1. Background
Bronchiolitis is the most common infection of the lower respiratory tract during the first year of life. It is characterized by obstruction of bronchioles and their necrotic epithelium, increased secretion of mucus, inflammatory cell infiltration, submucosal edema, and constriction of the smooth muscles in the walls of the bronchioles (1, 2). Bronchiolitis usually occurs in three- to six-month-old infants (3). About 70% of cases of bronchiolitis are caused by respiratory syncytial virus and 80% to 100% of them occur during the cold months (4).
Only 10% of children with bronchiolitis and wheezing require hospitalization; however, hospitalization rates for lower respiratory tract infection associated with bronchiolitis has increased from 22.2% in 1980 to 47.4% in 1996 (5). In the first two to three days, bronchiolitis begin with symptoms of runny nose and sneezing (6). Patients might have a mild fever or history of fever (7, 8). Thereafter, dry cough and wheezing occur (9, 10). In severe cases, loss of appetite occurs due to dyspnea, intercostal and supraclavicular retractions, and increased respiratory rate. Nutritional problems are often the reason for the admission to the hospital (6, 7, 11, 12). A diffuse inspiratory crackle is a common finding in acute bronchiolitis. Moreover, inspiratory wheezing would be heard (9, 12). Bronchiolitis is diagnosed based on history and physical examination; in addition, except in mild cases, the chest X-ray (CXR) and complete blood cell count (CBC) are helpful (11). Air trapping in chest or chest expansion is evident in 20% to 40%. Thickening of preibronchial interstitium or pneumonia are seen in 35% to 50% of cases (13).
In terms of clinical diagnosis, bacterial pneumonia is sometimes confused with bronchiolitis; however, the latter does not require antibiotic therapy. In a study based on differences in epidemiology, the lowest prevalence rates in infants younger than six months of age and the highest prevalence rate between six to eight months of age were reported (14). While in another study the highest prevalence rate was reported in infants between one month to one year of age (15), which could indicate that role of epidemiologic, racial, and health differences in the prevalence of bronchiolitis.
2. Objectives
The aim of this study was to to evaluate the clinical, and laboratory characteristics of bronchiolitis in hospitalized children.
3. Patients and Methods
In this cross-sectional comparative study, we studied 117 patients with one to 24 months of age who had developed the first episode of wheezing, were diagnosed with bronchiolitis based on clinical symptoms and were hospitalized in Ali-Ebne Abitaleb Hospital of Zahedan, Iran, from December 1, 2011 to December 1, 2013. We tried to select from the same epidemiology, racial and health conditions. All patients had criteria of bronchiolitis disease.
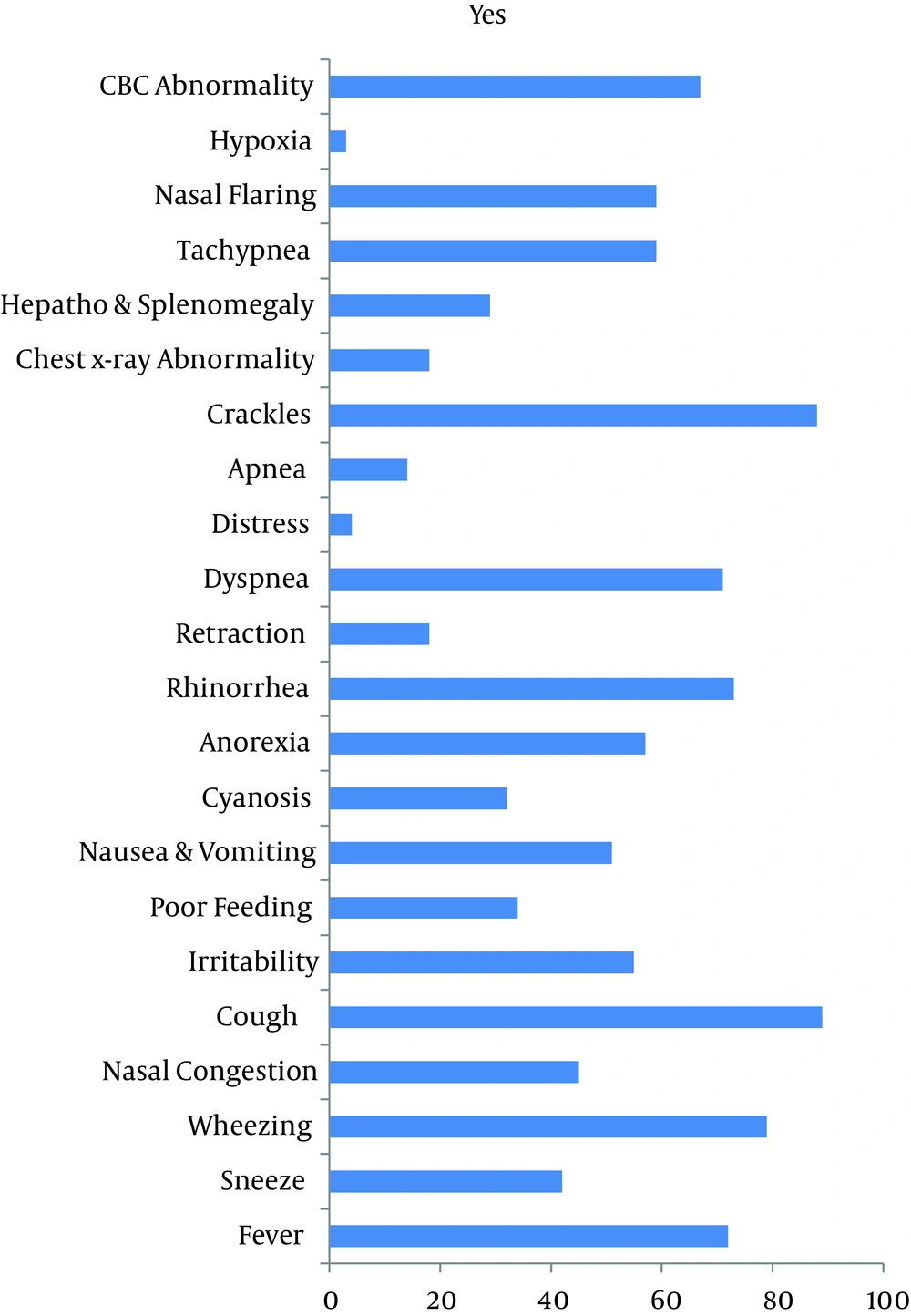
Those with chronic neurologic, renal, heart, or lung disease and patients with immune deficiency were excluded. Data were extracted from information forms. The assessment bronchiolitis parameters included fever, sneeze, wheezing, nasal congestion, cough, irritability, poor feeding, nausea and vomiting, cyanosis, and anorexia, which are described in the Table 1. The season of contracting bronchiolitis was also recorded. Moreover, data forms contained CBC parameters to report lymphocytosis and leukopenia. Finally, data was analyzed by SPSS 21 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) and qualitative variable was presented as number and percent.
| Signs | Frequency, % |
|---|---|
| Cough | 89 |
| Fine Crackles | 88 |
| Wheezing | 79 |
| Rhinorrhea | 73 |
| Fever | 72 |
| Dyspnea | 71 |
| Complete Blood Count Abnormality | 67 |
| Tachypnea | 59 |
| Nasal Flaring | 59 |
| Anorexia | 57 |
| Irritability | 55 |
| Nausea And Vomiting | 51 |
| Nasal Congestion | 45 |
| Sneeze | 42 |
| Poor Feeding | 34 |
| Cyanosis | 32 |
| Hepatosplenomegaly | 29 |
| Intercostal Muscle Retraction | 18 |
| Chest X-Ray Abnormal Findings | 18 |
| Apnea | 14 |
| Respiratory Distress | 4 |
| Hypoxia | 3 |
Symptoms and Signs in Studied Patients
4. Results
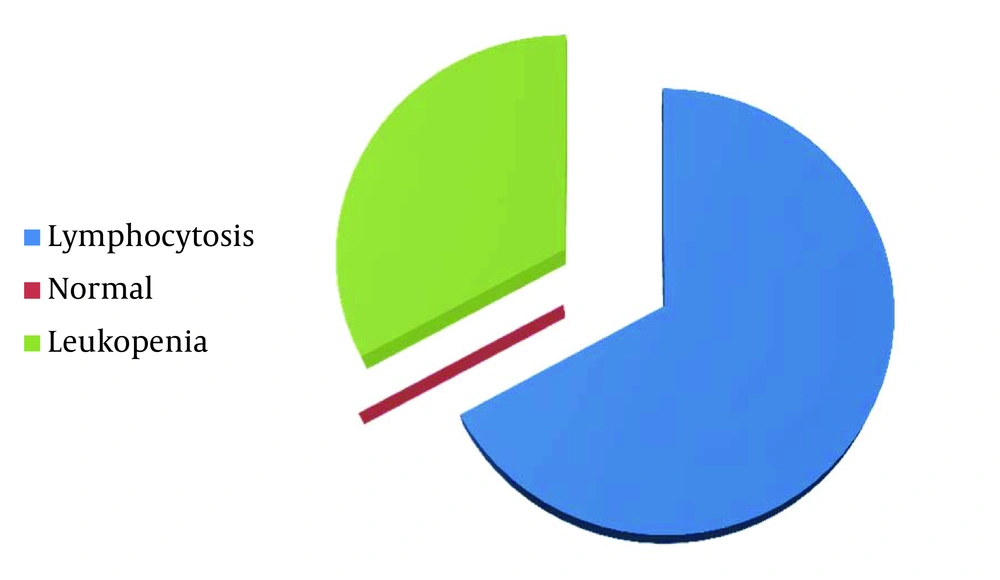
After excluding 17 patients, 100 patients remained including 57 males (57%) and 43 females (43%). Regarding age of the patients, 62 (62%) were one to six, 30 (30%) were six to 12, and eight (8%) were 12 to 24 months of age. Symptoms, signs, and abnormal clinical laboratory findings are shown in Table 1Figure 1. Most common sign detected by physical exam was cough (Figure 1). Lymphocytosis was reported in 67 patients (67%) and all others had normal results in CBC (33%) (Figure 2). Hyperinflation and pulmonary congestion were seen in CXR of 39% and 16% of patients, respectively; others had normal findings in CXR. Regarding season, 50% had contracted the disease during winter, 26% during spring, 15% during fall, and 9% during summer.
5. Discussion
Several studies on bronchiolitis were done in different countries and Iran (16), but none of them were performed in Zahedan City, southeast of Iran. In this area, people live with certain epidemiology, racial (Sistani and Baluchi), and health characteristics in the desert area. In this study, it was attempted to be selected the patients with moderate financial income levels. Moreover, all patients inhabited Zahedan City. The most common symptom in this research were cough (89%), fine crackles, wheezing, dyspnea and tachypnea, consecutively, in physical exam.
Liebelt et al. showed that there are episodes of cyanosis in 10%, apnea episodes in 9% and mutability in 40%; which can be caused by different viral genomes (17). In the present study, lymphocytosis was seen in 67% of patients and the most common radiologic findings were consecutively normal CXR findings, lung hyperinflation, and infiltrates. In contrary, Espínola et al. reported pulmonary infiltrates and atelectasis in 55% of patients with bronchiolitis (18). This study shows that the diagnosis of bronchiolitis also dependent on the living area.
The highest incidence of this disease was in winter, which was compatible with many other studies. Finally, the correct diagnosis of bronchiolitis can be made by considering the most common season of contracting disease, age, laboratory and radiologic signs, and clinical findings and therefore, inappropriate antibiotic use can be prevented.