1. Background
Metals as environmental and occupational toxicants, are a major source of concern due to their long-term contraindication in the development of adverse health conditions. Cadmium, nickel, chromium, to mention a few are vastly distributed metals, potentially giving rise to environmental and occupational exposure risks, which may have deleterious effects on human health (1). These metals are of great concern as a result of their non-biodegradable properties, which contribute to their tendency to accumulate in living organisms causing detrimental diseased conditions (2). Chromium and its salts, as well as chromium-containing compounds, play a major role in numerous manufacturing processes and have been contraindicated in carcinogenic, toxic, and mutagenic conditions in people involved in these processes (3, 4). Hexavalent chromium [Cr (VI)] is one of the valence state chromium majorly exists in the environment. It is found on surface coatings and in water systems under alkaline pH and mild oxidizing conditions posing a major environmental health challenge (5). It easily permeates the cell membrane with the aid of the sulphate anion transport system present in the membrane and thereafter reduced to other lower oxidation states, leading to accumulation in various organs and triggering a multiplex of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and organ damage (6-8).
Acacia nilotica (L.), commonly known as "Babool wood" or "Babul" is found in different parts of South Asia, and Africa belongs to the Fabaceae family and Mimosoideae subfamily (9). In these parts of the world where they are found, they are used as both medicinal and ornamental plants by the locals. Its ethnopharmacological applications include treatment of congestion, diarrhea, sclerosis, bleeding piles, coughs, diabetes, hemorrhages, dysentery, bronchitis, and fever. It is also used to treat oral, bone, and skin-related diseases by the locals by preparation of infusions and decoctions (9-11). A. nilotica plant parts are made up of rich and diverse phytocompounds such as ellagic acid, leucocyanidin, galloylated catechins, (+)-catechin, 5,7-digallateumbelliferone, γ-sitosterol, niloticane, catechin, kaempferol, rutin, apigenin, and others (10, 12). They have also been reported to exhibit antimutagenic, hepatoprotective, antimicrobial, antidiabetic, anticancer, nephroprotective, anti-inflammatory, anti-Alzheimer’s and antioxidative activities (13-15). Various researchers have also reported the adsorbent property of A. nilotica bark in removing hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions (16, 17). Based on these studies, we hypothesized the adsorbent potential of A. nilotica leaves in animals preventing Cr (VI) accumulation and related systemic damage. To investigate this hypothesis, this study aimed to investigate the ameliorative role of A. nilotica aqueous leave extract on potassium dichromate-induced hepato- and hemotoxicity in male and female rats. Phytochemical screening and nutritive composition of the extract was also assessed.
2. Methods
2.1. Chemical and Reagents
Potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) (PDC) was procured from Guangdong Guanghua SciTech Co., Ltd in Shantou, Guangdong, China, while perchloric acid, sulphuric acid, and trioxonitrate (IV) acid were procured from Sigma Chemical Company, Germany. Biochemical kits were gotten from Randox Ltd, UK. All other chemicals were products of Merck, Germany, and were of analytical grade.
2.2. Plant Collection, Identification, and Extraction
A. nilotica leaves were gotten from Birnin Kebbi, Kebbi State, identified by Dr. J. O. Popoola, and voucher specimen deposited at the herbarium of the University of Lagos with voucher number LUH 7553. Aqueous leaf (ANLA) extract was prepared as described by Iheagwam, Nsedu (18) with slight modification. Briefly, leaves were washed, air-dried under room temperature, and pulverized. Powder was macerated in distilled water by preparing a 10% (w/v) solution for 72 h with frequent gentle agitation before the filtrate was freeze-dried.
2.3. Phytochemical and Proximate Analysis
Qualitative phytochemical and proximate analysis were carried out according to standard methods as described by Iheagwam, Nsedu (18), and Elizabeth, Nonso (19), respectively.
2.4. Experimental Animals and Setup
Albino rats (n = 40; male = 20, female = 20) weighing between 180 - 200 g were purchased from the Estratop farm, Ifoyintedo, Ogun state. The animals were housed in the animal unit of the Department of Biochemistry, Covenant University, and maintained under standard conditions with the provision of feed and water ad libitum. All animal-handling methods were in compliance with the guidelines for the care and use of lab animals documented by the National Institute of Health. Approval was granted by the Biological Sciences Research Ethics Committee. Two weeks after acclimatization, the animals were divided into four groups of five rats each: (1) group 1 (Ctrl) was administered water and served as the control (n = 10; male = 5, female = 5); (2) group 2 (Cr) received potassium dichromate (PDC; K2Cr2O7; 0.635 mg/kg body weight) dissolved in distilled water by oral gavage (n = 10; male = 5, female = 5); (3) group 3 (Cr + A*) received PDC after seven days were co-treated with ANLA (650 mg/kg bwt) (n = 10; male = 5, female = 5); (4) group 4 (Cr + A) received PDC co-treated with ANLA (Cr + A) simultaneously (n = 10; male = 5, female = 5).
The experimental duration was 21 days. After that, rats were fasted on the last day for 12 h and sacrificed through cardiac puncture under mild euthanasia using diethyl ether.
2.5. Sample Collection
During the sacrifice, blood was collected into EDTA and heparin tubes for hematological and biochemical assays, respectively, while liver tissue was collected, cleaned, and placed in a homogenizing buffer (0.25 M sucrose solution). Liver tissue was collected, cleaned, and fixed in a 10% formalin solution for histological studies, while, liver, heart, intestine, spleen, kidney, muscle, and testis were digested and prepared for chromium concentration analysis.
2.6. Sample Preparation
Blood samples from the heparin tube were centrifuged at 2,000 g for 5 min, while liver tissues in 0.25 M sucrose solution were homogenized and centrifuged at 5,000 g for 10 min. The supernatants (plasma and liver homogenate, respectively) were collected into sterile tubes and stored at -20°C until they were required for biochemical analysis.
2.7. Biochemical Analysis and Histology
Plasma and liver alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, cholesterol, and triglyceride levels were carried out using Randox test kits, while protein concentration was assayed according to the method of Lowry and colleagues (20). Liver histology observation using hematoxylin and eosin staining as well as bioaccumulation of chromium in tissues were carried out according to the methods described by Kumari and colleagues (21).
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was done by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Duncan post hoc at P < 0.05 significant level using IBM Statistical Package for Social Scientists (SPSS). All experimental data were expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) of five replicates.
3. Results
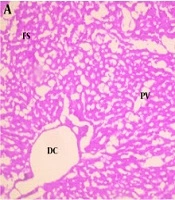
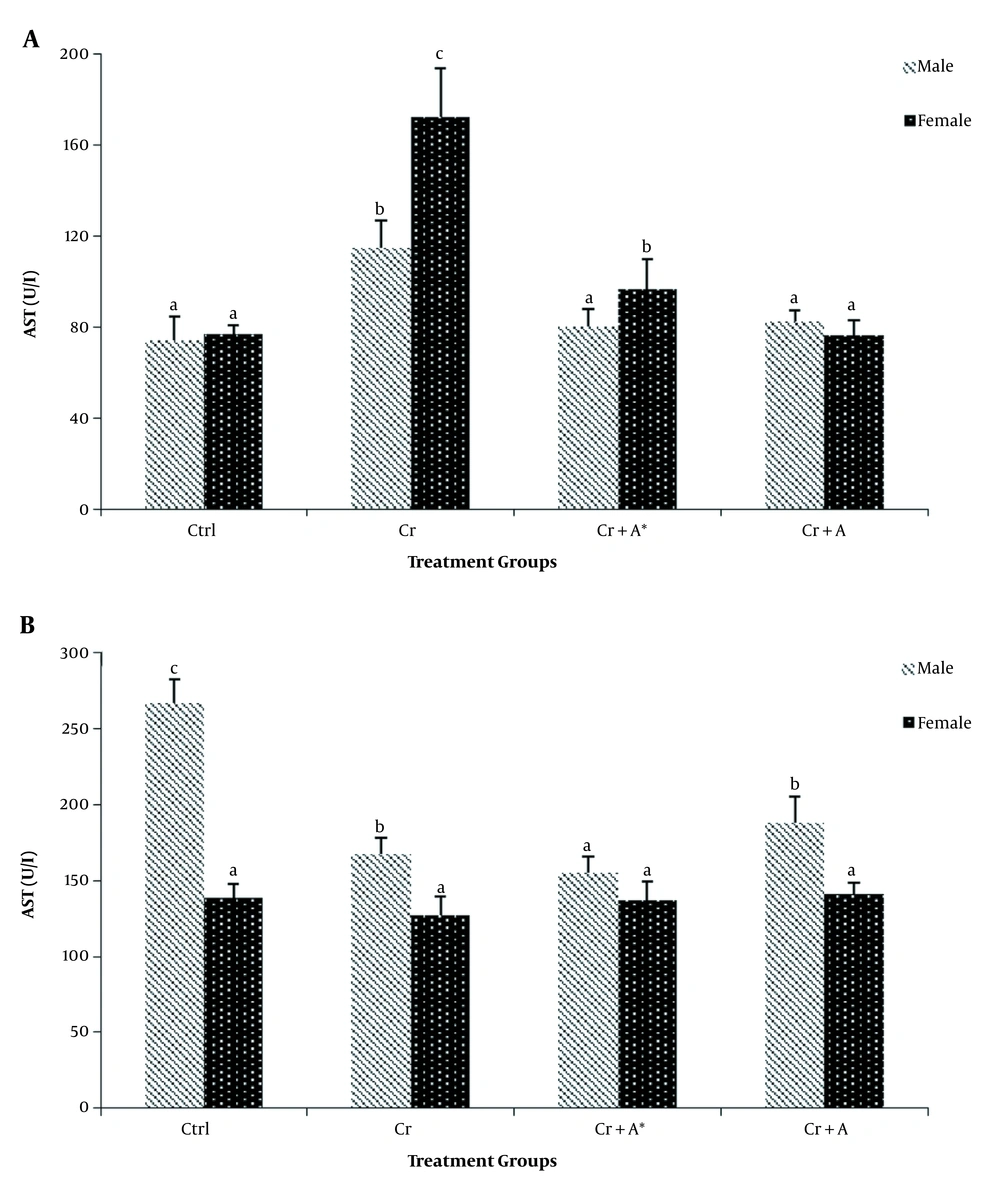
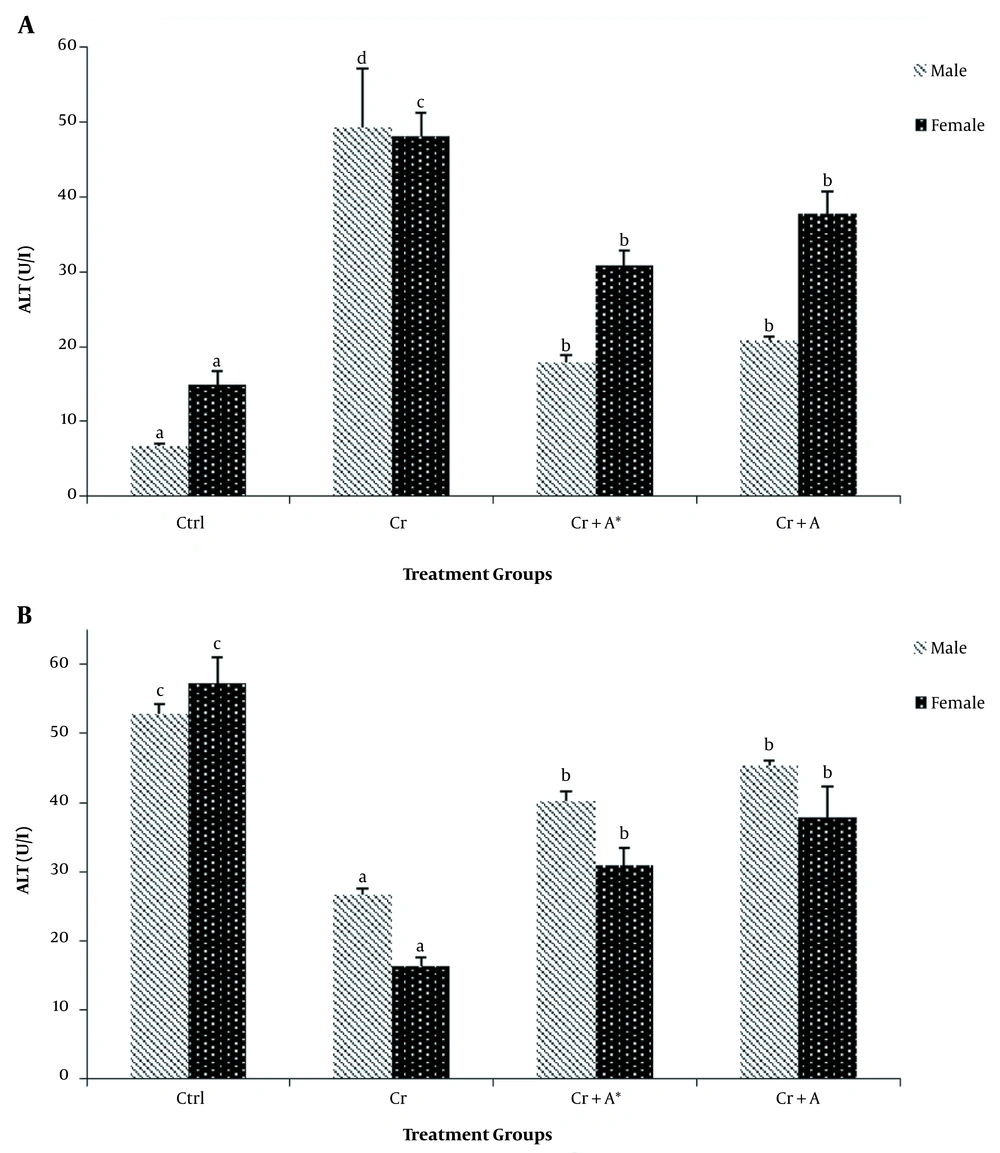
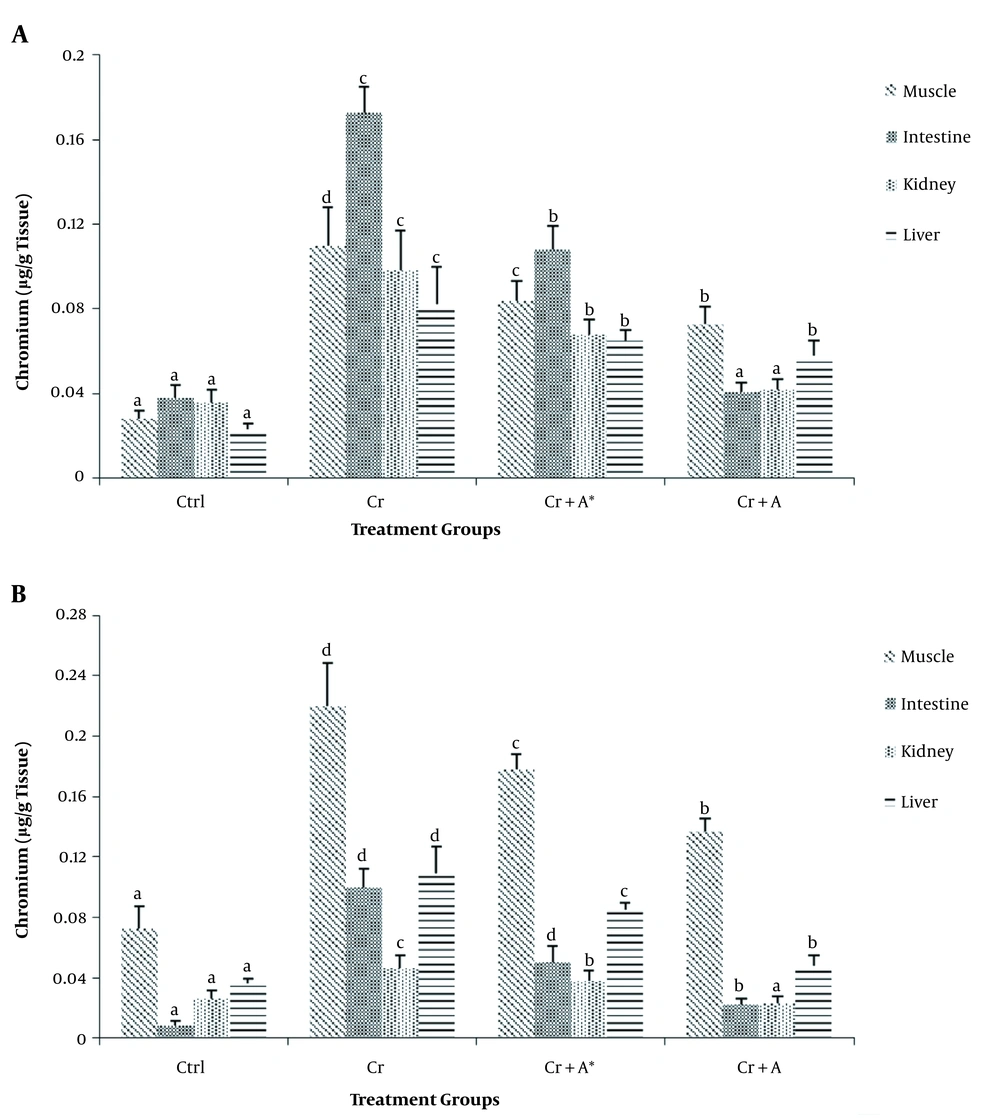
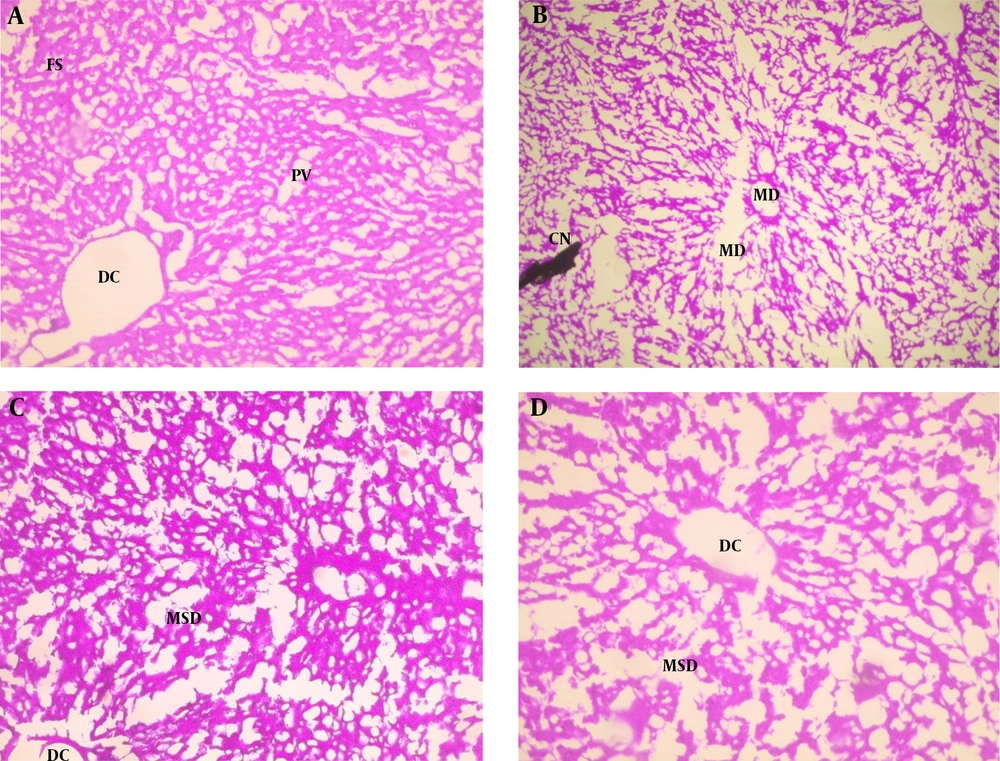
The results of phytochemical screening revealed the presence of flavonoids, terpenoids, saponins, cardiac glycoside, tannins, alkaloids, phenol, and anthraquinone in A. nilotica aqueous leaf extract (Table 1). Results, as presented in Table 2, showed the nutritive component of the crude extract was made up of plant and animal protein (67.41 ± 2.44%), carbohydrate (9.87 ± 1.87%), fiber (10.01 ± 1.21%), fat, and oil (6.63 ± 0.93%) and lastly mineral (6.41 ± 1.08%) being the least. Daily intake of PDC increased (P < 0.05) the activities of AST and ALT in the plasma whilst reducing (P < 0.05) their activity in the liver compared with the control. Oral administration of ANLA reduced (P < 0.05) the activities of plasma AST and ALT to normal and near-normal levels, respectively, while liver AST and ALT activities were increased (P < 0.05) to near-normal levels when compared with the Cr group (Figures 1 and 2). On the other hand, PDC did not have any observable effect (P > 0.05) on male rats' plasma protein concentration; however, it reduced (P < 0.05) that of the female rats while increasing (P < 0.05) the plasma triglyceride and cholesterol levels in both male and female rats when compared with the control group (Table 3). Also, ANLA administration increased (P < 0.05) the female rats’ plasma protein concentration, whereas reduced (P < 0.05) plasma triglycerides and cholesterol levels in both male and female rats to near normal levels when compared with the Cr group. ANLA administration in the Cr + A* group did not have any effect (P > 0.05) on the increased plasma cholesterol; however, it significantly (P < 0.05) reduced plasma triglyceride in Cr + A group to normal level when compared with the Cr group (Table 3). Moreover, PDC did not induce any change (P > 0.05) in male liver protein concentration; however, it reduced (P < 0.05) female liver protein concentration while increasing (P < 0.05) hepatic triglyceride and cholesterol levels in both male and female rats when compared with the control group (Table 4). Female rats’ liver protein concentration increased (P < 0.05); however, male hepatic triglycerides and cholesterol levels reduced (P < 0.05) to near normal levels upon ANLA administration when compared with the Cr group. In the female group, ANLA administration reduced (P < 0.05) hepatic triglyceride to a normal level without changing (P > 0.05) the increased hepatic cholesterol level when compared with the Cr group (Table 4). The effect of ANLA on hematological indices in potassium dichromate-induced toxicity in rats is shown in Table 5. Here, PDC increased (P < 0.05) neutrophils, lymphocytes, while basophils, hemoglobin, packed cell volume, and mean corpuscular hemoglobin (Hb) concentration were reduced (P < 0.05) when compared with the control group in both male and female rats. Nevertheless, ANLA treatment reversed (P < 0.05) these anomalies to a normal level when compared with the Cr group. Eosinophils and monocytes were not altered (P > 0.05) by PDC when compared with the control group in both male and female rats. Figure 3 indicates that PDC increased (P < 0.05) chromium concentration in the muscle, intestine, kidney, and liver of both male and female rats compared with the control group. Upon treatment with ANLA, a time-dependent reduction (P < 0.05) of chromium concentration was observed in the organs. In Cr + A group, the male and female kidney chromium concentration, as well as that of the male intestine, were reduced (P < 0.05) to the normal level. The hepatic tissue structure in the control group, as shown in Figure 4A, was regular with a distinct centriole (DC), portal vein (PV), and fenestrated sinusoids (FS). Liver histology in chromium intoxicated group, as shown in Figure 4B, reveals marked cell necrosis (CN), sinusoidal and portal vein dilation with multifocal distortion (MD). The tissue structure in ANLA administered groups depicted improvement compared with the chromium intoxicated group, showing distinct centriole (DC) with mild sinusoidal and portal vein dilation (MSD) (Figure 4C and D).
| Components | Presence |
|---|---|
| Flavonoids | ++ |
| Terpenoids | ++ |
| Saponin | +++ |
| Cardiac glycoside | +++ |
| Tannins | +++ |
| Alkaloids | + |
| Phenol | +++ |
| Anthraquinone | + |
a +, mildly present; ++, moderately present; +++, highly present.
| Constituents | Composition (%) |
|---|---|
| Plant and animal protein | 67.41 ± 2.44 |
| Carbohydrate | 9.87 ± 1.87 |
| Fiber | 10.01 ± 1.21 |
| Fat and oil | 6.63 ± 0.93 |
| Mineral | 6.41 ± 1.08 |
a Values are expressed as mean ± SEM of five replicates.
The effect of Acacia nilotica on A, plasma; and B, liver AST activities in potassium dichromate-induced toxicity in rats. Bars are expressed as mean ± SEM of five replicates (bars with different letters in superscript across the treatment groups are considered statistically significant at P < 0.05).
The effect of Acacia nilotica on A, plasma; and B, liver ALT activities in potassium dichromate-induced toxicity in rats. Bars are expressed as mean ± SEM of five replicates (bars with different letters in superscript across the treatment groups are considered statistically significant at P < 0.05).
| Variables | Ctrl | Cr | Cr + A* | Cr + A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Protein (mg/g wet tissue) | ||||
| Male | 2.08 ± 0.22 | 1.98 ± 0.11 | 2.03 ± 0.14 | 2.33 ± 0.13 |
| Female | 3.17 ± 0.58 C | 1.96 ± 0.20 A | 2.79 ± 0.38 B | 2.87 ± 0.42 B |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | ||||
| Male | 81.17 ± 9.52 A | 133.79 ± 13.08 C | 103.84 ± 13.85 B | 106.08 ± 15.33 B |
| Female | 86.21 ± 2.80 A | 180.53 ± 13.43 C | 122.72 ± 12.20 B | 84.81 ± 5.77 A |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | ||||
| Male | 24.19 ± 6.61 A | 47.18 ± 7.08 C | 34.40 ± 7.43 B | 33.35 ± 6.44 B |
| Female | 41.81 ± 10.11 A | 56.02 ± 9.85 B | 46.31 ± 12.08 B | 50.21 ± 12.89 B |
a Values are expressed as mean ± SEM of five replicates.
b Values with different capital letters (A - C) in superscript across a row are considered statistically significant at P < 0.05.
| Variables | Ctrl | Cr | Cr + A* | Cr + A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Protein (mg/g wet tissue) | ||||
| Male | 1.91 ± 0.20 | 2.07 ± 0.36 | 1.65 ± 0.18 | 1.85 ± 0.28 |
| Female | 2.26 ± 0.13 B | 1.34 ± 0.14 A | 3.30 ± 0.91 C | 3.76 ± 0.58 C |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | ||||
| Male | 94.32 ± 4.76 A | 154.50 ± 12.52 C | 114.19 ± 17.69 B | 137.42 ± 6.25 B |
| Female | 131.757 ± 5.77 A | 307.49 ± 12.44 B | 149.46 ± 5.04 A | 167.09 ± 11.68 A |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | ||||
| Male | 16.17 ± 3.51 A | 38.41 ± 8.19 C | 30.68 ± 2.91 B | 30.89 ± 2.74 B |
| Female | 42.83 ± 14.41 A | 66.69 ± 13.07 B | 64.73 ± 12.21 B | 63.35 ± 11.73 B |
a Values are expressed as mean ± SEM of five replicates.
b Values with different capital letters (A - C) in superscript across a row are considered statistically significant at P < 0.05.
| Variables | Ctrl | Cr | Cr + A* | Cr + A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neutrophils (× 109/L) | ||||
| Male | 31.33 ± 0.67 A | 43.00 ± 0.58 B | 29.00 ± 0.77 A | 33.67 ± 0.33 A |
| Female | 31.33 ± 0.66 A | 39.00 ± 0.57 B | 33.67 ± 0.33 A | 28.00 ± 0.82 A |
| Lymphocytes (× 109/L) | ||||
| Male | 41.33 ± 2.76 A | 50.33 ± 1.45 B | 42.67 ± 0.67 A | 41.00 ± 0.85 A |
| Female | 40.67 ± 0.58 A | 57.00 ± 0.77 B | 41.00 ± 0.75 A | 41.00 ± 0.58 A |
| Eosinophils (× 103/mm3) | ||||
| Male | 2.73 ± 1.67 | 2.53 ± 0.88 | 3.17 ± 0.66 | 2.90 ± 0.58 |
| Female | 2.53 ± 0.88 | 1.70 ± 0.66 | 1.90 ± 0.0.57 | 2.10 ± 0.72 |
| Basophils (× 103/mm3) | ||||
| Male | 8.00 ± 1.00 B | 5.00 ± 0.53 A | 5.67 ± 0.77 A | 4.00 ± 0.34 A |
| Female | 8.33 ± 0.67 B | 5.00 ± 0.76 A | 4.00 ± 0.57 A | 4.00 ± 0.58 A |
| Monocytes (%) | ||||
| Male | 2.33 ± 0.33 | 2.00 ± 0.55 | 1.33 ± 0.33 | 2.00 ± 0.57 |
| Female | 3.33 ± 0.67 | 3.00 ± 0.57 | 2.00 ± 0.56 | 3.00 ± 0.41 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | ||||
| Male | 16.80 ± 0.10 B | 11.43 ± 0.13 A | 16.80 ± 0.57 B | 16.53 ± 0.23 |
| Female | 16.30 ± 0.37 B | 12.23 ± 0.39 A | 16.53 ± 0.23 B | 18.00 ± 0.58 B |
| PCV (%) | ||||
| Male | 51.00 ± 0.57 B | 41.00 ± 0.58 A | 48.67 ± 1.00 B | 51.00 ± 0.70 B |
| Female | 47.67 ± 0.33 B | 37.00 ± 0.58 A | 48.67 ± 0.73 B | 51.67 ± 0.34 B |
| MCHC (g/dL) | ||||
| Male | 33.33 ± 0.03 B | 30.60 ± 0.20 A | 33.27 ± 0.33 B | 33.20 ± 0.10 B |
| Female | 33.37 ± 0.20 B | 30.10 ± 0.10 A | 33.20 ± 0.23 B | 33.33 ± 0.08 B |
Abbreviations: PCV, packed cell volume; MCHC, mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration.
a Values are expressed as mean ± SEM of five replicates.
b Values with different capital letters (A - C) in superscript across a row are considered statistically significant at P < 0.05.
The effect of Acacia nilotica on organ chromium retention in potassium dichromate-induced toxicity in A, male; and B, female rats (bars are expressed as mean ± SEM of five replicates; Bars with different letters in superscript across the treatment groups are considered statistically significant at P < 0.05).
Hematoxylin and eosin staining of hepatic tissues from A, control showing distinct centriole (DC), portal vein (PV) and fenestrated sinusoids (FS); B, Cr showing marked cell necrosis (CN), sinusoidal and portal vein dilation with multifocal distortion (MD); C, Cr + A*; and D, Cr + A showing distinct centriole (DC) with mild sinusoidal and portal vein dilation (MSD) (× 400).
4. Discussion
Chromium plays a major role in various industrial applications; thus, high industrial pollution of the environment with this metal compound, especially its hexavalent form, is a significant problem (5, 22). This study revealed the potential of A. nilotica leaves to abate K2Cr2O7 induced hepato- and hematotoxicity in male and female experimental animals. Phytocompounds have been linked to various medicinal and pharmacological activities of plants. The presence of these compounds such as flavonoids, terpenoids, phenols, and others, corroborate previous reports (23, 24). Reports on the nutritive value of the leaf are scarce; however, a lot has been done on the pod, fruit, raw, and fermented seeds. The fiber, protein, mineral, fat, and oil contents of ANLA were highly suggestive that ANLA could provide the much-needed energy required rather than other reported leaves (25). Although fiber, mineral, fat, and oil compositions were comparable with other plant parts from previous reports, the protein was way higher. The carbohydrate composition was, however, way lower than other reported plant parts (25-27). Nonetheless, the fiber and mineral values were lower when compared with the seeds from Southern Iran (28). These differences could be attributed to the difference in plant parts and the regions where these plants were located. The liver is the biotransformation site of xenobiotics, making it the major target for toxicants where they can be transformed to less or more toxic intermediates (29). K2Cr2O7 is a hexavalent form of Cr and has been reported to induce toxicity to organs, notably the liver, at various routes and doses (30, 31). Serum enzyme activity is an important pointer for detecting damage to organs and tissues in addition to the severity of the injury. AST and ALT are the common sensitive biomarkers in the serum/plasma used in investigating hepatic function and integrity (32). The uptake of Cr (VI) increased the plasma activities of AST and ALT, while a concomitant decrease of these enzymes in the liver was also observed, indicating hepatic damage. This observation was previously reported in mice, rats, and rabbits (33-35). The increase of these enzyme activities could be as a result of Cr (VI) induced oxidative stress hepatic damage releasing the enzymes from the cytoplasm of hepatocytes into the plasma (36). It was found that after administration of ANLA, these altered activities were normalized, signifying the hepatoprotective ability of ANLA (37). This property could be attributed to the presence of phytochemicals such as flavonoids, terpenoids, and phenols which have been reported to exhibit antioxidant properties (18). They may be involved in mitigating Cr (IV)-induced hepatic damage associated with oxidative stress, as similarly reported by Hfaiedh and colleagues (38). Since hexavalent chromium is a known hepatotoxicant that easily permeates the membrane and accumulates not only in the liver but also other targets, systemic exposure will increase retention in various organs as observed (39). However, antioxidants exert their effect by chelating heavy metals. This might explain the mechanism by which ANLA administration reduced the concentration of chromium in the organs of the rats. These antioxidants may also be associated with the reversed decrease of protein level caused by Cr (IV)-induced toxicity in the female rats (39). It has been demonstrated that ROS generated by Cr (IV) induces tissue and cell damage by disrupting macromolecule arrangement. Also, the high protein content in ANLA is responsible for the synthesis of new protein molecules. The changes in cholesterol and triglycerides levels after Cr (IV) exposure may indicate abnormal lipase enzyme activities, leading to a rise in plasma triglycerides and cholesterol levels. The liver is cholesterol and triglycerides synthesis site, and these abnormalities may be attributed to Cr (IV)-induced hepatic damage via K2Cr2O7 inhibition of triglyceride lipase and unspecific esterase (8). However, when administered with K2Cr2O7, ANLA restores the observed cholesterol and triglycerides modifications, indicating potential hepatoprotective activity agreeing with other reports (33, 40). The blood is a pathological indicator of toxicants effect and other conditions of exposed animals. Hemoglobin concentration in most cases determines red blood cells (RBC) population. In the cause of infection, white blood cells (WBC), including monocytes, granulocytes, and lymphocytes, tend to increase. Thus, the observed WBC increase after PDC administration, suggesting its role as a hemotoxicant. The decrease in Hb and a concomitant decrease in packed cell volume (PCV) and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) may be due to disrupting erythropoietin release by PDC or intracellular reduction of Cr (VI) to Cr (III), which then binds subsequently to several intracellular molecules such as hemoglobin. This result agrees with the findings of Balakrishnan et al. (31) and Momo et al. (35). The more tissues retain chromium, the higher tendency for chromium-induced oxidative stress to occur, altering various metabolic pathways in the process of inducing toxicity (22, 37, 41, 42). The ameliorative role of ANLA in reducing tissue retention might be due to its ability to chelate Cr (VI) ion truncating Cr (VI) reduction pathways (43). This may prevent the generation of other Cr ion intermediates implicated in inducing oxidative stress and toxicity (44-46). Chronic administration of ANLA might have reduced liver histology damage by reversing Cr (VI)-altered histoarchitecture of the hepatocytes. These histological changes have been previously reported (30, 39).
4.1. Conclusion
A. nilotica leaves palliated both hepatic and hematologic toxicity associated with chromium intake. It is also a good source of protein and other nutrients. It can also be used for supplementation of animal feed due to its high protein, fiber, mineral, fat, and oil contents. Nonetheless, further studies should be examined for the development of therapeutic products from A. nilotica leaves in abating Cr (VI)-induced systemic damage for occupational exposure population. Moreover, the exact mechanisms by which A. nilotica ameliorates Cr (VI)-induced systemic damage can be further studied.