1. Background
Episiotomy is a surgical incision in the perineal region, which aims at increasing the vaginal diameter during delivery (1-4). Episiotomy mainly is to prevent severe perineal tears and facilitate delivery (5-8). In Asian countries, episiotomy is used as a standard method in vaginal delivery regarding the differences in the anatomical characteristics of the perineum (9, 10). For example, the prevalence rate of episiotomy is reported to be 66%, 82%, and 100% in Oman, China, and Taiwan, respectively (11-13). However, the prevalence rates of episiotomy in Denmark and the United States are 4.9% (14) and 9.4% (15), respectively. There is no exact statistics on episiotomy in Iran; however, cross-sectional studies have reported its frequency to be 88.7% in Sari and 97.3% in Tehran (16, 17).
The pelvic floor muscle is involved in many daily activities, including sitting, walking, standing, squatting, urination, and defecation (18-20). Accordingly, episiotomy and the rupture of relevant muscles may be associated with postpartum pain and discomfort (4, 10, 16). In most cases, episiotomy wounds are completely healed with no interference, such as infection by 3 weeks postpartum (21). Since the perineal region is not well visible by women and the possibility of infection is high for episiotomy wound by vaginal and rectal bacteria, there is a risk of infection and delay in the wound healing process, which can be associated with anatomical consequences, dangerous complications, and even death from infection (22, 23).
Low-cost, effective, appropriate, and affordable methods approved by women to heal episiotomy incisions have always been of interest to researchers (23, 24). In this regard, the World Health Organization (WHO) has emphasized on using herbal medicines as an alternative to chemical drugs arousing some side effects (16). Accordingly, herbal options have increased, and the herbal treatment has become one part of the WHO's medicine policies (25). Honey is a natural disinfecting agent among herbal medicines, which accelerates wound healing (26-31). Olive oil is effective in wound healing due to its antioxidant properties and a component called polyphenol (9, 23, 32-34). Sesame can also reduce inflammation and pain by inhibiting the synthesis of prostaglandins and its antioxidant properties. It also stops cell damage and facilitates the tissue repair process (28, 29, 35, 36).
Olea ointment is an herbal mixture of honey (33.4%), olive oil (33.3%), and Sesame oil (33.3%), which effectively prevents infection. Moreover, the decreased pain and inflammation accelerates wound healing and the emergence of new tissues and facilitates necrotic tissue destruction (29). According to a study, olive oil accelerates episiotomy wound healing in primiparous women (23, 37). Another study revealed the association between honey cream and episiotomy wound healing (38). The researchers also claimed that the Olea ointment was effective in healing second-degree burns and preventing wound infection. Furthermore, it facilitates and accelerates tissue regeneration (29).
Considering the significance of accelerating the perineum tissue healing, the present researchers developed and implemented the present study to investigate the effect of Olea ointment on episiotomy wound healing among primiparous women referring to Al-Zahra Education, Research, and Remedial Center in Rasht, Iran, during 2017 - 2018.
2. Objectives
The present study aimed to detect the effect of Olea ointment on episiotomy wound healing among primiparous women.
3. Methods
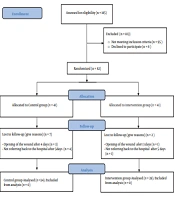
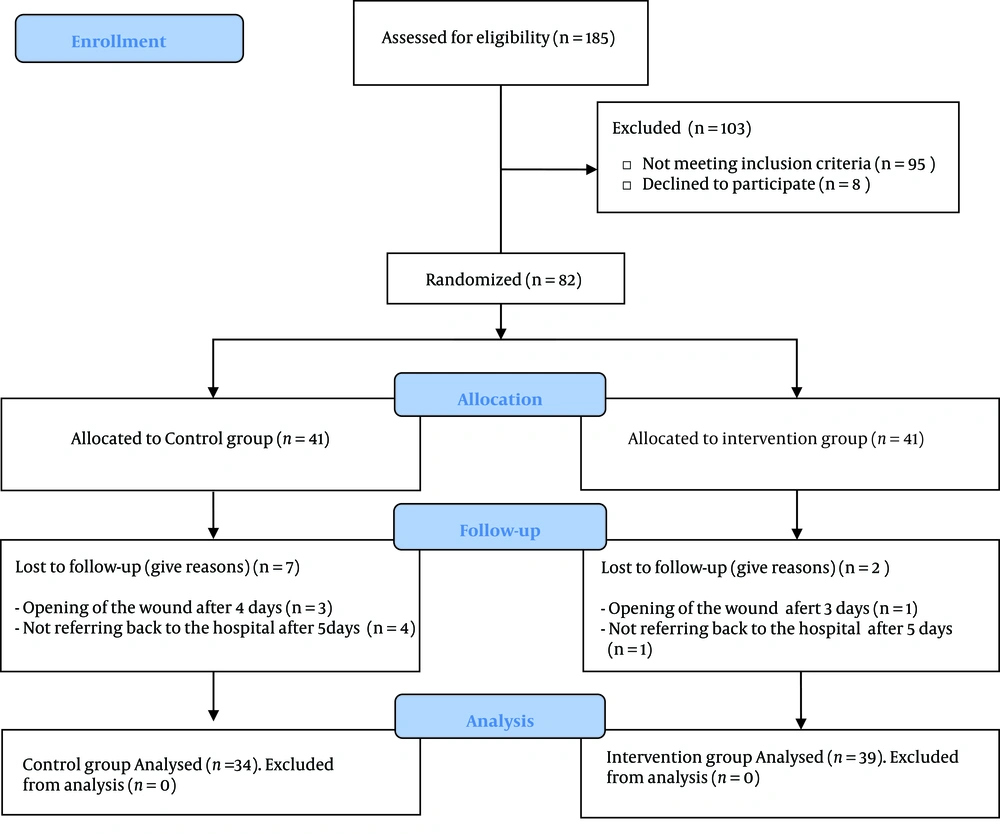
This study was extracted from a larger randomized, controlled clinical trial. Part of the data obtained for this research is reported in a published paper (39). Another part of the collected data aimed to examine the effect of Olea ointment on episiotomy wound healing has been reported in this present study. This research project included primiparous women who had normal vaginal delivery with episiotomy. According to Jahdi et al.'s (40) study, the sample size was estimated using the confidence interval of 95% and the test power of 90%. Accordingly, at least 36 women should have been allocated to each group; however, given the possibility of 15% dropouts, 41 women were assigned to each of the intervention and control groups. Accordingly, 82 primiparous women who met the inclusion criteria were selected using the purposive sampling method. Next, they were randomly divided into two groups [intervention (n = 41) and control (n = 41)] by drawing cards A or B. The required data was collected from December 2017 to May 2018. Inclusion criteria were as follows: Iranian nationality, primiparous, age between 18 - 35 years, reading and writing literacy, willingness to participate in the study, live term singleton pregnancy with vertex presentation, mediolateral episiotomy with no rupture, no chronic systemic diseases hindering wound healing (e.g., cardiac, renal, pulmonary, and coagulation disorders, diabetes, anemia, mental illness, and malnutrition), no history of previous injury, surgery, and visible lesions in perineum (genital warts, hemorrhoids), persistent constipation according to the patient's self-reports, no premature rupture of the membrane for more than 18 hours, duration of the first, second, and third stages of delivery < 14 hours, 2 hours, and half an hour respectively, no manual removal of placenta, no postpartum hemorrhage (PPH), no perineal hematoma, infant weight between 2500 - 4000 g, and non-hospitalization of newborn or neonatal anomalies. On the other hand, exclusion criteria were reluctance to further participate in the study, use of other supplements for wound healing during the study, incorrect usage of the ointment for more than two nights, sensitivity to the Olea ointment, failure to refer to the hospital on Days 5 and 10 postpartum, sexual contacts within the first five days postpartum, and the manipulation of perineum after wound healing. In general, nine women were excluded from the study (four women having approximation and five women not referring back to the center) (Figure 1).
The required data were collected using demographic forms addressing age, level of education, occupation, and income as well as reproductive information forms with items on gestational age, gravida, abortion rate, gender and weight of newborn, newborn head circumference, and duration of the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd delivery stages. Moreover, perineal healing was assessed using the REEDA scale, which dealt with redness, edema, ecchymosis, discharge, and approximation. The REEDA scale is an international instrument developed by Davidson in 1974 (41). The scale is scored based on the 4-point Likert, with a higher score indicating the presence of the concerned subscale. The minimum and maximum scores were 0 and 15, representing the degree of wound healing. In this scale, the scores 0, 1 - 5, 6 - 10, and 11 - 15 indicate complete, moderate, poor, and no wound healing, respectively. Sheikhan et al. and Pazandeh and Savadzadeh used this scale in their studies and confirmed its validity and reliability (42, 43). In this study, the face and content validity of the demographic, obstetrics, and delivery information forms were confirmed.
The data were extracted from interviews, patients' medical files, observation, and examination, with the direct participation of researchers. Both groups were trained on how to care for the perineal region and episiotomy, personal hygiene, nutrition, and physical mobility using the face-to-face method and pamphlets. Prior to the intervention, the wound status was assessed in terms of redness, edema, ecchymosis, discharge, and approximation in each group using the REEDA scale.
Olea ointments were ordered in 30 g tubes, containing the same portions of olive oil, Sesame oil, and honey from Farateb Yazd Company, Yazd, Iran, and were delivered via post. The first intervention was performed 4 hours post-episiotomy. The intervention group were asked to place ointment on the suture after washing and drying the perineum region and to cover it using a clean, sanitary pad after 1 - 2 minutes. They were also requested to repeat this procedure every other 8 hours until the Day 10 after childbirth. Note that the researchers did the first intervention, while the women themselves performed the next interventions.
Meanwhile, the women in the Olea ointment group were persuaded to use normal saline (twice per day until Day 10) to wash the perineal region accompanied by Olea at home. The second group received only routine hospital care as washing with normal saline twice per day until Day 10 postpartum. A bottle of normal saline 0.9% (1000 cc) and one tube of Olea ointment were used for each woman in the Olea group. The second group members also used a bottle of normal saline 0.9% (1000 cc). The researchers assessed the episiotomy status 2 and 24 hours after the first intervention and on Days 5 and 10 postpartum. If episiotomy was not healed, it was re-assessed by the researchers on Day 14 after childbirth. Furthermore, the patient were asked to contact the researchers in the case of any difficulties such as fever, chills, burning, itching, and allergy to Olea ointment, scarring, pain, and swelling in the wound area.
Statistical analysis was then performed using the SPSS software version 16. To this end, statistical tests (namely frequency, central indices, standard deviation, Mann-Whitney U test, Fisher’s exact test, independent-sample t-test, repeated-measure test, Friedman test, and chi-square) were used. P < 0.05 was also set as the significance level.
4. Results
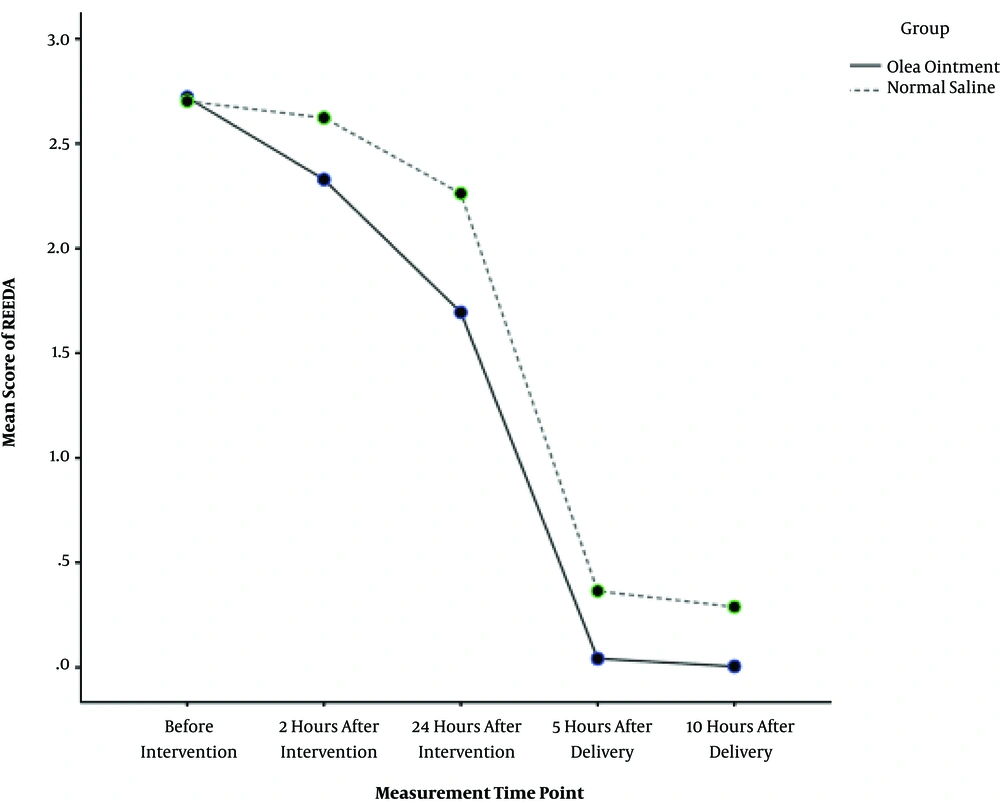
No statistically significant difference was observed between the two groups in terms of all demographic and obstetric characteristics (P > 0.05), except for the duration of the first stage of labor (U = 410.00, P = 0.005), The mean baseline (before intervention) REEDA scores were 2.72 ± 0.46 and 2.71 ± 0.46 in the Olea ointment and control groups, respectively. The episiotomy healing scores in the Olea ointment group were significantly lower than that of the control group at the four intervals of the follow-up assessments: -0.34 (95% CI: -0.56 to -0.12) 2 hours after intervention, -0.63 (95% CI: -0.89 to -0.37) 24 hours after intervention, -0.30 (95% CI: -0.48 to -0.12) on Day 5 postpartum, and -0.29 (95% CI: -0.46 to -0.13) on day 10 postpartum (Table 1). Regarding the repeated-measure test, the estimated marginal means of REEDA score in the Olea ointment group [1.36 (95% CI: 1.30 - 1.42)] was significantly lower than the score in the control group [1.65 (95% CI: 1.58 - 1.72)] (P < 0.001) (Figure 2). In other words, Olea ointment improved the episiotomy wound healing.
| Group | REEDA Scale (0 - 15) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Intervention | 2 Hours After Intervention | 24 Hours After Intervention | 5 Days After Delivery | 10 Days After Delivery | |
| Olea ointment | 2.72 (0.46) | 2.31 (0.47) | 1.67 (0.62) | 0.05 (0.22) | 0.00 (0.00) |
| Normal saline | 2.71 (0.46) | 2.65 (0.49) | 2.29 (0.46) | 0.35 (0.49) | 0.29 (0.46) |
| Mean difference (95% CI) b | 0.01 (-0.20 - 0.23) | -0.34 (-0.56 - -0.12) | -0.63 (-0.89 - -0.37) | -0.30 (-0.48 - -0.12) | -0.29 (-0.46 - -0.13) |
| P-value c | 0.91 | 0.004 | < 0.001 | 0.001 | < 0.001 |
Comparison of Wound Healing Status Between Groups at Different Intervalsa
Furthermore, there was no significant difference between the two groups at baseline (P > 0.05) and 2 h after intervention regarding all REEDA components, except for redness (P = 0.001). Further, there were significant differences between the two groups 24 h after the intervention regarding redness (P < 0.001), edema (P < 0.05), ecchymosis (P < 0.001), and discharge (P < 0.001). The two groups were not significantly different in terms of redness, ecchymosis, discharge, and approximation on Days 5 and 10 postpartum. However, this did not come true for edema on Days 5 and 10 postpartum (P < 0.001; P = 0.001, respectively).
5. Discussion
The present study was the first clinical trial conducted in Iran to investigate the effect of Olea ointment on episiotomy wound healing among primiparous women. According to the findings, Olea ointment has effects on episiotomy wound healing 2 and 24 hours after the first intervention and on Days 5 and 10 postpartum.
Imran et al. assessed the effect of honey on the treatment of diabetic foot ulcer using a randomized clinical trial with two groups and noticed that honey reduced the healing period of diabetic foot ulcer and was more effective in treating and healing the wound, as compared to the control group (44). In their study, Dubhashi et al. compared the effects of honey and phenytoin on the treatment of chronic ulcers. They claimed that honey and phenytoin were more effective in eliminating infection and pain in the experimental group, and honey was far more effective than phenytoin in relieving pain and reducing the ulcer odor (45).
Honey can positively affect wound healing because of its antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties (46, 47). The presence of large amounts of sugar in honey decreases the bacteria proliferation and growth by creating osmotic effects. The antioxidant properties of honey are also produced by compounds such as phenolic and gallic acid (46). In addition to the chemical properties of honey, its physical properties (namely low pH and high viscosity) also play a critical role in wound healing. Honey acts as an anti-inflammatory agent by decreasing the concentration of inflammatory cells in the wound and reducing edema. Furthermore, it enhances proliferation and tissue regeneration by increasing blood flow to the wound (46, 48, 49).
Behmanesh et al. compared the effects of perineal sitz bath using olive oil on improving postnatal perineal injury and reported that olive oil was more effective in improving episiotomy wound than distilled water (37). According to a study by Donato-Trancoso et al., who examined the impact of olive oil on rats with compression ulcers, olive oil was more effective in healing and treating rats with ulcers than the control group (26). The polyphenols in the olive oil bring it anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties and improve the wound healing process (50). Moreover, olive oil is effective in accelerating wound healing by improving blood flow to the wound site, reducing inflammation, and maintaining skin moisture (34, 48).
In a study comparing the effects of Sesame alcoholic extract on healing diabetic wounds in male Wistar rats, Sesame alcoholic extract accelerated the recovery of skin ulcers in the healthy and diabetic rats (51). As with honey and olive oil, Sesame oil has anti-inflammatory (52) and antioxidant (53) properties. Sesame oil lowers the inflammation rate by reducing inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-6, IL-1α, IL-1β, TNF-α) and reducing oxidative stress by modulating the activity of antioxidant enzymes (e.g., superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase, catalase, etc.) (54).
Olea ointment is a herbal product containing olive oil, honey, and Sesame oil; hence, it bears the positive effects of each of the ingredients and can be effective in improving wound healing. According to Zahmatkesh et al. (29), who evaluated the effect of Olea ointment and acetate mafenide on burn healing, Olea ointment was beneficial in the treatment of burns, prevented the onset of infection, accelerated the tissue repair, and facilitated wound healing (debridement). In contrast, Amani et al. compared the effect of topical olive oil and cold compress using Gel packs on episiotomy wound healing and reported no significant difference between the groups in terms of REEDA scale items within the first 12 hours after delivery and on Day 5 after delivery. Although episiotomy redness was less noticed in the olive oil group on Day 10, there was no difference between the groups regarding healing on Days 5 and 10 after delivery (23). Afshari et al. showed the superiority of Lavender to Sesame oil in burn wound healing. Furthermore, the Lavender composition in Sesame oil had an effect similar to the sulfadiazine ointment (36).
In this study, approximation was observed in three women in the control group and one of the participants in the Olea ointment group. This difference may be due to the positive effect of Olea ointment on wound healing. However, more clinical trials using a placebo are recommended.
One of the weaknesses in this study might be not using a placebo; hence, further similar clinical trials using a placebo are recommended. Moreover, it was not possible to blind the subjects and researchers in this study; however, the statistical analyst was blinded.
The present findings showed that the Olea ointment facilitated the episiotomy wound healing; however, further studies are required to support these data.