1. Background
Group B streptococcus (GBS), also known as Streptococcus agalactiae, is a normal flora of human body. In adult people, it most commonly resides in the vagina (particularly in pregnant women), urinary tract, and colon. GBS is among the most prevalent and the most asymptomatic colonizing agents in pregnant women and a common cause of neonatal sepsis and postpartum fever (1, 2). Maternal GBS colonization increases the risk of neonatal GBS colonization and infection during birth so that around 60% of the neonates born to GBS-colonized women are colonized with GBS (3, 4).
GBS was described in 1930 in England as the cause of the postpartum fever. It increases the risk of preterm delivery and prolongs the membrane rupture time. Preterm delivery among women with GBS is a risk factor for early-onset neonatal sepsis. GBS can also cause a wide range of infections among neonates such as septicemia, meningitis, cellulitis, conjunctivitis, pneumonia, adenitis, and otitis. Despite antimicrobial treatments, sepsis and meningitis are associated with high mortality rates (5-7).
GBS rectovaginal colonization is affected by different factors such as age, number of parities, and socioeconomic status. Moreover, GBS can be transmitted to hospitalized women by healthcare providers, particularly in case of heavy workload. Other factors behind GBS rectovaginal colonization are race, history of intrauterine contraceptive device use, and the time at which samples are collected during pregnancy for laboratory studies (8-10).
The American congress of obstetricians and gynecologists and the center for disease control and prevention highlighted the relevance of screening programs for identifying and treating GBS colonization among pregnant women (8, 11). General screening for pregnant women is based on genital culture, particularly for those who have risk factors for GBS colonization. Antibiotic prophylaxis for pregnant women with GBS rectovaginal colonization can reduce the prevalence of neonatal GBS infection (12, 13).
Right decisions about the best strategies for neonatal sepsis prevention and GBS rectovaginal management necessitate authoritative information about the local prevalence of GBS colonization and its contributing factors. Therefore, the present study was conducted to assess the prevalence of GBS rectovaginal colonization and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern among pregnant women.
2. Methods
This descriptive-analytical study was conducted from June 2013 to June 2014 in 500 pregnant women with a gestational age of thirty weeks or more who were admitted to the maternity unit of Valiasr hospital, Birjand, Iran. Women were included if they had not received antibiotics in the past four weeks before the study, had not used vaginal creams during the past week before the study, and had no genital herpetic lesions.
Recruited women were initially asked to complete a demographic and clinical characteristics questionnaire, which contained items on age, gestational age, number of parities, place of residence, educational status, history of urinary tract infection, history of vaginal infection, and history of drug abuse. Then, the trained staff collected rectal and vaginal samples from each woman using sterile cotton swabs. The samples were transported to a university laboratory in one cubic centimeter of Todd Hewitt broth. In the laboratory, the samples were cultured in blood agar medium and incubated at 37°C for 24 - 48 hours. Colonial growths in the medium (both with and without beta hemolysis) were tested for the chemical characteristics of GBS. The definite diagnosis of GBS was established based on routine biochemical and microbiological tests such as cotrimoxazole sensitivity, bacitracin sensitivity, hippurate hydrolysis, and culture on bile esculin agar (14).
Antimicrobial susceptibility was tested via the agar disc diffusion method using Mueller-Hinton culture medium containing 5% - 10% sheep blood based on the guidelines of the clinical and laboratory standards institute (15). The antibiotic discs used in this study were penicillin (10 µg), ampicillin (10 µg), cefazolin (30 µg), clindamycin (2 µg), erythromycin (15 µg), tetracycline (30 µg), trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (1.25/23.75 µg), and nitrofurantoin (300 µg), all manufactured by the MAST Co., England. Streptococcus pneumonia strain ATCC 49619 was used as a control.
The data were analyzed using the SPSS software (v. 18.0) by running the Chi-square and Fisher exact tests at a significance level of less than 0.05.
All components and parts of this study were approved by the ethics committee of Birjand University of Medical Sciences, Birjand, Iran (with the code of 92.02.07). We provided all participants with information about the study aim and asked them to provide informed consent for participation. The ethics committee of Birjand University of Medical Sciences approved the ethical considerations of the present study under No. 920207.
3. Results
In total, 500 pregnant women were studied in this survey. They were aged 16 - 37 with a mean of 26.13 ± 4.76. Most women were multigravida (70.2%) and their number of parities was 2.06 ± 0.93, on average. They mostly held a secondary diploma or lower degrees (83.8%) and lived in urban areas (78.6%). Only 22 women (4.4%) used an intrauterine contraceptive device and eleven (2.2%) used opium derivatives. The prevalence of urinary tract and vaginal infections among the participants was 18% and 10%, respectively. Histories of intrauterine fetal death and neonatal death were reported by 3.6% and 1.8% of the participants, respectively. Around 79% of the participants had a gestational age of 38 - 40 weeks and 97.8% had a mean membrane rupture time fewer than eighteen hours. The mean of membrane rupture time was 6.71 ± 7.64 hours. Tables 1 and 2 summarize participants’ demographic and clinical characteristics.
| Risk Factors | Positive Culture | Negative Culture | Total | P Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, y | 0.005b | |||
| < 27 | 6 (2.4) | 243 (97.6) | 249 (100) | |
| ≥ 27 | 20 (8) | 231 (92) | 251 (100) | |
| Educational status | 0.034c | |||
| Illiterate | 5 (16.7) | 25 (83.3) | 30 (100) | |
| Primary and secondary | 11 (5.9) | 176 (94.1) | 187 (100) | |
| Secondary diploma | 8 (3.4) | 224 (96.6) | 232 (100) | |
| University degrees | 2 (3.9) | 49 (96.1) | 51 (100) | |
| Place of residence | 0.092b | |||
| Urban areas | 17 (4.3) | 376 (95.3) | 393 (100) | |
| Rural areas | 9 (8.4) | 98 (91.6) | 107 (100) | |
| History of drug abuse | 0.05b | |||
| Yes | 2 (18.2) | 9 (81.8) | 11 (100) | |
| No | 24 (4.9) | 465 (95.1) | 489 (100) |
aValues are expressed as No. (%).
bThe Chi-square test.
cThe Fisher exact test.
| Risk Factors | Positive Culture | Negative Culture | Total | P Valueb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of parities | 0.003 | |||
| Primigravida | 1 (0.7) | 147 (99.3) | 149 (100) | |
| Multigravida | 25(7.1) | 326 (92.9) | 351 (100) | |
| Membrane rupture time, h | 0.05 | |||
| < 18 | 24 (4.9) | 465 (95.1) | 489 (100) | |
| > 18 | 2 (18.2) | 9 (81.8) | 11 (100) | |
| History of intrauterine fetal death | 0.026 | |||
| Yes | 3 (16.7) | 15 (83.3) | 18 (100) | |
| No | 23 (4.8) | 459 (95.2) | 482 (100) | |
| History of neonatal death | < 0.001 | |||
| Yes | 3 (23.3) | 6 (66.7) | 9(100) | |
| No | 23 (4.7) | 468 (95.3) | 491(100) | |
| Intrauterine contraceptive device | < 0.001 | |||
| Yes | 9 (40.9) | 13 (59.1) | 22 (100) | |
| No | 17 (3.6) | 461 (96.4) | 478 (100) | |
| History of vaginal infection | < 0.001 | |||
| Yes | 18 (36) | 32 (64) | 50 (100) | |
| No | 8 (1.8) | 442 (98.2) | 450 (100) | |
| History of urinary tract infection | < 0.001 | |||
| Yes | 17 (18.9) | 31 (81.1) | 90 (100) | |
| No | 9 (2.2) | 401 (97.8) | 410 (100) |
aValues are expressed as No. (%).
bThe results of Chi-square test.
5.2% of the cultures were positive for GBS. GBS rectovaginal colonization was significantly more prevalent among pregnant women who were aged more than 27 (P = 0.005), had a history of drug abuse (P = 0.050) and held a secondary diploma or lower degrees (P = 0.032). However, women who lived in rural and urban areas did not significantly differ from each other respecting GBS rectovaginal colonization (P > 0.92; Table 1). On the other hand, GBS rectovaginal colonization was found to have significant relationships with the history of using intrauterine contraceptive device (P < 0.001), history of vaginal infection (P < 0.001), history of urinary tract infection (P < 0.001), history of intrauterine fetal death (P = 0.026), and history of neonatal death (P < 0.001). Moreover, the prevalence of GBS rectovaginal colonization was significantly higher among multigravida women (P = 0.003) and those with a membrane rupture time of more than eighteen hours (P = 0.050) (Table 2).
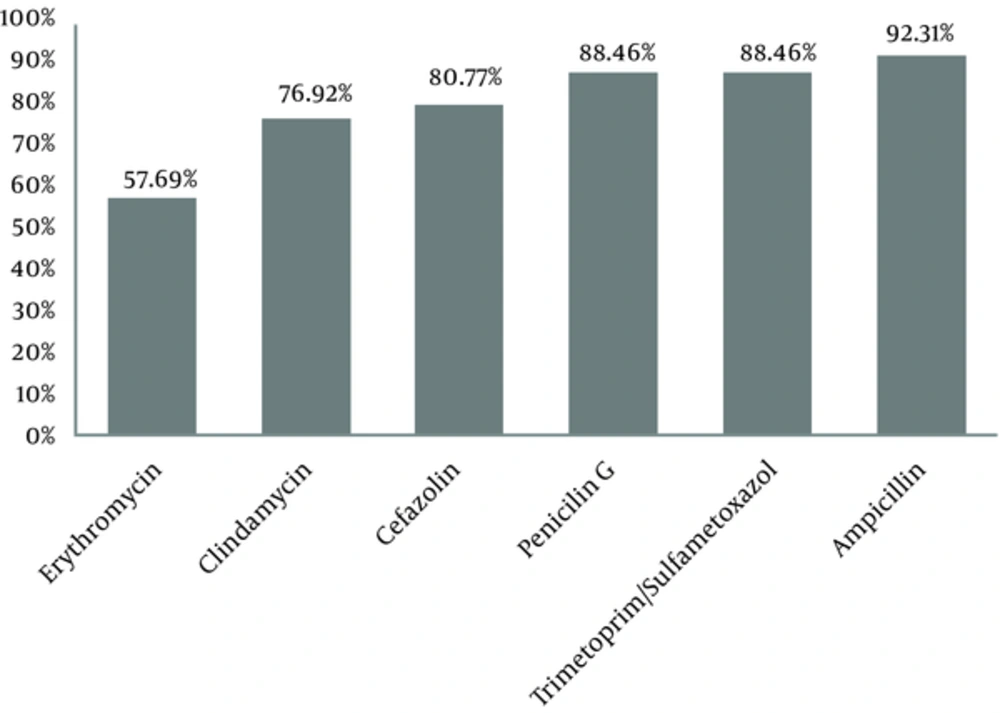
The results of antimicrobial susceptibility testing also showed that GBS was susceptible mainly to ampicillin (92.2%), trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (88.5%), and penicillin G (88.5%) (Figure 1). The intermediate antimicrobial resistance of GBS was 19.2% against erythromycin, 7.6% against cefazolin, penicillin G, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and 3.9% against ampicillin and clindamycin.
4. Discussion
GBS is found in the vagina and the colon of 15% - 40% of healthy women. GBS rectovaginal colonization during pregnancy is directly related to neonatal infections. Therefore, screening pregnant women for GBS colonization and determining antimicrobial susceptibility are the essential prerequisites for the prevention and management of streptococcal infections among both women and their neonates (16-18).
The study findings revealed that the prevalence of GBS rectovaginal colonization was 5.2%. This finding is in line with the findings of previous studies that reported GBS colonization prevalence of 5.3% and 8.4% in Tehran (19, 20), 9.6% in Tabriz (21), and 9.2% in Kerman (22), Iran. However, two studies reported that the prevalence of GBS colonization was as high as 20.6% in Tehran (23) and 26.7% in Hamadan (24), Iran. This wide difference in the prevalence of GBS colonization can be due to the differences in the socioeconomic and demographic characteristics of the samples in the studies as well as the differences in the laboratory methods used for colonization testing.
Our findings also showed that the prevalence of GBS colonization was higher among women aged 27 or more. However, previous studies reported that GBS colonization was more prevalent among younger women (25, 26). Moreover, studies showed that the prevalence of GBS infections and early-onset neonatal sepsis was significantly higher among the neonates of adolescent mothers (27, 28). This contradiction between the findings of the studies may be due to the greater number of parities among our participants.
We also found the higher prevalence of GBS colonization among women who held a secondary diploma or lower degrees, particularly illiterate women. Some previous studies reported the same finding (26, 29), while some others reported no significant relationship between educational status and GBS colonization (19, 30). Another finding of the present study was the significantly higher prevalence of GBS colonization among women who had a history of drug abuse. This finding may be due to the significant correlations of drug abuse and GBS colonization with educational and socioeconomic status. Of course, we could not find any study respecting the relationship of drug abuse with GBS colonization among pregnant women.
The study findings also indicated the significant relationships of GBS colonization with the use of an intrauterine contraceptive device as well as the histories of intrauterine fetal death and neonatal death. Moreover, the prevalence of GBS colonization was significantly greater among multigravida women than among their primigravida counterparts. An earlier study also reported the same finding (25). Moreover, prolonged membrane rupture time in the present study was associated with higher GBS colonization prevalence. Similarly, previous studies showed that prolonged time of membrane rupture is associated with increased risks of GBS colonization and neonatal sepsis (22, 26). We also found a higher prevalence of GBS colonization among women with a history of vaginal and urinary tract infections. An earlier study also reported the same finding (26).
Our findings also showed that the antimicrobial susceptibility of GBS to all the assessed antibiotics was more than 50%, with the highest susceptibility to ampicillin (92.2%), trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (88.5%), and penicillin G (88.5%), in sequence. This is in line with the findings of previous studies (31-33). Therefore, these antibiotics can treat GBS colonization in pregnant women and prevent GBS colonization among susceptible pregnant women.
4.1. Conclusions
The prevalence of GBS rectovaginal colonization among pregnant women is 5.2%. GBS colonization among these women is related to different factors. Ampicillin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and penicillin G are the most effective antibiotics for the management of GBS colonization in this population. Therefore, these antibiotics can be used to prevent or manage GBS colonization among pregnant women, particularly during delivery. Future studies are recommended to assess GBS colonization using more advanced laboratory methods such as polymerase chain reaction.