1. Background
The genus Tanacetum L. (Asteraceae family) has 26 annual herbaceous plants in Iran (1). The Tanacetum species is a group of plants with a long tradition of being used as preservatives and herbal drugs (2). In traditional medicine, these plants are used for the treatment of fever, inflammation, women’s conditions such as dysmenorrhea and facilitating delivery, psoriasis, toothache, and stomachache (3). Tanacetum persicum (Boiss.) Mozaff., which is endemic to Iran, has not been studied well thus far.
Different research resources showed that only one study has identified the chemical composition of the aerial part essential oil of T. persicum (Dehdez, Province of Khuzestan, Iran) (4). Borneol (24.3%), menthyl acetate (17.3%), isobornyl 2-methyl butyrate (16%), and artedouglasia oxide D (14.3%) were the main components of the essential oil of T. persicum.
2. Objectives
In this study, we evaluated the antibacterial property of the essential oil of T. persicum (Boiss.) Mozaff. against three important pathogenic bacteria, namely, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella enterica, and Helicobacter pylori. The antioxidant activity of the essential oil of T. persicum was screened against ABTS free radicals.
3. Methods
3.1. Plant Material
The aerial parts of T. persicum were collected from Chahar-Va-Mahal Bakhtiari Province, Iran, in June 2015. Voucher specimens were deposited at the herbarium center of Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran.
3.2. Essential Oil Extraction and Chemical Composition Determination by Gas Chromatography (GC) and Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectroscopy (GC-MS) Analysis
The essential oil from air-dried aerial parts of T. persicum was obtained by hydro distillation using a Clevenger-type apparatus for 3 hours. The essential oil was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate.
The essential oil underwent GC analysis using Agilent 5975 C technology (HP-5 MS) with a capillary column of HP-1MS (30 m × 0.25 mm, film thickness 0.25 µm) and GC-MS analysis using Agilent technology (HP) 6890 coupled with a 5975 network mass selective detector system. The oven temperature program was initiated at 60°C, held for 1 minute and increased to 280°C at a rate of 3°C/min, and then held for 10 minutes. Helium was used as the carrier gas at a flow rate of 1.0 ml/min with a split ratio equal to 1/50 injector. The detector and injector temperatures were 250°C and 230°C, respectively. Components of the essential oil were identified by comparison with Retention Indices (RI) relative to the homologous series of n-alkanes, and the results were determined using the libraries of Wiley 275.L and Wiley 7n.1 (5).
3.3. Microbial Strains and Antimicrobial Activity Evaluation
S. enterica BAA-708, H. pylori ATCC 26695, and S. aureus ATCC 25923 were used in this study. The bacteria were cultured on suitable agar mediums and incubated at 30°C - 35°C in suitable conditions separately. The turbidity of each bacterium was adjusted to 0.5 McFarland by Spectrophotometer instruments (1 × 108 CFU/ml) by inoculating one or two colonies of each strain into normal saline solution.
The antibacterial activity of the essential oil was evaluated by two different methods, namely, disc diffusion and micro-broth dilution assays.
In the disc diffusion method, the inhibition zone diameters (mm) of the essential oil against bacteria were determined by inoculating the above microbial strains (1 × 108 CFU/ml) into the agar media culture by sterile cotton swabs. Sterile disks containing 5 µl of essential oil were placed on these inoculated plates and then incubated. The inhibition zone diameters were measured and reported as means ± standard deviation (6).
The minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimal bactericidal concentration (MBC) values of the essential oil in the micro-broth dilution assay were determined by dissolving the essential oil in DMSO (stock solution) and then serially diluting it in distilled water (6-0.094 µl/ml). A total of 100 µl of each dilution was added into the wells of 96-microtiter plates. Then, 100 µl of diluted microbial suspensions (106 CFU/ml) were added to each well and incubated at 37°C for 24 hours. The first wells with no turbidity and the first well without any growth on the solid media were determined as the MIC and MBC values, respectively (7).
3.4. Antioxidant Evaluation of the Essential Oil by ABTS Radicals
The antioxidant activity of the essential oil against ABTS free radicals was determined by preparing a solution containing 7 mM ABTS in 2.45 mM persulfate (1:1). This solution was kept in a dark place (12 - 16 hours) and then diluted to 1:25. Different concentrations of essential oil were prepared. About 3 ml of ABTS solution was added to 40 µl of different concentrations of essential oil. After 15 min, the absorbance of each concentration was read at 734 nm, and the inhibition percent of the essential oil were estimated as follows:
Where Ablank is the absorbance of the control and Asample is the absorbance of the different concentrations of essential oil. Ascorbic acid was used as the control (8).
4. Results and Discussion
Forty components were identified in the essential oil of T. persicum, and they represented 82.5% of the total essential oil composition. Borneol (33.5%), bornyl acetate (12.8%), linalool (9.1%), 1- hexane 3-en-2,5,5, and trimethyl (6.8%) were the main components of the essential oil of T. persicum (Table 1).
| Compound | RI | (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1- hexane 3-en-2,5,5, trimethyl | 866 | 6.8 |
| α-thujone | 929 | 0.03 |
| α-pinene | 936 | 0.5 |
| Camphene | 950 | 2.1 |
| Verbenone | 967 | 0.1 |
| Sabinene | 981 | 0.2 |
| β- pinene | 984 | |
| 1,5-dimethyl hepta, 1,3,5-trian | 995 | 1.4 |
| α-phellandrene | 1006 | 0.3 |
| α-terpinene | 1017 | 0.3 |
| p-cymene | 1024 | 0.9 |
| Limonene | 1028 | 0.3 |
| 1,8-cineole | 1030 | 0.7 |
| γ- terpinene | 1057 | 0.7 |
| Cis-sabinene hydrate trans linalool oxide | 1066 | 0.2 |
| Cis linalool oxide | 1071 | 0.2 |
| Linalool | 1102 | 9.1 |
| Chrysantenol-trans pinocarveol | 1137 | 0.1 |
| Cis-verbenol | 1139 | 0.2 |
| Camphor | 1145 | 2.1 |
| Borneol | 1165 | 33.5 |
| Terpinene-4-ol | 1177 | 0.9 |
| α-terpineol | 1189 | 0.3 |
| Myrtenol | 1194 | 0.2 |
| Verbanol | 1207 | 0.2 |
| chrysanthemyl acetate | 1232 | 0.4 |
| Thymol methyl | 1239 | 0.1 |
| Cis-chrysanthenyl acetate | 1257 | 0.9 |
| Bornyl acetate | 1283 | 12.8 |
| Thymol | 1286 | 1.5 |
| Carvacrol | 1295 | 0.5 |
| Trans-caryophyllene | 1413 | 0.4 |
| Trans-β-Farnesene | 1448 | 1.7 |
| Germacrene-d | 1474 | 0.2 |
| α-farnesene | 1490 | 0.2 |
| Elymol | 1542 | 0.3 |
| Caryophyllene oxide | 1573 | 0.2 |
| Davanone | 1580 | 0.7 |
| γ-eudesmol | 1625 | 1.2 |
Abbreviation: RI, Retention Index.
The first main component of the essential oil of T. persicum in this study was consistent with the first major component found by Habibi et al. (4), who reported borneol (24.3%) as the main component of the essential oil of T. persicum. The other main components were different from those in the other study. The second main component of T. persicum essential oil from Shahr-E-Kord was bornyl acetate, and that from Khuzistan Province was menthyl acetate (4).
Generally regarded safe by the food and drug administration, borneol (C10H18O) is used as an important ingredient in food and medicine and as food flavoring (9). Some biological activities of borneol, such as central and peripheral antinociceptive effects (10), vaso-relaxant effect on rat thoracic aorta (11), and neuroprotective activity (12), have been confirmed. Therefore, because of the high amount of borneol in the essential oil of T. persicum, this essential oil can be used for different purposes in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
The antibacterial activity evaluation of the essential oil of T. persicum against three different pathogenic bacteria was evaluated. In the disc diffusion assay, S. aureus had the highest inhibition zone diameter (23 mm), followed by S. enterica (20 mm) and H. pylori (17 mm). In the micro broth dilution assay, S. aureus had MIC and MBC values of 0.325 and 0.75 µl/ml, and it showed the highest sensitivity to the essential oil of T. persicum, followed by S. enterica (MIC and MBC values of 0.75 and 1.5 µl/ml) and H. pylori (MIC and MBC values of 0.75 and 3 µl/ml), respectively. Although the MIC values of the essential oil of T. persicum for S. enterica and H. pylori were the same, the effects of this essential oil on H. pylori was inhibitory, and higher doses of the essential oil was required to kill this bacterium (Table 2).
| Disc Diffusion, mm | Micro-broth Dilution Assay, µl/ml | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. platyloba | Tetracycline | MIC | MBC | |
| Salmonella enterica | 20 | 20.8 | 0.75 ± 0.03 | 1.5 ± 0.05 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 23 | 14 | 0.325 ± 0.05 | 0.75 ± 0.05 |
| Helicobacter pylori | 17 | 21 | 0.75 ± 0.02 | 3.0 ± 0.03 |
Abbreviations: MBC, Minimal Bactericidal Concentration; MIC, Minimal Inhibitory Concentration.
The antimicrobial activity of borneol was confirmed against Candida albicans, S. aureus, and Escherichia coli (13). Furthermore, the antibacterial activities of some oxygenated monoterpenes, such as borneol, borneol acetate, camphor, 1,8-cineol, linalool, terpinen-4-ol, and α-terpineol, were evaluated against 63 bacteria strains, and these compounds were confirmed to have different degrees of antibacterial activities against different bacteria. However, some compounds such as linalool, α-terpineol, and terpinen-4-ol, have extended limited antibacterial effects, and compounds such as camphor and 1,8-cineol showed no antibacterial activity (14). Therefore, the considerable antibacterial activity of the essential oil of T. persicum is related to the major or minor components present in this essential oil.
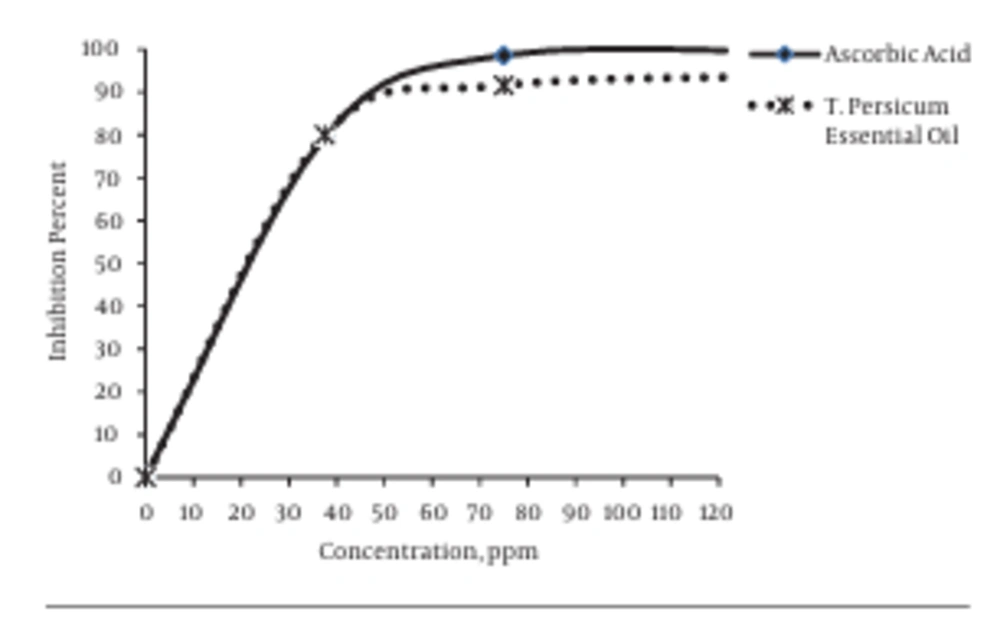
The antioxidant evaluation of the essential oil of T. persicum showed that IC50 was equal to 20 ppm and that this essential oil was the same as ascorbic acid in being a synthetic antioxidant. At a high concentration of the essential oil of T. persicum, the antioxidant activity of this essential oil was higher than that of ascorbic acid (Figure 1).
The antioxidant activity of thymol and carvacrol was reported previously (15). Borneol was confirmed to have no antioxidant activity in the antioxidant system, but it could protect cell DNA against Fe2+-induced damage (15). Therefore, the other components of the essential oil or the synergistic effect among compounds plays an important role in the antioxidant potency of the essential oil. Linalool, the other main component of the essential oil, is a lead compound in the synthesis of vitamins A and E. Linalool-rich essential oils were confirmed to express a high antioxidant activity (16).
Therefore, the antioxidant activity of the essential oil of T. persicum is related to linalool or its other components. This essential oil can be a suitable antioxidant agent for human consumption and a preservative in food or drugs instead of chemical ones.
5. Conclusion
For the first time, the essential oil of T. persicum was shown to have desirable antioxidant and antimicrobial activities in vitro because of its main components, namely, borneol, bornyl acetate, and linalool. As the other pharmacological activities (i.e., anti-inflammatory, antinociceptive, and analgesic) of borneol and linalool have already been confirmed, the other pharmacological activities of this valuable plant aside from its antioxidant and antimicrobial effects can be investigated to introduce the essential oil of T. persicum as a new treatment for other ailments.