Dear Editor,
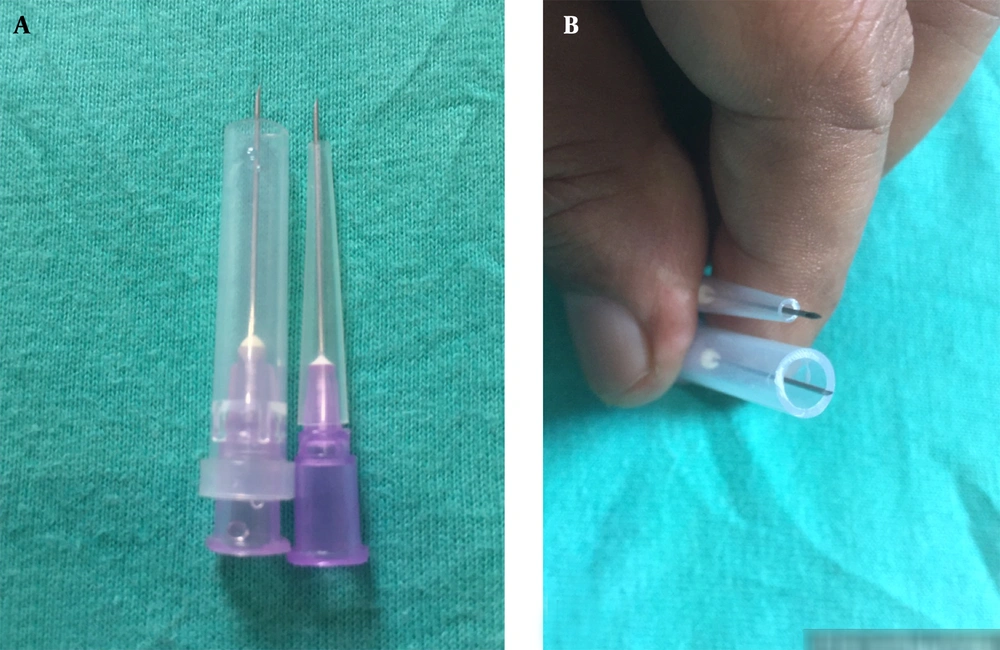
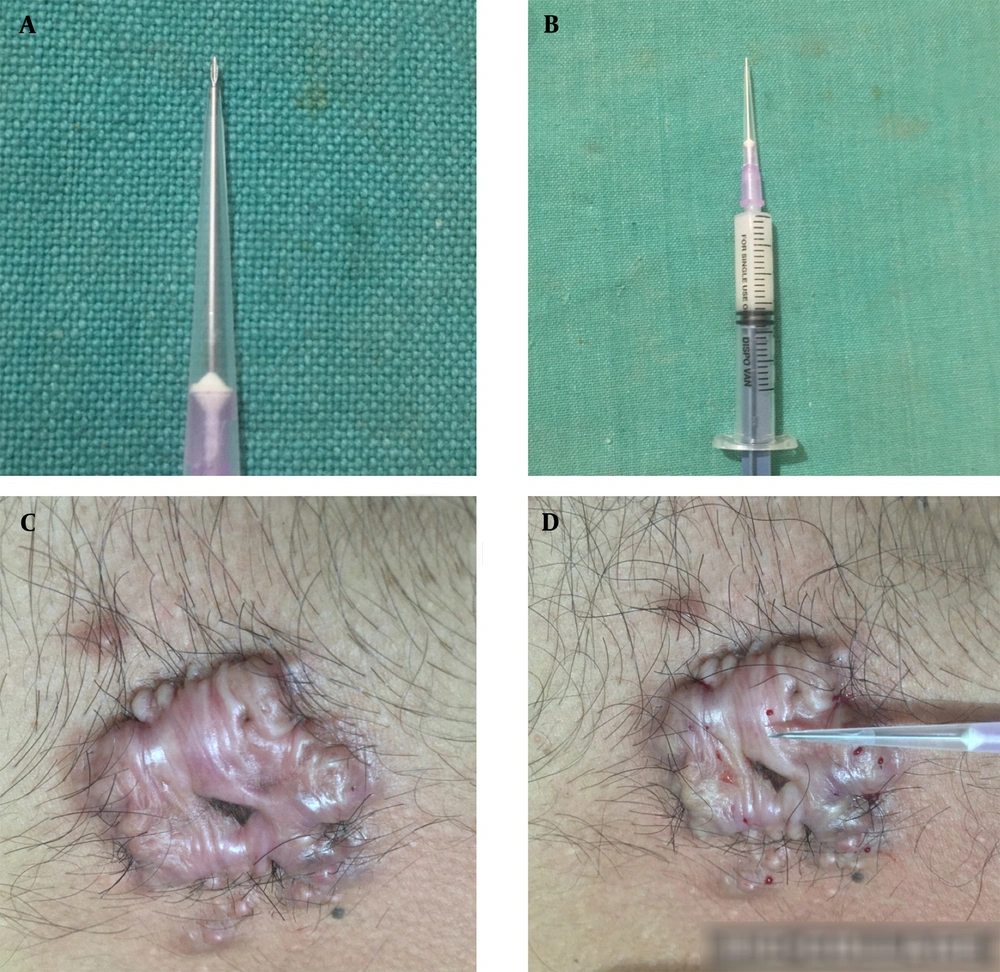
Intralesional injection therapy is a common treatment for hypertrophic scars and keloid in dermatology (1). This injection is frequently given without a needle guard. There is a risk of deep tissue injury during injection in this situation. The needle has been guarded with its cap for safe intralesional therapy for keloid (2). The author describes an alternative method for creating a conical needle guard from a micropipette tip for safe and effective intralesional therapy.
To guard the needle, the distal part of the disposable micropipette tip is cut with a surgical blade to the required length. The cut tip is then attached to the hypodermic needle. After mounting the guard, approximately 2 mm or more of the needle shaft, excluding the bevel of the needle (depending on the height of the keloid from the skin surface), should be kept outside the guard to inject the drug at a controlled depth and to avoid drug leakage. It is simple to make an approximation/alignment of the needle with the surface of the keloid and hypertrophic scar lesions in any plane, such as horizontal, inclined, or vertical, by using a guard with a conical shape as opposed to a cylindrical one (Figure 1A and B). As a result, the customized micropipette tip is an appropriate guard for intralesional therapy for keloid and hypertrophic scars (Figure 2A - D). It may be used for intralesional treatment of alopcecia areata, vitiligo, and other skin disorders after bending the guarded needle by 15 to 20 degrees for better alignment with the skin surface.