1. Context
Reflexology is an ancient healing method (1) and a popular type of Complementary and Alternative Medicine (CAM), which can be easily applied even by the patient and has almost no side-effects (2). In this method, the feet (often the foot soles) represent the entire body. Applying controlled pressure on particular reflex zones on the feet can stimulate their interconnected internal organs (3) .The purpose of this treatment is to create balance in the function of the body systems (4) and facilitate homeostasis (5).
Constipation is a common gastrointestinal disorder in both adults and children (6). The prevalence of constipation is reported to be as high as 30% in the general population (7). Constipation is associated with a low quality of life (8) and some undesirable symptoms (9). It is generally divided into a primary (idiopathic) and a secondary type. Primary constipation is categorized as 1) Normal transit, 2) Slow transit, a prolonged transit time in the colon, 3) Dyssynergic constipation, an abnormal rectal discharge, or functional impairment with no anatomical or physiological etiology (10). Secondary constipation may be associated with endocrine, metabolic, or neurologic diseases or may be due to the continuous use of laxatives and other drugs (10-12).
The first-line treatment of constipation involves increasing dietary fiber and fluid consumption and proper use of laxative use (13, 14). However, laxatives are expensive and have some side-effects (15). As a CAM, reflexology has been used to improve constipation symptoms (4). Previous systematic reviews on the subject have merely used abdominal massage or hand reflexology (16, 17). Some high-quality Controlled Trials (CTs) have measured the effect of foot reflexology on the constipation symptoms. According to some authors, there were no systematic reviews of clinical trials on the effect of foot reflexology on constipation under any circumstances.
2. Objectives
The present systematic review was conducted to critically evaluate the data from Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) of foot reflexology as a treatment for constipation due to any medical conditions.
3. Methods
This systematic and meta-analytical study was conducted based on PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses).
3.1. Inclusion Criteria
The PICOS (Participant, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome, study design) framework wa used as the tool for the inclusion of articles. The ‘Population’ consisted of pediatric, adult, or older patients with a diagnosis of constipation receiving foot reflexology. The population was compared with ‘Controls’ receiving no placebo or other treatments. The ‘Intervention’ consisted of foot reflexology. The primary ‘Outcome’ in this study consisted of constipation symptoms, which were measured using the Modified Constipation Assessment Scale (MCAS), the Constipation Assessment Scale (CAS) that is a two-part questionnaire inquiring about children’s defecation characteristics, the Clayden Constipation Questionnaire (CCQ), and the Bristol Stool Scale. In this systematic review, we also included the randomized, controlled, and clinical trials which have evaluated the effect of foot reflexology on constipation symptoms.
3.2. Exclusion Criteria
Two reviewers independently selected the studies based on the pre-defined eligibility criteria. The exclusion criteria for the study consisted of the absence of a comparison group and receiving any other type of reflexology or massage treatment other than foot reflexology. We also excluded the editorials, reviews, books, case reports, case series, letters to editors, qualitative studies, and short communications. There was no limitation for the length of follow-up or treatment.
3.3. Search Strategy
The English databases (e.g., Web of Science, Cochrane Library on the Wiley platform, PubMed, Scopus, Embase, and Google Scholar) and the Iranian database (e.g., Scientific Information Database and Magiran) were systematically searched for articles published without time limitations until June 2020. The MESH terminology used in the search included "foot reflexology" OR "foot massage" combined with "constipation" (Table 1). Also, a manual search of the reliable journal databases was performed, and the references in all the included articles were assessed for additional related papers. To search for unpublished papers (grey literature), we assessed European Association for Grey Literature Exploitation (EAGLE) and Health Care Management Information Consortium (HMIC). The electronic search strategy is available in Appendix 1. The investigated data were transferred to the reference management software of Endnote to delete duplicate records.
| Database | Search Strategy |
|---|---|
| PubMed | (((foot reflexology) AND (constipation)) OR ((foot massage) AND (constipation))) AND (randomized controlled trial) |
| Scopus | ((constipation and foot massage AND randomized controlled trial) OR (foot reflexology AND constipation and randomized controlled trial)) |
3.4. Data collection
We used a pre-specified form for the data extraction, including the name of authors, publication year, country, type of clinical trial, participant characteristics, age range, sample size in the intervention and comparison groups, measurement tools, follow-up time, intervention, and results.
3.5. Quality Assessment of Included Studies
The methodological quality of the articles was assessed individually by two reviewers via the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool (18), and any sorts of disagreements were resolved by the third researcher. The methodological information extracted for the assessment of internal validity included random allocation, allocation concealment, participants or personnel blinding, blinding of data assessor, number and reasons for participant’s loss to follow up, and the use of validated outcome measures (19). Since the number of included studies in the meta-analysis was lower than 10 studies, the graphical or statistical methods were not used to evaluate the publication bias (20). However, due to the language limitation, publication bias was considered high risk.
3.6. Statistical Analysis
The pooled Standardized Mean Difference (SMD) and 95% Confidence Interval (95% CI) were determined for the mean score of constipation. Sub-group analysis was conducted according to the comparison group (Golgand or routine care). The Cochrane Q-test and the I2 index were used to assess the heterogeneity (21). Due to high heterogeneity, the random effect model was used instead of the fixed effect model. Whenever more than ten studies are entered into a meta-analysis, the possibility of publication bias should also be investigated (22). The meta-analysis was conducted using RevMan software version 5.3. (Cochrane Collaboration, Copenhagen, Denmark) 5.0 (Cochrane Collaboration, Copenhagen, Denmark).
4. Results
4.1. Results of the Literature Search
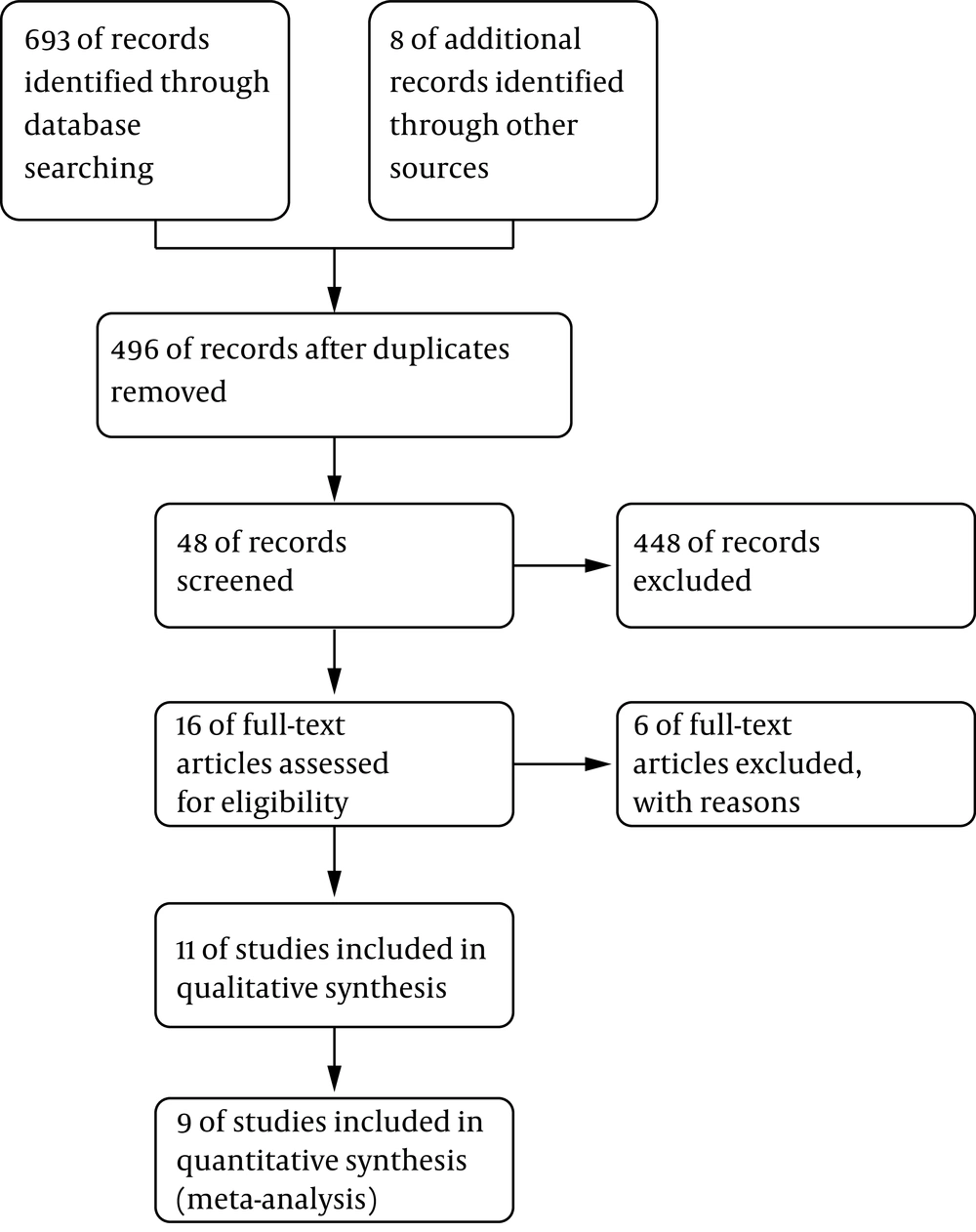
The search led to the retrieval of 701 articles. After reviewing the article titles or abstracts, the full text of 17 potentially eligible studies was evaluated, and six articles were excluded due to: 1) Absence of a comparison group (23, 24), 2) Being descriptive (5), 3) The participants receiving another type of reflexology (abdominal massage or other type of massage) (25-27). Finally, 11 articles (28-38) were entered into this study, out of which nine studies (a total of 611 participants) entered the meta-analysis. The trials were conducted in different countries and their treatment period ranged from six days to 12 weeks (Figure 1).
4.2. General Characteristics
Two studies on pregnant women (28, 29), three studies on children (30-32), one study on patients with multiple sclerosis (33), three studies on the elderly (34-36), and two studies were conducted on adults (37, 38). The participants’ age differed from one to 65 years. The sample size of the studies varied from 34 (37) to 184 (32). The follow-up periods ranged from four to 12 weeks, and the countries of the selected studies included Iran, Turkey, and the UK. The outcome measures consisted of subjective outcomes, including constipation score and stool consistency; the objective outcome included bowel frequency. The treatments were slightly different from each other, and the overall frequency of treatment ranged from six to 84 sessions. In two of the studies, we used oil or cream for foot massage (30, 31). Instructions were given for foot massage in one of the studies (32). In two studies, the control group administered the same procedure as the intervention group except that it did not receive foot reflexology (35, 37). The data collection tool used in the studies by Tovey et al. and Elbasan et al. was the Modified Constipation Assessment Scale (MCAS), and the level of constipation improvement was reported as mean and standard deviation (31, 37). Ghaffari et al. (28), Seyyedrassoli et al. (38), Fakhrzade et al. (35), Mohammadzadeh Moghadam et al. (36), Sehhatti et al. (29), Sajadi et al. (33), also described the constipation score using the Constipation Assessment Scale (CAS) as mean and standard deviation. Inkaya described the constipation score using the Constipation Severity Instrument (CSI) (34). Canbulat Sahiner et al. employed a two-part questionnaire developed by the researchers and reported the stool number and stool consistency as categorical variables in number and percentage (30). Gordon applied the Clayden Constipation Questionnaire for assessing constipation characteristics and the Bristol Stool Scale for evaluating bowel movements and reported the results as mean and standard deviation (32). In all the studies, the intervention group received foot reflexology treatment. Meanwhile, in one trial, the intervention and control groups both received a neurodevelopmental treatment program. In the study of Mohammadzadeh Moghadam et al., Golghand was administered as the comparison group (36). In one trial, the control group received no treatments (28). In one study, there were three study groups; one received foot reflexology, the other received abdominal massage, and the third one received no interventions except the routine care (38). In one trial, nonspecific massage was given to the control group (35). In another trial, both the intervention and control groups received toilet/diet/motivation training (30), and in another trial, three groups were assessed: Group 1 (routine care), Group 2 (foot massage along with the routine care), and Group 3 (foot reflexology along with the routine care) (32).
The results of the study by Elbasan et al. demonstrated that despite the effectiveness of reflexology in improving the symptoms of constipation, the difference between the group receiving reflexology combined with neurodevelopmental therapy and the group receiving neurodevelopmental therapy alone was not statistically significant (31). The results of the studies by Ghaffari et al. (28), Sajadi et al. (33), Sehhatti et al. (29), and Inkaya et al. (34) showed significant differences in the mean constipation scores after reflexology. Seyyedrassoli et al. (38) found that constipation severity reduced significantly with foot reflexology compared to abdominal massage and routine care from day three to six after the treatment. Foot reflexology improved the symptoms of constipation better than abdominal massage from day three to six after the treatment, but the difference was not statistically significant. There were critical differences between foot reflexology and abdominal massage in comparison with routine care in terms of constipation symptoms from day three to six after the intervention (38). According to the results of a study by Fakhrzade et al., the difference was significant in the severity of constipation between the foot reflexology and nonspecific massage groups (35). The results of Tovey’s trial did not show any significant differences in constipation improvement between the foot reflexology and control groups (37). The results of a study by Mohammadzadeh Moghadam et al. showed that the difference between the golghand and foot reflexology groups was statistically significant in terms of the severity of constipation and the frequency of bowel movements (36).
The results of the study by Canbulat Sahiner et al. showed no significant differences between the foot reflexology and control groups in terms of frequency and consistency of defecation (30). Gordon et al. conducted a study with three groups, including the control group, the massage group, and the reflexology group, showing that bowel movement and total score of constipation and subscales scores including soiling, pain, medicine use, general behavior, and health differed significantly between the groups. In that study, the bowel frequency differed from baseline in all the groups, but the greatest improvement was observed in the reflexology group. A significant difference was observed between the reflexology and control groups, but there was no significant difference between massage and control groups. Also, there was a significant difference between the control and reflexology groups in terms of the total score of constipation, although the bowel movements did not differ significantly (32) (Table 2).
| Author (s) Location/(Year)/Study Typea | Study Population | Participants’ Age | Intervention Group | Blinding | Intervention/Follow-up | Comparison | Sample Size in Both Groups | Scale | Finding Source | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elbasan & Bezgin Turkey /(2017) (32) | 40 children diagnosed with CP | 3-15 years | Group 1: Neurodevelopmental therapy Group 2: Foot reflexology with neurodevelopmental therapy | No blinding | Foot reflexology with neurodevelopmental therapy (twice a week, with each session lasting for 20 minutes for a total duration of eight weeks) | Neurodevelopmental therapy (each session lasting for 45-60 minutes) | 40 children using simple random sampling assigned to two groups of 20. Number of drop-outs (Group 1: 5; Group 2: 7) Group 1: 25 Group 2: 27 | Modified ConstipationAssessment Scale (MCAS). The total score ranged from 0 to 18. | PubMed | Foot reflexology in combination with neurodevelopmental therapy can decrease constipation scores significantly (P value = -0.081) |
| Ghaffari, et al. Iran /(2007) (29) | 100 pregnant women with constipation | No information given | Group 1: Foot reflexology Group 2: Control | No blinding | Foot reflexology (weekly sessions lasting 30 minutes, for six weeks) | No intervention | Foot reflexology (n=50) Control (n=50) (Randomized=125, group 1=65, Group2=60, Drop-outs in group 1 =15, in group 2 =10) | Constipation Assessment Scale (CAS). The total score ranged from 0 to 32. | Scopus | Foot reflexology improved constipation symptoms significantly (P value < 0.001). |
| Seyyedrassoli et al., Iran/(2016) (39) | 60 hospitalized patients with scores of 5 and above on the CAS | >18 years | Group 1: Foot reflexologyGroup 2: Abdominal massage Group 3: No intervention (received routine care) | Single-blind | Foot reflexology with routine care, each session lasted 40 minutes; abdominal massage with routine care, 20 minutes daily for six days | No intervention or abdominal massage | Foot reflexology (n=20) Abdominal massage (n=20) Control (n=20) (Randomized =60, no drop-outs in the groups) | Constipation Assessment Scale (CAS) | Google scholar | There were no statistically significant post-intervention differences between the groups in terms of severity of constipation until the second day of the treatment (P value > 0.05), but from the third day to sixth day after the treatment, a significant difference was observed (P<0.05). |
| Fakhrzade et al. Iran/ (2015) (36) | 28 older women with constipation | >65 years | Group 1: Foot reflexologyGroup 2: Nonspecific massage | Double-blind | Foot reflexology given weekly for six weeks and each session lasting 35-40 minutes | Nonspecific massage | Foot reflexology (n=28) Nonspecific massage (n=28) (Randomized=56, no drop-outs in the groups) | Constipation Assessment Scale (CAS) | Scientific Information Database (SID) | Significant differences were observed in the severity of constipation in both groups at the end of the first six weeks (P value < 0.001). |
| Canbulat Sahiner, et al. Turkey / (2017) (31) | 37 children with functional constipation | 3-6 years | Group 1: Foot reflexology and toilet/diet/ motivation training Group 2: Toilet/diet/ motivation training | No blinding | Each child received 10-min foot massage for five days a week and education about toilet and diet was provided to their parents for 30 min once a week for a period of four weeks | Toilet/diet/ motivation training | Received reflexology and toilet/diet/ motivation training (n=20), toilet/diet/ motivation training (n=20) (Randomized=37, Drop-outs in group 1 =3, in group 2=0) | A two-part questionnaire consisting of 23 questions. A table was included in the second part of the questionnaire, in which the defecation frequency and quality were recorded. The status of the child was recorded in this table at the end of each week. | PubMed | No significant differences were detected between the intervention and control groups in terms of constipation frequency (P value > 0.05); stool frequency increased in both groups from the second week onwards. Stool consistency improved as of the second week. There was a significant difference between groups (P value = .032) in the following weeks, but it never reached the level of statistical significance (P value > 0.05) ". |
| Gordon UK /(2007) (33) | 184 Children diagnosed with chronic idiopathic (functional) | 1-12 years | Group 1: Control- Routine care only Group 2: Foot massage + routine care Group 3: Reflexology + routine care | Single blind (assessor was blinded) | Simple foot massage and reflexology techniques were trained to the parents/caregivers by the nurse to apply daily on the patient for 12 weeks. | Standard care | Group 1: 59 Group 2: 59 Group 3: 66 (Randomized=184, Drop-outs in group 1 =2, group 2 =4 Group 3 =2) | The number of bowel movements for four weeks was recorded in the forms as a four-week diary. The Bristol Stool Chart was used to help record the bowel movements. | Google scholar | Reflexology improved the total constipation score, bowel movement frequency and general health significantly after 12 weeks of the intervention (P value = 0.047). Reflexology and Massage improved the constipation score significantly, not the bowel movement frequency (P value = 0.063). |
| Tovey UK / (2002) (38) | 34 patients with IBS based on the Rome Criteria (28 women and six men) | 19-72 years | Group 1: Reflexology Group 2: Nonspecific massage | Single-blind | Intervention included 30-min sessions. IBS symptoms were completed two weeks before the first session, during the intervention, two weeks after and again two weeks later at the first follow-up and finally three months after the last session at the second follow-up | The control group received nonspecific massage. The number of sessions were same with experimental group. | Foot reflexology (n=19) Control (nonspecific massage; n=15) (Randomized=34, drop-outs in group 1 =0, in group 2 =0) | IBS symptoms were evaluated daily with a five-point scale (0 to 4). The scale was completed by all participants two weeks before the first session, during the intervention, two weeks after the intervention and again two weeks later at the first follow-up and finally three months after the last session at the second follow-up. | PubMed | There was no evidence of any differences between the groups (P value = 0.47). |
| Sajadi Iran / (2020) (34) | 63 patients with MS. | 18-50 years | Group 1: ReflexologyGroup 2: Foot surface massage without pressure was applied | Double- blind | In the intervention group, the Rwo Shur method of reflexology was used. This method is a combination of pressure techniques and thumb sliding (each session for each foot lasted about 30−40 min). Foot reflexology was done twice a week for 6 weeks. | For the control group, to simulate the interventions similar to the experimental group, foot surface massage without pressure was applied. | Foot reflexology (n=33) Control (n=30) | CAS was used to determine the severity of constipation. | PubMed | The severity of constipation significantly decreased in the reflexology group compared to the control group after the intervention (P value < 0.05). |
| Sehhatti Iran / (2020) (30) | Nulliparous pregnant women with a single pregnancy | 16-45 years | Group 1: Reflexology Group 2: Routine care (Comparison group | double- blind | The intervention group received reflexology treatment that each session lasting 12 minutes for six weeks. | The control group received routine care. | Foot reflexology (n=36) (Randomized=37, drop-out=1 Control (n=36) (Randomized=37, drop-out=1 | CAS in both Study groups to determine constipation severity weekly for six weeks. | PubMed | Results showed the Severity of constipation in the reflexology group was significantly lower than that in the comparison group. No ide events were reported among women. |
| Inkaya Turkey/ (2020) (35) | Elderly people in a private nursing home in Ankara province | Mean= 75.5 years | Group 1: Reflexology Group 2: Routine care (control group | Double- blind | The experimental group received foot reflexology for 1 month. Reflexology sessions are done via a relaxation massage along with ankle rotations. The foot was relaxed primarily by applying effleurage followed by stretching, shaking, and rotation methods. | In the control group, foot surface massage was applied without pressure. | Foot reflexology (n=30) (Randomized=30, drop-out=0 Control (n=29) (Randomized=30, drop-out=1 | Turkish version of the CSI (Constipation Severity Instrument) was studied by Kaya and Turan. There is a total of 16 questions on the scale. Higher scores indicate that the symptoms are serious. The total score range is 0-73. | Google scholar | After the implementation of reflexology, the rate of emptying bowels on alternate days significantly increased in the experimental group compared to the control group, (P value < 0.001). |
| Mohammadzadeh Moghadam Iran/ (2019) (37) | 60 elderly people with constipation | 60-75 years | Group 1: Reflexology Group 2: Golghand | Single-blind | The relaxation techniques were performed to relax the feet and prepare for reflexology. After warming the hands, the patient's legs (shins, ankles, soles, and fingers) were oiled with sweet almond oil to facilitate massage. The reflexology was performed twice daily for 15 minutes each time for 2 weeks. | For people in the Golghand group, Golghand was taken half an hour before lunch (a teaspoonful mixed in a cup of cooled boiled water) for 2 weeks. | Foot reflexology (n=30) (Randomized=30, Golghand (n=30) (Randomized=30) | CAS questionnaire | Google scholar | After intervention, the number of bowel movements increased in both groups. However, this increase was higher in the Golghand group than the foot reflexology group (P value < 0.001). |
aAll studies were randomized controlled trial.
4.3. Methodological Quality
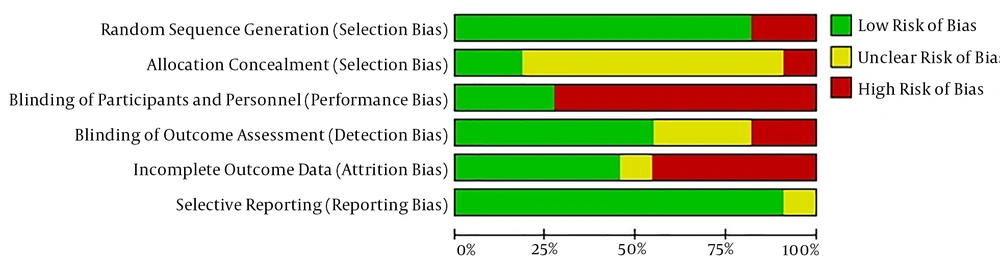
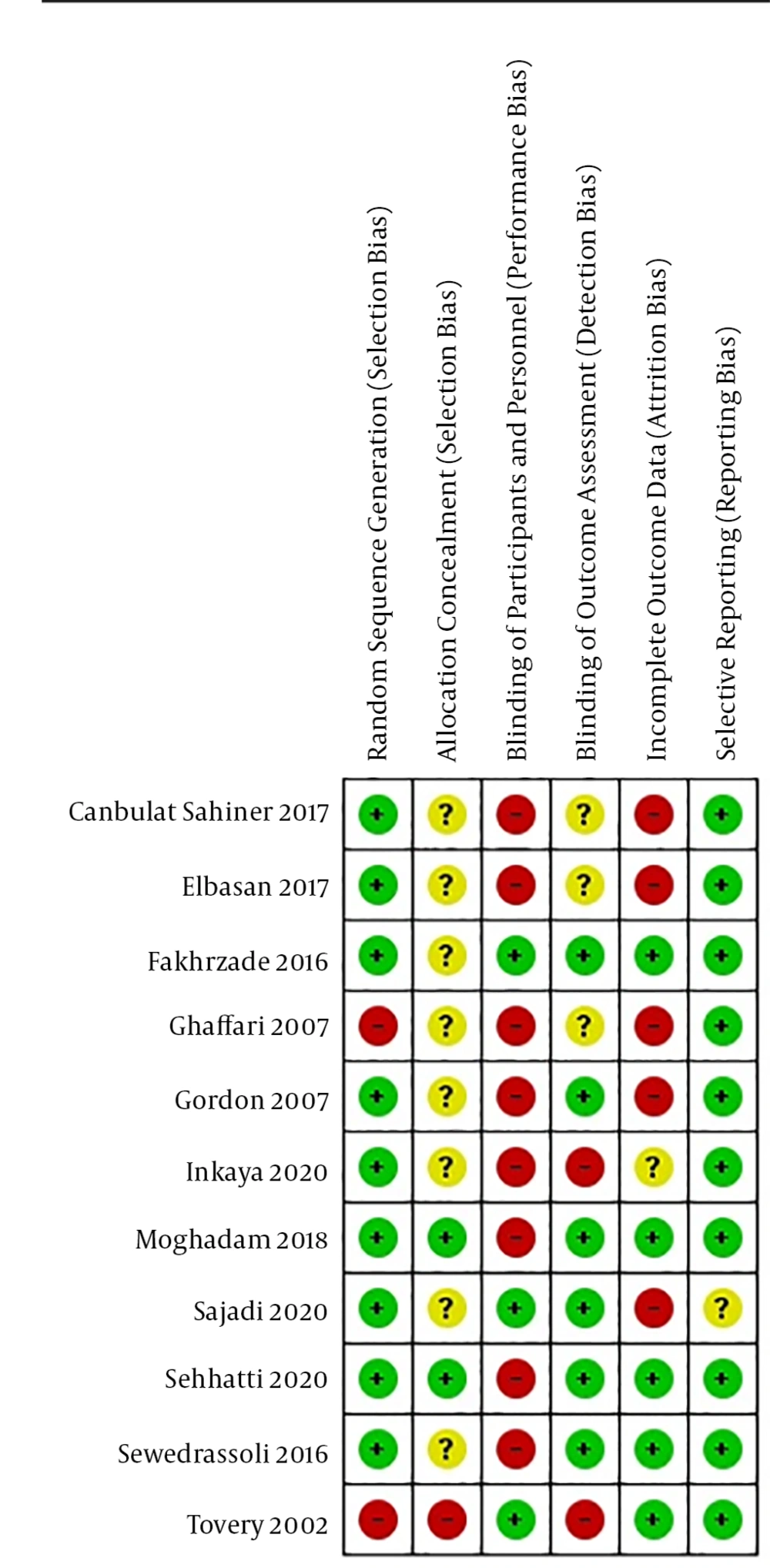
In assessing the methodological quality of the included studies, nine studies mentioned the method of generating allocation sequences (using a table of random numbers and a computer) (29-36, 38). Only two studies reported allocation concealment (29, 36). In regarding blinding of participant and personnel, three studies (33, 35, 37) blinded to allocation of groups by nonspecific massage, and in terms of blinding of outcome assessor, six studies (29, 32, 33, 35, 36, 38) had low risk of bias. In three studies, it was unclear whether or not the outcome assessor was blinded (28, 30, 31). Five studies (29, 35-38) had a low risk of bias, one study (34) was unclear, and five studies (28, 30-33) had a high risk of bias for incomplete outcome data (Figures 2 and 3).
4.4. Result of Meta-Analysis
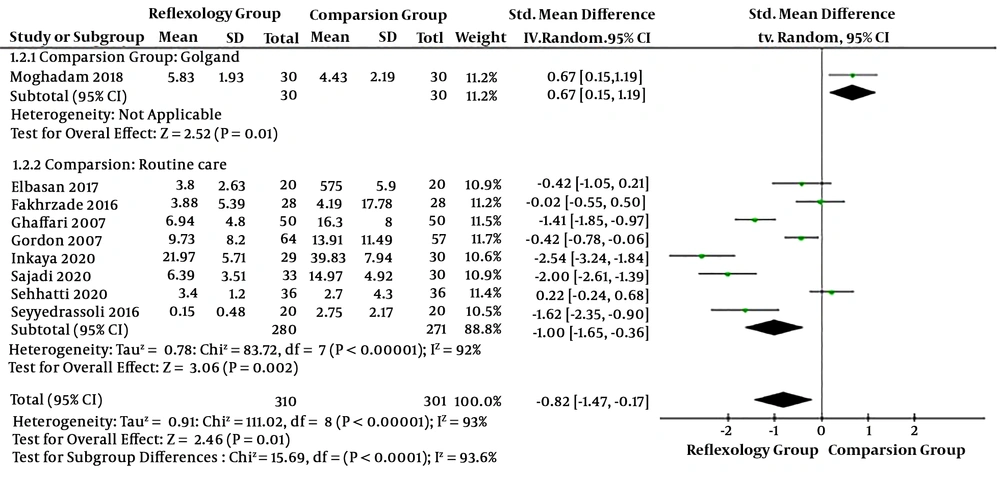
The pooled SMD showed that the total constipation score in the foot reflexology group was significantly lower than the comparison group (routine care or golgand) (SMD: -0.82; 95% CI: -1.47 to -0.17; P value = 0.0001). Due to high heterogeneity (I2 = 93%, P value < 0.0001), the random effect model was used. Based on the comparison group, the subgroup analysis showed that the total constipation score in the golgand group was significantly lower than the foot reflexology group. (SMD: 0.67; 95% CI: 0.15 to 1.19; P value = 0.01)However, the total constipation score in the foot reflexology group was significantly lower than the routine care group (SMD: -1.0; 95% CI: -1.65 to 0.36; P value = 0.002) (Figure 4).
5. Discussion
5.1. Summary of the Main Results
The analysis of the data from nine studies showed that foot reflexology was associated with significant improvements in constipation. The quality of the most included studies was not high. The results of the risk of bias assessment in the included studies showed that nine studies of the eleven studies used the correct method to generate random sequence. Only three studies reported the method used for allocation concealment, and in eight studies, it was unclear. No participants and personnel were blinded in 70% of the studies. Blinding is a significant stage in clinical trials. Without it, studies may cause an exaggeration in the estimated effect (39). Although only about 40% of the studies had no incomplete outcome data, the selective reporting bias in 90% of studies was low risk. It is necessary that the researchers address the issue of missing outcome data for their systematic reviews so that they could be considered as a valid source of evidence (40).
5.2. Interpretation of Findings
The findings of this systematic review showed that foot reflexology improved constipation significantly. Cherniack conducted a narrative review, entitled "The use of complementary and alternative medicine to treat constipation in the elderly" and included a study on 19 participants receiving 35-45-min sessions of foot reflexology every week, in which 11 participants showed improvements in colon transit time after the intervention (11). Wang et al. and Hussain et al. performed systematic reviews, including a single-blind trial on reflexology conducted by Tovey that evaluated the effectiveness of reflexology on the irritable bowel syndrome. These systematic reviews demonstrated that no statistically significant changes were observed between the reflexology and sham foot massage groups (16, 17).
The primary treatment options (10) for constipation include non-medical treatments (8). Although certain types of laxatives have some benefits for constipation symptoms, they have some side-effects when used for a long time (31-43). Reflexology is a popular type of CAM and an ancient healing method (44) that is commonly used in clinical practice and has become increasingly prevalent in various health care areas (45). Seo et al. (2015) performed a systematic review of the effect of self-administered foot reflexology in people with chronic health conditions and included three Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) and one before-after study. The results of the studies included self-administered foot reflexology in patients with chronic conditions, such as hyperelevension, urinary incontinence, or diabetes type 2, and showed insufficient evidence to determine the treatment effectiveness (46). Nonetheless, most of the cases claimed that reflexology was free of side-effects (3). Zeng et al. conducted a systematic review, entitled "Complementary and Alternative Medicine in Hospice and Palliative Care" and included 17 studies, two of which evaluated the efficacy of reflexology in improving the QoL. In one of the studies, 12 patients were randomly divided into two groups to receive reflexology or placebo treatment. The study evaluated constipation and several other symptoms in both groups, and a short-term improvement was reported in terms of QoL and constipation (47).
5.3. Strengths
The strengths of the present study include being among the first systematic reviews of foot reflexology for improving constipation symptoms. Previous systematic studies have reviewed the effects of abdominal massage on constipation. Also, the present study considered the objective outcomes in addition to subjective outcomes.
According to the existing literature, foot reflexology is an appropriate integrative treatment for symptom alleviation in patients with constipation; however, further research is needed to review the style of reflexology applied using well-designed and high-quality RCTs (48).
5.4. Limitations
The limitations of this systematic review include the trials using different types of controls depending on what they consider ‘foot reflexology’ or the control groups of the studies receiving another type of CAM (such as abdominal massage or nonspecific foot massage). Also, blinding of participants and personnel is difficult due to the nature of this intervention.. Sham reflexology is one example of the methods used to blind the participants on foot reflexology; however, these methods yield mixed results due to their uncertain reliability as a placebo. Most of the measurement tools used in the studies were subjective, though a few studies used objective measurement tools, such as bowel movement or stool frequency forms. Although the major English and Persian databases were searched comprehensively, studies published in other languages are missing on the subject.
5.5. Implications for Research
We suggest a better-designed, randomized, and controlled clinical trial to compare the effect of foot reflexology on constipation symptoms with other treatments, such as massage or standard treatments. Randomization, allocation concealment, and proper blindness of the participants, performers, and outcome assessors are essential for higher-quality trials. Valid tools to measure the outcomes should also be considered. In the end, it is necessary for all authors to include international standard statements such as the CONSORT statement in reports of their trial results.
5.6. Conclusion
The present study reviewed the effectiveness of foot reflexology in relieving constipation symptoms. The result of the meta-analysis showed that foot reflexology can effectively improve constipation symptoms. However, due to the poor quality of the articles and high heterogeneity, the findings are inconclusive , so clinical trials with better designs are recommended.