1. Background
Control of pain in a successful treatment is an important point and requires careful consideration of appropriate dosage, type of medication and cognitive disease (1). Using opioids to control pain in acute conditions is different with chronic conditions. In these cases, other factors must be considered, particularly the rate of tolerance and physical dependence (2).
Methadone hydrochloride (synthetic derivative of diphenyl heptane) is an opioid analgesic used for moderate to light pain and detoxification and maintenance treatment of addiction to opioid (3). Methadone is similar to morphine, but its effect is somewhat longer than morphine. At least its potency and efficiency is equal to morphine. Methadone is effective via orally consumption and drug tolerance and physical dependence is slower than morphine. Symptoms of drug withdrawal after abrupt discontinuation of methadone are milder but longer than morphine. These characteristics made methadone as a medication for detoxification and maintenance treatment of chronic addiction to heroin (4). Methadone is a part of admitted program of FDA to detoxification, which acts through binding to opioid receptors in CNS and inhibition of pain pathway and general CNS depression (3). Methadone clearance is increased in pregnant women and its half-life is decreased in the third trimester of pregnancy. Therefore, to achieve an effective result, its dosage should be increased and frequency of dosages should be reduced. Detoxification by methadone is performed long-term and short-term and alcohol, benzodiazepines and medications for HIV or hepatitis can be used concomitantly (5).
With chronic exposure to some physical, chemical or biological conditions, mutation probability can be increased by several times. These include medicines that can damage the DNA of cells (6). Using some compounds in a long-term (7) or simultaneous usage of some medications may produce metabolites able to cause mutation. Results regarding methadone genotoxicity are controversial and need a comprehensive evaluation to obtain unequivocal conclusions. Brambilla and colleagues in 2009 studied the effects of genetic toxicity and carcinogenicity of 120 analgesics, anti-inflammatory and anti-pyretic. Due to long-term use of methadone and higher risk of side effects, it was selected for evaluation and finally positive results were demonstrated in three assays as below:
Gene mutation, mouse lymphoma L5178Y cell, Tk locus
Chromosomal aberrations, mammalian spermatogonia in vivo
Dominant lethal test, mice (7).
Gorazd et al. studied genetic toxicity of methadone in 23 patients recovering methadone maintenance therapy. Lymphocytes of two control groups were exposed to known mutagenic agents. Higher proportion of cells with elevated numbers of chromatid exchanges demonstrated methadone genotoxicity (8). In another study, Skowronska et al. evaluated genotoxic effect of methadone on peripheral blood lymphocytes of 12 addict patients; sampling was performed during and at beginning of maintenance therapy (9). Surprisingly, DNA breaks and damages were reported to be reduced in methadone treated groups. Same results were reported by Zimmering et al. and Badr et al., using drosophila melanogaster and dominant lethal mutation consecutively (10, 11).
Apoptotic effects of methadone may directly or indirectly contribute to its proposed DNA toxic effects. In this regard, Friesen and colleagues found that methadone is a potent inducer of programmed cell death in leukemic cells and Non-leukemic lymphocytes. Methadone treatment resides and resistance to chemotherapy decreased (12).
2. Objectives
Given controversial results regarding methadone genotoxicity, we investigated the effect of methadone genotoxicity. Altogether, research on mutagenesis of methadone may uncover its potential adverse effects contributing to overall health of patients.
3. Patients and Methods
HEPES, Na2HPO4 and Disodium EDTA were obtained from Sigma (USA), C15H28NO3Na, Tris Hydrochloride and Triton x-100 from Merck (Germany), LMPA and Agarose normal from Fermentas (EU) and Methadone from Exir (Tehran, Iran).
3.1. Patients and Healthy Subjects
This study was performed to evaluate mutagenic effect of methadone in addicted patients referred to Imam Khomeini Hospital in Ahvaz. Total samples of 90 subjects were divided into dichromate treated group, no treated healthy volunteers group and test group. Each group included 30 subjects as follows:
No treated healthy volunteers group: normal subjects without any history of opioid consumption in the last six months. All individuals filled a detailed questionnaire according to the published protocol by the International Commission for Protection against Environmental Mutagens and Carcinogens.
Dichromate treated group: 500 μM of dichromate was added to samples as a positive agent for induction of DNA breakage (13).
Test group: all 30 subjects in this group met the inclusion criteria.
Inclusion criteria were methadone use 60 to 120 mg daily, age of 18 to 65 years, minimum period of three years for methadone consumption and IQ above 75 (10, 11). Consents were obtained from all subjects participated in this study according to university Ethics Committee.
Exclusion criteria were use of any medicines such as benzodiazepines, amphetamine derivatives, antipsychotics, mood stabilizers, use of substances such as marijuana, crack, opiates, tramadol, mental disorders (personality disorders, mood disorders, anxiety disorders, psychoses), organic disease and positive results for HIV Ab , HCV Ab or HBS Ag (7, 10, 11).
3.2. Isolation of Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes
Two milliliters of peripheral blood were collected from each patient in heparinized tubes. Whole blood with Hank's solution was diluted to a ratio of 1 to 2.5 mL of sterile Ficoll solution (in the dark and temperature of 2-8°C), added to a centrifuge tube and diluted blood poured slowly to form a layer on top of the tube. The tubes were centrifuged for 20 minutes 1000 rpm (at this stage centrifugal brake or stopping using hand was avoided). After centrifugation, mononuclear cells (including lymphocytes) settle as a white layer between Ficoll and plasma. Lymphocytes were collected using pipette and transferred to another tube. The tube was filled with Hank's solution and centrifuged at 440 rpm for 10 minutes. The supernatant discarded, deposited again on Hank's solution added and mixed gently and centrifuged again for 15 minutes at 230 rpm. Besides, washing repeated with 110 rpm again. At this point, fully isolated lymphocytes achieved (14).
3.3. Comet Assay
Afterwards, 100 µL of cell suspension premixed with low melting point agarose (LMA 1%) poured on a slide coated with normal melting point agarose (NMA 1%) and covered with cover slips. Slides were kept for 15 to 20 minutes horizontally in the ice tray to solidify. Next, the cover slips were removed from the slides and placed in a lysis solution (14.61 g NaCl, 3.72 g EDTA, 0.125 g Tris ,0.9 g NaOH , 1 g sodium lauryl sarcosinate %1, DMSO 10% , Triton x-100 1% and pH = 10) for one hour and then washed by deionized water, kept for 20 minutes in electrophoresis buffer (NaOH 12 g, EDTA 372.0 g, dH2O to 1000 mL and pH = 13) and electrophoresed at 25 V and 300 mA for 20 minutes and then washed with neutralized buffer (Tris 1.12 g, dH2O to 250 mL and pH = 7.5) for five minutes three times. Slides were immersed in ethidium bromide solution for five minutes and according to the method described by Speit and Hartmann (15), which is based on the original work of Singh et al. (16), slides were analyzed by fluorescence microscope. The extent and distribution of DNA damage indicated by comet assay was evaluated by examining cells. The cells were visually scored into comet classes according to tail size class (17-19): 0 = no tail, 1 = tail shorter than the diameter of the head (nucleus), 2 = tail length 1 to 2x the diameter of the head and score 3 = tail longer than 2x the diameter of the head. Comet without head and those with nearly all the DNA in the tail or with a very wide tail were excluded from the evaluation, because they probably represented dead cells (20, 21). Tail length and the mutagenic index were calculated according the following formula MI = (0 NMC+ 1 SMC+ 2 MMC+ 3 LMC)/200, or we could express it as NMC = No migration cells (score 0), SMC = Short migration cells (score 1) MMC = Medium migration cells (score 2), LMC = Long migration cells (score 3) (22).
3.4. Statistical Analysis
Using SPSS software, Chi-square was performed to compare the groups.
4. Results
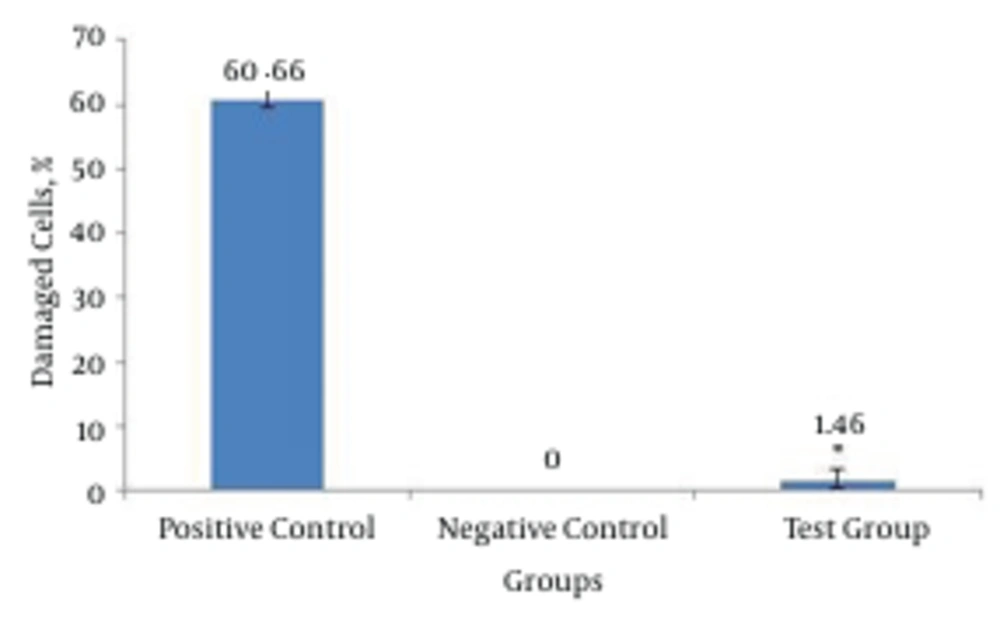
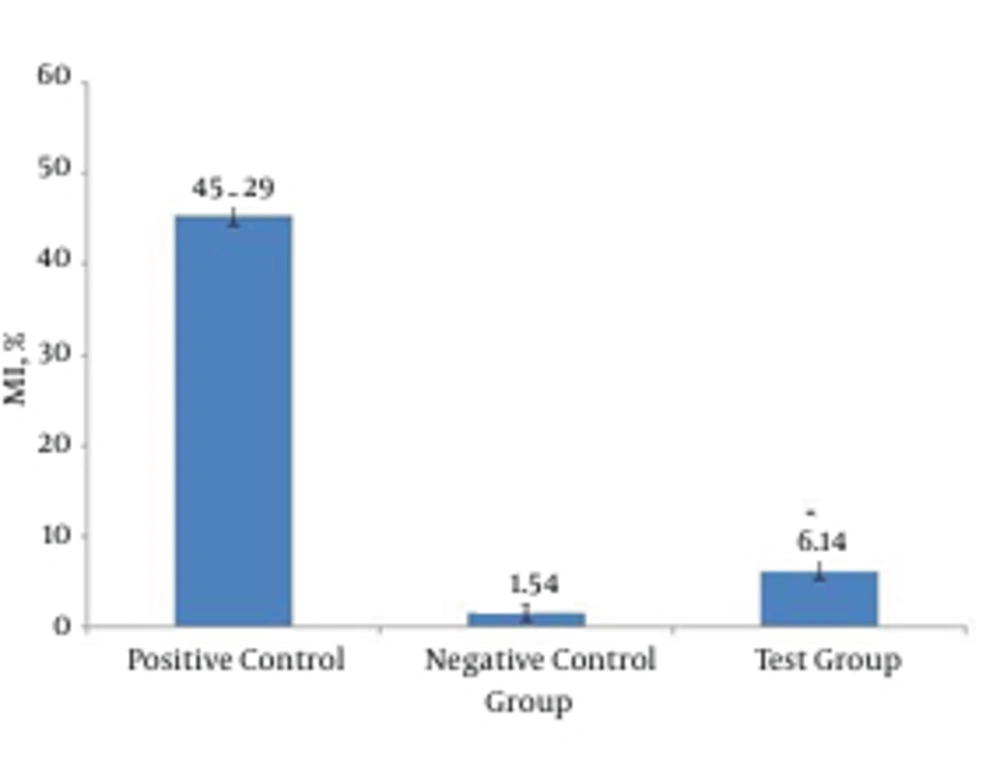
Peripheral blood was collected from 30 addicted patients screened to be exclusively on methadone and lymphocytes were separated to assess the genotoxicity by the comet assay. Percent of mutagenicity index (MI) was significantly lower in the test group compared to positive control and conversely, it was higher compared to the negative control group. Addicted patients showed more than two fold MI% compared to negative control or normal samples. Damaged cells in the test group were significantly higher compared to negative control. Altogether, instability of genome was demonstrated for addicted patients according to scores obtained for damaged cells.
5. Discussion
Brambilla et al. studied the carcinogenic effects of 120 different drugs including analgesics, anti-inflammatory and antipyretics. Methadone, because of its predominant and long-term use for treating severe pain, and its possible side effects was investigated. Results were deemed positive in the following three areas: gene mutation, chromosomal aberrations and dominant lethal test in mice (7).
Gorazd and Kamenczak studied genetic toxicity of methadone in lymphocytes cultures of 34 patients treated with methadone. Micronuclei occurrences along with number of chromatids’ changes taking place in the metaphase indicate genetic mutation. Two control groups with elements of genetic mutation were used. Increased ratio of number of cells to immense chromatid changes are indicators of genetic toxicity of methadone, although these changes are not so apparent in other groups facing mutagen (8). As indicated by these studies, genetic mutation in patients treated with methadone is controversial and therefore in this study we investigated its possible genotoxic effect. Lowest concentration of sodium dichromate, which causes a break in DNA strand is 50 µM, correlating to the dosage can increase to its maximum amount of 500 µM. higher concentrations of dichromate would cause the curve of DNA strand breaks vs. dichromate concentrations to turn into plateau. The reason for this phenomenon could be cross binding of DNA-DNA and protein-DNA, which would prevent DNA migration or could be saturation of activation paths to dichromate (like decrease in GSH) or even modifications in improved mechanism of DNA. Therefore, sodium dichromate in 500 µM concentration can be used as a positive control for comparison or revealing other unknown mutating agents (13).
Hodges et al. studied sodium dichromate’s abilities in breaking DNA chains in three different kinds of cells: human blood cells, separated lymphocyte and cultures of A549 cells of lung’s epithelial tissue. In the experiment using comet assay, increasing concentrations (10 µM, 50 and 500) had a correlating effect in breaking the number of DNA strands (23). Percentages of healthy and mutated cells (in pattern of comet) for the experimental group were determined and compared to percentage of health and mutated cells in the control groups (Figure 1). Figure 2 demonstrated the rate of mutation of experimental group and control groups, rate of mutation of experimental group compared to control group is deemed negative. There is a significant difference between the two groups. This can be an indication of instability of genome in patients participating in the experiment, compared to control group regarding scores in the experiment.
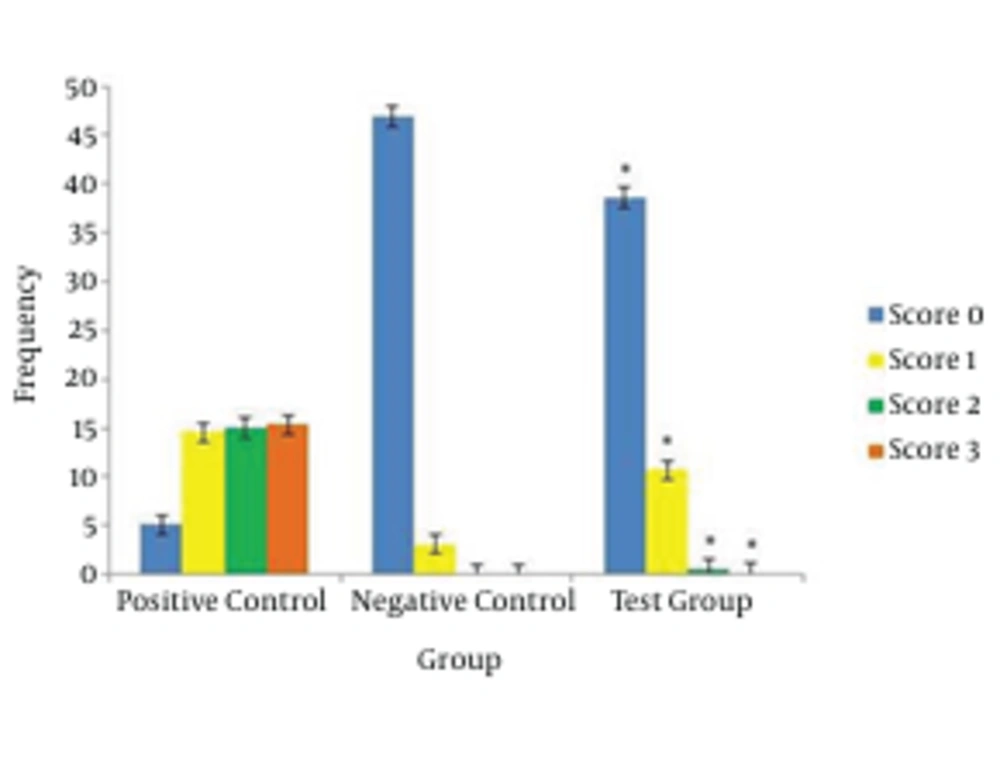
Figure 2 compares percentage of comet mass patterns between the experimental and control groups. In the control groups, zero scores were most prevalent and score ones were next in the numbers. In the experimental groups, scores of 1 and 3 reduced respectively. There are no 2 and 3 scores in the negative control groups. Although, there were 2 and 3 scores in the experimental group, and there was a significant statistical difference with these scores in the negative control group, this difference could indicate instability in the genome of experimental group compared to the negative control group.
In Figure 3, percentage of comet mass patterns between the experimental and control groups were compared. Zero scores in the experimental group were less compared to negative control group, which showed a meaningful difference. On the other hand, scores of 1, 2 and 3 in the experimental group increased compared to negative control group and the two had a meaningful difference regarding 1, 2 and 3 scores with each other. Increased 2 and 3 scores indicates instability in genome of experimental group compared to negative control group.
In Figure 1, percentage of mutated cells in the experimental group and control groups were compared. Mutated cells are sum of cells with 2 and 3 for a score. Percentage of experimental groups’ mutated cells increased compared to control group, and showed a significant difference. This difference could be an indication of less stability of genome of experimental group patients compared to negative control group. Perez-Alvarez and Cuenca-Lopez observed that high concentrations of methadone are needed to induce death in SH-SY5Y cells. Methadone leads to a kind of cellular death and has greater similarity to necrosis than apoptosis. Cell cultures show a change in outer mitochondria membrane potential and it has been compromised and penetrable. No engagement was observed by controlling proteins of apoptosis such as BCL-XL and p53 in this process. This study showed that a reduction in cell energy level would result in cell necrosis (24).
Garcia-Fuster et al. studied external and internal apoptosis pathways in prefrontal cortex of persons using methadone and heroin. Their findings showed that in such individuals these pathways were not activated in an abnormal manner. Instead, slowing or continuous manipulation of some parts of these pathways (downregulation cytochrome C and upregulation BCL-21) induces anti apoptosis activity (25).
Friesen et al. indicated methadone as a strong inducer of death in leukemia cells. Methadone controls the proliferation of leukemia cells and induces apoptosis in them. Contrary to leukemia cells, non-leukemic lymphomas after treatment with methadone remain healthy and alive. The study showed that methadone kills leukemia cells and eliminates resistance to chemotherapy and apoptosis (12).
There was a significant difference between mutation indicators of the experimental and negative control groups (P < 0.0001). Individuals who used methadone during this study had a less stable lymphoma genome compared to healthy individuals. Although on this subject and the reasons for instability of genome, study showed conflicting results, but continuous manipulation of immune system via methadone can induce or modify cellular death. Proving genotoxic effects of methadone requires further studies for a longer time of usage. To get more conclusive findings from this and previous studies, it is necessary to:
- Perform an extensive review of methadone usage periods and its effects on genome and cellular deaths.
- Conduct studies reviewing methadone usage and its relation to autoimmune diseases and allergies.
- More detailed review of reasons for instability of genome by methadone as means of new clinical targets.