1. Context
Jaundice is prevalent in neonates, and it is the most common cause of hospitalization. About 60% of term neonates and 80% of premature ones develop jaundice in their first week of life due to the accumulation of non-conjugated, non-polar, and lipid-soluble bilirubin in their skin (1, 2). In the normal state, non-conjugated bilirubin level in the blood serum of the umbilical cord is 1 - 3 mg/dL, which increases to 5 mg/dL in 24 hours.
Physiologic jaundice appears on the second and third days after birth and reaches its peak of 5 - 6 mg/dL on the second to fourth days. After this, its level gradually decreases to less than 2 mg/dL on the fifth day (3-6). Jaundice is a common clinical problem during the neonatal period and can damage the neonate’s brain in severe cases.
In prevalent cases where brain barrier is damaged, increased level of serum bilirubin can damage brain cells, particularly the brain nuclei and hippocampus, leading to the occurrence of kernicterus (7-11). Phototherapy has been used to treat neonatal jaundice since the early 1970s and it is the most commonly used treatment nowadays (4, 12). During the past years, natural remedies, especially medicinal herbs, have been considered as side therapies in the treatment of jaundice; many of the raw materials of these treatments are also used in the pharmaceutical industry. Other methods of treatment include the administration of less absorbent food, such as herbal-derived preparation, the most important of which are Alhagi maurorum Medik (Taranjebin) and Cotoneaster (Shirkhesht) (6, 10, 13-17).
Cotoneaster is a sweet substance with a bitter aftertaste. It is considered as a mild laxative that can remove toxins from the bile duct, liver, stomach, and gallbladder and is the best remedy for febrile patients. Avicenna in his book titled Ghanoon expresses the features of Cotoneaster as being moderate in terms of temperament with the ability to cause diarrhea. He also indicated that Cotoneaster effects are stronger than Alhagi maurorum Medik (5, 16, 18, 19). Alhagi maurorum Medik and Cotoneaster are used as traditional medicines in the treatment of neonatal jaundice in many areas of Iran, including Fars, Lorestan, and Khorasan provinces (14, 16, 20). Cotoneaster is a sweet yellowish-white substance known as purgative manna (19). Alhagi maurorum Medik manna is a resinous sweet substance which appears on plants in the form of dew drops due to the activity of a hard-winged insect known as Larinos (21). It reduces the liver’s circulatory flow by decreasing the activity of beta-glucuronidase enzyme and causes a greater excretion of bilirubin through stool (22).
Barley is also a plant with a cold and dry nature used in traditional medicine for the treatment of fever, anemia, and liver diseases, especially hepatitis, and as a diuretic (for the urinary tract) in renal and heart diseases (21). Barley flour is used to treat neonatal jaundice in Lorestan, Iran. Some studies have also evaluated plants such as jujube, chicory, and orchid (23, 24).
2. Objective
Given the fact that no systematic reviews on the effects of natural products on neonatal jaundice have been conducted in Iran and the results of previous studies are diverse, the present systematic review was carried out.
3. Data Sources
The current research is a systematic review that evaluated all concluded articles on the efficacy of natural products in preventing or treating jaundice in Iranian neonates. The reviewed articles were independently searched by two researchers from domestic databases including IranMedex, SID, Magiran, IranDoc, and Medlib and international databases including ScienceDirect, PubMed, Scopus, Cochrane, Embase, Web of Science, and Medline. Keywords such as “jaundice”, “hyperbilirubinemia”, “neonates”, “natural products”, “herbal medicine”, “traditional treatment”, “systematic review”, “meta-analysis” and “Iran”, as well as the combination of these words were used. There was no limitation in terms of time, language, and sample size and the search was updated until the end of June 2017 (Figure 1).
4. Study Selection
The main criterion for the inclusion of different studies in this research was being in reference to the effect of natural products on neonatal jaundice. Titles, keywords, and abstracts of the articles retrieved from the databases were screened, and all the articles that had the above-mentioned keywords were selected. The inclusion criteria included: being carried out in Iran, being performed on neonates, and using a natural product (herbal or non-herbal) to reduce neonatal jaundice. The articles that did not meet these criteria were excluded.
5. Data Extraction
The ideal reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis (PRISMA) (25) checklist was used to evaluate the quality of the articles. Finally, a checklist was designed by the researchers to collect the data. The items of the checklist were the name of the first author of article, study objective, study settings, age, weight, number and gender of the neonates, name, dose and frequency of the use of the natural product, route of delivery, and method of using the natural product (such as oral/non-oral).
6. Results
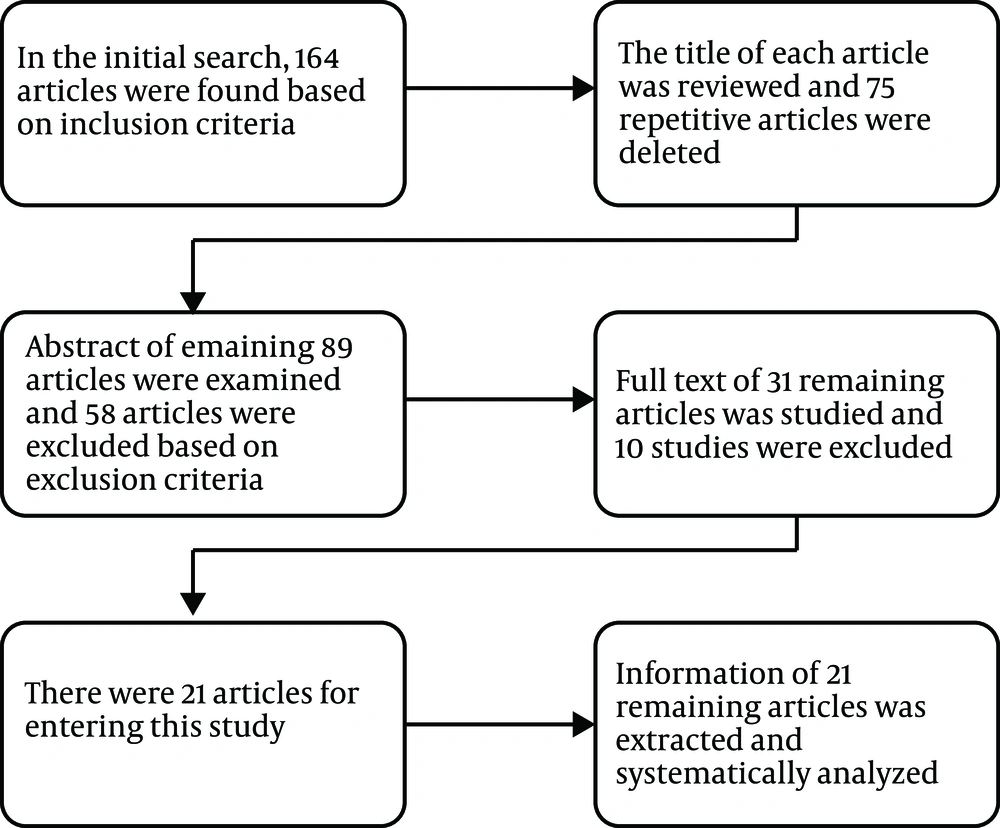
The abstracts of all the articles were initially studied and evaluated, and unrelated articles were removed and the related ones were identified. At this stage, the complete text of the remaining articles was screened, and the required and appropriate articles for the systematic review process were determined based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria (Figure 2). Articles that entered the systematic review are listed in Table 1.
| First Author | Year | Location | Type of Study | Purpose (Treatment/Prevention of Jaundice) | Mean Age of Infants (Days) | Mean Weight of Infants | Number of Infants | Product Name | Type of Use | Product Usage Interval (Hours) | Method and Dosage of Use | P Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shah Farhat (20) | 2002 | Mashhad | Prospective and double-blind | Treatment | - | > 2500 | 104 | Purgative manna | Oral | 12 | The solution contains 6 grams of purgative manna dissolved in 8 cc distilled water | 0.45 |
| Mansouri (26) | 2009 | Sanandaj | Clinical trial Double blind | Prevention | - | 3200 | 140 | Purgative manna | Oral | - | 5 drops of bilineaster three times a day for three days | 0.54 |
| Azadbakht (1) | 2004 | Mazandaran | Clinical trial | Treatment | 3 - 8 | ≥ 2500 | 200 | Purgative manna | Oral | 12 | 5 drops 3 times a day | 0.00001 |
| Ameli (27) | 2015 | Mashhad | Clinical trial | Treatment | 2 - 14 | 3200 | 98 | Bilineaster | Oral | 12 | 5 drops of bilineaster per kilogram of body weight and three times a day | 0.001 |
| Fallah (28) | 2014 | Yazd | Clinical trial random | Treatment | - | - | 60 | Bilineaster | Oral | 12 | 5 drops of bilineaster per kg body weight every 8 hours | 0.001 |
| Ebrahimi (29) | 2008 - 2009 | Yasuj | Clinical trial | Treatment | - | 3108 | 121 | Jujube | Oral | 12 | 150 mg per kilo of body weight three times a day | 0.026 |
| Nassirian (30) | 2007 | Mashhad | Interventional laboratory | Treatment | 7.35 | 2691 | - | Chicory | Laboratory blood sample vessel | 3 | The solution was made from 50 g of plant and 250 cm of alcohol and 50 cm of water at a concentration of 6%. 100 lambda (each 600 lambda equals 0.001 cc) was added from the solution to each container | 0.297 |
| Saboute (14) | 2010 | Tehran | Clinical trial | Treatment | - | - | 97 | Alhagi maurorum Medik | Oral | 24 | 10 g of Alhagi maurorum Medik in the form of a suspension of 30 g of tangerine dissolved in distilled water and straightened | 0.789 |
| Mohsenzadeh (31) | 2004 | Khorramabad | Clinical trial | Treatment | - | 2500 | 90 | Barley flour | On the entire body of the baby, apart from the face and cord | 24 | plant flour was spread over the entire body, except for the head and face and cord | 0.05 |
| Tarhani (32) | 2004 | Lorestan | Clinical trial | Treatment | - | - | 86 | Alhagi maurorum Medik | oral | 24 | A suspension of 30 grams of Alhagi maurorum Medik | 0.014 |
| Nabavizadeh (23) | 2004 | Kakan (Yasuj) | In vitro | Treatment | - | > 2500 | 42 | Fumaria officinalis | Laboratory blood sample vessel | 3 | A sample of 20 mL of blood in infants with hyperbilirubinemia was taken at the beginning of the transfusion of mL/mL and after removing 0.5 mL of the extract from Fumaria officinalis, Chicory, purgative manna, Jujube, Alhagi maurorum Medik (prepared separately by hydro-alcoholic distillation) was added to one mL of the serum separately and after about three hours, the bilirubin was tested in Optical and Blanc mode | 30.28 |
| Pashapour (33) | 2004-2005 | Orumieh | Clinical trial | Treatment | - | 3120 | 80 | Dextrose 5% | Venous | 48 | 10 cc dextrose 5% | 0.014 |
| Bahman Bijari (34) | 2009 | Kerman | Clinical trial Double-blind | Prevention | 5.17 | 2964 | 50 | Agar gel | Oral | 24 | To each of the infants, 12 tubes containing 500 mg of oral agar in 2.5 cc distilled water in the case group. The contents of the tube are given every 6 hours to the patient for three days. | 0.2 |
| Ebrahimi (35) | 2000 - 2001 | Yasuj | Clinical trial | Treatment | 5.66 | 3059 | 60 | Dextrose 10% | Venous | 24 | In the case group, in addition to phototherapy, 24 hours of Dextrose 10% was 1.5 times the amount of preservative with sodium, 3 mmol/100 cc. | 0.039 |
| Panjvani (22) | 1991 | Mashhad | Clinical trial | Prevention | 7.52 | 3018 | 126 | Alhagi maurorum Medik | Oral | Bilirubin was measured on the first, third, fifth and seventh days | 10 mL | 0.05 |
| Sakha (36) | 1999 | Tabriz | Clinical trial | Treatment | 4 | 2500 - 4000 | 150 | Lactulose | Oral | Bilirubin was measured on the first, third, fifth and seventh days | 4.5 – 5 mL | 0.0029 |
Data of Articles Included in the Systematic Review
In a study conducted at Imam Reza Hospital in Mashhad, Iran, in 2002, serum bilirubin levels were not statistically different between intervention group and control groups. This study showed that the use of 6 g of purgative manna was not more effective than a placebo in the treatment of neonatal jaundice (37). With the objective of evaluating the effect of oral carrageenan on reducing physiological jaundice in neonates, Tarhani et al. showed that neither the duration of hospitalization nor the total and direct bilirubin levels were significantly different between carrageenan and phototherapy groups after 24 hours (32).
Panjvani et al. also reported the lack of effectiveness of carrageenan in the prevention of hyperbilirubinemia in healthy and full-term neonates (22). According to the study of Mansouri et al., five drops of purgative manna three times a day for three days had no effects on neonatal jaundice on the third to fifth days after birth (26). In an in vitro study, Nabavizadeh et al. reported that even though jujube, purgative manna, and carrageenan had a laxative effect and reduced the intestinal-liver cycle in bilirubin reabsorption from the intestine and intestinal excretion of bilirubin, only chicory was effective in lowering bilirubin without affecting the internal factors (23).
In another study by Nassirian and Eslami the effect of chicory on neonatal jaundice was found to be insignificant (30). The effects of three traditional treatments (i.e., camel’s thorn, flixweed, and sugar water) were evaluated at Ghaem Hospital in Mashhad, Iran, between 2005 and 2009 on 336 neonates. These medications reduced the weight of the neonates, which caused an increase in hyperbilirubinemia. It was stated that this method could raise pseudo-confidence in parents resulting in delayed treatment of the affected neonates (38).
The effect of natural products on neonatal jaundice in the above studies was not statistically significant. On the other hand, the following studies showed that the use of natural products has been effective in reducing jaundice in neonates in Iran. Panahandeh et al. showed that purgative manna can cause somatic diarrhea due to the lack of gastrointestinal absorption in the intestine. This mannitol property in purgative manna increases the defecation frequency and can probably lower the level of bilirubin by reducing the intestinal–liver cycle of this substance, thus eliminating it through stools (39). Ameli et al. (27) and Fallah et al. (28) concluded in their studies that a bilineaster drop can significantly decrease the levels of total and direct bilirubin in neonates. In a study performed by Panahandeh et al., the effect of barley meal on neonatal jaundice was found to be significant (39).
The studies of Mansouri et al. (26) and Azadbakht et al. (1) revealed that purgative manna is effective in lowering neonatal jaundice. A plant extract rich in mannitol was used in the study of Azadbakht, but a full-nutrient purgative manna was used in Mansouri et al.’s study, which is the same substance used in Iranian traditional medicine (26). The effect of purgative manna was also reported to be positive in Saboute et al.’s study (14). In another study carried out by Ebrahimi et al. to evaluate the effect of jujube extract on neonatal jaundice, it was concluded that this plant can be effective over a short period of time, but it is not recommended for long-term treatment (29). In a study conducted by Mohsenzade et al. to evaluate the efficacy of barley flour in the treatment of neonatal jaundice, it was concluded that this treatment in combination with phototherapy was more effective than phototherapy alone (31). We could not perform a meta-analysis due to the limited number of studies and discrepancies in findings (Table 2).
| Natural Product’s Name | Number of Studies (P < 0.05) | Number of Studies (P ≥ 0.05) | Total Number of Studies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purgative manna | 2 | 3 | 5 |
| Bilineaster drop | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| Jujube | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Alhagi maurorum Medik | 1 | 3 | 4 |
| Distilled water | - | 1 | 1 |
| Fumaria officinalis | - | 1 | 1 |
| Chicory | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Barley flour | - | 2 | 2 |
| Agar | - | 1 | 1 |
| Dextrose | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| Lactulose | 1 | - | 1 |
| Camel’s thorn, Flixweed and sugar water | - | 1 | 1 |
| Totala | 10 | 16 | 26 |
Classification of Studies Performed on the Effects of Natural Products on Jaundice in Iranian Neonates
7. Conclusions
All the evaluated articles had used natural products to treat neonatal jaundice, except for the studies of Panjvani et al. (22), Mansouri et al. (26), and Bahman Bijari et al. (34), who respectively used Alhagi maurorum Medik, purgative manna, and agar gel for preventing neonatal jaundice. Furthermore, the relationship between the use of these medicinal plants and the prevention of jaundice in neonates was not statistically significant.
In the studies of Nassirian and Eslami (30) and Nabavizadeh et al. (40), the effect of natural products on neonatal blood parameters was measured. Also, in studies performed using barley flour, barley flour was sprayed on the entire body of the neonates other than the face and cord (39). Additionally, the studies examined the effect of dextrose intravenously (33, 35, 41), but in other cases, a certain amount (dose) of natural products was given orally to neonate to determine the significance of the relation between the use of natural products and the serum bilirubin levels in neonates. So far, there have been several reviews on the use of natural products to reduce neonatal jaundice. This is due to the importance of the issue, the side effects of jaundice in neonates, and the benefits of using natural products. For example, Khodashenas et al. in a study showed that herbal medicines alone cannot treat neonatal jaundice, but the use of these along with phototherapy can be beneficial. The effect of oral Alhagi maurorum Medik and purgative manna on neonatal jaundice has been evaluated in various articles, which showed that the use of such herbal medicines is recommended in the treatment of neonatal jaundice (5).
In a systematic review, Raeisi et al. reported various types of herbs that are used to treat jaundice at different ages. The most important of these herbs are purgative manna, jujube, barley flour, Alhagi maurorum Medik, Fumaria officinalis, and chicory, which are used in the treatment of neonatal jaundice (24). A meta-analysis by Zeng et al. performed on 2594 neonates (target group of 1307 and control group of 1287) in China showed that the use of Yin Zhi Huang oral liquid was more effective in treating jaundice than placebo (42).
Today, herbal medicines are used in countries such as China, Egypt, Greece, India, Mexico, Ethiopia, Cuba, and Turkey. In Singapore, ginger root (Lava Teluk) and sunflower seeds are used to reduce jaundice (43). In East Asia, the mixture of four plants (i.e., Oriental flushes, Roberts, beetles root, and Gardenia), known as Yin Zhi Huang, is used to treat neonatal jaundice, which has recently been shown to act as an activator of the liver receptors (44-46). Common wormwood is usually used in China for the treatment of jaundice in neonates. Glycyrrhiza glabra, Rheum officinale, and root of baikal are other herbal plants used for this purpose (43, 47). Activated charcoal, agar gel, and cholestyramine are non-absorbable foods that probably attach to bilirubin in the intestine or decrease the enterohepatic cycle and reduce bilirubin intestinal absorption and its serum level (48-50). In a research conducted in Turkey in 2014, it was shown that oral agar along with phototherapy was more effective than phototherapy alone in the reduction of jaundice in neonates.
In conclusion, neonatal jaundice is highly prevalent among term and preterm infants, and common therapeutic interventions such as phototherapy have many complications or are sometimes dangerous. It is supposed that the use of some natural products like medicinal plants, especially Cotoneaster (10), along with phototherapy may be effective in treating neonatal jaundice; it can also reduce the use of phototherapy and hospitalization time, and in turn, diminish the incidence of phototherapy complications and hospitalization costs. However, further studies are warranted to clarify the role of natural products in the prevention and treatment of neonatal jaundice.
7.1. Recommendations
The total number of neonates studied in the 21 articles reviewed was 2237. In these studies, a variety of products (such as purgative manna, cinnamon, chicory, Fumaria officinalis, agar, dextrose, and lactulose) were used to treat or prevent neonatal jaundice. Most of the evaluated products were herbal and most of the studies were clinical trials. Not all the studies related to the prevention of neonatal jaundice yielded significant results. Among natural products, Cotoneaster was studied more commonly and still more studies are needed (10).
However, for better evaluations of standardized natural products, strong clinical support from multi-centered trials is required. Since these products are often evaluated among a small number of samples, there is a lack of strong evidence regarding the effect of natural products on the prevention and treatment of neonatal jaundice. Therefore, strong clinical trials are still needed to gain a better understanding of the effects of natural products. Hence, the use of natural products for the prevention and treatment of neonatal jaundice requires further studies. Performing a meta-analysis seems necessary due to the diversity in the effects of natural products and the difference in the number of studies conducted on each of these products. Undertaking such a study will help with precise evaluation of the effects of each of these products on neonatal jaundice in Iran.