1. Background
Teucrium is a large, polymorphic genus belonging to the Lamiaceae family that includes more than 300 species having been distributed worldwide (1). Several reports have indicated that Teucrium species have anti-microbial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-ulcer, and anti-cancer properties (2-4). Chemical analyses of essential oils or extracts from Teucrium species have confirmed the existence of various flavonoids and phenolic compounds with biological activities (5-7).
In addition to Teucrium persicum Boiss, T. macrum Boiss et. Hausskn and T. melissoides Boiss et. Hausskn also are well-known Iranian endemic plants of this genus (8). Teucrium persicum Boiss grows in Fars province on the south of Iran and is called marv-e-talkh. As a traditional remedy, T. persicum has been used for treating headaches, abdominal pains, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and inflammation (9). Many attempts have been made to identify the chemical compositions of the essential oils extracted from T. persicum. Furthermore, studies have shown that the essential oils of T. persicum possess valuable antioxidant properties (9-11). A few studies investigating the biological activities of T. persicum have also indicated that the aqueous extract of T. persicum exhibits anti-inflammatory activity (12), and T. persicum methanolic extract significantly impedes the proliferation of PC-3 cells (13).
2. Objectives
The antioxidant properties of ethyl acetate and chloroform extracts of T. persicum have been already evaluated by several studies. In the present study, therefore, the cytotoxicity effects of these two extracts on PC-3 (human prostate adenocarcinoma), SW-480 (human colorectal adenocarcinoma), and HEK-293T (human embryonic kidney) cell lines were evaluated.
3. Methods
3.1. Preparation of Extracts
Teucrium persicum plants were collected from the southern parts of Iran and confirmed by Dr. Alireza Naqinezhad from the Department of Biology, Faculty of Sciences, University of Mazandaran (9008-HUMZ). Then, 50 gr of the powdered aerial parts of T. persicum were soaked in 100 mL of ethyl acetate and chloroform separately and shaken for 48 hours. The concentrated supernatants were dried using a freeze dryer (Christ, Germany), dissolved in DMSO (25 µg/mL), and stored at -20ºC for later application.
3.2. Determination of Total Phenolic Contents
The total phenolic contents (TPC) of chloroform and ethyl acetate extracts were calculated according to the Singleton and Rossi method with minor modifications (14). Briefly, 50 and 150 µg/mL of the gum were added to 1.6 mL of deionized-distilled water, and 100 µL of Folin-Ciocalteu phenol reagent was added and preserved for 3 min at 37°C. Then, 300 µL of saturated Na2CO3 (7%) was added, and the mixture was transferred to a 10 mL tube with the addition of deionized-distilled water. The concoction was held in a dark room for 120 min, and the absorbance was quantified at 765 nm by an ELISA reader (BioTek, USA). The gallic acid was used as a reference standard, and the TPC was expressed as mg of gallic acid equivalents per gram of the gum on a dry basis.
3.3. Total Flavonoid Contents Determination
In this study, the aluminum chloride colorimetric method was applied in order to determine the total flavonoid contents (TFC) of chloroform and ethyl acetate extracts (14). Then the absorbance was measured at 510 nm by using an ELISA reader (BioTek, USA). The quercetin was applied as a standard reference, and the TFC was expressed as a milligram of quercetin equivalents per gram of extracts on a dry basis. All assays were performed in triplicates.
3.4. Evaluation of DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
One mL of 0.1 mM solution of DPPH radical in methanol was added to 20, 50, and 100 µg/mL of chloroform and ethyl acetate extracts. After performing vigorous vortextion and 30 min incubation in the dark room, the absorbance was measured at 517 nm by an ELISA reader (BioTek, USA), and the scavenging activity (SDPPH) in percent was calculated adopting the following formula:
SDPPH [%] = 100 × [(Ablank-Asample)/Ablank]
where Ablank indicates the absorbance of the control, and Asample shows the absorbance of the extract. Then, 50% of DPPH- radical scavenging activity (IC50) was calculated from a graph by plotting SDPPH against the concentrations of extracts. All assays were performed in triplicates.
3.5. Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power (FRAP) Assay
Concentrations of 25, 75, and 125 µg/mL of chloroform and ethyl acetate extracts were added to a mix containing 2 mL of distilled water and 3 mL of the FRAP reagent. After performing a vigorous vortex and 10 min of incubation at 37°C, the absorbance was measured at 593 nm using an ELISA reader (BioTek, USA). The quercetin and aqueous solution of FeSO4 were applied as positive control and standard, respectively (15). All assays were performed in triplicates.
3.6. Gas Chromatography
Analytical GC-MS assay was carried out on an Agilent 5975C MSD, which was coupled to an Agilent 7890A (Agilent Technologies, USA) and equipped with a flame ionization detector, FID. The GC separation was performed on DB5 column of 60 m × 0.25 mm i.d. and 0.25 µm film thickness in temperature program: initial temperature of 50°C was maintained for 4 min, then increased to 120°C at 5°C/1 min, and the final temperature of 260°C was maintained for 13 min with a constant helium flow rate of 1 mL min-1. Taking into account the library data from Wiley 9th ed. & NIST 2008 Lib. SW (Version 2010) or other data from the literature, the individual compounds were recognized by matching their mass spectra, studying their retention times, and corresponding mass spectra with those of reliable standards.
3.7. Cell lines and Cell Culture
HEK-293, PC-3, and SW-480 cell lines were obtained from the National Cell Bank of Iran (NCBI, Pasteur Institute, Tehran, Iran). The cells were cultured in RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Sigma) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (Sigma) and incubated in a 5% CO2 humidified incubator at 37°C.
3.8. MTT Assay
To perform MTT assay, 4 × 103 cells were seeded in 150 µL of growth medium in each well of a 96-well plate and allowed to grow to 70% confluency. The cells were then treated with different concentrations of chloroform and ethyl acetate extracts (1 - 200 µg/mL) for 48 hours. After removing the medium, 100 µL of MTT solution (3- [4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide) (5 mg/mL in PBS) was added to each well. The MTT solution was changed to 100 µL of DMSO three hours later, and the absorbance was measured at 590 nm using an ELISA reader (BioTek, USA). Cell survival rate was calculated as (%) = (a-c)/(b-c) x100, which a = absorbance at every concentration of the test reagent, b = absorbance at 0 μM of the test reagent, and c = absorbance of the blank. The IC50 values were calculated by adopting approximate linear regression of the percentage survival versus the drug concentration (16). All assays were conducted in triplicates.
3.9. Statistical Analysis
The data from all three replicates were reported as means ± standard deviations. Statistical analyses were carried out using SPSS (IBM Statistics 25.0). A P-value < 0.05 was found to be statistically significant. The IC50 value was computed using Excel (Microsoft office 2016) and GraphPad Prism software version 8 (California, USA).
4. Results
4.1. Total Phenolic Contents of Chloroform and Ethyl Acetate Extracts of T. persicum
The average total phenolic content of chloroform and ethyl acetate extracts of T. persicum were calculated by adopting the Folin-Ciocalteu method, and it was found that the chloroform extract contained more phenolic contents than the ethyl acetate extract (Table 1) (P < 0.05).
Total Phenolic, Flavonoids, and Radical Scavenger Activities of Chloroform and Ethyl Acetate Extracts of Teucrium persicum
4.2. Total Flavonoid Contents of Chloroform and Ethyl Acetate Extracts of Teucrium persicum
The average total flavonoid content of T. persicum chloroform and ethyl acetate extracts was calculated, and no significant difference was observed between the total flavonoid contents of these two extracts (Table 1) (P < 0.05).
4.3. Radical Scavenging Activity Chloroform and Ethyl Acetate Extracts of Teucrium persicum
The radical scavenging activity of the chloroform and ethyl acetate extracts was evaluated by adopting the DPPH method. The DPPH and ascorbic acid were used as a stable free radical and as a standard, respectively. As Table 1 shows, the concentrations responsible for 50% inhibition for both extracts were not significantly different (Table 1). These concentrations were detected to be 2.5 ± 0.013 and 3 ± 0.0023 μg/mL for the chloroform and ethyl acetate extracts, respectively. The IC50 value of ascorbic acid was calculated as 8 μg/mL.
4.4. Antioxidant Potential of Chloroform and ethyl Acetate Extracts of Teucrium persicum
The antioxidant potential of the extracts was assessed by performing the FRAP analysis. The average ferric reducing antioxidant power of the chloroform and ethyl acetate extracts and quercetin were 3.5 ± 0.003, 4.5 ± 0.01 µM of FeSO4, respectively; while the power of quercetin was found to be 1.2 µM of FeSO4.
4.5. Composition of Chloroform and Ethyl Acetate Extracts
The results from phytochemical screening of chloroform and ethyl acetate extracts of T. persicum are presented in Tables 1 and 2. (-)-Spathulenol (17.87%), (-)-Neoclovene-(I), dihydro (9.98), isoaromadendrene epoxide (7.39%), culmorin (6.6%), oxiranecarboxaldehyde, 3-methyl-3-(4-methyl-3-pentenyl)- (5.44%), and caryophyllene oxide (5.31%) were the most abundant components of the chloroform extract (Table 2). Longifolenaldehyde (11.5%), culmorin (6.42%), α-Farnesene (5%), alloaromadendrene oxide-(1) (4.65%), 1-Heptatriacotanol (4.38%) were the most abundant components of the ethyl acetate extract (Table 3).
| Compound Name | Extract (%) | Retention Time | Chemical Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. 1-Pentanol | 0.17 | 7.074 | C5H12O |
| 2. Eucalyptol | 0.32 | 11.180 | C10H18O |
| 3. Culmorin | 6.60 | 26.737 | C15H26O2 |
| 4. Santolina triene | 0.14 | 12.190 | C10H16 |
| 5. Caryophyleine-(I3) | 0.35 | 36.229 | C15H24 |
| 6. α-Farnesene | 3.27 | 26.498 | C15H24 |
| 7. Globulol | 0.54 | 22.878 | C15H26O |
| 8. Isocaryophillene | 0.40 | 21.435 | C15H24 |
| 9. Octadecanoic acid | 0.51 | 33.732 | C17H35CO2H |
| 10. Ferruginol | 0.25 | 36.550 | C20H30O |
| 11. Ledol | 0.32 | 36.731 | C15H26O |
| 12. Isomyocorene | 1.59 | 30.280 | C10H16 |
| 13. 3-Octadecyne | 0.20 | 15.975 | C18H34 |
| 14. β-Humulene | 1.19 | 23.399 | C15H24 |
| 15. Phytol | 0.24 | 32.921 | C20H40O |
| 16. Isoledene | 1.98 | 23.910 | C15H24 |
| 17. Platambin | 3.28 | 28.660 | C15H26O2 |
| 18. Thunbergol | 0.49 | 32.189 | C20H34O |
| 19. Longifolenaldehyde | 1.85 | 23.987 | C15H24O |
| 20. (-)-Spathulenol | 17.87 | 26.736 | C15H24O |
| 21. Isobornyl propionate | 0.35 | 16.796 | C13H22O |
| 22. Cedran-diol, 8S,14 | 0.35 | 16.796 | C15H26O |
| 23. Isomyocorene | 1.59 | 30.280 | C10H16 |
| 24. 3,4-Decadiene | 0.30 | 14.676 | C11H20 |
| 25. Cyclononene | 0.09 | 13.389 | C9H16 |
| 26. Isoaromadendrene epoxide | 7.39 | 24.050 | C15H24O |
| 27. dl-Thioctic acid | 0.14 | 34.952 | C8H14O2S2 |
| 28. Isobornyl propionate | 0.35 | 16.796 | C13H22O |
| 29. cis-Linaloloxide | 0.16 | 11.835 | C10H18O |
| 30. 1-Eicosene | 0.46 | 33.299 | C20H40 |
| 31. 5-Caranol, (1S,3R,5S,6R)-(-)- | 0.43 | 20.714 | C10H18O |
| 32. α-Santalol | 0.30 | 14.676 | C15H24O |
| 33. trans-2-Caren-4-ol | 0.83 | 21.091 | C10H16O |
| 34. 17-(Acetyloxy)-kauran-18-al | 0.29 | 21.335 | C23H36O |
| 35. Coprostan-3 β16β-diol | 0.41 | 22.068 | C27H48O2 |
| 36. cis-Linaloloxide | 0.22 | 14.477 | C10H18O |
| 37. 2,6-Dimethyl-3,7-octadiene-2,6-diol | 0.32 | 13.888 | C10H18O2 |
| 38. 8,14-Cedranoxide, | 2.82 | 28.793 | C15H24O |
| 39. dl-Thioctic acid | 0.14 | 34.952 | C8H14O2S2 |
| 40. Artemisia alcohol | 0.09 | 13.289 | C10H18O |
| 41. Alloaromadendrene oxide-(1) | 1.62 | 27.113 | C15H24O |
| 42. Lavandulol, trifluoroace | 0.11 | 14.621 | C12H17F3O2 |
| 43. (6Z)-Nonen-1-ol | 0.77 | 18.473 | C9H18O |
| 44. cis-13-Octadecenoic acid | 0.46 | 33.299 | C18H34O2 |
| 45. 1,6,9-Tetradecatriene | 0.20 | 15.975 | C14H24 |
| 46. 1,3,5-Heptatriene | 0.22 | 13.578 | C7H10 |
| 47. Aristolene epoxide | 1.96 | 25.552 | C15H24O |
| 48. γ-Gurjunene | 0.88 | 23.044 | C15H24 |
| 49. Epi-β-Santalol | 0.22 | 13.578 | C15H24O |
| 50. Oxiranecarboxaldehyde, 3-methyl-3-(4-methyl-3-pentenyl)- | 5.44 | 29.670 | C10H16O2 |
| 51. 5-Caranol, (1S,3R,5S,6R)-(-) | 0.43 | 20.714 | C10H18O |
| 52. (+)-δ3-Carene | 3.85 | 28.948 | C10H16 |
| 53. Caryophyllene oxide | 5.31 | 25.230 | C15H24O |
| 54. Morphinan-6-one, 4,5-epoxy-3,14-dihydroxy-17-(2-propenyl)-, (5 α)- | 0.25 | 36.550 | C19H21NO4 |
| 55. Pentadecyl pentafluoropropionate | 0.98 | 24.465 | C18H31F5O2 |
| 56. Murolan-3,9(11)-diene-10-peroxy | 2.56 | 25.297 | C15H24O2 |
| 57. β-Cedren-9-α-ol | 1.96 | 28.793 | C15H24O |
| 58. (-)-Neoclovene-(I), dihydro | 9.98 | 29.866 | C15H26 |
| 59. Neogammacer-22(29)-ene | 1.57 | 32.489 | C30H50 |
| 60. 7,8-Epoxy- α -ionone | 1.59 | 30.280 | C13H20O2 |
| Total identified compounds | 98.18 |
The Chemical Composition of Chloroform Extract of Teucrium persicum
| Compound Name | Ethyl Acetat Extract (%) | Retention Time | Chemical Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Ledol | 2.34 | 39.378 | C15H26O |
| 2. Myrcenylacetat | 0.15 | 23.590 | C12H20O2 |
| 3. Ethisterone | 3.64 | 42.229 | C21H28O2 |
| 4. Culmorin | 6.42 | 35.153 | C15H26O2 |
| 5. Phytol | 0.52 | 23.686 | C20H40O |
| 6. Ocimene | 0.15 | 22.695 | C10H16 |
| 7. γ-Elemene | 0.52 | 28.672 | C15H24 |
| 8. Isophytol | 0.22 | 22.543 | C20H40O |
| 9. Camphene | 0.22 | 24.594 | C10H16 |
| 10. 7-Nonenamide | 0.59 | 28.199 | C9H17NO |
| 11. α-Farnesene | 5.02 | 27.937 | C15H24 |
| 12. α-Irone | 0.49 | 29.085 | C14H22O |
| 13. γ-Santalol | 0.52 | 28.672 | C15H24O |
| 14. (-)-Spathulenol | 14.8 | 32.569 | C15H24O |
| 15. Falcarinol | 0.86 | 32.521 | C17H24O |
| 16. γ-himachalene | 0.11 | 27.000 | C15H24 |
| 17. Longifolenaldehyde | 11.5 | 31.589 | C15H24O |
| 18. Cholesterol | 0.59 | 34.438 | C27H46O |
| 19. Tetratetracontane | 1.61 | 37.164 | C44H90 |
| 20. 1-Heptatriacotanol | 4.38 | 35.197 | C37H76O |
| 21. 7-Nonenamide | 0.31 | 26.359 | C9H17NO |
| 22. γ-Gurjunenepoxide-(2) | 3.20 | 35.704 | C15H24O |
| 23. Tetracosane | 1.04 | 43.099 | C24H50 |
| 24. Cadala-1(10),3,8-triene | 0.40 | 30.234 | C15H22 |
| 25. 5(10)-Estrene-3β,17α-diol | 4.08 | 41.250 | C18H28O2 |
| 26. 17-(acetyloxy)-Kauran-18-al | 0.68 | 33.619 | C23H36O3 |
| 27. Tricosane | 0.52 | 39.841 | C23H48 |
| 28. 8S,14-Cedrandiol | 0.49 | 40.161 | C15H26O2 |
| 29. Diazoprogesterone | 0.86 | 32.531 | C21H30N4 |
| 30. beta.-Cedren-9-α-ol | 2.61 | 35.586 | C15H24O |
| 31. Pyridine | 0.06 | 8.695 | C5H5N |
| 32. Eucalyptol | 0.11 | 16.237 | C10H18O |
| 33. cis-Linalol oxide | 0.22 | 17.469 | C10H18O2 |
| 34. Trans-Linalool oxide | 2.56 | 21.428 | C10H18O2 |
| 35. trans-3-Penten-2-ol | 0.11 | 18.347 | C5H10O |
| 36. 1,5,8-Menthatriene | 0.13 | 19.276 | C10H14 |
| 37. (Z)6-Pentadecen-1-ol | 0.06 | 19.656 | C15H30O |
| 38. E-12-Tetradecenal | 0.72 | 23.085 | C14H26O |
| 39. Dodecane | 0.13 | 21.564 | C12H26 |
| 40. 2,4-Hexadiene, (E,Z) | 0.22 | 23.252 | C6H10 |
| 41. 1-Chloro-2-phenylazetidine | 0.06 | 15.393 | C4H8ClN |
| 42. Propanedioic acid, 2-propenyl | 0.06 | 23.995 | C10H16O4 |
| 43. 17-Octadecenal | 0.13 | 24.079 | C18H34O |
| 44. 13-Tetradece-11-yn-1-ol | 0.13 | 24.763 | C14H24O |
| 45. 3-Octadecyne | 0.11 | 24.814 | C18H34 |
| 46. 5-Octen-1-ol | 1.09 | 25.692 | C8H16O |
| 47. Guanidine, N-[3-[(2-bromophenyl) | 0.59 | 29.592 | C10H14BrN3 |
| 48. cis-Z-α-Bisabolene epoxide | 0.40 | 29.592 | C15H24O |
| 49. Ledene oxide-(II) | 0.27 | 30.538 | C15H24O |
| 50. Alloaromadendrene oxide-(1) | 4.65 | 31.767 | C15H24O |
| 51. Epianastrephin | 0.22 | 31.027 | C12H18O2 |
| 52. α-Bulnesene | 0.74 | 31.171 | C15H24 |
| 53. (E)-3(10)-Caren-4-ol | 0.99 | 32.821 | C10H16O |
| 54. 2-Tetradecene | 1.09 | 32.158 | C14H28 |
| 55. Calarene epoxide | 3.20 | 35.704 | C15H24O |
| 56. Ledene oxide-(I) | 4.24 | 35.831 | C15H24O |
| 57. Diepicedrene-1-oxide | 1.45 | 35.957 | C15H24O |
| 58. (-)-Neoclovene-(I), dihydro- | 1.45 | 37.722 | C15H26 |
| 59. [1,2,4]Triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine | 0.04 | 45.210 | C5H4N4H28O |
| 60. (-)-Isolongifolol, methyl ether | 1.29 | 39.933 | C16H28OO |
| 61. Ergost-22-en-3-ol, (3β, 5α, 22E,24R) | 0.36 | 28.376 | C28H48O |
| Total identified compounds | 96.83 |
The Chemical Composition of Chloroform Extract of Teucrium persicum
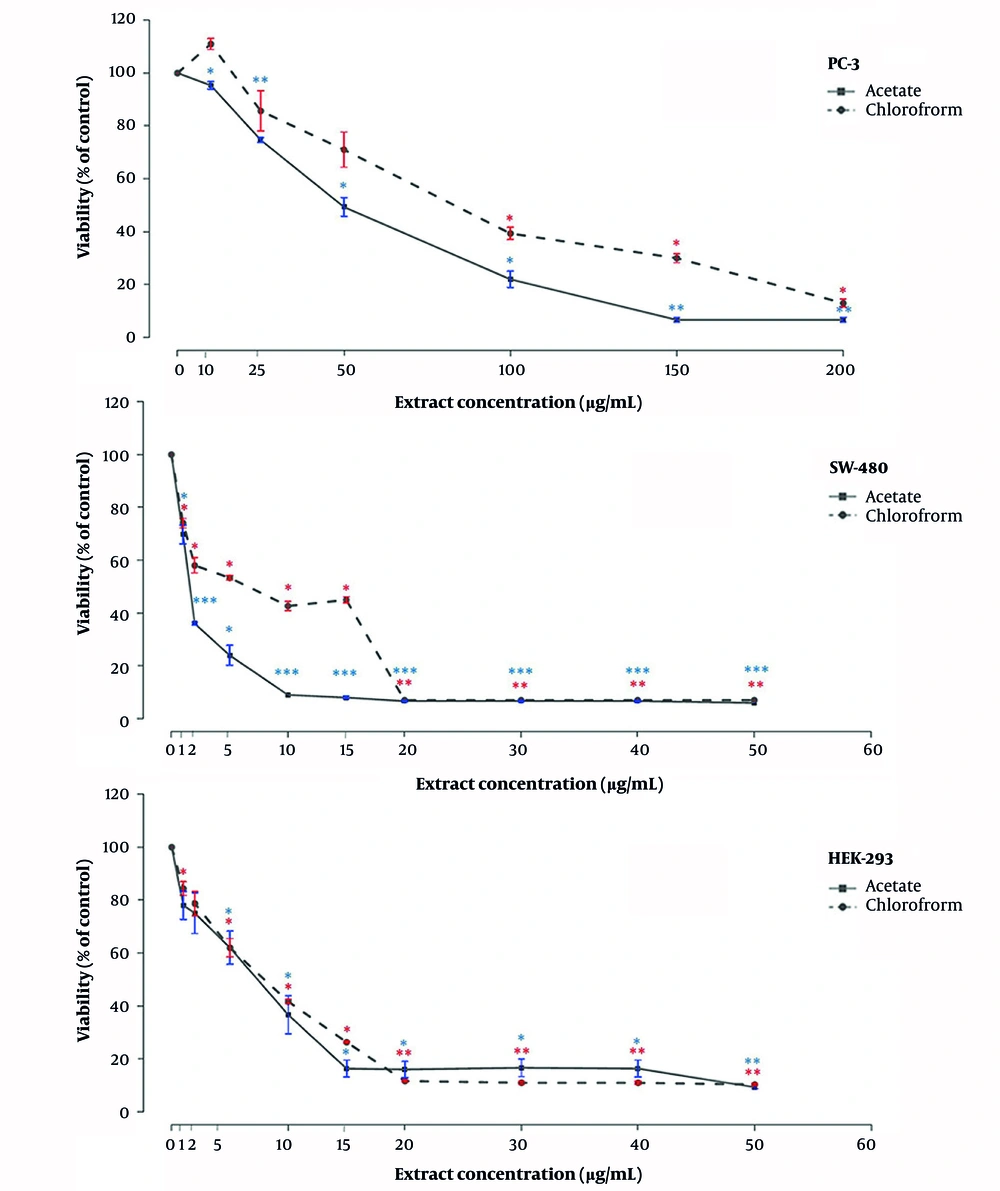
4.6. The Cytotoxic Effects of Chloroform and Ethyl Acetate Fractions on Different Cell Lines
In this study, two human cancer cell lines including PC-3 (human prostate adenocarcinoma), SW-480 (human colorectal adenocarcinoma), and normal HEK-293 (human embryonic kidney) cells were treated with different concentrations of chloroform and ethyl acetate extracts of T. persicum for 48 hours followed by measuring the viability of cells by MTT. As shown in Figure 1, the chloroform extract of T. persicum showed a higher toxicity effect on PC-3 cells compared to the ethyl acetate extract. However, the ethyl acetate extract showed greater growth inhibition on SW-480 cells compared to the chloroform extract. As shown in Figure 1, the chloroform extract exerted higher inhibitory effects on SW-480 cells compared to PC-3 and HEK-293 cells. The IC50 values of chloroform extract for PC-3, SW-480, and HEK-293 cells were calculated as 39, 4.453, and 6.574 μg/mL, respectively. Our MTT results demonstrated that although 10 and 25 μg/mL of ethyl acetate extract caused a small increase in the number of viable PC-3 cells (up to 15%), the treatment of PC-3 cells with higher concentrations of the extract led to a considerable reduction in cell viability (Figure 1). The ethyl acetate extract exerted stronger inhibitory effect on the viability of SW-480 cells followed by HEK-293 cells (Figure 1). The IC50 values of ethyl acetate extract for PC-3, SW-480, and HEK-293 cells were calculated as 65.9, 1.65, and 5.181 μg/mL, respectively (Table 4).
Chloroform and ethyl acetate extracts of Teucrium persicum reduces the viability of PC-3, SW-480, and HEK-293T cell lines. The cells were seeded in 96-well plates and allowed to grow to 70% confluency. The cells were then treated with different concentrations of the extract for 48 hours, and the cell viability was calculated using the MTT assay. The shown data are mean ± SD of three separate experiments repeated in 10 wells (*: P < 0.05; **: P < 0.01; ***: P < 0.001 vs. control).
| Cell Line | Chloroform Extract (μg/mL) | Ethyl Acetate Extract (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| PC-3 | 39 | 65.9 |
| SW-480 | 4.453 | 1.65 |
| HEK-293 | 6.574 | 5.181 |
The IC50 Values of Chloroform and Ethyl Acetate Extracts of Teucrium persicum
5. Discussion
There is a body of evidence suggesting that plants and their phytochemicals may have therapeutic properties; some of them are currently used in the clinics to treat various diseases, including different types of cancer (17-19).
Teucrium persicum is an Iranian endemic plant with potentially unknown properties, which has been used in Iranian traditional medicine to treat various diseases as well as hyperlipidemia, diabetes, and obesity (6).
This study aimed to investigate the antioxidant and cytotoxic potential of chloroform and ethyl acetate extracts of T. persicum. According to the results from our previous studies, the methanolic extract of T. persicum had significant antioxidant and cytotoxic properties (13). Our biochemical analyses indicated that chloroform and ethyl acetate extracts of T. persicum contained noticeable total phenolic and flavonoid contents. Moreover, it was found that 2.5 μg/mL of chloroform extract was required to scavenge 50% of DPPH radicals (compared to 8 ± 0.005 μg/mL of ascorbic acid) (P < 0.05). This value for ethyl acetate was detected to be 3 μg/mL.
According to the results from MTT experiments, PC-3 cells were discovered to be less sensitive than SW-480 and even HEK-293 cells. It was also found that the chloroform extract was capable of exerting stronger inhibitory effect on PC-3 cells, but the opposite was the case as for SW-480 and HEK-293 cells (Table 4). Taking the laboratory results into consideration, these different inhibitory effects may have been attributed to the synergistic effects of two or more compounds in the extracts (19, 20). Previous reports have indicated that Teucrium species contain considerable amounts of phenolic and flavonoid compounds that are the main cause of their biological activities (11-13). Therefore, it is suggested that the cytotoxic potential of the ethyl acetate and chloroform extracts of T. persicum may be due to the presence of phenolic and flavonoid compounds. Compared to our previous study (16), the present study showed that the chloroform and ethyl acetate extracts of T. persicum had more phenolic contents than the methanolic extract.
Due to the difference in polarity of solvents used in this study, the chemical profile of these three extracts may have been different and, therefore, the variability in antioxidant and cytotoxicity properties of these extracts may have been reasonable. GC and GC/MS analysis facilitated the identification of 60 and 61 compounds representing 98.18% and 96.52% of the chloroform and ethyl acetate extracts, respectively. The relative concentrations of the identified components of chloroform and ethyl acetate extracts are presented in Tables 2 and 3, respectively.
Previous studies conducted to analyze the essential oils of Teucrium species had already documented the general dominance of the sesquiterpenes group (21-23). Our results were in agreement with the findings from the given studies.
Reviewing the literature demonstrated that some of these compounds including α-pinene, β-caryophyllene, and β-caryophyllene-oxide had significant anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-hypercholesterolemic, anticancer, and antibacterial effects (24-29). Laboratory findings had already suggested that the presence of various compounds in the essential oils or extracts of plants may have been the underlying cause of their biological properties (30-32). Therefore, it was hypothesized that one or more compounds may have been responsible for the inhibitory effects of chloroform and ethyl acetate extracts of T. persicum.
5.1. Conclusions
The results from our previous studies and the current study suggested that the antioxidant and cytotoxic effects of T. persicum extracts may have been attributed to the presence of various compounds, including phenolic and flavonoid compounds. However, it was recommended that further studies should be conducted in order to investigate phytochemical profiles of T. persicum extract, facilitate the process of studying its anti-cancer potential, and investigate the underlying molecular mechanism(s) by isolating and identifying the effective compounds.