1. Background
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) affects a considerable number of people worldwide. It progresses when there is a disparity between the aggressive and protective factors at the luminal surface of the epithelial cells of the stomach. Aggressive factors include Helicobacter pylori, hydrochloric acid (HCl) secretions, pepsin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), bile acids, ischemia, hypoxia, smoking, and alcohol. Defensive factors include bicarbonate, mucus layer protection, mucosal blood flow, prostaglandins, and growth factors (1).
Non-selective NSAIDs, including indomethacin, inhibit the cyclooxygenase1 (COX-1), which leads to the blocking of the gastric mucus secretion. In addition, the inhibition blocks the platelet production of thromboxane (TXA), which causes increased bleeding during active gastric bleeding (2).
Helicobacter pylori infections alone are the major causative factor of duodenal ulcers (95%) and gastric ulcers (80%). Sometimes lifestyle factors, such as smoking, alcohol, eating spicy foods, and stress, are also associated with peptic ulcer formation (3).
Although many products are used for the treatment of gastric ulcers, including antacids and antihistamines, most of these drugs, produce adverse reactions, such as arrhythmias, impotence, gynecomastia, and hematopoietic changes. Extracts of herbal plants have produced promising results in the treatment of gastric ulcers (4).
Terminalia catappa (TC) is a species of the family Combretaceae. This plant grows widely in southern Iran in the Hormozgan and Sistan-Baluchestan provinces where it is popularly known as garom zangi and bidam. It is also widely distributed in countries with tropical and subtropical climates (5).
TC is a tall tree (25 m in height) with horizontal branches (6). The fruit is ovoid, 5 cm in length (7), and green or red. The fruit has two winged corners, and tastes range from sweet to bitter and astringent (5). The leaves contain carbohydrates, glycosides, flavonoids, steroids, tannins, saponins, triterpenoids, and alkaloids (8).
Studies in the literature have shown that the polar extract from different parts of the plant, such as the leaves, fruits, and bark of TC have the following biological activities: antimicrobial, antifungal (9), antioxidant (10), antimetastatic (11), anti-inflammatory (12), hepatoprotective (13-15), mutagenic (16), aphrodisiac (17), and anti-diabetic (18).
2. Objectives
The present study was designed to assess the antiulcer activity of the hydroalcoholic extract of the leaves of TC.
3. Methods
3.1. Drugs and Chemicals
Indomethacin and ranitidine were purchased from the Exir Pharmaceutical Co. (Borujerd, Iran) and Chemidarou Pharmaceutical Co. (Tehran, Iran), respectively. The drugs and the hydroalcoholic extract of the TC leaves were diluted in normal saline.
3.2. Plant Material and Extract Preparation
After collecting the plants from Bandar Abbas (southern Iran), TC was identified by the agriculture research and education and natural resources center (ARENRC), Bandar Abbas, Iran (registration number 7088). In order to prepare the hydroalcoholic extract of the leaves, the leaves were powdered and 300 g of the powder was dissolved in 4,000 mL of 70% ethanol (v/v) and macerated for 72 hours. The solution was then shaken and filtered, and then vacuum evaporation was performed to remove the solvent. The semisolid extract that was obtained was oven-dried at 38°C for 72 hours (19).
3.3. Animals
Wistar rats that weighed between 200 - 250 g were provided by the animal house of Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz, Iran. The rats were kept under regular 12-hour light/dark cycles at a temperature of 23 ± 2°C. Standard pellet food and tap water were available ad libitum.
3.4. Experimental Models of Gastric Ulceration in Rats
During the 48 hours before the experiment, the rats were deprived of food, but were provided with water. In order to exclude the diurnal variations in the putative regulatory factors involved in gastric functions, all experiments were conducted at the same time each day. Indomethacin (30 mg/kg) suspended in CMC (1%) was administered orally using a feeding tube (20, 21).
3.5. Experimental Groups
The present experiment compared the effects of TCLE and ranitidine, an H2 receptor blocker, on the indomethacin-induced gastric damage in rats. Six rats were allocated to 13 groups. The groups received indomethacin (30 mg/kg) orally administered plus oral TCLE (100, 200, 400, and 600 mg/kg), ranitidine (50 mg/kg) (22, 23), or normal saline (5 mL/kg).
Other groups received only TCLE (100, 200, 400, and 600 mg/kg), ranitidine (50 mg/kg), CMC (1% solution), or indomethacin.
3.6. Evaluation of Gastric Ulcers
After 5 hours, all animals were anesthetized by ether (24, 25) and sacrificed. Their stomachs and greater curvature were then dissected and rinsed with normal saline. The sum of the length (mm) of all lesions was designated as the ulcer index (UI). The mean UI and inhibition (%) were calculated using the following equations:
mean UI = sum of the total lengths of lesions in each group/number of rats in each group
3.7. Histopathological Studies
After evaluating the stomach ulcers, a longitudinal section of the anterior portion of the stomach was fixed in a 10% formalin solution for 24 hours. The fixed samples were embedded in a paraffin block, cut into 5-µm sections, placed on glass slides, and stained with hematoxylin-eosin.
3.8. Statistical Analysis
One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with the least significant difference (LSD) test was performed to analyze the data. Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) and P < 0.05 were considered to be significant. Statistical computations were calculated using SPSS statistics 20 for windows (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
4. Results
4.1. Therapeutic Effects of TCLE on Indomethacin-Induced Gastric Ulcers
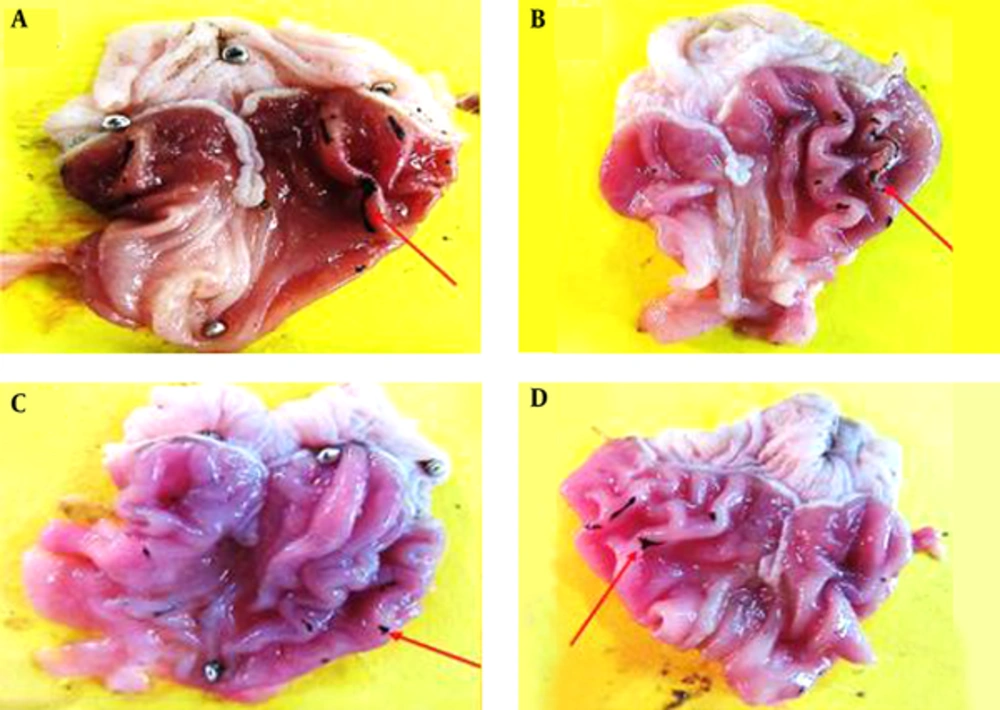
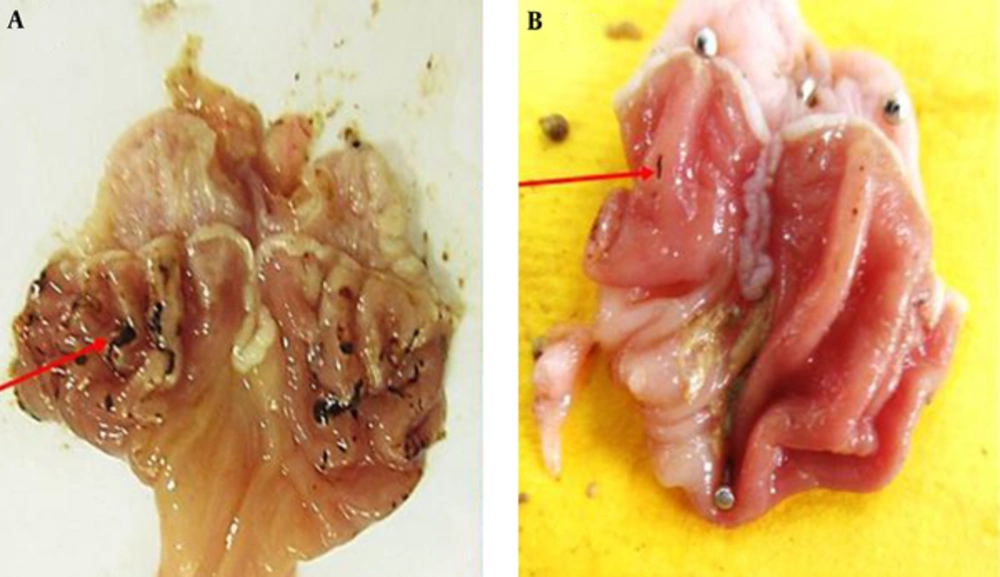
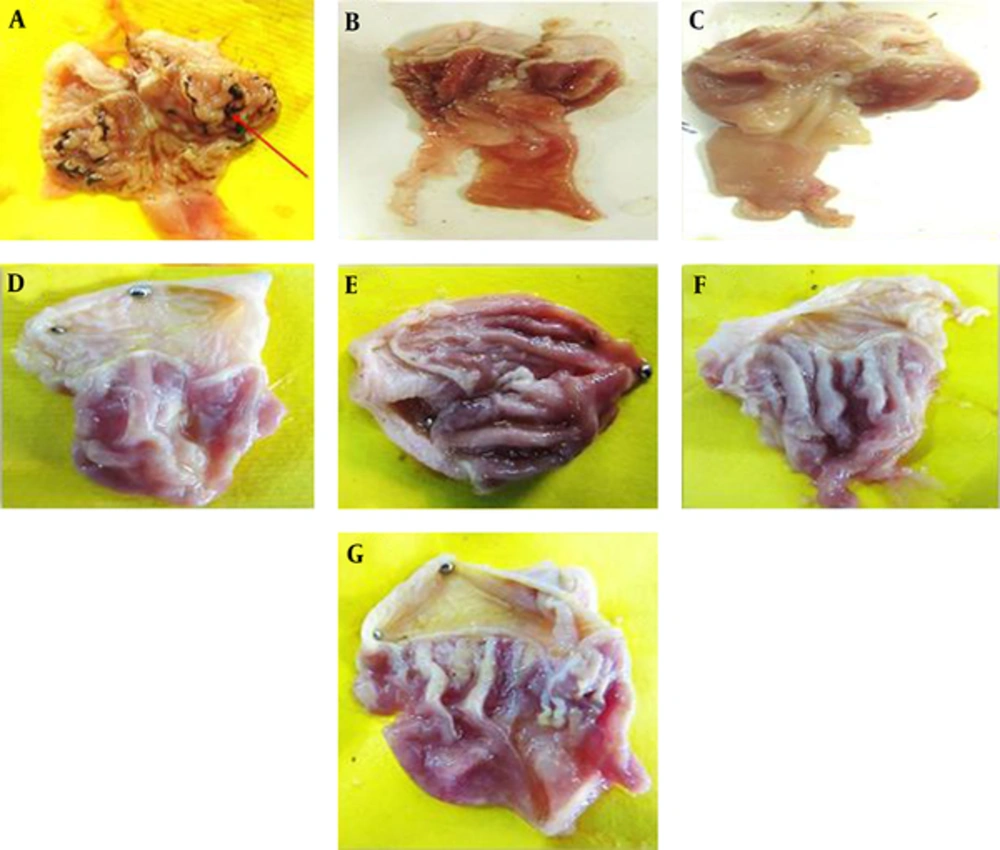
Macroscopic evaluations were performed to determine the therapeutic effects of the different doses of TCLE (100, 200, 400, and 600 mg/kg) on indomethacin-induced gastric damage (Table 1). The administration of indomethacin led to very high UIs in the stomachs of the rats. While all doses of TCLE and ranitidine significantly reduced the UI in rats with indomethacin-induced gastric ulcers, the effects of TCLE (400 mg/kg) and ranitidine were not significantly different. To eliminate the effects of TCLE, ranitidine, and 1% CMC-water solution on the indomethacin ulcers, only TCLE, CMC, or ranitidine were administered to six groups; these groups did not show any damage or ulcers (Figures 1 to 3 and Table 1). Table 1 presents the protection percentage obtained by different doses of drugs.
| Group | Dose, mg/kg | Ulcer Index, mm2 | Protection (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TCLE + indomethacin | 100 | 13.5 | 52.12 |
| 200 | 8.5 | 69.85 | |
| 400 | 3 | 89.36 | |
| 600 | 4.8 | 82.97 | |
| Ranitidine + indomethacin, positive control | 50 | 0.5 | 98 |
| Normal saline + indomethacin, negative control | 26.6 | 5.67 | |
| TCLE only | 100 | 0 | 100 |
| 200 | 0 | 100 | |
| 400 | 0 | 100 | |
| 600 | 0 | 100 | |
| CMC only | 0 | 100 | |
| Ranitidine only | 50 | 0 | 100 |
| Indomethacin only | 30 | 28.2 | 0 |
4.2. Histopathology
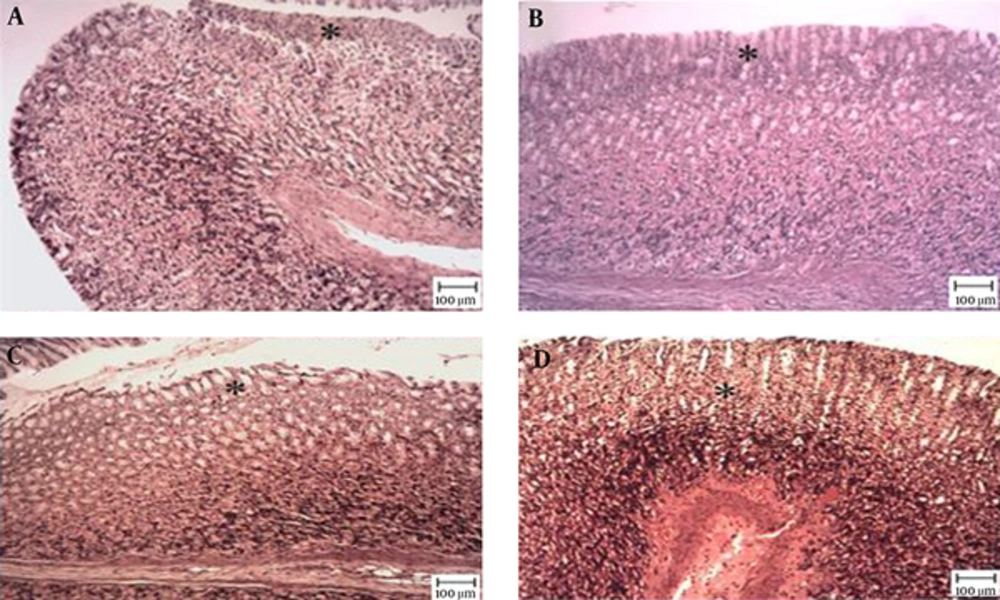
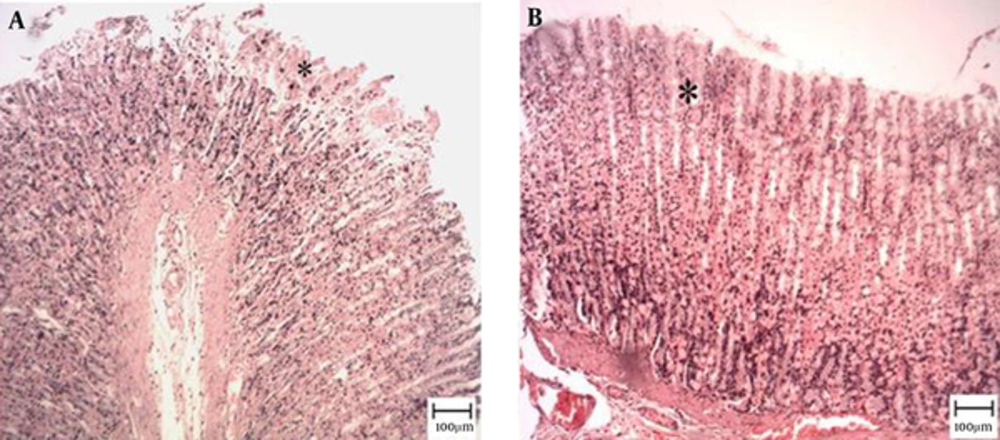
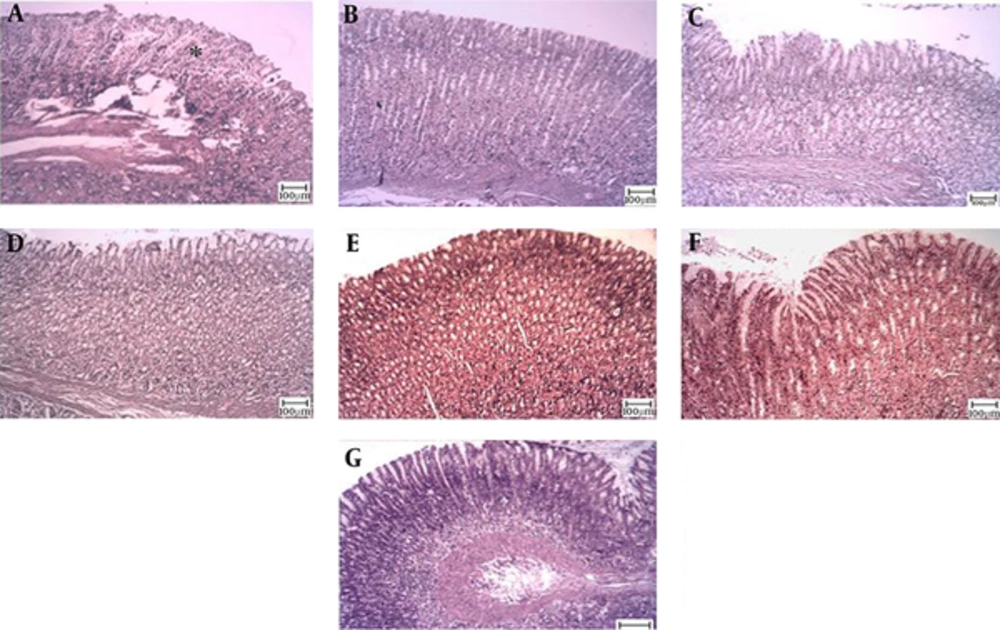
The microscopic examination of the gastric mucosal surface cells in the indomethacin-induced groups showed some extent of necrosis, identified by highlighted cytoplasm and compressed and dingy nuclei. Some parts of the mucosal cells were separated and the glandular epithelium cells were necrotic up to the middle. The depth of the ulcers was less in the treatment groups than in the indomethacin groups. Microscopic examination showed no pathological changes in the mucosa of the six control groups. Most cases showed columnar mucosal cells with clear cytoplasm and, in some cases, capillary hyperemia (Figures 4 to 6).
Tthe star shows healthy mucosal cells, magnification ×100, hematoxylin and eosin staining. A, TCLE (100 mg/kg) + indomethacin shows mucosal regeneration and reduced inflammatory and ulcerous cells; B, TCLE (200 mg/kg) + indomethacin shows mucosal regeneration and reduced inflammatory and ulcerous cells; C, TCLE (400 mg/kg) + indomethacin shows mucosal regeneration and reduced inflammatory and ulcerous cells; and D, TCLE (600 mg/kg) + indomethacin shows mucosal regeneration and reduced inflammatory and ulcerous cells.
Magnification ×100, hematoxylin and eosin staining. A, Indomethacin (30 mg/kg) shows mucosal ulceration with inflammation; B, TCLE (100 mg/kg) shows mucosal ulceration with inflammation (the star shows a necrotic cell); C, TCLE (200 mg/kg) shows normal gastric mucosa with normal glands; D, TCLE (400 mg/kg) shows normal gastric mucosa with normal glands; E, TCLE (600 mg/kg) shows normal gastric mucosa with normal glands; F, CMC (1%) shows normal gastric mucosa with normal glands; and G, Ranitidine (50 mg/kg) shows normal gastric mucosa with normal glands.
5. Discussion
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are believed to cause gastric ulcers by inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis and epithelial cell proliferation in the ulcer margin; epithelial cell proliferation is essential for the reepithelization of the ulcer crater (26). The role of ROS in the development of mucosal damages induced by indomethacin, ethanol, and other similar agents has also been highlighted (27). Growing attention has been paid to the use of herbal antioxidants as alternatives to synthetic agents for the effective management of drug toxicity in such cases as peptic ulcers (28).
The current study examined the effects of TCLE on the treatment of indomethacin-induced gastric ulcers in rats. Previous phytochemical studies confirmed the presence of carbohydrates, glycosides, flavonoids, steroids, tannins, saponins, triterpenoids, and alkaloid compounds in TCLE (8). Saponins, terpenoids, and flavonoids are known to possess antiulcer properties (29). According to our findings, the oral administration of TCLE could significantly reduce UI caused by indomethacin.
In a study on rats, Devi et al. (30) assessed the gastroprotective effects of the methanolic extract from Terminalia arjuna (TA) bark on gastric ulcers induced by diclofenac sodium (80 mg/kg). They measured several parameters, including lesion index, volume of gastric juice, pH, free and total acidity, pepsin concentration, and acid output in gastric juices to determine the effects of the TA extract. They also evaluated the levels of non-protein sulfhydryls, lipid peroxide, and reduced glutathione, as well as the activities of enzymatic antioxidants, such as super oxide dismutase and catalase, in the gastric mucosa. Adherent mucus content assessment and histological examinations were also performed on the stomach tissue. The researchers confirmed the gastroprotective effects of TA extract and attributed such effects to the free radical scavenging activity and cytoprotective nature of the extract.
In a study on Swiss albino rats, Gupta et al. (31) reported that the ethanol extract of Terminalia pallida Brandis (EETP) fruit had antiulcer activity against drug-, histamine-, and ethanol-induced ulcers. The researchers concluded that the extract reduced mucosal damage by increasing the antioxidant potential of the gastric mucosa.
Jawanjal et al. (32) examined the antiulcer properties of the methanolic extract of Terminalia belerica Roxb. fruit against several models of ulcers in rats. They found the extract to protect rats against aspirin-induced ulcers. However, it did not exert similar effects on cold stress restraint models of ulcer. Overall, the 70% methanolic extract of Terminalia belerica enhanced resistance to necrotizing factors, directly protected the gastric mucosa, and showed antiulcer activity.
Kumar et al. (8) performed UI evaluations and histopathological examinations to measure the protective activity of methanolic extract of TC leaves against gastric ulcers induced by pyloric ligation in rats. The researchers observed significantly lower pH, gastric volume, free and total acidity, and UI in rats treated with the extract compared with the control group. The effects of the extract were dose-dependent and no toxic effects were detected even at high doses. The researchers attributed the antiulcer activity of TC extract to its flavonoid content.
In a study on rodents, Silva et al. (33) used a variety of methods, including matrix metalloproteinase activity, microdilution, direct flow analysis-ionization electrospray ion-trap tandem mass spectrometry, and high performance liquid chromatography coupled with a photodiode array, to assess the gastroprotective and anti-Helicobacter pylori effects of the aqueous fraction (FrAq) extracted from the TC leaves. The analyses were conducted 7 and 14 days after treatment. Their findings confirmed the potent preventive and healing effects of the FrAq from TC leaves against not only acute and chronic induced gastric ulcers, but also H. pylori.
Annegowda et al. (34) evaluated the antioxidant activity of hydrolyzed extracts of TC leaves and reported a strong correlation between the phenolic content and the antioxidant activity of the extracts. They concluded that the polyphenolic content of the extracts played a major role in the antioxidant properties. According to Mininel et al. (16), punicalagin, the most abundant polyphenolic compound in the hydroalcoholic extract of TC leaves, possesses anti-inflammatory properties (35) and can decrease oxidative stress and prevent apoptosis (33).
The role of TCLE in increasing the peptic ulcer activities in rat was demonstrated in this study for the first time. Regarding the role of TCLE in the elimination of free radicals and oxidative stress, it seems that TCLE works as an antioxidant to decrease some of the indomethacin-induced gastric ulcer.