdoors during the day in spring and summer due to the very hot weather, resulting in reduced sun exposure.
4.4. Conclusions
Given that only 17.6% of children in this region of Iran have sufficient levels of vitamin D, it is recommended that every child seen by a pediatrician or general physician be screened for vitamin D deficiency and receive appropriate treatment if necessary.