1. Background
In late December 2019, COVID-19 emerged as a respiratory disease in China and quickly spread worldwide (1). COVID-19 was the third deadly outbreak in less than two decades after severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) (2). The World Health Organization (WHO) declared COVID-19 a global pandemic on March 11, 2020. Despite global efforts to control its spread, the pandemic continued to affect millions of people, with over 514 million documented infections and 6.2 million deaths worldwide. The first confirmed case of COVID-19 in Iran was reported in Qom province in February 2020 (3). As of May 3, 2022, over 7.2 million Iranians have been diagnosed with COVID-19, which has caused 141,114 deaths.
The outbreak of COVID-19 has had a severe effect on various aspects of society, including social welfare, economic activities, population health, healthcare delivery, and use of health services, particularly in resource-poor countries (2, 4, 5). Previous studies have indicated that over a billion people, primarily from low- and middle-income countries, cannot access healthcare services (6). The highly contagious nature of the virus has further exacerbated the underutilization of health services during this period, becoming a crucial public health concern. The decision of individuals to seek healthcare services is influenced by a complex interplay of factors related to their characteristics, such as affordability and acceptability, and factors related to the healthcare system, such as availability and accessibility (6, 7). The COVID-19 disease has significantly disrupted the health system and how healthcare is delivered and received (8).
Numerous studies have been conducted in different countries, which demonstrated the significant effect of the pandemic on the usage of healthcare services with a drastic decline (9, 10). Telemedicine as a substitute for in-person visits did not fill the gap (10-12), but it remained unclear from this evidence whether the decline in utilization occurred across all services. Few studies have been conducted in Iran regarding this issue (13). The effects of COVID-19 on health services are complex and multifaceted. However, the outbreak and detection of infection cases may have led to an increase in the use of technological medical equipment and telehealth services.
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of high-technological medical equipment such as CTS and MRI in accurately diagnosing and dynamic assessing COVID-19 pneumonia, representing a more sensitive and practical diagnostic approach (14). Previous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of high-resolution MRI and CTS in detecting pulmonary abnormalities suggestive of pneumonia in patients with COVID-19 (14-16). However, CTS and MRI may not be readily available due to the rapid spread of the disease and the subsequent increase in infections and workload. Additionally, the reduction in hospital finances due to the pandemic has threatened the sustainability of hospitals and may lead to a shortage of financial resources and equipment. Hospital revenues support a significant portion of healthcare services and equipment, and any reduction in revenues can have a detrimental effect on the provision of services. The COVID-19 pandemic has also affected the use of healthcare services in Iran, similar to many countries worldwide. Previous studies have identified inefficient equipment as the primary challenge facing the Iranian healthcare system (13, 17).
2. Objectives
The current study aimed to evaluate the effects of the pandemic on the use of high-technological medical equipment in Iran. The data extracted from hospitals’ health information systems (HIS) were utilized to achieve this aim. The impact of the pandemic on the use of health services was measured by comparing the utilization rates of CTS and MRI before and after the outbreak of COVID-19.
3. Methods
3.1. Study Design
This quasi-experimental study was conducted in Kermanshah province, Iran. This study aimed to investigate the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on the use of CTS and MRI in all public hospitals between February 2017 and December 2021. The province’s population was estimated to be approximately two million in 2016 (18). A total of 18 public hospitals in the province provide healthcare services, of which 12 provide CTS services, and only two public hospitals provide MRI services. Both hospitals are located in Kermanshah, Iran, the province’s capital.
In this study, monthly data on the utilization frequency of CTS and MRI were collected from hospitals’ health information systems (HIS) using a checklist developed by the researchers. The data collection period extended over 58 months (36 months before and 22 months after the pandemic), which was first confirmed on February 19, 2020. February 19, 2017, to February 18, 2020, was considered as before the pandemic period, and February 19, 2020, to December 21, 2021, was regarded as the post-pandemic period. Population data were obtained from the Iranian Statistical Center (ISC) to calculate the rates of CTS and MRI utilization.
3.2. Data Analysis
An interrupted time series analysis was employed to examine the relationship between the COVID-19 pandemic and using CTS and MRI per 100,000 population. The Newey-West approach was utilized to address potential autocorrelation and heteroscedasticity issues (19, 20). The actest command was used to determine the appropriate lag (i.e., lags 2 for both variables) to correct autocorrelation in each dependent variable (i.e., MRI and CTS utilization). In addition, a segmented regression model was employed to estimate the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the use of CTS and MRI per 100,000 population (Equation 1) (20, 21):
In the described model, the variable
All data related to the interrupted time series analysis (ITSA) model were analyzed using Stata statistical software with a significance level of 0.05, considered statistically significant. The version of Stata used for the analysis was 16.0, developed by Stata Corporation, based in College Station, TX, USA.
4. Results
During the study period, the average monthly number of CTS and MRI performed in the studied hospitals was 9344 and 1007, respectively. There was a significant difference in using CTS and MRI before and after the pandemic. The results of the descriptive analysis revealed that the use of CTS increased by 67.1% following the outbreak, whereas the use of MRI decreased by 50.8%. Table 1 provides a brief overview of the variables.
| CTS Per 100,000 Population | MRI Per 100,000 Population | |
|---|---|---|
| Before the pandemic | 376.1 ± 74.3 | 6.3 ± 0.7 |
| After the pandemic | 628.4 ± 240.3 | 3.1 ± 2.2 |
| % change | +67.1 | -50.8 |
a Values are expressed as mean ± SD.
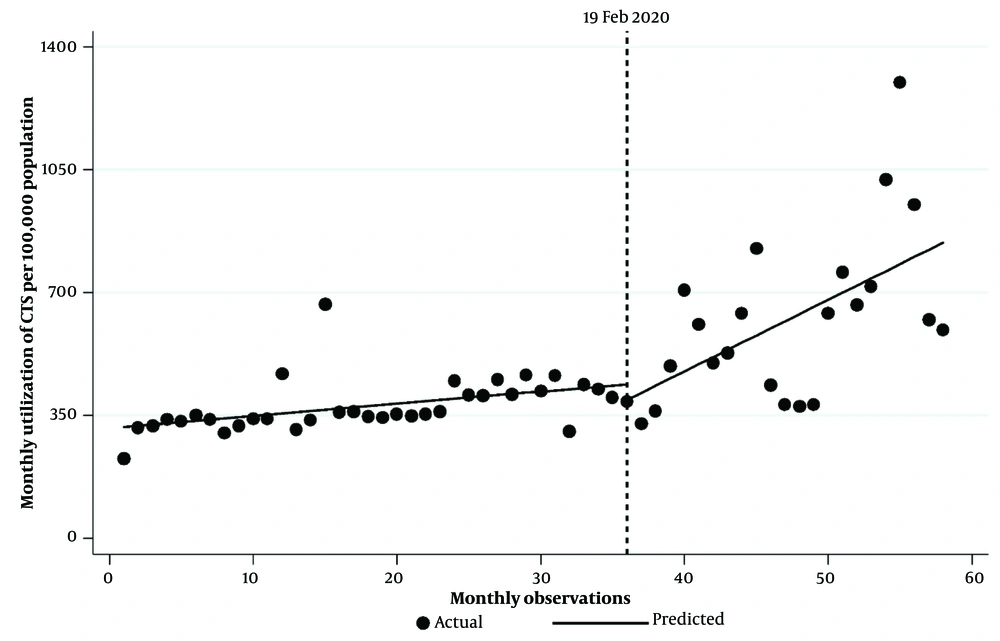
As shown in Table 2, the regression results indicate that the starting level of CTS utilization per 100,000 population was 312.90. Before the COVID-19 pandemic, there was a significant monthly increase in CTS utilization by 3.49 per 100,000 population (P < 0.0001, 95% CI = [1.95, 5.02]). In the first month of the pandemic, there was an insignificant decrease in CTS utilization per 100,000 population of 44.9 (P = 0.512, 95% CI = [−181.23, 91.42]). However, there was a significant rise in the monthly trend of CTS utilization by 16.9 per 100,000 population per month when compared with the pre-pandemic trend (P = 0.031, 95% CI = [1.63, 32.16]). Furthermore, there was a significant monthly increase in CTS utilization per 100,000 population at 20.39 after the COVID-19 pandemic (P = 0.009, 95% CI = [5.21, 35.56]). Figure 1 shows a visual representation of these findings.
| Variables | Coefficient | SE | P-Value | Confidence Interval (CI 95%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||
| Intercept, | 312.90 | 18.37 | < 0.001 | 276.07 | 349.73 |
| Pre-intervention slope, | 3.49 | 0.76 | < 0.001 | 1.95 | 5.02 |
| Change in slope, | -44.90 | 67.99 | 0.512 | -181.23 | 91.42 |
| Change in trend, | 16.90 | 7.61 | 0.031 | 1.63 | 32.16 |
| Post-intervention linear trend a | |||||
| Linear trend, | 20.39 | 7.56 | 0.009 | 5.21 | 35.56 |
Abbreviation: SE, standard errors.
a This obtained from the following time trend equation: Yt = β0 + β1 ∗ timet + ϵt; where Yt is the value of utilization of CTS at time t after the intervention and timet is the time trend variable.
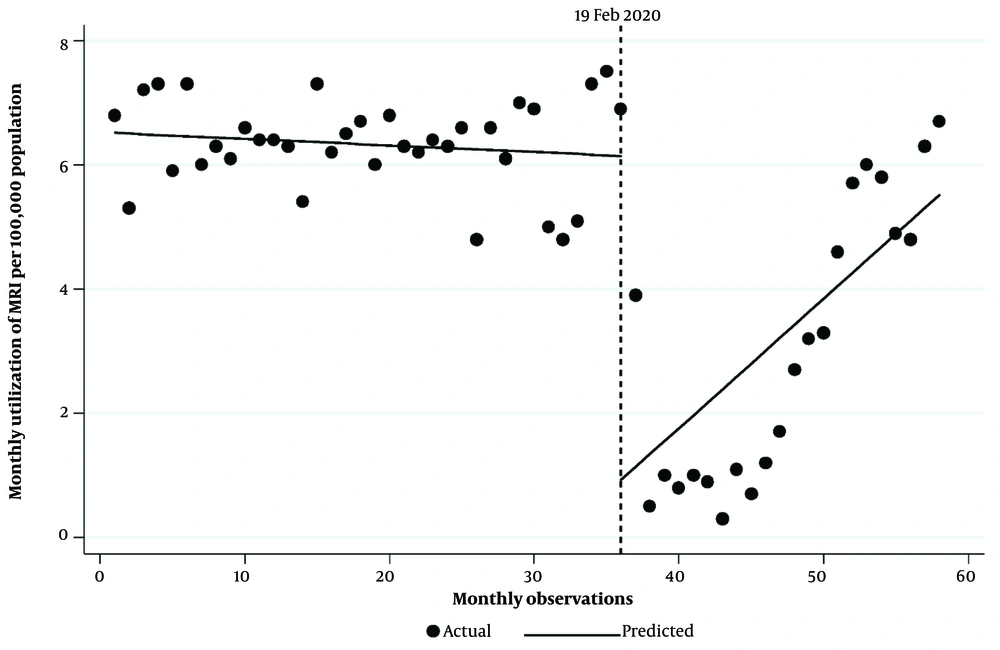
As reported in Table 3, the MRI utilization rate per 100,000 population was 6.52 at the beginning of the study period. Before the COVID-19 pandemic, the MRI use rate decreased by 0.01 every month, but this trend was insignificant (P-value = 0.308). In the first month of the pandemic, a significant decline was observed in MRI use of 5.22 per 100,000 population (P < 0.001, 95% CI = -0.700, -2.49). There was a significant rise in MRI utilization months after the pandemic compared to the period before, estimated to be 0.22 MRI utilization per 100,000 population (P = 0.033, 95% CI = [0.02, 0.41]). Segmented regression analysis also indicated a monthly increase in MRI utilization rate of 0.21 per 100,000 population after the COVID-19 pandemic (P = 0.031, 95% CI = 0.09, 0.39). Figure 2 represents the MRI utilization rate per 100,000 population pre- and post-period of the pandemic.
| Variables | Coefficient | SE | P-Value | Confidence Interval (CI 95%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||
| Intercept, | 6.52 | 0.15 | < 0.001 | 6.22 | 6.82 |
| Pre-intervention slope, | -0.01 | 0.01 | 0.308 | -0.03 | 0.01 |
| Change in slope, | -5.22 | 1.35 | < 0.001 | -7.94 | -2.49 |
| Change in trend, | 0.22 | 0.10 | 0.033 | 0.02 | 0.41 |
| Post-Intervention Linear Trend a | |||||
| Linear trend, | 0.21 | 0.09 | 0.031 | 0.09 | 0.39 |
Abbreviation: SE, standard errors.
a This obtained from the following time trend equation: Yt = β0 + β1 ∗ timet + ϵt; where Yt is the value of utilization of MRI at time t after the intervention and timet is the time trend variable.
5. Discussion
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly affected various aspects of healthcare systems worldwide, including changes in the use of healthcare services. This study aimed to explore the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on the usage of MRI and CTS services in all public hospitals in the west of Iran.
The average per capita use of CT scans per 100,000 population during the 36 months before the COVID-19 pandemic increased (approximately 67%) compared to the 22 months after the pandemic. However, the segmented regression model results revealed an insignificant decrease of 44.9 in CT scan utilization per 100,000 population in the first month following the pandemic. The mentioned decrease can be attributed to fear of contracting the disease among the general public and unfamiliarity among healthcare providers with diagnostic and therapeutic tools for COVID-19. Despite the initial decrease, an overall upward trend was observed in CT scans per capita utilization throughout the post-pandemic period.
Heydarian et al. (22) indicated a significant and sudden increase in the use of CT scans in public hospitals after the first COVID-19 case. Several reasons can explain the rise in CT scan utilization post-pandemic. Firstly, healthcare providers need faster and more precise diagnoses for patients with infections. Secondly, CT scans have been identified as an essential tool in the diagnosis of COVID-19 disease, as reported in other studies (22, 23). In line with the present findings, Loftus et al. showed that weekly emergency department CT utilization increased from 35.9 CTs per 100 visits to 41.8 per 100 in pre- and post-pandemic periods (24). The increased CT use may reflect additional factors such as local practice patterns and rising patient acuity, admission rates, and patient age, which may all have contributed (25, 26).
In contrast, Agrawal et al. found that emergency department CT volumes significantly decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic, predominantly because of fewer examinations with new or unexpected findings. This finding suggests that COVID-19 public information campaigns have influenced the behaviors of patients presenting to the ED (27).
In contrast to the usage of CT scans, the descriptive data show that the per capita use of MRI after the COVID-19 pandemic decreased by more than 50% compared to the months before the pandemic. The rate of MRI usage per 100,000 population significantly decreased in the first month after the pandemic. However, an increasing trend was observed in the usage of MRI in the months following the pandemic. Luxenburg et al. (28) examined MRI utilization before and after the COVID-19 pandemic in Israel and found a decrease in the volume and rate of MRI examinations after the first wave of the pandemic with a relative reduction of 47.5% in April 2020 compared to April 2019 and 42.2% compared to 2018. Other studies have also reported decreased MRI usage rates in the US (29) and the UK (30), as much as 30 and 34%, respectively. Luxenburg et al. noted that changes in MRI utilization might be due to differences in the burden of COVID-19 disease and unequal distribution of MRI scanners among regions (28). Rivera-Sotelo indicated that MRI and PET/CT were used in more than 50% of the selected studies. The diagnostic and others like socio-economic impact and pathogenesis in developed countries had an advantage by having hospitals with more resources, including MRI and PET/CT facilities (31).
5.1. Limitations
This study has some limitations, such as the generalizability of the findings. Since only data from public hospitals in Kermanshah province were used and access to data from other provinces or non-governmental hospitals in Kermanshah province was not possible, the generalizability of the results to the entire country may be limited. Additionally, it would have been possible to study the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on different types of hospitals when data from private and social security hospitals had been available. This would have provided a better understanding of the behavior of non-governmental hospitals in using imaging services during critical situations such as a pandemic.
5.2. Conclusions
Based on the results, there was an increase in CT scans and a decrease in MRI after the pandemic, consistent with previous studies in other countries. Further research is needed to analyze the factors affecting the use of healthcare services during crises, which can help improve preparedness for future pandemics. Understanding the effect of such problems on healthcare services can enhance the planning and allocation of resources to ensure that the population’s healthcare needs are met effectively and efficiently.