1. Background
Improving critical thinking (CT) skills is an important goal in higher education, especially nursing education. CT is an essential skill for nurses in the modern world because unstable clinical conditions require nurses to make appropriate decisions. Nurses with high CT skills can use CT to solve patients' problems by expanding their decision-making areas (1, 2).
Clinical judgment is the outcome of CT, which is a process and an outcome of learning. Developing clinical judgment (clinical reasoning skills) is one of a nurse's most critical and challenging tasks, which is essential in their professional and personal life (3). CT tries to achieve specific results through cognitive skills, including problem-solving, logical inference, and decision-making.
The most es task in bringing about a transformation in educational methods is to change the teacher’s attitude toward teaching thinking, especially TC. Teachers can grow and develop people's CT using active teaching methods (4, 5). Several reasons require the nursing education system to pay attention to CT skills. Nurses without thinking skills are at a disadvantage when trying to solve problems. In addition, nurses should be able to make independent and quick decisions in urgent situations. CT skills enable nurses to identify critical data and distinguish life-threatening problems requiring immediate intervention. Therefore, nurses should be able to think about their actions and consider the possible consequences of each step to make appropriate decisions (6).
Problem-solving-based learning (EBPS) has found a high place in high academic levels as a relatively new educational method (7) to strengthen CT and perseverance (8, 9). EBPS is one of the new approaches using problems as a starting point for acquiring and combining new knowledge (10). Several studies have indicated the effectiveness of problem-solving-based learning (PSBL) in nursing education and empowering nursing students. PSBL has been recommended for use in the education of nursing students in the studies mentioned above (6, 10-12). The method of problem-solving has been the focus of many researchers as a valuable tool to improve the coherence of learning and increase social competence (4).
2. Objectives
This study aimed to determine the effect of education by problem-solving-based learning method on the CT skills of nursing students of the Islamic Azad University of Golestan province, Iran, in 2022.
3. Methods
This experimental study used a pre-test and post-test method and a control group. The population included undergraduate nursing students of the Islamic Azad University of Golestan province in the 7th and 8th semesters. The study was conducted after receiving the code of ethics and permission from the Islamic Azad University of Golestan province, Iran.
The inclusion criteria were no previous use of these scenario-based educational methods, age 18 - 25 years, no probation, no failed courses, and more than three absences from classes. The exclusion criteria included being a guest student from other provinces of Iran and withdrawing from participating.
The sample size was determined by using the results of a similar previous study, in which the control group's mean (standard deviation) was 9.42, and the case group was 12.43. In addition, the minimum sample size for each study group was estimated as much as 18, considering the confidence level of 95% and the test power of 80%. Finally, the total sample size was determined as much as 25 for each study group based on 30% attrition.
The sampling method was non-probability convenient among nursing students at Islamic Azad University in Bandar-e Gaz, Aliabad, Gorgan, and Gonbad. First, 75 students who met the inclusion criteria were selected among 190 students in training and divided into three groups using a simple random assignment method, including problem-solving, network-based, and control groups.
Informed consent was obtained from the students after explaining the research objectives. Further explanations were given to the participants, including the non-compulsory participation, the possibility of being randomly placed in any of the groups, and the ability to withdraw from the study at any time. Then, topics were selected from nursing courses where the students had related backgrounds.
The students completed the CTDI demographic and CT tendency questionnaire containing 75 questions to evaluate the seven components of CT tendency. A total of 12 questions were about truth-seeking, 12 about criticism, 11 about analysis power, 11 about systematic and organizing information, ten about curiosity, nine about self-confidence, and ten about the growth rate. The questionnaire validity was evaluated by ten professors of Islamic Azad University, and the reliability was reported in a previous similar study with Cronbach's alpha of as much as 85%. The scores varied between 75 and 450, and higher scores indicated the more significant the power of CT.
The problem-solving-based learning was explained to each group separately in a 90-minute session in the first session. A sample scenario was presented for each session separately during eight 90-minute sessions. Researchers presented problems to the students in the problem-solving group that could familiarize them with the subject in every lesson, and then the students communicated face-to-face in groups of five to six people. In the following, a comprehensive nursing planning stage was designed based on North American Nursing Diagnosis Association (NANDA) for different scenarios raised by the students. Nursing educators selected the methods among patients admitted to the ward. At the end of the eighth session, the students performed the CTDI test again. The test group students were requested not to share their knowledge with other groups to prevent the exchange of information between the test and control groups. The results were analyzed by SPSS software version 16 using descriptive and inferential statistics, including independent t-test and t-test, as well as ANCOVA.
4. Results
Based on the demographic characteristics of the problem-solving training groups, the independent t-test control group did not show a significant difference regarding age (P = 0.28) and overall grade point average (P = 0.44). The chi-square test showed no significant difference in terms of gender (P = 0.67) and academic semester (P = 0.81) (Table 1).
| Variables | Studied Groups | P Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PBL | Control | ||
| Age | 21.64 ± 0.75 | 22.16 ± 1.9 | 0.28 |
| Overall grade point average | 16.55 ± 1.16 | 17.09 ± 2.19 | 0.44 |
| Sex | 0.67 | ||
| Girl | 17 (34) | 15 (30) | |
| Boy | 8 (17) | 10 (33) | |
| Semester | 0.81 | ||
| 7th | 14 (28) | 12 (24) | |
| 8th | 11 (22) | 13 (26) | |
a Values are expressed as mean ± SD or No. (%).
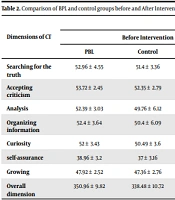
The independent t-test before the intervention showed a significant difference between the problem-based learning (PBL) and the control group (P = 0.003). However, the independent t-test before the intervention did not show a significant difference between the CT dimensions in both groups (Table 2).
| Dimensions of CT | Studied Groups | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Intervention | After Intervention | |||||
| PBL | Control | P | PBL | Control | P | |
| Searching for the truth | 52.96 ± 4.55 | 51.4 ± 3.36 | 0.09 | 58.4 ± 3.58 | 51.52 ± 4.26 | < 0.01 |
| Accepting criticism | 53.72 ± 2.45 | 52.35 ± 2.79 | 0.07 | 64.52 ± 3.48 | 52.04 ± 4.9 | < 0.01 |
| Analysis | 52.39 ± 3.03 | 49.76 ± 6.12 | 0.07 | 55.3 ± 3.7 | 46.58 ± 2.69 | < 0.01 |
| Organizing information | 52.4 ± 3.64 | 50.4 ± 6.09 | 0.18 | 54.7 ± 3.7 | 49.21 ± 2.75 | < 0.01 |
| Curiosity | 52 ± 3.43 | 50.49 ± 3.6 | 0.07 | 50.48 ± 3.02 | 49.21 ± 2.75 | 0.2 |
| Self-assurance | 38.96 ± 3.2 | 37 ± 3.16 | 0.06 | 43.32 ± 3.03 | 49.28 ± 3.57 | 0.03 |
| Growing | 47.92 ± 2.52 | 47.36 ± 2.76 | 0.46 | 50.84 ± 3.42 | 47.96 ± 4.01 | 0.009 |
| Overall dimension | 350.96 ± 9.82 | 338.48 ± 10.72 | 0.003 | 377.4 ± 17.95 | 340.2 ± 10.38 | 0.01 |
PBL and control groups significantly differed after the intervention (P = 0.01). In addition, a significant difference was observed between all CT dimensions in both groups after the intervention (Table 1).
A significant difference was observed in the PBL group before and after the intervention following the paired t-test in different dimensions, including truth-seeking (P < 0.01), criticism (P < 0.01), analysis (P < 0.01), information organization (P = 0.04), curiosity (P = 0.043), self-confidence (P < 0.01), growth (P < 0.01), and overall dimension (01 /0 > P) (Table 2).
There was no significant difference in the control group before and after the intervention following the paired t-test in different dimensions, including truth-seeking (P = 0.91), criticism (P = 0.82), organization (P = 0.74), Curiosity (P = 0.52), and overall dimension (P = 0.06). At the same time, there was a significant difference in the dimensions of analysis (P = 0.03) and self-confidence (P < 0.01) (Table 2). The ANCOVA test showed a significant difference (P < 0.01, Eta = 0.55) by removing the pre-test. Thus, 55% of post-test changes could be related to problem-solving skills (Table 3).
| Source of Variance | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean of Squares | F Value | Significant Level | Eta |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modified model | 19519.21 | 2 | 9759.6 | 56.37 | < 0.01 | 0.70 |
| Post-test separator | 2183.99 | 1 | 2326.6 | 12.61 | < 0.01 | 0.21 |
| Group | 1017.52 | 1 | 1017.52 | 58.59 | < 0.01 | 0.55 |
| Error | 8126.8 | 47 | 13.173 | |||
| Sum | 6466681 | 50 | ||||
| Total | 27651.2 | 49 |
5. Discussion
The nursing profession needs CT to make appropriate decisions in challenging situations. Therefore, new and student-centered educational methods, such as problem-solving-based learning strategies, can help improve nursing students' CT. Based on this study, students' tendency to CT increased in all dimensions after participating in problem-solving sessions, which was in line with the results of Seibert (8), Song (13), Liu and Pásztor as cited in Smith et al. (14).
Ar-yuwat et al. showed that many nursing students accepted problem-solving-based education as a new educational method, and instructors of the Thai School of Nursing significantly impacted all dimensions of CT, similar to the present study (15). Another study also compared the educational method based on problem-solving and concept mapping at Khomein University of Medical Sciences, Iran, and showed that the CT score increased more in the problem-solving training group. In addition, higher scores in the sub-groups of criticism, self-confidence, search, and growth were consistent with those of the present study. However, the analysis of power and organization management of the two groups did not reveal a significant difference in the truth-seeking subgroups, which is contradictory to the present study. This difference may be due to the smaller sample size, educational level, intervention type, and course content.
The PBL process is rooted in the constructivist theory of Jean Piaget (1896 - 1980), based on which students actively produce the meaning of concepts and construct their understanding. Al-Najar et al. reported that the PBL method had a more significant effect on the improvement of CT and active learning of Saudi Arabian nursing students than the lecture method (16). Further, Lapuz and Fulgencio found that PBL effectively improved students' critical thinking (17), which was consistent with the results of this study. Rasouli et al. concluded that both lecture and PBL educational methods effectively improve the knowledge and performance of nursing students, but the PBL method was more effective than the lecture method (18). Since nursing performance had a direct relationship with the tendency to CT (19), it can be concluded that the present study is in line with the study of Rasouli et al. (18) and was consistent.
A review study on the problem-solving-based learning field by Hajibabaee and Ashrafizadeh (20) showed that the PBL method is effective in nursing education and empowering students. Therefore, this method in nursing education was suggested to be widespread and extensive. A few studies have contradicted the positive effect of this educational approach, while most studies have shown students' satisfaction with using this method in classrooms (10). Increasing learners' satisfaction can improve the quality of care provided (21, 22), which can be a suggestion to conduct more research on the obstacles to applying this educational method by nursing educators.
This study indicates the need for revision of current training strategies to prepare nurses to make appropriate decisions based on the current conditions of the nursing profession. Therefore, faculty members and nursing instructors are recommended to pay more attention to modern and student-oriented methods in pushing educational practices. Critical thinking in nursing is logically considering the existence of more than one existential dimension in a patient's problem and making the appropriate decisions in challenging situations. CT enables nurses to make correct judgments about the issues related to the patient.