1. Background
Urinary stones are common problems among patients admitted to emergency and urology departments (1). Incidence of urinary stones in different locations is reported at 1% - 5%; it is estimated to be 2% - 3% in developed countries and 0.5% - 1% in the developing countries (2). In children, it is usually different. Urinary stones in children are more common in males and 70% of cases are located in the upper urinary tract (3, 4). Studies indicated that about 90% of calcium urinary stones are associated with a metabolic disorder. Vitamin D is one of the important metabolic factors in patients with urinary stones (5-8).
Many studies showed the relationship between urinary stones and hypervitaminosis D (9). But in most studies in Iran, more people with kidney stones were with hypovitaminosis D (10).
2. Objectives
The current study aimed to determine the role of vitamin D in urinary stone formation in children.
3. Materials and Methods
The current cross-sectional study was conducted after receiving the ethics approval and patient informed consent from 20 March to 20 November 2014. One-hundred 1-16 year-old children with renal stone, were selected using a simple sampling method in Baqiyatallah hospital of Tehran, Iran. Renal stone was diagnosed based on ultrasound technique by a pediatric nephrologist and a pediatric urologist.
The parents were asked to fill out a questionnaire including demographic data: age, gender and family history of renal stone, ultrasound findings including uni- or bilateral stone and laboratory data including calcium and vitamin D serum levels. The level of vitamin D (cholecalciferol for serum levels of 25 (OH) = 25 OH D ) in one unit ng / mL was measured using Aylksys chemiluminescent methods with Dia Sorin kit and then interpreted based on the following table: 30 - 100 ng/mL = normal, 10 - 30 ng/mL= insufficient and < 10 ng/mL = deficient.
One to sixteen year-old children with renal stones were enrolled in the study. Cases with any vitamin D disturbances were excluded.
3.1. Statistical Analysis:
Data were analyzed using statistical package for social sciences (SPSS) version 18 (SPSS Inc. Chicago, IL) for windows. Normal distribution variables (approved by one-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test) were compared using independent sample T-test between the groups and paired sample T-test within the groups. Chi-square test was also used to compare categorical variables in the two groups. A P value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
4. Results
A total of 100 children (64 males and 36 females) with urinary stones and the mean age of 4.46 ± 2.11 years were evaluated. Table 1 shows demographic data. According to the table, the mean age of patients in both groups showed no significant difference between males and females (P = 0.13).
| Age | Positive Family History | Uni/Bilateral | Vitamin D3 | Vitamin D Deficiency | Calcium Level | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unilateral | Bilateral | Deficient | Insufficient | Sufficient | |||||
| Male | 4.96 ± 2.27 | 14 (21.9%) | 42 | 22 | 37.19 ± 10.66 | 3 | 18 | 43 | 9.96 ± 1.05 |
| Female | 4.03 ± 1.75 | 6 (16.7%) | 29 | 7 | 37.92 ± 11.35 | 1 | 13 | 22 | 10.24 ± 0.79 |
| P Value | 0.13 | 0.52 | 0.08 | 0.74 | 0.66 | 0.16 | |||
A total of 20 children (20%) had a positive family history of renal stones. There was no significant difference between male and female patients in terms of positive family history of renal stones (P = 0.52) (Table 1).
According to Table 1, 29 children (29%) and 71 children (71%) had bilateral and unilateral renal stones, respectively. There was no significant difference in distribution of uni- and bilateral stone between males and females (P = 0.08).
Serum level of vitamin D3 in total was 37.45 ± 10.86 ng/mL. The mean serum levels of vitamin D3 showed no significant difference between male and female subjects (P = 0.74). Four children (4%) had vitamin D deficiency, 31 children (31%) had insufficient vitamin D levels and 65 children (65%) had sufficient vitamin D levels. There was no significant difference between males and females regarding vitamin D deficiency (P = 0.66) (Table 1).
The mean total serum calcium level was 0.97 ± 10.6 mg/dL. According to Table 1, serum calcium levels showed no significant difference between male and female subjects (P = 0.16).
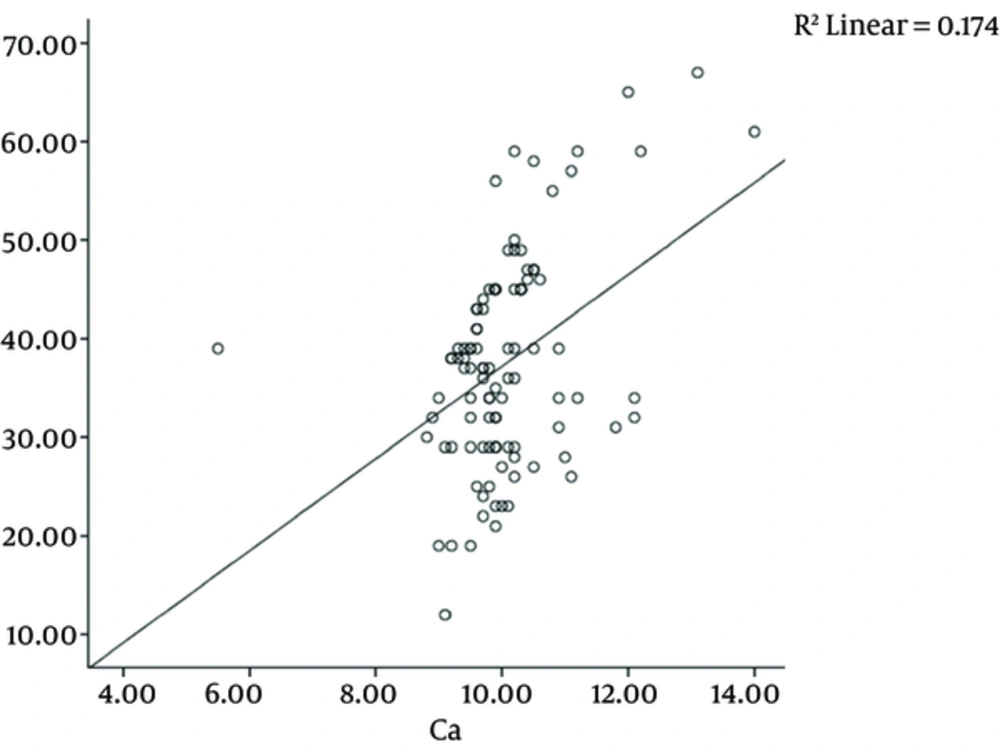
Pearson correlation test showed significant correlation between serum levels of calcium and vitamin D3 (P < 0.001 and r = 0.41) (Figure 1). The serum levels of calcium in patients with a deficiency of vitamin D3 was 9.20 ± 0.21 mg/ dL, in patients with insufficient vitamin D3 was 9.95 ± 0.62 mg/dL and in patients with sufficient vitamin D3 was 10.16 ± 1.09 mg/dL. Serum calcium level was the highest in patients with adequate vitamin D levels and the lowest in patients with vitamin D deficiency, but this difference was not statistically significant.
The mean serum levels of vitamin D3 and calcium in patients with a positive family history of renal stones were 35.05 ± 12.64 and 9.89 ± 1.4 ng/mL and in patients without a family history of renal stones were 38.05 ± 18.37 and 10.10 ± 0.83 ng/mL, respectively. Serum levels of vitamin D and calcium level were not significantly associated with family history of renal stones (P = 0.27 and P = 0.38, respectively).
The mean serum levels of vitamin D3 and calcium in patients with unilateral renal stones were 35.87 ± 10.31 and 10.03 ± 1.18 ng/mL and in patients with bilateral stones were 41.31 ± 11.39 and 10.07 ± 0.87 ng/mL, respectively. Vitamin D levels were significantly higher in patients with bilateral renal stones (P = 0.03). Serum calcium level was not significantly associated with uni- or bilateral stones (P = 0.84).
Vitamin D levels in children < 4 years were 36.4% and 63.6% insufficient and normal, respectively. Vitamin D levels in children 4 - 6 years were 31.7% and 63.8% insufficient and normal, respectively; vitamin D levels in children > 6 years were 40% and 60% insufficient and normal, respectively. There was no significant difference between the groups (P = 0.82).
5. Discussion
The study found that urinary stones were more common in males and vitamin D levels were significantly higher in children with bilateral stones than patients with unilateral stones.
Fallahzadeh et al. (9) showed significant relationship between vitamin D and calcium levels. This finding confirmed the current study results. But the current study demonstrated that vitamin D level was lower in children with urinary stones. Perhaps due to the different age groups; Fallahzadeh et al. examined infants, while in the present study investigated children. Fallahzadeh did not compare the variables in males and females because of equal prevalence of urinary stones in male and female newborns. In the present study, due to higher prevalence of urinary stones in males, the impact of gender on all variables was examined.
Ramos et al., (11) concluded that calcium plus vitamin D supplements did not increase urinary stones, but played a role as a protective factor in the development of stones. According to the current study, vitamin D supplements may reduce development of urinary stones.
Mohammadjafari et al., (12) showed the prevalence of 64% in male patients, which was higher than that of the present study, and positive family history.
Nguyen et al., (13) demonstrated no relationship between vitamin D levels and urinary stones. The current study concluded that vitamin D levels were significantly higher in children with bilateral stones than those with unilateral stones.
5.1. Conclusion
The current study concluded that serum levels of vitamin D in children with urinary stones were low and it was significantly associated with severity of the disease and the patients’ serum calcium. Finally, it is recommended to evaluate metabolic disorders. It is also recommended to consider a number of healthy children as a control group and compare the results with those of a control group. Researchers can also evaluate the role of vitamin D supplements on the development of urinary stones.