1. Background
Emergency medical services (EMS) are emergency services that provide immediate prehospital care to serious patients and transport them to the hospital for definitive treatment if needed (1). The EMS providers are the first providers of professional care to patients suffering from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) (2). Emergency prehospital care is unique and could significantly impact the patient's outcome (3). In the United States, about 420,000 OHCA and Europe approximately 275,000 OHCA occur annually (4). Approximately 10.8% of adult patients with a cardiac arrest that had received resuscitative efforts by EMS providers survived hospital discharge (5).
The survival probability of patients with OHCA is directly related to the onset of the first aid, especially the cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) process (6), which is a lifesaving technique through which the hypoxia of vital organs, such as the heart and brain, can be prevented and if performed timely and properly, in addition to saving the person's life, it will prevent many irrecoverable injuries (7).
The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends that high-quality CPR, defibrillation, and medications must be administered by EMS providers on the scene to restart normal heart rhythm in patients with sudden cardiac arrest (8). American Heart Association has suggested that there may be barriers for EMS providers as well as emergency medical dispatchers (EMD) (9). Emergency medical services systems with limited resources face serious challenges in implementing cardiac resuscitation systems of care and keeping continuous CPR, and these systems also suffer from poor destination protocol (10). Significant ambiguity exists in EMDs, especially in the identification of the cardiac arrest victim and telephone CPR instructions as well (AHA 2010). Limited education and training programs, poor automated external defibrillator (AED) accessibility, and ambiguous decision-making processes were major barriers that contributed to delays in prehospital emergency medical services CPR (11). In this way, it is worth mentioning that large agencies providing advanced life support care succeed sooner to implement the updated protocol, implying that agencies' structure can play a role as a barrier (12, 13). Incompetent team leadership has been observed that a management barrier to obtaining a well-coordinated effort (10, 14, 15).
While EMS providers’ role is pivotal to ensuring that patients with sudden cardiac arrest receive immediate high-quality CPR and basic and advanced emergency medical services, it is important to fully understand what barriers exist in the prehospital emergency care for patients with OHCA. On the other hand, due to the increase in mortality, complications, and negative consequences of unsuccessful CPR, the views of EMS providers can certainly be helpful to reduce the obstacles to the success of CPR. Moreover, few studies have investigated barriers in prehospital emergency medical services CPR. Therefore, it is necessary to identify these barriers from the perspective of EMS providers in order to improve the quality of resuscitation.
2. Objectives
Given that evidence is limited to few studies and narrow scope, this study aimed to identify barriers to the success of CPR from the perspectives of EMS providers in the EMS.
3. Methods
3.1. Study Design
The current study was a cross-sectional analytical study that was conducted from May 2015 to Jan 2016. The research population consisted of all EMS providers in the EMS affiliated to Birjand University of Medical Sciences (BUMS). According to the following formula and based on Kavosi's study, a sample size of 150 participants was obtained by considering a confidence interval of 95%, a d of 0.08, and an S of 0.5 (16). To compensate for probable 5% dropouts, we recruited 160 EMS providers.
3.2. Participants
In this study, 160 EMS providers were selected through a simple random sampling method using a random number table, according to predetermined inclusion criteria. Inclusion criteria were as follows: EMS providers with an associate degree or bachelor of science (BSc), at least one year experience in EMS, the experience of doing CPR, and willingness to participate in the research. EMS providers who incompletely filled out their questionnaires were excluded from the study.
3.3. Data Collection
To collect the data, participants fulfilled a demographic questionnaire and a researcher-made questionnaire that has been developed to assess barriers to the success of CPR in the EMS by EMS providers. The data in the demographic questionnaire included marital status, educational status, work experience, workplace, and CPR experience. The questionnaire consisted of 60 questions categorized in six subscales: barriers related to patients’ characteristics (8 questions), barriers related to EMS providers’ competencies (15 questions), barriers related to CPR management (10 questions), barriers related to CPR equipment (6 questions), barriers related to CPR training (4 questions), and barriers related to EMS structure (17 questions). EMS providers rated questions on a five-point Likert scale (0: none, 1: slight, 2: moderate, 3: strongly, and 4: very strong), and each question scored 0 to 4, respectively. The main question was, "please specify to what extent this item affects the success of CPR?”. At first, according to demographic variables, the mean score of barriers to successful CPR was calculated by summing the scores questions and dividing them by the number of the participants. Thus, the mean score of barriers to successful CPR would be 0 to 240. As a result, the comparison between demographic variables and the mean score of barriers to successful CPR was reported. Afterward, the mean score of each subscale was calculated by summing the scores of its questions and dividing them by the number of questions in that subscale. Besides, the mean score for each question was computed by averaging the scores of each question. Accordingly, the mean score for each subscale as well as for each question was obtained from 0 to 4. Consequently, the most important obstacles were reported in each subscale.
The questionnaire was prepared by three emergency experts as well as based on the existing article in this area (16). Then, to determine content validity, the questionnaire was presented to five experts in the field of emergency from the BUMS, and their comments were used to revise the questionnaire. Assessment of reliability of the questionnaire was performed using a pilot study with 20 EMS providers who were not included in the present study. The Cronbach's alpha of the questionnaire and its subscales were 0.87 and 0.71 to 0.92, respectively.
3.4. Ethics Considerations
The BUMS Ethics and Research Committee approved the research protocol (approval Code: IR.BUMS.REC.1394.11). The purpose of this research was explained to the participants, and from all of them, informed consent was obtained.
3.5. Statistical Analysis
Study data were analyzed using SPSS software, version 16. The measures of descriptive statistics such as frequency, mean and standard deviation (SD) were used for reporting the findings. The normal distribution of data was confirmed by the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, and therefore, one-way ANOVA and independent t-test were used for data analysis. The significance level for all tests was less than 0.05.
4. Results
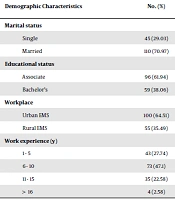
In this study, 155 (out of 160) EMS providers completed and returned the questionnaire. The participants’ demographic characteristics are presented in Table 1. Independent t-test revealed that the mean score of barriers to successful CPR among EMS providers with BS degree was significantly greater than EMS providers with associate one (P = 0.003). Furthermore, independent t-test and one-way ANOVA revealed the mean score of barriers to successful CPR had no significant difference with the other demographic characteristics of the participants (P > 0.05; Table 1).
| Demographic Characteristics | No. (%) | Mean Score of Barriers to Successful CPR a | P-Valueb |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marital status | 0.81* | ||
| Single | 45 (29.03) | 173.17 ± 14.80 | |
| Married | 110 (70.97) | 173.92 ± 18.53 | |
| Educational status | 0.003* | ||
| Associate | 96 (61.94) | 170.52 ± 16.57 | |
| Bachelor’s | 59 (38.06) | 178.89 ± 17.81 | |
| Workplace | 0.96* | ||
| Urban EMS | 100 (64.51) | 173.65 ± 19.15 | |
| Rural EMS | 55 (35.49) | 173.80 ± 14.23 | |
| Work experience (y) | 0.31** | ||
| 1 - 5 | 43 (27.74) | 170.93 ± 14.98 | |
| 6 - 10 | 73 (47.1) | 174.14 ± 17.71 | |
| 11 - 15 | 35 (22.58) | 177.72 ± 21.88 | |
| > 16 | 4 (2.58) | 179.28 ± 17.31 |
aValues are expressed as Mean ± SD unless otherwise indicated.
b*The results of the independent-sample t-test, ** The results of the one-way analysis of variance.
Among the subscales of barriers to successful CPR, the EMS structure subscale was the most important in this area. Between the barriers related to EMS structure subscale, public inaccessibility AED and lack of telephone-CPR advice by the dispatcher, have been perceived by EMS providers as the most important barriers to the success of CPR. As well as, poor knowledge regarding CPR protocol among the items of EMS providers’ competencies subscale was another important obstacle (Table 2).
| Subscales | Mean ± SD | Highest Item Score | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| EMS structure | 3.06 ± 0.38 | 1. Public inaccessibility AED | 3.59 ± 0.49 |
| 2. Lack of telephone-CPR training by dispatcher | 3.58 ± 0.55 | ||
| EMS providers` competencies | 3.05 ± 0.38 | 1. Poor knowledge regarding CPR protocol | 3.40 ± 0.82 |
| 2. Lack of timely presence of EMS providers at the patient's bedside | 3.35 ± 0.75 | ||
| CPR equipment | 2.99 ± 0.54 | 1. Daily Unchecked CPR equipment | 3.40 ± 0.63 |
| 2. Lack of CPR equipment in any ambulance completely | 3.39 ± 0.84 | ||
| Patients’ characteristics | 2.75 ± 0.43 | 1. Initial cardiac rhythm | 3.28 ± 0.73 |
| 2. Age of patients | 3.11 ± 0.50 | ||
| CPR management | 2.73 ± 0.41 | 1. Poorly motivated CPR leadership | 3.12 ± 0.77 |
| 2. Lack of EMS providers awareness of job descriptions | 2.89 ± 0.65 | ||
| CPR training | 2.42 ± 0.40 | 1. Irregular training sessions | 2.93 ± 0.62 |
| 2. Lack of adequate training facilities | 2.82 ± 0.68 |
5. Discussion
This study aimed to identify barriers to the success of CPR in the EMS by EMS providers. The findings showed that the EMS structure subscale was the most important in this area among the subscales of barriers to successful CPR. In this subscale, public inaccessibility AED was one of the most important barriers to successful CPR from the perspectives of EMS providers. In this regard, Nielsen et al. (2013) reported further evidence of the lifesaving potential of public-access defibrillation (17). Also, in a study on the use of AED in US federal buildings, the results demonstrated that placement of AEDs in public locations and use of AEDs in public locations increases to double a patient’s odds of survival from cardiac arrest (18). In patients with OHCA, early defibrillation plays a key role in the success of the CPR, and the application of public-access AEDs by bystanders can help reduce the time to defibrillation for such patients (19). These findings demonstrate the importance of public accessibility AEDs to increase the success of CPR in patients with OHCA. Therefore, considering that public accessibility AEDs have not yet been used in our country, it is recommended to include them in the country's emergency programs. To support this suggestion, similarly, the results of several other studies indicate the importance of this issue (20-23).
In the EMS structure subscale, lack of telephone-CPR training by dispatchers has also been identified as a remarkable barrier to the success of CPR by EMS providers. Several studies have also supported that dispatcher-assisted training via telephone instruction, had a significant development in bystander CPR rates and improvements in survival and neurological outcome after OHCA (24-26). These results show that telephone-CPR training by dispatcher can be effective in initiating faster chest compression by bystanders until EMS providers reach the patient’s bedside, thereby the success of CPR will increase in patients with OHCA.
The other barrier to success CPR in the present study was poor knowledge regarding CPR protocol. Similarly, a study by Bigham et al. (2010), which indicated instruction delays, including limited training instructors and materials, may contribute to the delay in implementation of the CPR guidelines in EMS agencies (11). Pourmirza Kalhori et al. (2014) reported that only 20% of EMS providers had been fully aware of the 2010 AHA CPR guideline (27). Although shallow chest compression, fast ventilation, and prominent interruptions significantly reduce the chance of survival, poor expertise among EMS providers has been reported (28). In another study, Dyson et al. (2015) has indicated that low exposure of EMS providers to resuscitation may contribute to poor performance (29). Therefore continuing and regular training sessions, especially simulation in training, has been recommended to cover deficiencies in performance levels of EMS providers (11, 30).
The other finding of the present study showed that the mean score of barriers to successful CPR had a significant difference compared with educational status. This could be attributed probably to the higher level of knowledge that the EMS providers with BS degrees have considered items of these subscales as major obstacles to success CPR. However, no similar study was found in this area. Nevertheless, several barriers may marginalize CPR in the EMS. Unprepared and unchecked CPR equipment and poorly motivated CPR leadership point out that EMS context does not prioritize CPR systematically. Leadership skills as an integral part of CPR have a significant impact on optimum outcomes (14). Besides, people pressure EMS providers to transfer cardiac arrested patients to hospitals immediately, as well as poor policy to support EMS providers to terminate CPR in place make the situation more complicated (31). Furthermore, non-emergency medical calls provide substantial EMS providers’ workday, so frustrated EMS providers are less sensitive to situations that may cause patients to need CPR treatment (10). These factors are under the skin of the EMS context and play a considerable role in CPR.
Training first responders, sophisticated redistribution of resources to CPR may help EMS agencies to provide effective resuscitation services. Besides, the development of the multidisciplinary approach to cardiac arrest care from the first responder to hospital discharge must be prioritized (32). We investigated perceived barriers to the success of CPR in EMS that have rarely been considered. On the other hand, we acknowledge that study has limitations. One of the limitations of the present study was a self-reported questionnaire, which may lead to a significant amount of bias. Another limitation was that all participants were men, which may lead to ignoring female EMS provider’s knowledge on the subject. Therefore, it is recommended that these limitations be considered in future research, and further studies are needed before a definitive conclusion can be drawn.
5.1. Conclusions
EMS providers perceived public inaccessibility AED and lack of telephone-CPR training as the most important barriers to the success of CPR in prehospital emergency care. The results of this study revealed the necessity to address the barriers to the success of CPR to improve CPR outcomes. To achieve this, public access to AED and telephone-CPR advice are critical to improving the survival of OHCA events. Some barriers need administrative and legislative support to be overcome.