1. Background
Chronic pain (CP) is one of the most significant global health challenges due to its high prevalence, impact on disability, and economic burden (1). Notably, a substantial proportion of CP sufferers are women (2). The recognition of sex and gender disparities in CP prevalence has been well-established, with numerous epidemiological studies highlighting differences across various CP conditions, including back pain, musculoskeletal pain, headaches, and arthritis (3). Murray et al. (4) reviewed 43 studies involving 97,437 young adults from 22 countries, finding an overall pooled prevalence of CP in young adults at 11.6%, indicating that approximately 1 in 9 young adults worldwide experience CP.
In recent years, there has been increasing attention to the link between CP and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) (5). Post-traumatic stress disorder is a common anxiety disorder that can arise after exposure to traumatic events such as accidents, violence, or war (6). It is characterized by three primary symptom clusters: Hyperarousal, intrusive memories of the traumatic event, and avoidance of situations and stimuli associated with the event (7). Post-traumatic stress disorder is associated with an increased risk of both psychological and physical health issues, often leading to significant physical, occupational, and social impairment (8). Pain is frequently reported among the physical symptoms of PTSD, regardless of the type of trauma experienced (9).
Åkerblom et al. (10) found that individuals with both CP and PTSD exhibited higher levels of pain severity, pain interference, depression, and cognitive fusion, along with lower levels of pain-related acceptance and committed action compared to those without PTSD. Similarly, Akhtar et al. (11) reported that 28% of 300 consecutive CP patients screened positive for PTSD, a rate higher than that of the general population. Those who screened positive were typically younger and experienced greater pain intensity than those without PTSD.
The biopsychosocial approach to CP is widely regarded as the most effective framework for understanding and managing CP (12). According to this model, numerous studies have emphasized the impact of CP on psychosocial factors, including psychological distress (PD), such as anxiety, depression, and stress (13, 14). The duration of pain and individuals' beliefs about its persistence play key roles in shaping their experience of pain and PD (15). Despite the chronic nature of pain and its significant life disruptions, the role of psychological time remains largely unexplored (16). Psychological distress, a key psychological concern linked to pain, affects various health outcomes (17). It encompasses a range of emotional states, primarily those related to depression and anxiety (18). As a concept, distress is positively associated with both poor mental health and clinical psychological disorders, making it an important measure in assessing general well-being (19).
Beyond its connection to pain, PD emerges as a significant factor in absenteeism and recovery (20). Unseld et al. (21) found that 63.5% of cancer patients experienced pain, with 31.2% showing significant PTSD, and notable levels of depression, anxiety, and distress in 13.9%, 15.1%, and 25.3% of patients, respectively. Women were more likely to report these symptoms. Dany et al. (18) also identified a significant relationship between PD and CP, finding that patients with disorganized thoughts reported higher distress and greater pain intensity.
Patients with CP face an uncertain future, unsure of when or if they will find relief from their illness and the associated disability (22). This ambiguity can lead to feelings of learned helplessness (LH) and ineffective coping mechanisms (23). Learned helplessness is particularly important in understanding the high rates of depression and functional limitations observed among CP patients (24). It is characterized by an attributional style in which individuals perceive minimal control over life events, leading them to respond passively to challenges (25, 26). Patients may feel incapable of effecting change despite their best efforts, resulting in a passive attitude toward their illness (27). This feeling often stems from multiple failed attempts to manage their pain. In CP cases, even with proper treatment, results may not be rapid or satisfactory (28). Learned helplessness closely correlates with depression due to their shared attributional process regarding negative events (29).
As a result, individuals experiencing negative situations may attribute them to their inability to manage the situation, believing this inability is unlikely to improve (30). Moyano et al. (25) conducted a cross-sectional study comparing LH and perceived self-efficacy in patients with fibromyalgia (FM) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA), examining their associations with functional disability, pain levels, and fatigue. Among 215 patients, FM patients exhibited higher levels of LH and depression but lower self-efficacy than RA patients. Similarly, Nowicka-Sauer et al. (24) explored the relationship between LH and illness perception, depression, and anxiety among lupus patients. They found that LH was positively correlated with illness perception, depression, and anxiety, suggesting a connection between LH and psychological factors in lupus patients.
2. Objectives
This study investigates the relationship between PTSD, PD, and LH in individuals with CP.
3. Methods
3.1. Study Design
This was a descriptive-comparative study.
3.2. Participants
The statistical population of this study consisted of patients with CP referred to pain clinics and physiotherapy centers in Tehran in the years 2022 - 2023.
3.3. Sampling
G*Power software version 3.1.9.2 was used to calculate the sample size (31). A sample size of 120 individuals was determined for each group, accounting for a 10% dropout rate, which resulted in 150 individuals per group. The inclusion criteria for the study were experiencing CP in the past two years, not having received psychological interventions, and personal satisfaction with participation. Exclusion criteria included pain exacerbation, incomplete questionnaire responses, and random answering of questions.
3.4. Scales
3.4.1. Post-traumatic Stress Disorder Checklist
The PTSD checklist was developed based on the diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders-5 (DSM-5). It is a self-report measure used to screen patients with PTSD from both normal individuals and other patients (32). The diagnostic cut-off point is 50. The reliability coefficients for Cronbach's alpha and test-retest reliability for the entire scale and its subscales were all higher than 0.70, indicating satisfactory reliability (32). In this study, Cronbach's alpha coefficients for re-experiencing, avoidance, negative alterations, hyper-arousal, and emotional numbness were 0.89, 0.83, 0.79, 0.89, and 0.89, respectively.
3.4.2. The Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Scale
The short form of the PD Scale consists of 21 items and 3 subscales: Depression, anxiety, and stress (33). Respondents are asked to rate the extent to which they experienced each condition in the past week using a 4-point intensity/frequency scale. Lovibond and Lovibond (33) reported Cronbach's alpha coefficients of 0.93 for the entire scale, and 0.88, 0.82, and 0.90 for the subscales of depression, anxiety, and stress, respectively. In the present study, the Cronbach's alpha coefficients for depression, anxiety, and stress were 0.87, 0.81, and 0.89, respectively.
3.4.3. Learned Helplessness Questionnaire
This questionnaire, designed by Quinnells and Nelson (34), consists of 20 items. Participants respond to the questions using a 4-point Likert Scale, ranging from 1 (completely disagree) to 4 (completely agree). Quinnells and Nelson (34) reported the questionnaire's validity as 0.79, with a reliability coefficient and Cronbach's alpha of 0.86. When compared with other established questionnaires, such as the Beck Depression Scale, the correlation coefficient was 0.25, while it was 0.62 with a self-esteem scale. The reliability of the scale was reported as 0.85, and the Cronbach's alpha coefficient was 0.86.
3.5. Data Collection
For data collection in this research, necessary coordination was first established with relevant pain clinics and physiotherapy centers. The research questionnaires were then distributed among CP patients, with the study objectives thoroughly explained to them. After completing the sampling process, patients who scored higher than 50 on the PTSD Checklist (PCL) were categorized into the high-grade PTSD group, while the remaining patients were placed in the low-grade PTSD group.
3.6. Data Analysis
The data analysis was conducted using SPSS-24 software, and multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) was employed to analyze the data (P < 0.005).
3.7. Ethical Consideration
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Tarbiat Modares University (code: IR.MODARES.REC.1401.197).
4. Results
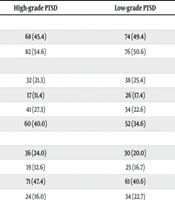
A total of 300 patients with CP were analyzed, consisting of 150 patients with high-grade PTSD (mean age = 30.86, SD = 6.79) and 150 patients with low-grade PTSD (mean age = 29.38, SD = 7.08). The age range for patients with CP was 18 to 45 years (Table 1). The demographic data in Table 1 show no statistically significant differences between the two groups (P > 0.005).
| Variables | High-grade PTSD | Low-grade PTSD | P-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marital status | P > 0.053 | ||
| Single | 68 (45.4) | 74 (49.4) | |
| Married | 82 (54.6) | 76 (50.6) | |
| Types of CP | P > 0.071 | ||
| Migraine | 32 (21.3) | 38 (25.4) | |
| FM | 17 (11.4) | 26 (17.4) | |
| Neck pain | 41 (27.3) | 34 (22.6) | |
| Musculoskeletal disorder | 60 (40.0) | 52 (34.6) | |
| Education | P > 0.069 | ||
| Diploma | 36 (24.0) | 30 (20.0) | |
| Associate degree | 19 (12.6) | 25 (16.7) | |
| Bachelor | 71 (47.4) | 61 (40.6) | |
| Master degree | 24 (16.0) | 34 (22.7) |
Abbreviation: CP, Chronic pain; FM, fibromyalgia
a Values are expressed as No. (%).
Table 2 presents the mean and standard deviation (SD) for the two groups. To assess the normality of the data, the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test was conducted, and the results confirmed that the assumption of normality was met (P > 0.05).
| Variables | High-grade PTSD | Low-grade PTSD | K-S Z | P-Value b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTSD | 70.42 ± 5.68 | 33.71 ± 3.7 | 0.094 | 0.062 |
| Depression | 16.64 ± 4.41 | 10.09 ± 3.32 | 0.086 | 0.057 |
| Anxiety | 16.88 ± 4.14 | 10.16 ± 3.47 | 0.106 | 0.069 |
| Stress | 18.28 ± 3.34 | 11.21 ± 2.96 | 0.079 | 0.051 |
| LH | 71.59 ± 12.63 | 42.93 ± 1.47 | 0.114 | 0.072 |
Abbreviations: K-S Z, Kolmogorov-Smirnov test; PTSD, post-traumatic stress disorder; LH, learned helplessness.
a Values are expressed as mean ± SD.
b P = K-S Z Significance level.
To assess differences in depression, anxiety, stress, and LH between CP patients with and without PTSD, a multivariate analysis of variance was performed. Levene's test confirmed homogeneity of variance across groups (P > 0.005), ensuring that the research variables had equal variance. The M Box test demonstrated the equality of the covariance matrix between the two groups (Box's M = 36.84, F = 1.52, P > 0.005), confirming this assumption. The results (Wilks' Lambda = 0.251, F = 219.95, P < 0.001, and ETA = 0.74) indicated a significant effect of the independent variable on the dependent variables. A one-way analysis of variance was used to identify which variables showed significant differences between the groups. The results of the one-way analysis of variance are presented in Table 3.
| Variables | Type III Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. | Partial Eta Squared | Observed Power |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depression | 32220.96 | 1 | 32220.96 | 211.09 | 0.001 | 0.415 | 1.000 |
| Anxiety | 3386.88 | 1 | 3386.88 | 231.06 | 0.001 | 0.437 | 1.000 |
| Stress | 3745.33 | 1 | 3745.33 | 374.85 | 0.001 | 0.557 | 1.000 |
| LH | 61604.67 | 1 | 61604.67 | 457.79 | 0.001 | 0.606 | 1.000 |
Abbreviations: LH, learned helplessness.
According to Table 3, the F statistic for depression (F = 211.09), anxiety (F = 231.06), stress (F = 374.85), and LH (F = 457.79) is significant at the 0.001 level. These findings indicate a significant difference between the two groups in PD and LH (P < 0.001). This suggests that CP patients with high-grade PTSD experience significantly higher levels of depression, anxiety, stress, and LH during their pain.
5. Discussion
This study explores the relationship between PTSD, PD, and LH in individuals with CP. The findings reveal a significant association between PTSD and elevated levels of PD, including depression, anxiety, and stress, among CP patients. Consistent with previous research by Dany et al. (18) and Unseld et al. (21), our results highlight the strength of this connection in the context of CP management.
Our study shows a significant link between CP and PTSD, indicating that individuals with CP who have high-grade PTSD are more likely to experience heightened PD, such as depression, anxiety, and stress (15). This finding underscores the complex relationship between physical and psychological health in CP patients. The association aligns with existing literature that suggests individuals with a history of trauma are at increased risk for psychological symptoms when dealing with CP (20). Our findings further support the notion that trauma can exacerbate PD in those with CP (11). These results emphasize the importance of addressing the psychological well-being of CP patients, particularly those with comorbid PTSD (16).
Healthcare providers should carefully assess and manage psychological symptoms in CP patients, as these symptoms significantly affect overall quality of life and treatment outcomes. Future interventions for CP management should take into account the presence of PTSD and related PD (17). Integrated approaches that address both the physical and psychological aspects of pain management may be especially effective in improving outcomes for CP patients with comorbid PTSD (18).
Additionally, our investigation revealed heightened levels of LH among CP patients with elevated PTSD, consistent with prior research by Nowicka-Sauer et al. (24) and Moyano et al. (25). This underscores the strong relationship between CP and PTSD comorbidity. The simultaneous presence of CP and PTSD may amplify feelings of helplessness, exacerbating the challenges of managing CP (30). Individuals with both conditions may struggle with a sense of powerlessness and diminished control over their pain and overall well-being (25). These findings highlight the importance of addressing the psychological dimension in CP management, particularly for patients with coexisting PTSD. Targeted interventions that reduce LH through empowerment strategies and effective coping mechanisms are essential for improving outcomes and quality of life in this population (22).
Our findings contribute to the growing body of evidence supporting integrated approaches to CP management that recognize and address the psychological effects of trauma (29). By focusing on LH in CP patients with PTSD, healthcare providers can offer more comprehensive support, helping individuals better manage their pain and enhance their well-being (10).
However, this study has certain limitations. The sample was drawn exclusively from patients referred to pain and physiotherapy clinics in Tehran, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to the broader CP population. Additionally, while the descriptive causal-comparative methodology provides insights into associations, it does not establish causality. Longitudinal studies could offer a more nuanced understanding of the temporal relationships between PTSD, PD, and LH in individuals with CP. Moreover, the reliance on self-report measures for assessing PTSD, PD, and LH may introduce response bias and may not capture the full complexity of these constructs.
5.1. Conclusions
This research provides valuable insights into the relationship between PTSD, PD, and LH in individuals with CP. It highlights the need to address psychological aspects in the evaluation and treatment of CP. Integrating interventions focused on alleviating PTSD symptoms and promoting adaptive coping mechanisms could significantly enhance the well-being and quality of life for CP sufferers. Further research is needed to explore the mechanisms underlying these associations and to develop targeted interventions tailored to this demographic's specific needs.