1. Background
Nociceptive, inflammatory, and neuropathic pain are among the many unpleasant sensory experiences associated with pain (1). Current analgesic medications have significant adverse effects, including gastrointestinal issues, emesis, tolerance, or addiction (1). Therefore, new medicines derived from plants, as a complementary or alternative approach, are needed to relieve pain and stress while reducing adverse effects. The hypothalamus, especially the lateral hypothalamus and periventricular nuclei, is considered an important central center for modulating pain. It is established that the hypothalamus receives inputs from multiple neural signaling pathways to integrate and coordinate the body’s response to pain. In fact, the induction and relief of pain somewhat depend on the release of several pain-related peptides from the hypothalamus. In response to pain, the hypothalamus activates the sympathetic nervous system, leading to the release of pain- and stress-related neuropeptides and hormones to modulate the perception and sensitivity of pain. Additionally, the hypothalamus is linked to brain regions involved in the descending pain modulation pathways, such as the periaqueductal gray (PAG), which can inhibit or facilitate pain signals traveling from the spinal cord to higher brain centers (2-4).
Phytoestrogens are natural compounds with a chemical structure similar to estrogen. Formononetin is an isoflavonoid found in many leguminous plants and red clover (5, 6). Previous studies have shown that formononetin exhibits significant estrogenic, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties, providing neuroprotection against oxidative stress and toxicity caused by hydrogen peroxide and L-glutamate (7-9). Another study demonstrated the pain-reducing effects of formononetin by reducing the levels of interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and preventing neuronal apoptosis by activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway (10). In a rat traumatic brain injury model, formononetin increased cortical proliferation and reduced serum IL-6 and TNF-α. Moreover, formononetin ameliorates neuroinflammation in LPS-stimulated microglia by significantly reducing the production of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. Another study shows that formononetin reduces hippocampal neuroinflammation and improves depressive-like behaviors in rats (11-13).
Orexin is coded by the hypocretin (HCRT) gene. Orexin-containing cell bodies are mainly located in the lateral hypothalamus; however, their axons are widespread throughout the central nervous system, highlighting their prevalence in the hypothalamus, other brain areas, and spinal cord (14). The physiological function of orexin in pain modulation has been confirmed by studying mechanical, chemical, and thermal-induced pain (15). Previous studies have shown that the activity of orexin neurons increases and that injection of orexin can alleviate pain in animal models of chronic neuropathic and inflammatory pain (16, 17). Additionally, previous studies demonstrated that orexin neurons of the lateral hypothalamus co-localize with substance P afferents of dorsal root ganglion neurons, further reinforcing its confirmed role in pain regulation (18).
Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), coded by the CRH gene, plays a key role in regulating the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis (19). Stress causes the hypothalamus to release CRH, which stimulates the anterior pituitary to release adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). Released CRH also accesses different parts of the central nervous system (CNS) and affects stress-related properties, including pain modulation (19). Based on previous findings, during the pain process, the CRH neurons of the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) of the hypothalamus are activated by pain-induced neurotransmitters such as glutamate, and their activation, in turn, modulates pain responses (20).
Melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH), coded by the MCH gene, acts as a neuromodulator or neurotransmitter to control a variety of physiological processes, including stress, pain, reward, feeding, and sleep (21). The lateral hypothalamus contains a large number of neurons that produce MCH (21). The results of Jang et al. showed that MCH plays an important role in pain modulation, and the administration of MCH showed analgesic effects in the hot plate test (22). Additionally, documented studies indicate that MCH neurons co-express glutamate and are activated by glutamatergic signals during pain induction (23, 24).
2. Objectives
Considering that the molecular mechanisms mediating the analgesic effects of formononetin are still unclear, the present study was conducted with the aim of evaluating the impacts of formononetin on hypothalamic CRH, HCRT, and MCH gene expression in a rat model of formalin-induced pain.
3. Methods
3.1. Animals
In this study, male rats (200 ± 10 g) were used to conduct research. The rats were kept in a controlled environment with a regular 12-hour light/12-hour dark cycle and a stable temperature (22 ± 2°C), and they had free access to food and water.
3.2. Stereotaxic Surgery
At the start of the test, rats were anesthetized by intraperitoneal administration of 10 mg/kg xylazine and 80 mg/kg ketamine. The cannula was placed in the third cerebral ventricle according to the stereotaxic coordinates of AP = 0.84 mm, ML = 0.0 mm, and DV = 6.5 mm (25). The animals were kept in individual cages for a one-week recovery period.
3.3. Experimental Design
The study involved twenty rats divided into four groups (n = 5): Groups 1 and 2 were the control and pain model groups, respectively, that received saline. Groups 3, 4, and 5 were the pain model rats that received 20 and 40 µg of formononetin and 20 µg of diclofenac, respectively (26). All injections were administered prior to the injection of formalin via the third cerebral ventricle in a volume of 3 µL. Thirty minutes following the drug administration, formalin (50 µL of 5%) was injected subcutaneously into the plantar surface of the hind paw. Behavioral tests were then performed to assess the pain responses. At the end of the experiment, the hypothalamus was separated and kept at -80°C until the mRNA level was checked. The mean relative gene expression of CRH, HCRT, and MCH was measured using the real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) method.
3.4. Behavioral Testing
Following the injection of formalin, the rats were immediately placed in a clear Plexiglas chamber (35 × 35 × 35 cm). The animals' behavior was observed using a 45° angle mirror. Four categories of behavior were described: Score 0, the time when the injected paw is completely on the ground; score 1, the time when a little weight is placed on the injected paw; score 2, the length of time the injected paw was elevated; score 3, the duration the injected paw was shaken, licked, or bitten. The duration of the test was 60 minutes, and 5-minute blocks of time were recorded for each type of activity. A pain score was then determined using the following formula (27).
A biphasic nociceptive response is induced by formalin injection. The first phase (0 - 5 minutes) is defined as the initial 5-minute block, and the second phase is longer, occurring between 15 and 60 minutes.
3.5. Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction
Based on the instructions of the kit, TRIzol reagent was used to extract total RNA from the hypothalamic samples. Complementary DNA (cDNA) was synthesized in accordance with the kit’s instructions (Biotech Rabbit, Germany). Using a SYBR Green I kit, RT-PCR was conducted based on the kit’s protocol (Takara, Japan). The PCR parameters were: 95°C for 15 minutes for one cycle, followed by 40 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 20 seconds, annealing at 60°C for 15 seconds, and extension at 72°C for 10 seconds. The sequences of primers are listed in Table 1. Using glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) as the reference gene, the equation 2-ΔΔC was used to determine any changes in the relative expression of the target genes (25, 28).
| Genes and Sequences of Primers | Amplified Product (bp) |
|---|---|
| CRH | 103 |
| 5′-TGGATCTCACCTTCCACCTTCTG-3′ | |
| 5′-CCGATAATCTCCATCAGTTTCCTG-3′ | |
| MCH | 195 |
| 5′-TCAGAAGGAAGATACCGCAGA-3′ | |
| 5′- ACTGCTGGTCCTTTCAGAGC-3′ | |
| HCRT | 87 |
| 5′-CTCCTTCAGGCCAACGGTAA-3′ | |
| 5′-AGGGCAGGGATATGGCTCTA-3′ | |
| GAPDH | 120 |
| 5′-AAGTTCAACGGCACAGTCAAG-3′ | |
| 5′-CATACTCAGCACCAGCATCAC-3′ |
Abbreviations: HCRT, hypocretin; CRH, corticotropin-releasing hormone; MCH, melanin-concentrating hormone; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
3.6. Statistical Analysis
The research utilized SPSS software for data analysis, presenting results as mean ± SEM, with significance set at P ≤ 0.05. For analyzing the data related to the behavioral results and gene expression levels of CRH, HCRT, and MCH, separate one-way ANOVA tests were used. To determine significant comparisons between groups, Tukey's post hoc test was performed following each one-way ANOVA test.
4. Results
4.1. Effects of Formononetin on Behavioral Tests
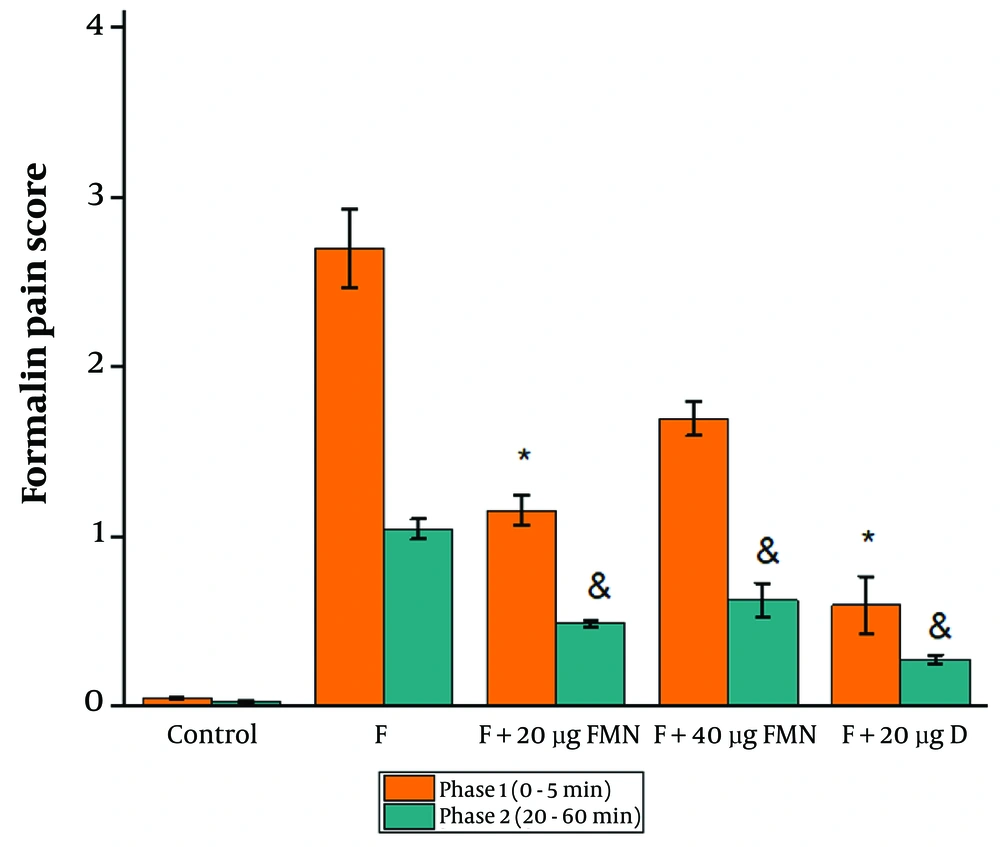
Based on the analysis of the behavioral test data, 20 µg of formononetin caused a significant decrease in the pain score of both phases 1 and 2 compared to the control (Figure 1, P ≤ 0.05). Injection of 40 µg of formononetin remarkably reduced the pain score compared to the control group only in phase 2 (Figure 1, P ≤ 0.05). The pain score in the group receiving 20 µg of diclofenac significantly decreased compared to the formalin group in phases 1 and 2 (Figure 1, P ≤ 0.05).
4.2. Effects of Formononetin on the Hypothalamic mRNA Levels of Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone, Melanin-Concentrating Hormone and Hypocretin
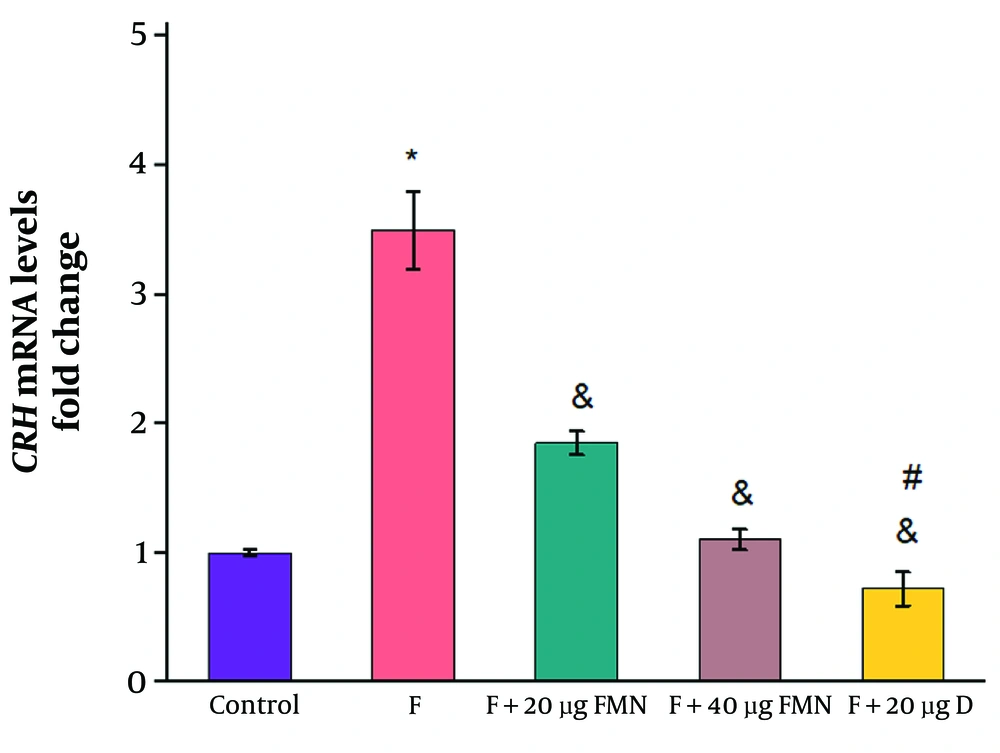
The relative gene expression of CRH in the formalin-induced rats was significantly increased compared to the control group receiving saline (control: 1 ± 0.026; formalin group: 3.5 ± 0.3) (Figure 2, P ≤ 0.05). Administration of 20 and 40 µg of formononetin significantly reduced the mRNA levels of CRH compared to the formalin group (20 µg formononetin group: 1.85 ± 0.09; 40 µg formononetin group: 1.1 ± 0.08) (Figure 3, P ≤ 0.05). Injection of 20 µg of diclofenac significantly reduced the mRNA levels of CRH compared to the formalin group (diclofenac group: 0.72 ± 0.13; control: 1 ± 0.023; formalin group: 3.5 ± 0.3) (Figure 3, P ≤ 0.05).
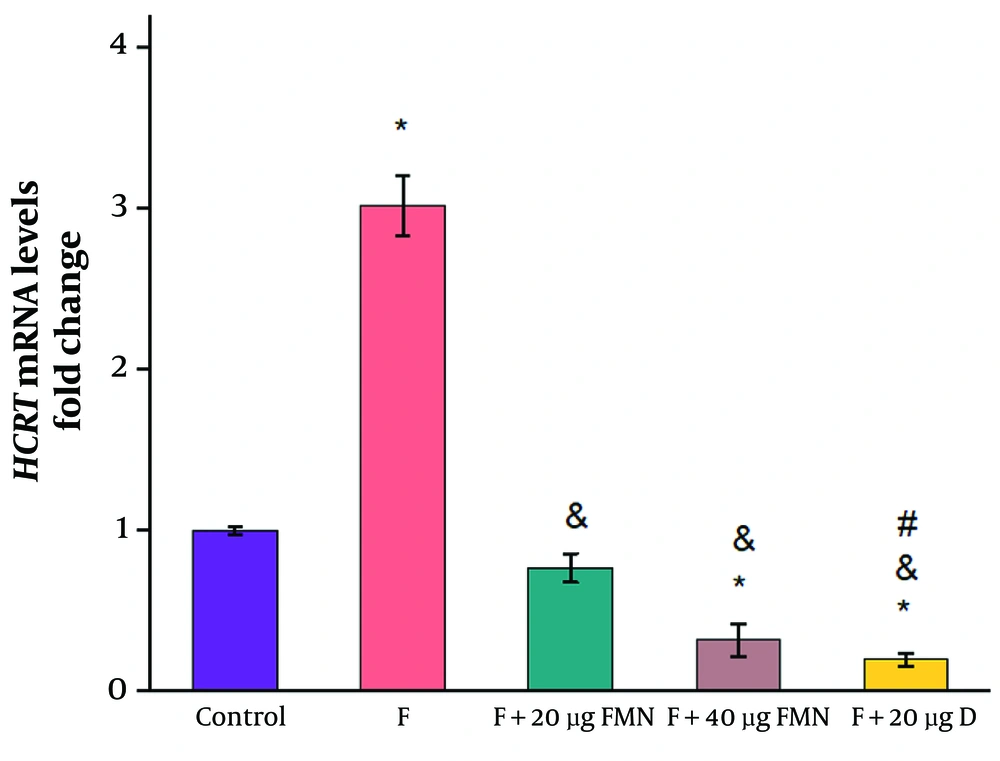
When compared to the control group receiving saline, the formalin-induced pain model exhibited a substantial increase in HCRT gene expression (control: 1 ± 0.023; formalin group: 3.02 ± 0.19) (Figure 2, P ≤ 0.05). The mean relative gene expression of HCRT was significantly lower in both groups receiving 20 and 40 µg of formononetin than in the formalin group (20 µg formononetin group: 0.77 ± 0.089; 40 µg formononetin group: 0.32 ± 0.1) (Figure 4, P ≤ 0.05). Injection of 20 µg of diclofenac significantly reduced the mRNA levels of HCRT compared to the control and formalin groups (diclofenac group: 0.2 ± 0.04; control: 1 ± 0.023; formalin group: 3.5 ± 0.3) (Figure 4, P ≤ 0.05).
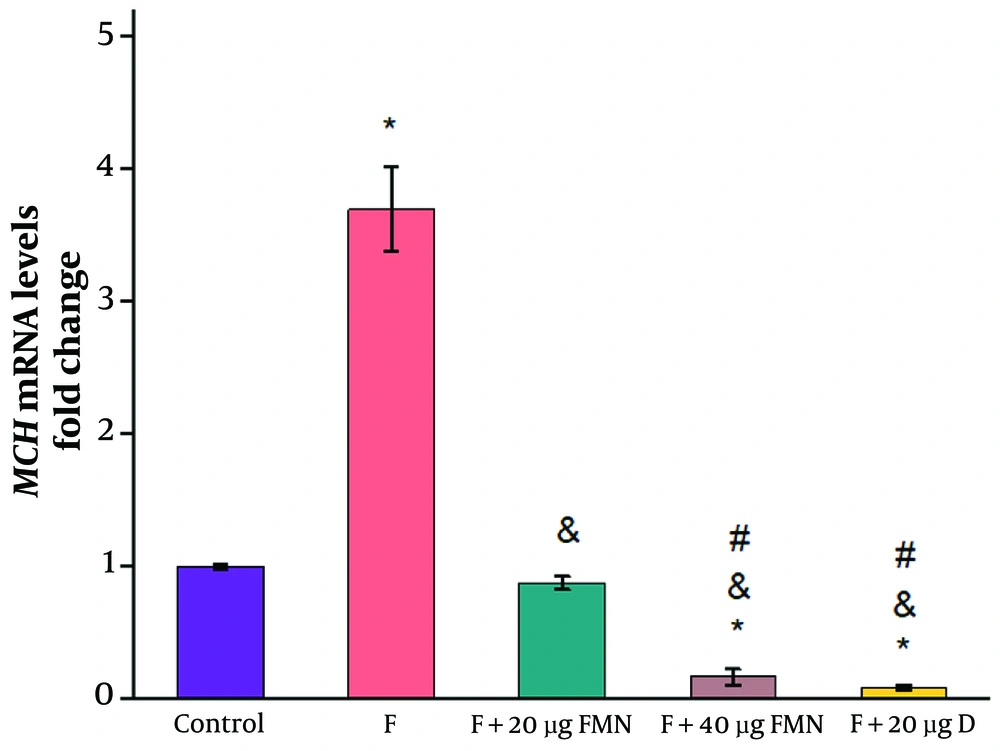
In comparison to the control group receiving saline, the formalin-induced pain model group exhibited a considerable increase in MCH gene expression (control: 1 ± 0.02; formalin group: 3.7 ± 0.32) (Figure 2, P ≤ 0.05). The MCH gene expression was substantially lower in the groups receiving 20 and 40 µg of formononetin than in the formalin group (20 µg formononetin group: 0.88 ± 0.05; 40 µg formononetin group: 0.17 ± 0.06) (Figure 2, P ≤ 0.05). Additionally, a remarkable decrease was observed between the effects of 20 and 40 µg of formononetin (Figure 2, P ≤ 0.05). Injection of 20 µg of diclofenac significantly reduced the mRNA levels of MCH compared to the formalin group (diclofenac group: 0.086 ± 0.018; control: 1 ± 0.023; formalin group: 3.5 ± 0.3) (Figure 2, P ≤ 0.05).
5. Discussion
The results of the behavioral tests indicated that both the first and second phases of the formalin test's response were suppressed by the injection of formononetin. These findings suggest that formononetin may operate centrally and peripherally to inhibit nociception. The anti-inflammatory properties of formononetin may somewhat explain its effect in the second phase of the formalin-induced pain test. As previously documented, formononetin effectively improves formalin-induced inflammatory edema by decreasing the levels of inflammatory markers such as TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and blocking the nuclear factor NF-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway, which are involved in the induction of inflammation (8, 12). In fact, the present data align with previous findings that confirmed the analgesic effects of formononetin (8, 9).
Additionally, the analgesic effect of formononetin is similar to that of other phytoestrogens such as genistein, daidzein, and resveratrol. Genistein reduces neuropathic pain caused by peripheral nerve damage. Daidzein reduced neuropathic pain sensitivity, and its administration led to the inhibition of neuroinflammation through increasing antioxidant enzymes and reducing oxidative stress markers. Resveratrol acts on various pathways related to pain perception and transmission, such as suppressing inflammatory mediator production through inhibiting NF-κB, as well as inhibiting cyclooxygenase enzymes (29-31). In the hot plate test and in the glutamate-induced pain model, formononetin exerted antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects (8, 9). Red clover has also been demonstrated to decrease pro-inflammatory cytokines, which in turn inhibits the production of inflammatory enzymes such as cyclooxygenase 2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) (32).
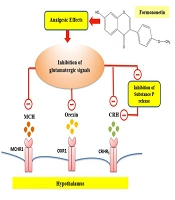
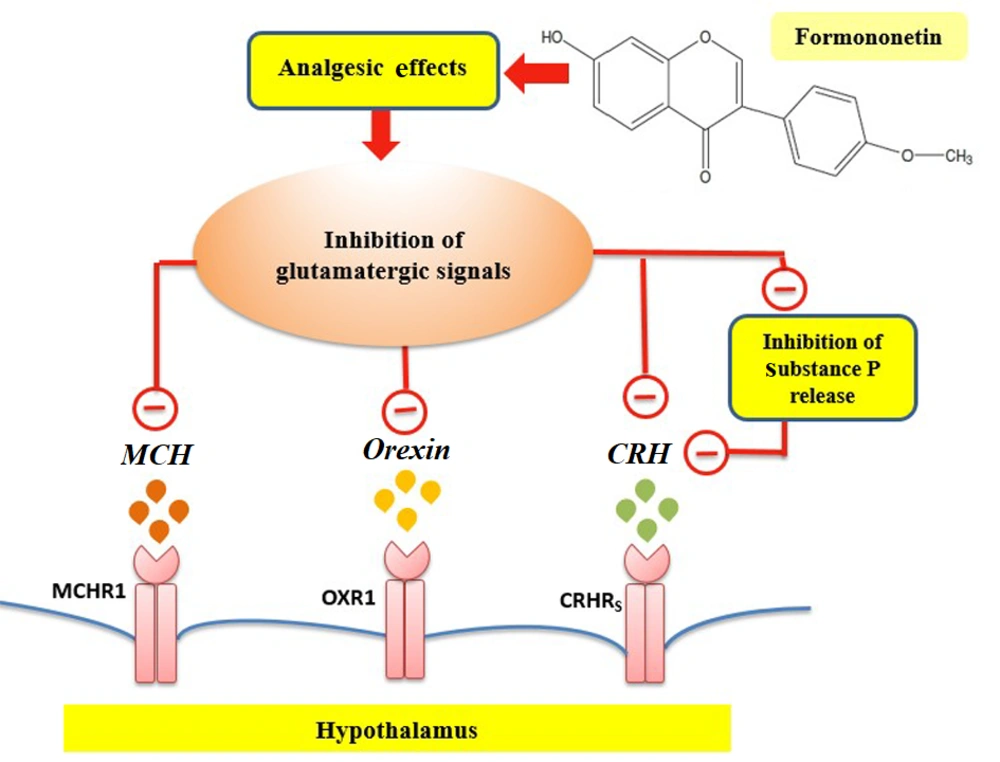
To elucidate some molecular mechanisms for the analgesic impacts of formononetin, this work aimed to determine the changes in mRNA levels of CRH, HCRT, and MCH. The results demonstrated that pain stimulates the gene expression of HCRT in the hypothalamus. Orexin, produced mainly by the lateral hypothalamus, plays a role in crucial body functions such as reproduction, stress response, and pain regulation (14, 17). Central administration of orexin reduced nociceptive responses in a mouse pain model, suggesting that orexin neurons may play a significant role in pain modulation due to their extensive innervation of brain regions involved in nociception (15, 17). Inputs from GABAergic and glutamatergic neurons of the lateral hypothalamus regulate orexin activity (33). Formononetin has been proven to have a regulatory effect on the glutamatergic system (34, 35). A previous study highlights glutamate's role as a primary excitatory neurotransmitter in the hypothalamus, particularly influencing orexin neurons. Glutamate could impact orexin neuron activities via NMDA and non-NMDA receptors (36). Additionally, synaptic connections of glutamatergic axon terminals were documented on orexin neurons (36). On the other hand, formononetin is able to protect neurons against glutamate-induced excitotoxic damage (34). Thus, formononetin may participate in the downregulation of HCRT gene expression due to its anti-glutamatergic impacts (Figure 5).
The present findings indicated that CRH gene expression was elevated in the formalin-treated animals. Based on previous reports, the induction of pain is shown to increase CRH release in the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) of the hypothalamus (20). As previously established, glutamate activates CRH neurons and increases pain responses (37, 38). Previous studies showed that formononetin is involved in protecting against the impacts of glutamate (34).
Formononetin may reduce CRH via affecting the activity of the glutamatergic signaling pathway on CRH neurons. It has been established that CRH mRNA levels in the hypothalamus and hippocampus are increased by various types of pain stimuli, such as the injection of formalin, acetic acid, or substance P in mice (20). Substance P and other members of the tachykinin family are found together with glutamate in primary afferent fibers (38). Substance P, released along with glutamate, plays a key role in pain conduction (38). Formononetin has estrogenic properties, and studies have shown a strong reduction of substance P and its mRNA in estrogen-treated animals (39). Therefore, formononetin may downregulate CRH gene expression by regulating substance P (Figure 5).
Formononetin may also downregulate CRH gene expression via interaction with the GABAergic system. Inputs from GABAergic neurons in the lateral hypothalamus regulate CRH activity through an inhibitory mechanism. A previous study showed that Cajanus cajan, one of whose main derivatives is formononetin, activates the GABAA receptors. Thus, the downregulation of the CRH gene by formononetin may be somewhat due to its influence on GABAergic neural pathways, which in turn affects the activity of the CRH neurons (40, 41).
In formalin-induced pain, the mRNA levels of MCH increased compared to the control group. The hypothalamic neuropeptide MCH has analgesic effects, and this fact was confirmed using an MCH receptor type 1 (MCHR1) antagonist (22). Previous studies have shown that estradiol decreases MCH synthesis (42). Melanin-concentrating hormone neurons are located in the lateral hypothalamus, and estrogen receptors (ERs) are expressed at high levels in this area (43). Estrogen receptors are also present in many areas of the brain where MCHR1 is found (43). Thus, estradiol may act locally to reduce MCH neuron activity in this brain area (42, 44).
Formononetin's antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and estrogenic properties stand out among its effects (7, 9, 10). Studies have shown that formononetin has a serotonergic regulatory role (6). The serotonergic system plays a role in modulating pain and can exert an inhibitory effect on the nervous system involved in pain-related behaviors (23). Therefore, it is possible that formononetin, with its serotonergic regulatory role and ability to bind to both ERα and ERβ subtypes, mediates the reduction of MCH mRNA levels in the pain model of rats. Additionally, documented studies indicate that MCH neurons co-express glutamate and are activated by glutamatergic signals (23, 24). Formononetin may somewhat inhibit hypothalamic MCH gene expression due to its anti-glutamatergic action (Figure 5).
Reducing the activity of the adrenergic signaling pathway may be another proposed mechanism for formononetin to decrease hypothalamic CRH and HCRT gene expression. A previous study demonstrated that formononetin reduces the expression of α1-adrenoceptors. It has also been established that α1-adrenoceptor expression increases on orexin and CRH neurons during painful conditions, activating the CRH and orexin neural signaling pathways. Therefore, the inhibitory effects of formononetin on the adrenergic pathway may be a possible mechanism in the downregulation of CRH and HCRT gene expression to reduce pain (15, 20, 45-49).
5.1. Conclusions
The present study demonstrates the analgesic potential of formononetin in formalin-induced pain through modulating mRNA levels of hypothalamic HCRT, CRH, and MCH. The estrogenic effects of formononetin may be involved in the downregulation of intrahypothalamic neuropeptide signaling pathways upstream of CRH neurons to relieve pain. One important limitation of the present study was the inability to use the Western blot technique to detect protein levels in samples. Additionally, in the present study, diclofenac, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, was used as a positive control to compare the pain-relieving effects of formononetin. The lack of using other analgesic drugs may be a limitation, and it is suggested that further studies aim to compare the pain-relieving effects of formononetin with analgesic drugs such as morphine, codeine, ibuprofen, naproxen, and pethidine.
Further studies are needed to investigate the precise analgesic mechanisms of formononetin by determining the mRNA and protein levels of other nociception-related neuropeptides such as substance P and dynorphin in the hypothalamus and spinal cord. To identify neural signaling pathways through which formononetin may exert inhibitory effects on HCRT, CRH, MCH, and other neuropeptides, it is strongly suggested that future research aim to study the analgesic effects of formononetin using antagonists of glutamatergic, opioid, noradrenergic, and GABAergic receptors in pain models. Additionally, the results of the present trial warrant further dose-response studies in humans and different animal pain models, such as fibromyalgia, inflammatory pain, spinal pain, and sciatica, to ensure the analgesic effects of formononetin without serious harmful consequences.